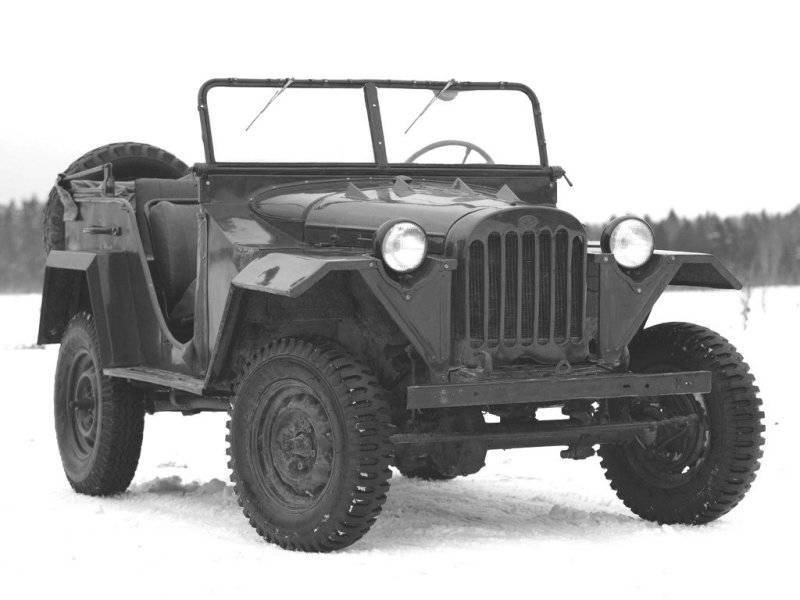
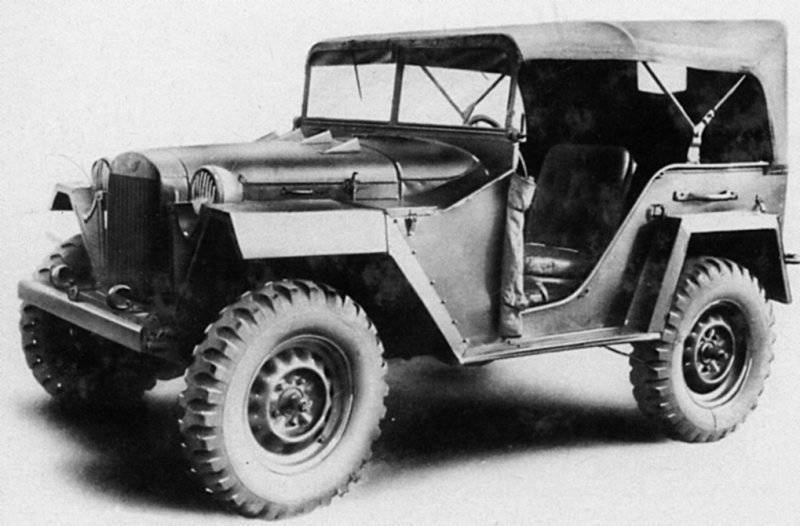
Car-all-terrain vehicle GAZ-67

However, GAZ-61 was not quite suitable for the tasks, as it turned out to be expensive and complicated, moreover, its engine was just being mastered by industry. Army needed a simplified, "soldier" car. By order of the People's Commissar Malyshev V.A. in January, 1941, NATI (leading designers Dushkevich AA and Shishkin VV) and the Gorky Automobile Plant were tasked to develop a lightweight all-terrain vehicle on a competitive basis. The payload of the car should have been 400 kg, the mileage before the decommissioning 5000 km. At the same time, one of the conditions was that the values of the wheel track and overall length are identical to the “Bunt” car. The fact is that the new car was also supposed to be used as an airborne, and it had to be placed in the cargo compartment of the PS-84 transport aircraft (more commonly known as Lee-2).
At GAZ, the lead designer of the project was Grachev Vitaly Andreevich, who proved himself by that time as an initiative and talented engineer, behind whom there were several successful developments.
Under the leadership of Grachev V.A. On the machine worked engineer Wassermann G.M. and technician Kuzin A.G. In addition to them, other designers were periodically connected to work: V.T. Komarevsky. (designed the body), Prosvirnin A.D. (steering link). The design of the new car, which received the GAZ-64-416 index, was launched on 3 February. 1941. February 12. The first drawings were put into the workshop. The design was developed in just 51 a day.
