Soviet post-war anti-tank artillery
After the end of the war, anti-tank artillery was in service in the USSR: 37-mm airborne cannons of the 1944 model of the year, 45-mm anti-tank guns arr. 1937 year and arr. 1942 of the year, 57-mm anti-tank guns ZIS-2, divisional 76-mm ZIS-3, 100-mm field model 1944, BS-3. Also used German captured 75-mm anti-tank guns Cancer 40. They were purposefully assembled, stockpiled and repaired if necessary.
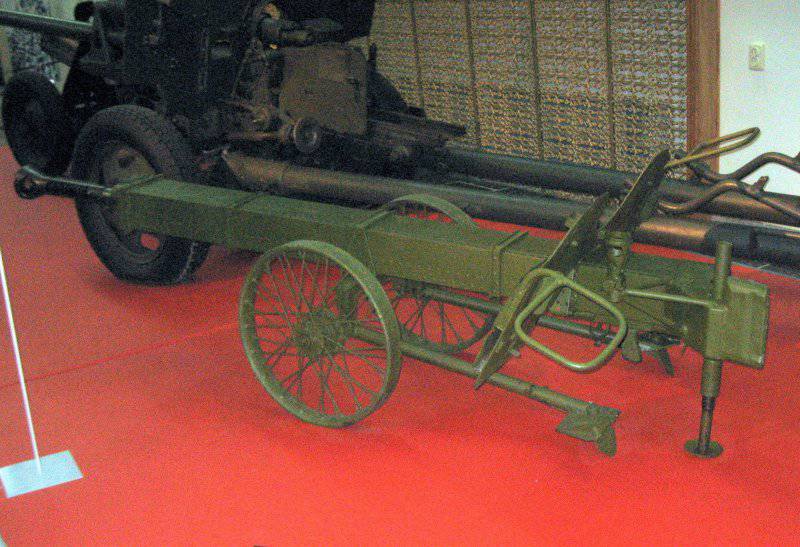
In the middle of 1944, it was officially adopted 37-mm airborne cannon CHK-M1.
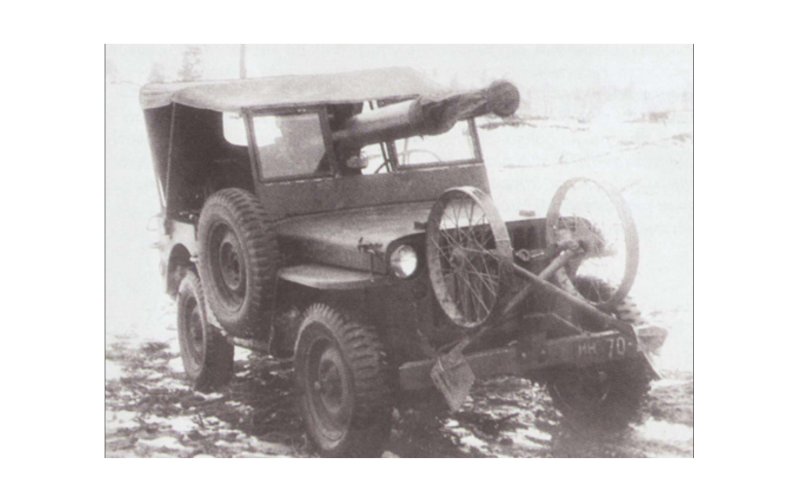
It was specially designed to equip parachute battalions and motorcycle regiments. The gun weighing 209 kg in combat position allowed air transportation and parachuting. It had good armor penetration for its caliber, which made it possible to hit medium and heavy side armor with a sub-caliber projectile at a short distance. tanks. The shells were interchangeable with the 37-mm 61-K anti-aircraft gun. The guns were transported in Willis and GAZ-64 vehicles (one gun per vehicle), as well as in Dodge and GAZ-AA vehicles (two guns per vehicle).
In addition, it was possible to transport the gun on a single-carriage or sleigh, as well as in a motorcycle pram. If necessary, the gun is disassembled into three parts.
The calculation of the gun consisted of four people - the commander, gunner, loader and podnoschika. When shooting calculation takes a prone position. The technical rate of fire reached 25-30 shots per minute.
Thanks to the original design of recoil devices, the 37-mm airborne gun obn.1944 combines powerful for its caliber anti-aircraft gun with small dimensions and weight. With close to 45-mm M-42, the values of armor penetration of the ChK-М1 are three times lighter and much smaller in size (much lower line of fire), which greatly facilitated the displacement of the gun by the forces of calculation and its disguise. At the same time, M-42 has a number of advantages - the presence of a full wheel course, allowing the vehicle to be towed by a car, the absence of a muzzle brake unmasking when firing, a more effective fragmentation projectile and the best armor-piercing action.
The 37-mm gun ChK-M1 was late for about 5 years, was put into service and put into production when the war came to an end. In hostilities apparently did not participate. A total of 472 guns were produced.
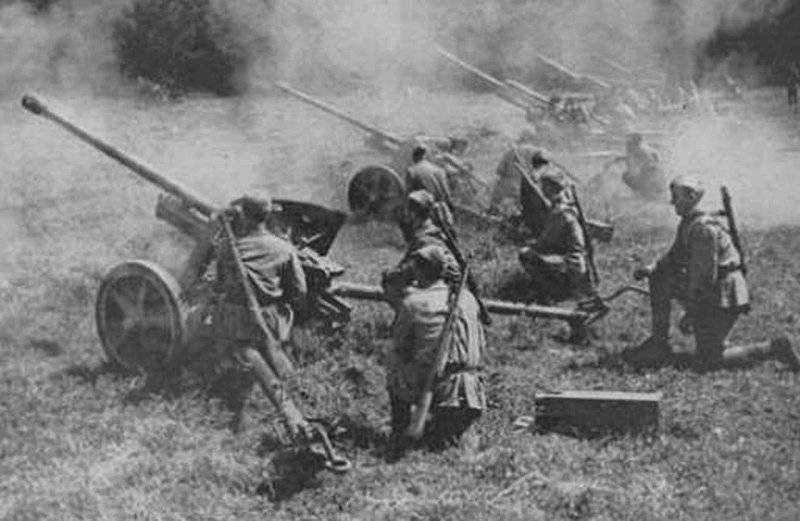
45-mm anti-tank guns by the time of the end of hostilities are hopelessly outdated, even the presence in ammunition 45 mm M-42 guns sabot projectile with armor penetration along the normal at a distance of 500 meters - 81-mm homogeneous armor could not remedy the situation. Modern heavy and medium tanks were only amazed when firing at the side, from extremely short distances. The active use of these guns until the very last days of the war can be explained by high maneuverability, ease of transportation and camouflage, huge accumulated stocks of ammunition of this caliber, as well as the inability of the Soviet industry to provide troops with the required number of anti-tank guns with higher characteristics.