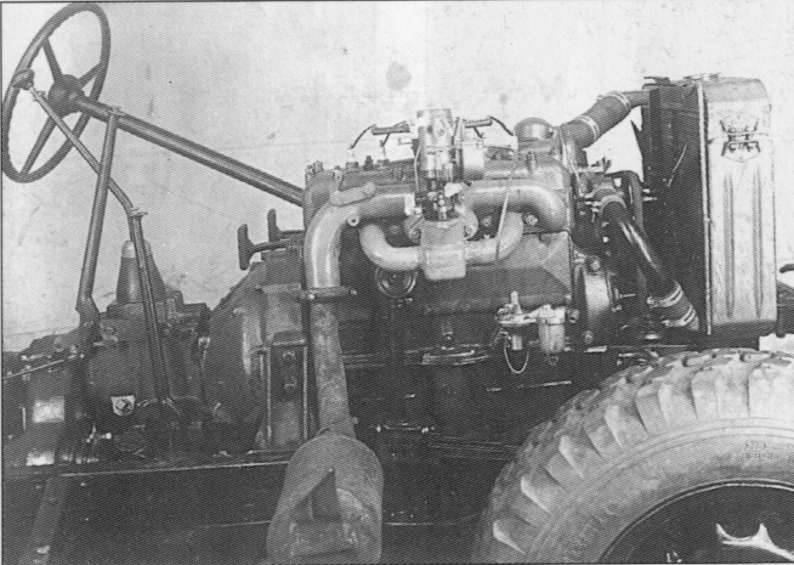
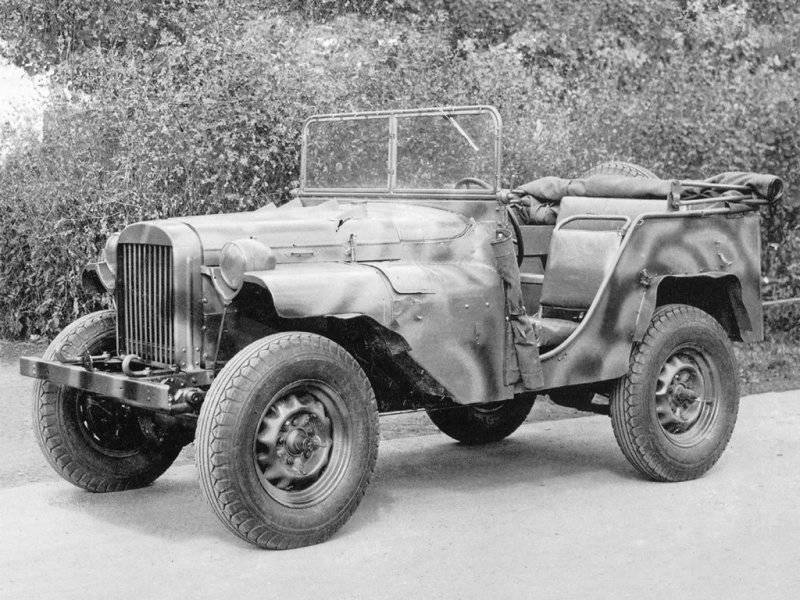
The basis of the future car Gorky were taken nodes and units GAZ-61 with a sufficiently high reliability. However, in accordance with the task significantly reduced the track of the car, which led to unjustified alteration of bridges. The all-terrain vehicle GAZ-64 had an open, easy-to-manufacture doorless body with side seats. The car was designed to carry 4-5 people. Windshield - leaning forward, top - canvas. The frame design with closed spars differed high strength. A hard bumper was installed at the front and a towing device at the rear. The gasoline four-cylinder 54-strong engine and 4-speed gearbox from the GAZ-MM truck, rear axle, front axle, transfer box, wheels, brakes and steering, were unified with the GAZ-61-40 passenger all-wheel drive. On the basis of the radiator of the GAZ-AAA truck, a new radiator was developed. The front axle suspension, which has four quarter-elliptical springs, had an original design.
4 March started to build the car. March 17 bodywork completed, and March 25 "gas" was painted. The new all-terrain vehicle, driven by Grachev V.A., left the factory yard the same day. 15 — 27 on April, the machine passed a brief troop test, after which it was launched into a series. In April 1941, the GAZ-64 was introduced to the military. After their approval in August, 1941 began its mass production. The car was quickly put on production, as the design used a large number of models already mastered by the plant. This was one of the main reasons for the victory of the plant in the competition. By the end of 1941, the 601 all-terrain vehicle was put into the Red Army, which successfully passed the tests of wartime.