Anyway, in the current army, the Forty-Pieces enjoyed immense popularity, only they could move by the forces of calculation in the battle formations of the advancing infantry, supporting it with fire.
At the end of 40's, forty-fives began to be actively withdrawn from parts and transferred to storage. However, for quite a long period of time they remained in service with the Airborne Forces and were used as training tools.
A significant amount of 45-mm M-42 was transferred to the then allies.
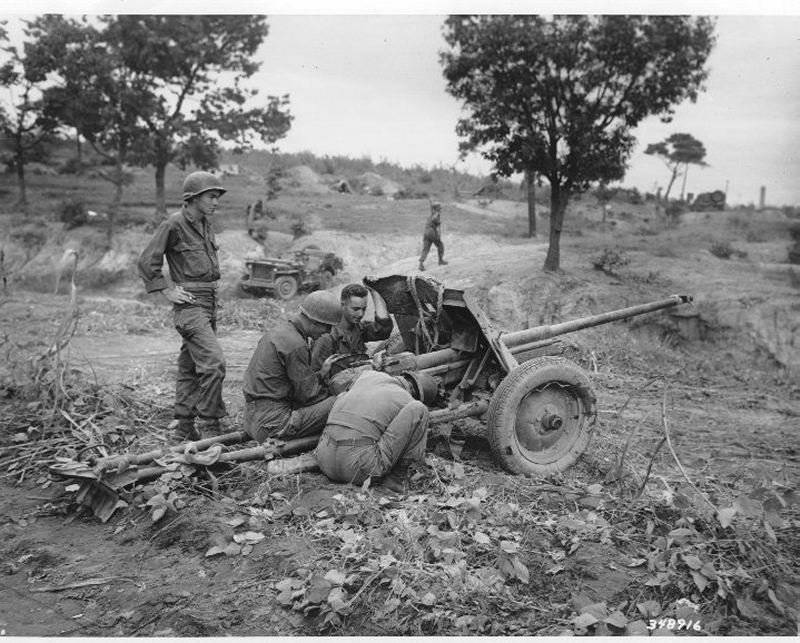

"Sorokapyatka" actively used in the Korean War. In Albania, these weapons were in service before the 90's.
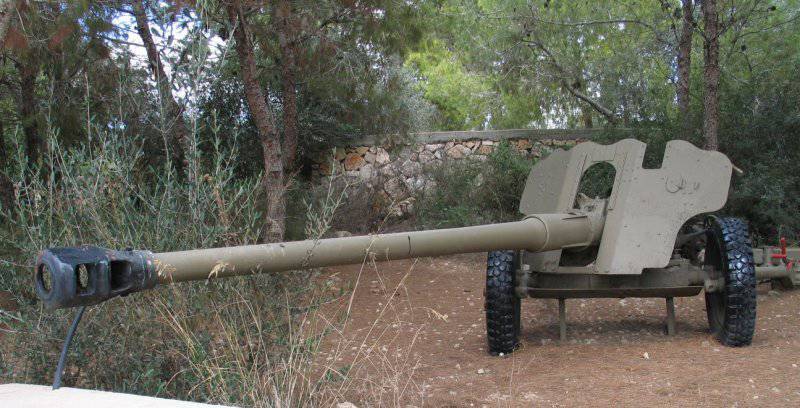
Mass production 57-mm anti-tank guns ZIS-2 It became possible in 1943 year, after the necessary metalworking machines were obtained from the USA. Restoration of mass production was difficult - again there were technological problems with the manufacture of barrels, in addition, the plant was heavily loaded with the production program of 76-mm divisional and tank guns, which had a number of common nodes with ZIS-2; under these conditions, the increase in the production of ZIS-2 on existing equipment could be carried out only by reducing the volume of production of these tools, which was unacceptable. As a result, the first batch of ZIS-2 for conducting state and military tests was released in May 1943 of the year, and the production of these tools was widely used preserved at the factory from 1941 year backlog. The mass production of ZIS-2 was organized by October - November 1943 of the year, after the commissioning of new production facilities, provided with equipment supplied under lend-lease.
The capabilities of the ZIS-2 allowed at typical combat distances to confidently hit 80-mm frontal armor of the most common German medium tanks Pz.IV and assault SAU StuG III, as well as onboard armor of the tank Pz.VI "Tiger"; at distances less than 500, the Tiger frontal armor was also struck.
In terms of cost and manufacturability, combat and service and operational characteristics of the ZIS-2 was the best Soviet anti-tank gun of the war.
From the moment production resumed, until the end of the war, more 9000 guns entered the army, but this was not enough to fully equip anti-tank units.
Production of ZiS-2 continued through the 1949 year, inclusive, in the post-war period around 3500 guns were fired. From 1950 th to 1951, only ZIS-2 trunks were produced. Since 1957, the modernization of the previously released ZIS-2 to the ZIS-2H variant has been carried out with the possibility of fighting at night due to the use of special night sights
In the 1950-ies for the gun were developed new sabots with increased armor penetration.
After the war, ZIS-2 was in service with the Soviet Army at least until 1970, the last combat use case was recorded in 1968, during the conflict with the PRC on Damanskiy Island.
ZIS-2 were supplied to a number of countries and took part in several armed conflicts, the first of which was the Korean War.
There is information about the successful use of ZIS-2 Egypt in 1956 year in battles with the Israelis. Guns of this type were in service with the Chinese army and were manufactured under license under the symbol Type 55. As of the 2007 year, ZIS-2 was still in service with the armies of Algeria, Guinea, Cuba and Nicaragua.
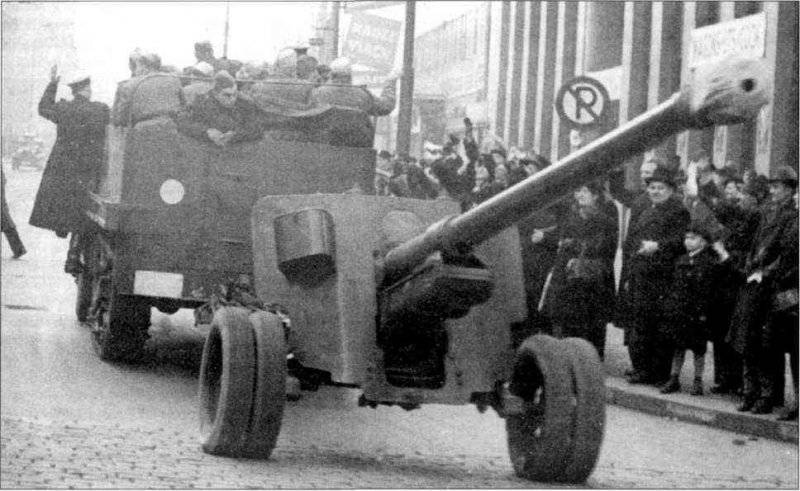
In the second half of the war, armed with fighter - anti-tank units consisted of captured German 75-mm anti-tank guns Cancer 40. During the offensive operations 1943-1944 g a large number of guns and ammunition were captured. Our military appreciated the high performance of these anti-tank guns. At a distance of 500 meters, the piercing pierced normal - 154 – mm armor.
In 1944, for the 40 Cancer in the USSR, firing tables and operating instructions were issued.
After the war, the guns were deposited, where they were at least until the middle of the 60-x. Subsequently, part of them was "recycled", and part transferred to the allies.

In fear of an invasion from the South, several anti-tank artillery battalions, armed with German 75-mm anti-tank guns of the World War II era, were formed as part of the army of North Vietnam. Such guns in large quantities were captured by the Red Army in 40, and now the Soviet Union has provided them to the Vietnamese people for protection against possible aggression from the South.
Soviet divisional 76-mm guns were designed to solve a wide range of tasks, primarily fire support infantry units, the suppression of firing points, the destruction of light field shelters. However, during the war, divisional artillery guns had to fire at enemy tanks, perhaps even more often than with specialized anti-tank guns.
From the 1944 of the year, due to the slowdown in the production of 45-mm guns and the lack of 57-mm guns ZIS-2, despite the lack of armor penetration for that time divisional 76-mm ZIS-3 became the main anti-tank gun of the Red Army.
In many ways, this was a necessary measure. The armor penetration capability of an armor-piercing projectile, piercing the 300-mm armor at the 75 distance in meters, was not enough to fight the average German tanks Pz.IV.
As of 1943, the booking of the heavy tank PzKpfW VI “Tiger” was invulnerable to the ZIS-3 in the frontal projection and weakly vulnerable at distances closer than 300 m in the onboard projection. Weakly vulnerable in frontal projection for the ZIS-3 were also the new German tank PzKpfW V Panther, as well as the upgraded PzKpfW IV Ausf H and PzKpfW III Ausf M or N; however, all these cars were confidently amazed from the ZIS-3 into the board.
The introduction of the sabot projectile from 1943 improved the anti-tank capabilities of the ZIS-3, allowing it at distances closer than 500 and m to confidently hit vertical 80-mm armor, but 100-mm vertical armor remained unbearable for it.
The relative weakness of the anti-tank capabilities of the ZIS-3 was realized by the Soviet military leadership, but until the end of the war, it was not possible to replace the ZIS-3 in anti-tank units. The situation could be corrected by the introduction of ammunition cumulative projectile. But such a projectile was adopted by ZiS-3 only in the postwar period.
Shortly after the end of the war and the release of 103 000 guns, the production of ZiS-3 was discontinued. The gun remained in service for a long time, but by the end of the 40's, it was almost completely removed from the anti-tank artillery. This did not prevent ZIS-3 from spreading very widely around the world and taking part in many local conflicts, including in the territory of the former USSR.
In the modern Russian army, the remaining operational ZIS-3 are often used as salute instruments or in theatrical performances on the theme of the battles of World War II. In particular, these guns are in service with the Separate Salyutniy Division at the Moscow commandant's office, which conducts salutes on the feast of February 23 and May 9.
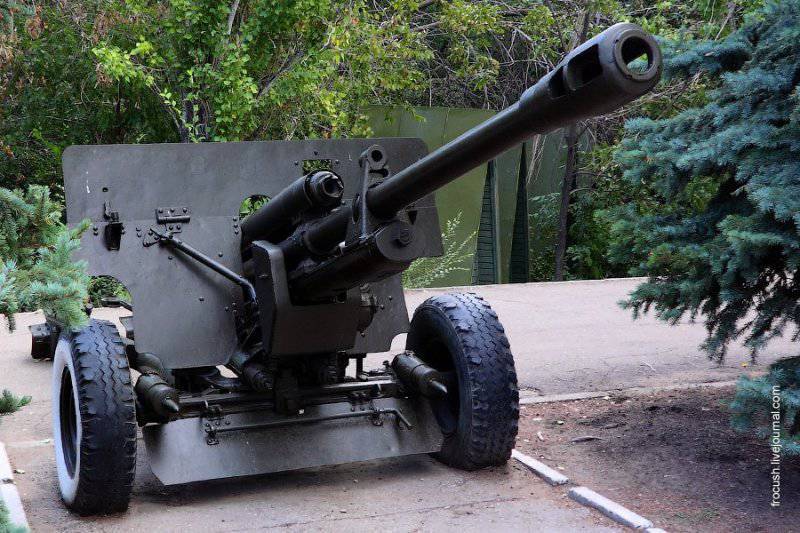
In 1946, the armament was created under the leadership of chief designer F. F. Petrov 85-mm anti-tank gun D-44. This tool would have been very popular during the war, but its development was dragged out for several reasons.
Externally, the D-44 strongly resembled the German 75-mm anti-tank 40 Cancer.
From 1946 to 1954, the plant 9 (“Uralmash”) produced 10 918 guns at the factory.
D-44 was in service with a separate anti-tank artillery division of a motorized rifle or tank regiment (two anti-tank artillery batteries consisting of two fire platoons) for 6 units in a battery (in the 12 division).
As ammunition, unitary cartridges with high-explosive fragmentation grenades, sub-caliber coil-shaped shells, cumulative and smoke shells are used. The range of the BTS BR-367 direct shot at the target with a height of 2 m is 1100 m. At a range of 500 m this projectile penetrates an armor plate with a thickness of 90 mm at an angle of 135 °. The initial speed of the BPS BR-365P is 1050 m / s, armor penetration is 110 mm from the distance 1000 m.
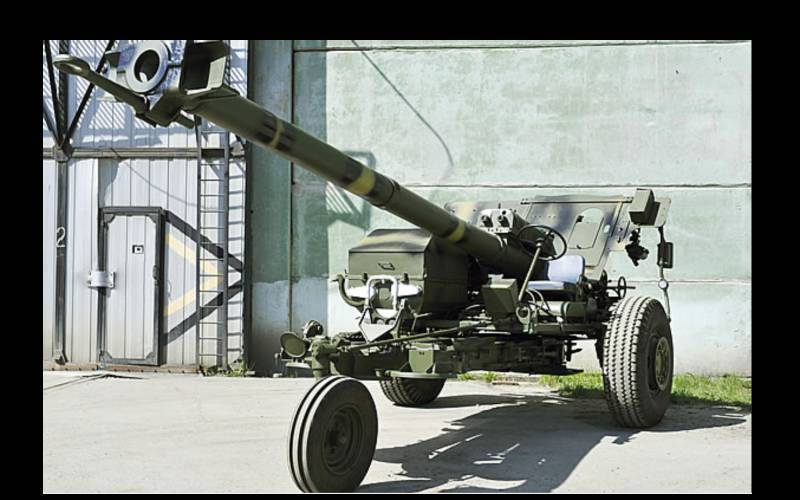
In 1957, night sights were installed on a part of the guns, a self-propelled modification was also developed. CD-44, which could move on the battlefield without a tractor.
The trunk and carriage SD-44 were taken from the D-44 with a few changes. So, on one of the gun beds was installed a casing-covered engine M-72 of the Irbit motorcycle plant with a power of 14 hp. (4000 rpm) providing self-propel speed up to 25 km / h. Power transmission from the engine was provided through the propeller shaft, differential and half-axles on both wheels of the gun. The gearbox, which is part of the transmission, provided six forward gears and two reverse gears. A seat is also fixed on the frame for one of the calculation numbers that performs the functions of a driver. At his disposal there is a steering mechanism that controls the additional, third, wheel of the gun, mounted on the end of one of the beds. A headlamp is installed to illuminate the road at night.
Subsequently, it was decided to use the 85-mm D-44 as a divisional to replace the ZiS-3, and the fight against tanks assigned to more powerful artillery systems and ATGM.
In this capacity, the weapon was used in many conflicts, including in the CIS. The extreme case of combat use was noted in the North Caucasus, during the “counter-terrorist operation”.
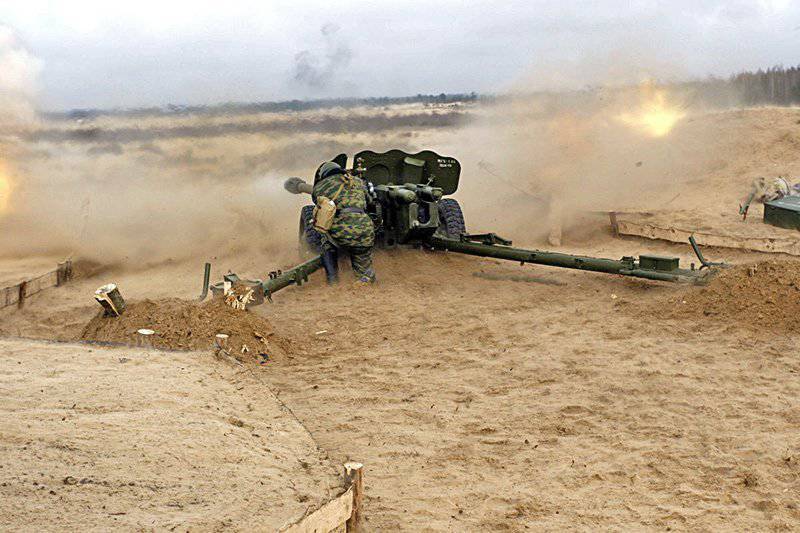

D-44 is still formally in service in the Russian Federation, some of these weapons are in the internal troops and in storage.
On the basis of D-44 under the leadership of the chief designer F. F. Petrov was created anti-tank 85-mm gun D-48. The main feature of the D-48 anti-tank gun was an exceptionally long barrel. To ensure maximum initial velocity of the projectile, the barrel length was brought to 74 gauges (6 m., 29 see).
Especially for this gun, new unitary shots were created. An armor-piercing projectile at a distance of 1 000 m pierced armor 150-185 mm in thickness at an angle of 60 °. A X-rayed projectile at a distance of 1000 m penetrates homogeneous armor 180 – 220 mm thick at an angle of 60 ° Maximum firing range of high-explosive fragmentation projectiles weighing 9,66 kg. - 19 km.
From 1955 to 1957 released: 819 copies of D-48 and D-48Н (with night sight АПН2-77 or АНН3-77).
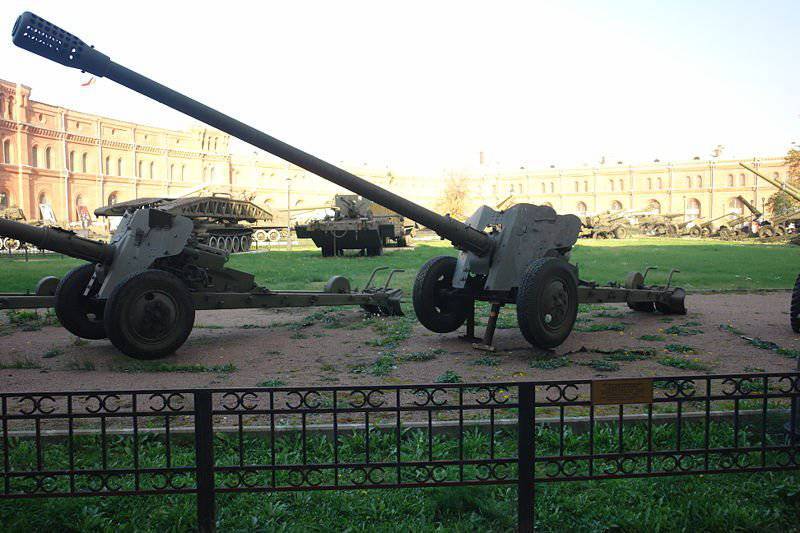

The guns entered service with individual artillery anti-tank battalions of a tank or motorized rifle regiment. As an anti-tank gun, the D-48 cannon quickly became obsolete. At the beginning of the 60-ies of the XX century in the NATO countries appeared tanks with more powerful armor sewn. A negative feature of the D-48 was the "exclusive" ammunition, which is not suitable for other 85-mm guns. For firing from the D-48, the use of shots from the D-44, KS-1, 85-mm tank guns and self-propelled guns is also prohibited, this significantly narrowed the scope of the gun.
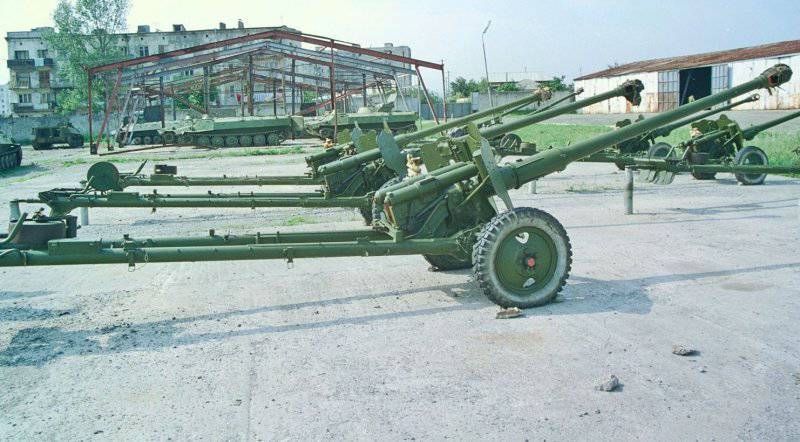
In the spring of 1943, the VG Grabin, in his memorandum addressed to Stalin, proposed, along with the resumption of production of the 57-mm ZIS-2, to begin designing the 100-mm cannon with a unitary shot, which was used in naval implements.
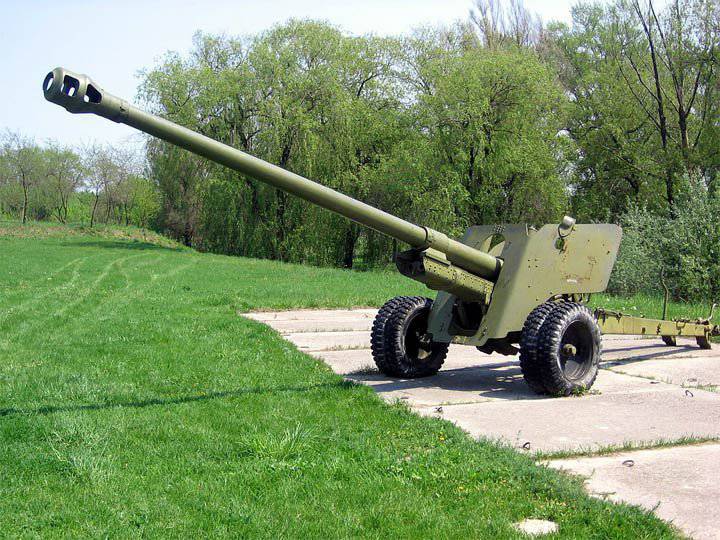

A year later, in the spring 1944 of the year 100-mm field gun model 1944, BS-3 was put into production. Due to the presence of a wedge gate with a vertically moving wedge with semi-automatic, the location of the mechanisms of vertical and horizontal pickup on one side of the gun, as well as the use of unitary shots, the firing rate of the gun is 8-10 shots per minute. Shooting from a cannon was carried out with unitary ammunition with armor-piercing tracer shells and high-explosive fragmentation grenades. An armor-piercing tracer with an initial speed of 895 m / s at a distance of 500 m at a meeting angle of 90 ° pierced armor with a thickness of 160 mm. Direct shot range was 1080 m.
However, the role of this weapon in the fight against enemy tanks is greatly exaggerated. By the time it appeared, the Germans practically did not use masses of tanks.
During the war, the BS-3 was released in small quantities and could not play a big role. At the final stage of the war, the 98 BS-3 were attached as a means of strengthening five tank armies. The gun was in service with light artillery brigades 3-regimental composition.
The artillery of the RGCs as of 1 in January of 1945 had 87 BS-3 guns. At the beginning of the 1945 of the year, in the 9 of the Guards Army, as part of three rifle corps, one cannon artillery regiment of BS-20 3 was formed.
Basically, thanks to the long range - 20650 m and a fairly effective high-explosive fragmentation grenade weighing 15,6 kg, the gun was used as a body cannon to fight enemy artillery and suppress long-range targets.
The BS-3 had a number of flaws that hampered its use as an anti-tank. When firing, the gun jumped heavily, which made the gunner’s work unsafe and knocked down the aiming installations, which, in turn, led to a decrease in the practical rate of aimed fire — qualities for a very important anti-tank gun.
The presence of a powerful muzzle brake with a small height of the line of fire and flat trajectories characteristic of shooting at bronzelem, led to the formation of a significant smoke-dust cloud that unmasked the position and blinded the calculation. The mobility of a weapon with a mass of more than 3500 kg left much to be desired, transportation by the forces of calculation on the battlefield was almost impossible.
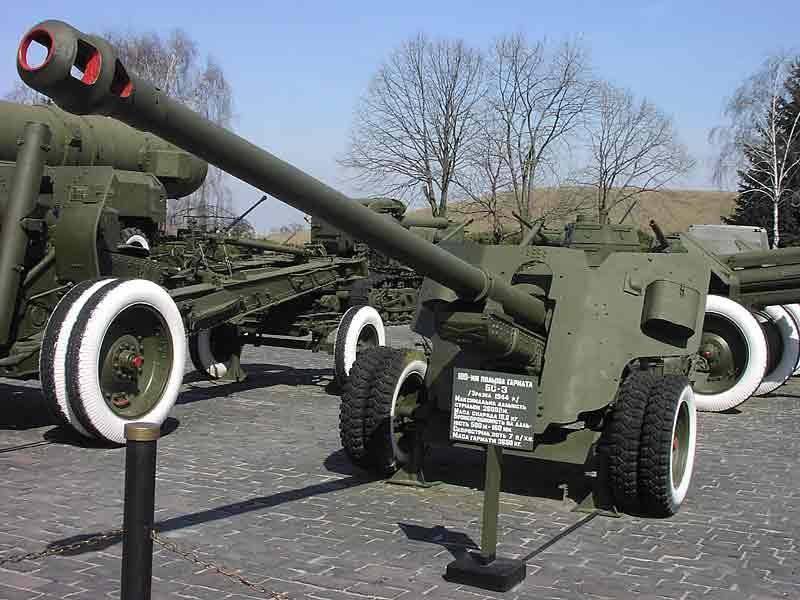

After the war, the gun was in production until 1951, inclusive, in total 3816 field guns BS-3 were released. In the 60-ies guns have been upgraded, this applies primarily to sights and ammunition. Prior to the start of the 60, the BS-3 could penetrate the armor of any Western tank. But with the advent of: M-48А2, Chiefen, M-60 - the situation has changed. New sub-caliber and cumulative shells were urgently developed. The next upgrade took place in the middle of 80-x, when the BS-3 ammunition kit received the 9М117 "Bastion" anti-tank projectile.
This weapon was also supplied to other countries, took part in many local conflicts in Asia, Africa and the Middle East in some of them it is still in service. In Russia, the BS-3 cannon until recently consisted of a coastal defense weapon in the 18 armament of the machine-gun and artillery division stationed on the Kuril Islands, and also a fairly large number of them are in storage.
Until the end of the 60s of the early 70s of the last century, anti-tank guns were the main means of fighting tanks. However, with the advent of the ATGM with a semi-automatic guidance system, which only requires keeping the target in sight, has changed the situation in many ways. The military leadership of many countries considered the metal-intensive, bulky and expensive anti-tank guns an anachronism. But not in the USSR. In our country, the development and production of anti-tank guns continued in significant numbers. And at a qualitatively new level.
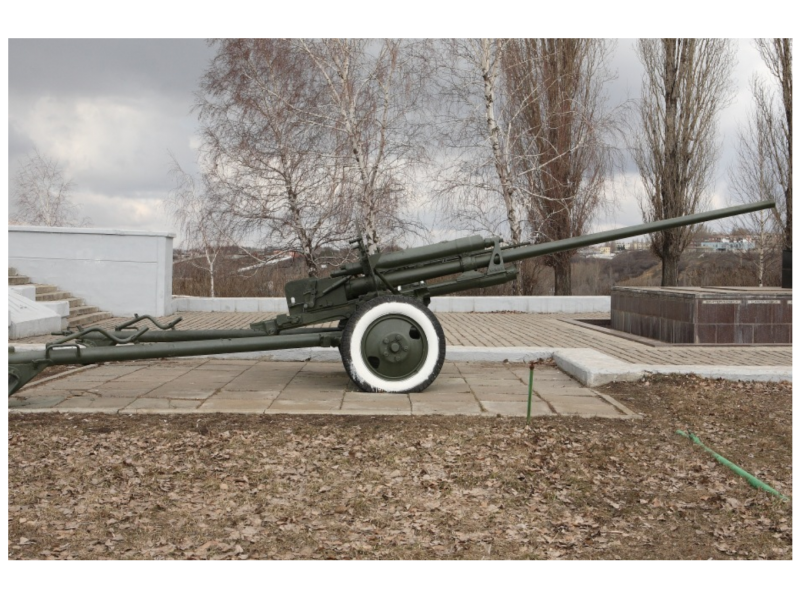
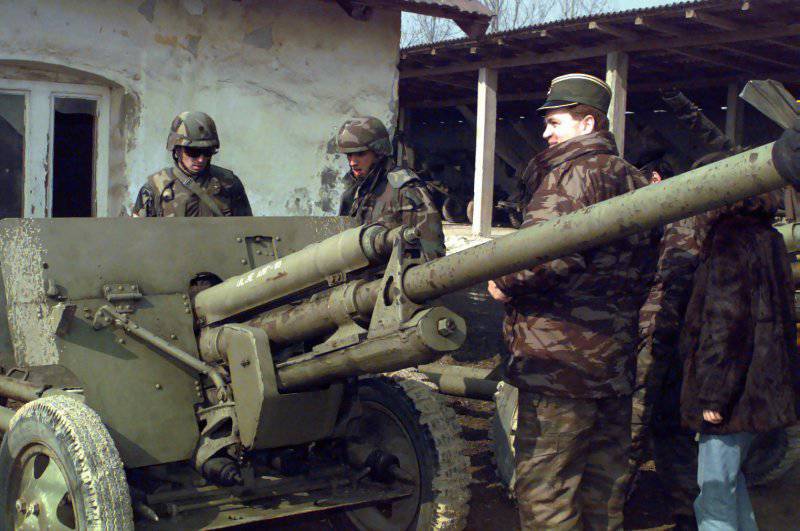
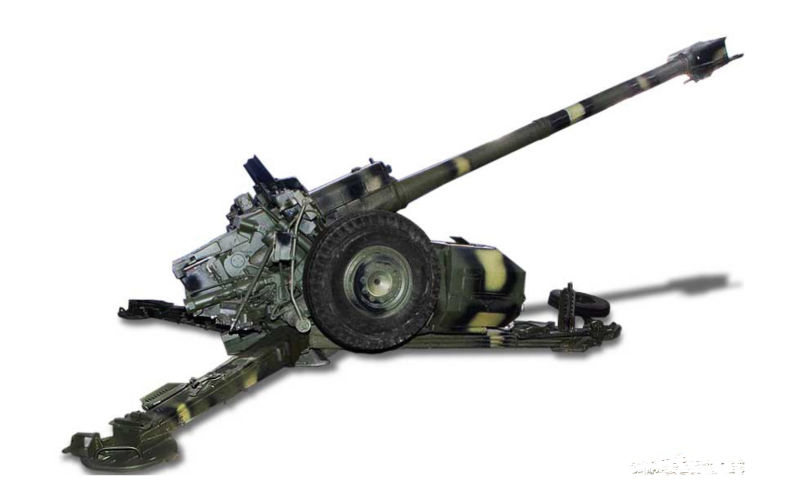
In the year 1961 entered service 100-mm smoothbore anti-tank gun T-12developed in KB Yurginsky machine-building plant number 75 under the direction of V.Ya. Afanasyev and L.V. Korneev.
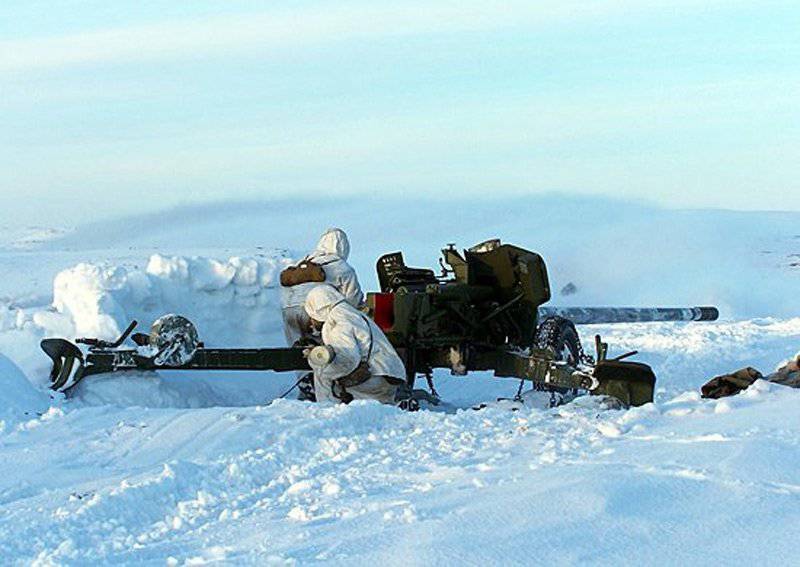

The decision to make a smooth-bore gun at first glance may seem rather strange, the time of such guns ended almost a hundred years ago. But the creators of the T-12 did not think so.
In a smooth channel, you can make the gas pressure much higher than in a rifled one, and accordingly increase the initial velocity of the projectile.
In a rifled barrel, the rotation of the projectile reduces the armor-piercing effect of the jet of gases and metal in the explosion of a cumulative projectile.
A smooth-bore gun significantly increases the survivability of the barrel - you can not be afraid of the so-called "washing" of the rifling fields.
The canal of the gun consists of a chamber and a cylindrical smooth-walled guide part. The chamber is formed by two long and one short (between them) cones. The transition from the chamber to the cylindrical section is a conical slope. Shutter vertical wedge with spring semiautomatic. Unitary loading. The carriage for the T-12 was taken from the 85-mm anti-tank rifled D-48 gun.
In the 60-ies for gun T-12 was designed more convenient to use carriage. New system received an index MT-12 (2A29), and in some sources referred to as "Rapier". The serial production of the MT-12 went into the 1970 year. The anti-tank artillery battalions of the motorized rifle divisions of the USSR Armed Forces included two anti-tank artillery batteries consisting of six X-NUMX-mm T-100 PTPs (MT-12).
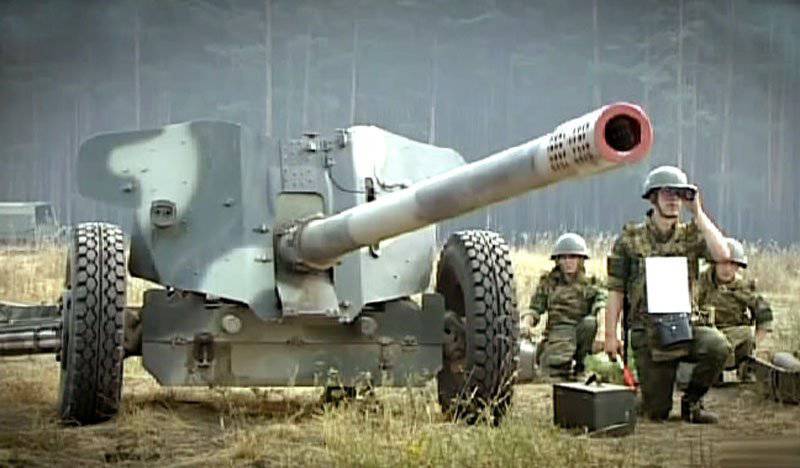

The T-12 and MT-12 cannons have the same warhead — a long, thin barrel with a 60 length of caliber with a muzzle brake “salt shaker”. Sliding beds are equipped with an optional retractable wheel installed on the coulters. The main difference of the modernized model MT-12 is that it is equipped with a torsion bar suspension, which is locked when fired to ensure stability.
When manually rolling the gun, a roller is inserted under the trunk of the bed, which is mounted with a stopper on the left bed. Transportation of guns T-12 and MT-12 is carried out by a standard tractor MT-L or MT-LB. For movement on snow, the ski machine LO-7 was used, which allowed fire from skis at elevation angles up to + 16 ° with a turning angle of up to 54 °, and at an elevation angle of 20 ° with a turning angle of up to 40 °.
A smooth barrel is much more convenient for firing guided projectiles, although in 1961 it was probably not thought of yet. To combat armored targets, an armor-piercing-sifting projectile with a swept warhead with high kinetic energy is used, capable of piercing armor 1000 mm thick at a distance of 215 meters. The ammunition includes several types of subcaliber, cumulative and high-explosive fragmentation projectiles.
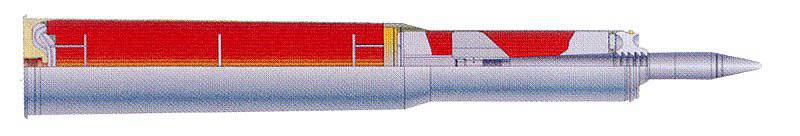
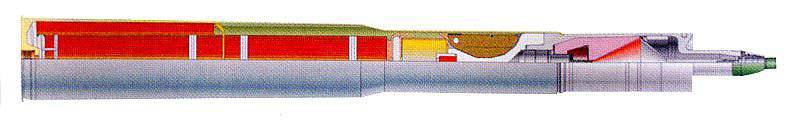
When mounted on a gun, a special guidance device can be used with shots with the anti-tank missile "Kastet". Rocket control is semi-automatic using a laser beam, firing range from 100 to 4000. The missile penetrates the armor for dynamic protection (“jet armor”) with thickness up to 660 mm.

For direct fire, the T-12 gun is equipped with a day sight and night sights. With a panoramic sight it can be used as a field gun from closed positions. There is a modification of the gun MT-12Р with mounted radar 1А31 "Ruth".
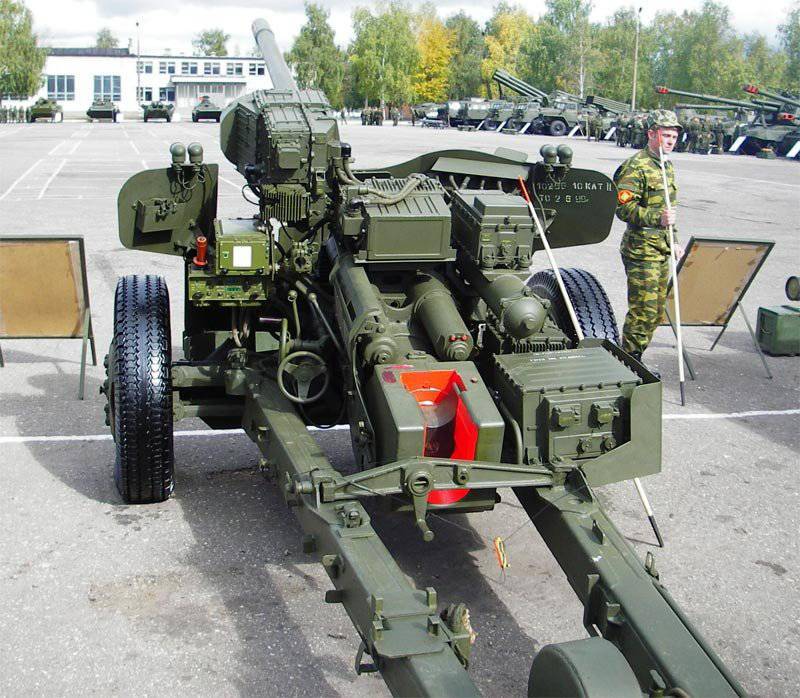

The gun was massively in service with the armies of the Warsaw Pact countries, delivered to Algeria, Iraq and Yugoslavia. Took part in hostilities in Afghanistan, in the Iran-Iraq war, in armed conflicts in the territories of the former USSR and Yugoslavia. In the course of these armed conflicts, 100-mm anti-tank guns are mainly used not against tanks, but as ordinary divisional or corps instruments.
Anti-tank guns MT-12 continue to be in service in Russia.
According to the press center of the Ministry of Defense 26 August 2013, an accurate fire from the UBK-8 cumulative projectile from the MT-12 “Rapier” cannon of the Yekaterinburg separate motorized rifle brigade of the Central Military District eliminated a fire at the well # Р23 U1 under the heading of the Novo XYNUMX Brigade of the Central Military District.
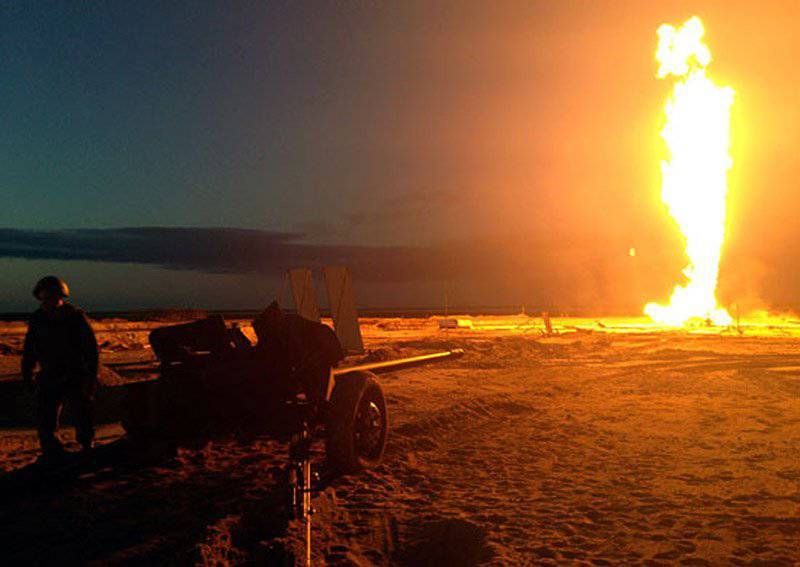

The fire began on August 19 and quickly turned into uncontrolled burning of natural gas, which breaks through faulty valves. The artillery crew was transferred to Novy Urengoy by a military transport aircraft aviationflying out of Orenburg. At the Shagol airfield, equipment and ammunition were loaded, after which the gunners, under the command of Colonel Gennady Mandrichenko, officer of the missile forces and artillery command of the Central Military District, were brought to the scene. The gun was mounted on direct fire from a minimum permissible distance of 70 m. The target diameter was 20 cm. The target was successfully hit.
In 1967, the Soviet experts concluded that the T-12 gun “does not ensure reliable destruction of the Chieftain tanks and the promising MVT-70. Therefore, in January 1968, OKB-9 (now part of Spetstekhnika JSC) was instructed to develop a new, more powerful anti-tank cannon with 125-mm ballistic smooth-bore tank gun D-81. The task was difficult to accomplish, since D-81, having excellent ballistics, gave a strong return, which was still tolerable for a tank weighing 40 tons. But on the testing ground D-81 fired from a tracked gun carriage 203-mm howitzer B-4. It is clear that such an anti-tank gun in 17 tons weighing and maximum speed of movement 10 km / h was out of the question. Therefore, in the 125-mm gun recoil was increased from 340 mm (limited by tank dimensions) to 970 mm and a powerful muzzle brake was introduced. This made it possible to install the 125-mm cannon on a three-wall gun carriage from the serial 122-mm howitzer D-30, which allowed circular firing.
The new 125-mm gun was designed by OKB-9 in two versions: towed D-13 and self-propelled CD-13 ("D" is the index of artillery systems of V. F. Petrov). The development of CD-13 has become 125-mm smooth-bore anti-cannon "Sprut-B" (2-45M). Ballistic data and ammunition tank gun D-81 and anti-tank gun 2-45M were the same.
The 2А-45М gun had a mechanized system for transferring it from a combat position to a stopping position and back, consisting of a hydraulic jack and hydraulic cylinders. With the help of a jack, the carriage rose to a certain height, necessary for the breeding or convergence of bedding, and then descended to the ground. Hydraulic cylinders lift the gun to the maximum clearance, as well as raising and lowering the wheels.
The Sprut-B is towed by the Ural-4320 or the MT-LB tractor. In addition, for self-movement on the battlefield, the gun has a special power unit, made on the basis of the MeMZ-967A engine with hydraulic drive. The engine is located on the right side of the gun under the casing. On the left side of the frame are installed the driver's seat and the control system of the gun during self-movement. The maximum speed at the same time on dry dirt roads - 10 km / h, and portable ammunition - 6 shots; fuel reserve is up to 50 km.
The 125-mm cannon “Sprut-B” includes ammunition of separate-sleeve loading with cumulative, sub-caliber and high-explosive fragmentation projectiles, as well as anti-tank missiles. 125-mm shotgun VBK10 with a cumulative projectile BK-14M can hit tanks like M60, M48, "Leopard-1A5". Shot VBM-17 with a sabot projectile - tanks type M1 "Abrams", "Leopard-2", "Merkava MK2". Shot VOF-36 with high-explosive fragmentation projectile OFNNXX is designed to engage manpower, engineering structures and other targets.
If there is a special guidance equipment 9C53, the Sprut can fire shots with the K-14 TOOTH with the 9М119 anti-tank missiles, which are semi-automatic, controlled by a laser beam, the firing range is from 100 to 4000 m. armor behind dynamic protection 24 – 17,2 mm thick.
Currently, towed anti-tank guns (100- and 125-mm smooth-bore) are in service with the countries of the former Soviet republics, as well as a number of developing countries. The armies of the leading Western countries have long abandoned special anti-tank guns, both towed and self-propelled. Nevertheless, it can be assumed that towed anti-tank guns have a future. Ballistics and ammunition 125-mm cannon "Sprut-B", unified with the guns of modern main tanks, can hit any serial tanks of the world. An important advantage of anti-tank guns over the ATGM is a wider choice of means of defeating tanks and the possibility of defeating them point-blank. In addition, the Sprut-B can also be used as a non-anti-tank weapon. Its high-explosive fragmentation projectile RP-26 is close in ballistic data and explosive mass to the RP-471 122-mm projectile A-19 projectile, which became famous in the Great Patriotic War.
Based on:
http://gods-of-war.pp.ua
http://русская-сила.рф/guide/army/ar/d44.shtml
Shirokorad A. B. Encyclopedia of domestic artillery. - Minsk: Harvest, 2000.
Shunkov V.N. Weapons of the Red Army. - Minsk: Harvest, 1999.















Information