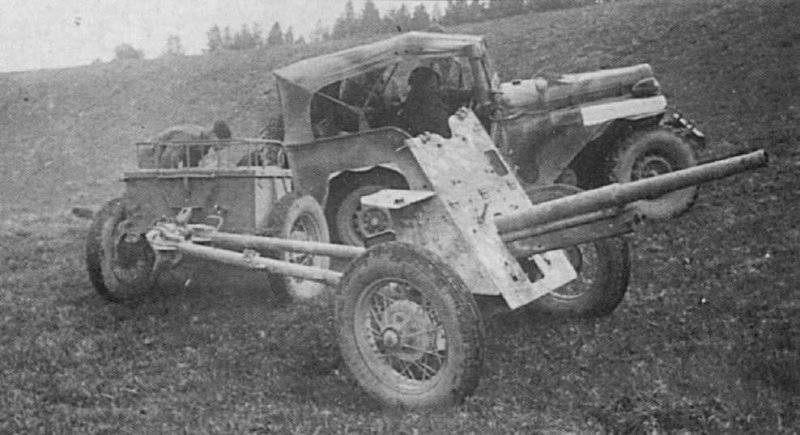
There was no car like the GAZ-64 in the Red Army (it was only later that Lend-Lease supplied the American Bantama and Willis, with which GAZ quite successfully competed). Before adopting the GAZ-64, light guns were carried on horseback, and GAZ-A and Emki were used as commanding and staff vehicles. The GAZ-64 turned out to be a light multipurpose truck capable of transporting and pulling 76-mm cannons up to the detachment of fighters. The open body, covered with a tarpaulin, was cramped for the fighters, but they appreciated its other quality - the unprecedented cross-country ability of the car in the sand, mud and snow. GAZ-64 was able to overcome short rises up to 42 degrees, long ones up to 38, and with a 45 mm caliber gun on a hook - up to 31. This was provided by a low-speed engine with high torque and a gearbox with a large power range. A short front overhang and a significant angle of entry (64 °) allowed the all-terrain vehicle to overcome vertical obstacles up to 50 cm, and a raised engine to overcome fords up to 80 cm. GAZ-25 did not have cars in the Red Army equal in dynamics and pickup.
High vehicle throughput was obtained due to both leading axles, frame reinforcement, increased gear ratio in the transmission, shortened base of the car, increased entry angles (front —75 °, rear —33 °), tires with special tires.
The front drive axle is driven by a transfer case located behind the gearbox. The on / off of the bridge is made by the driver with a lever.
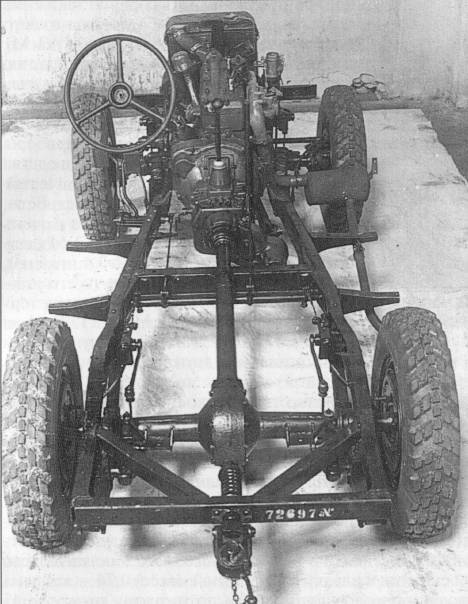
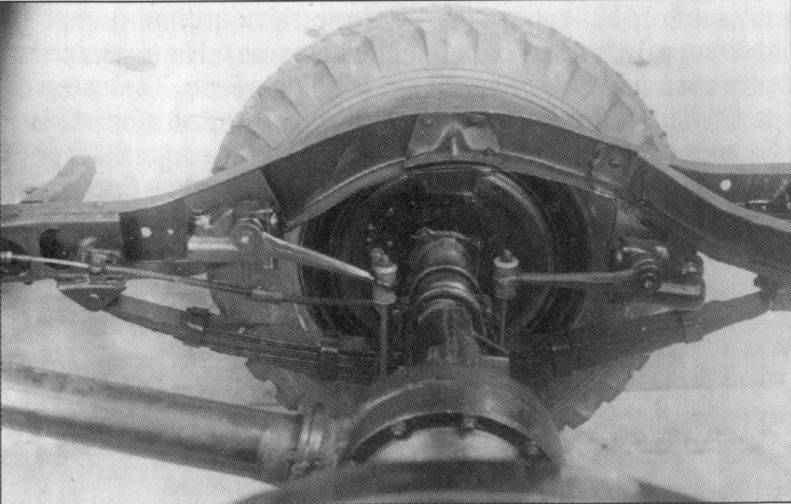
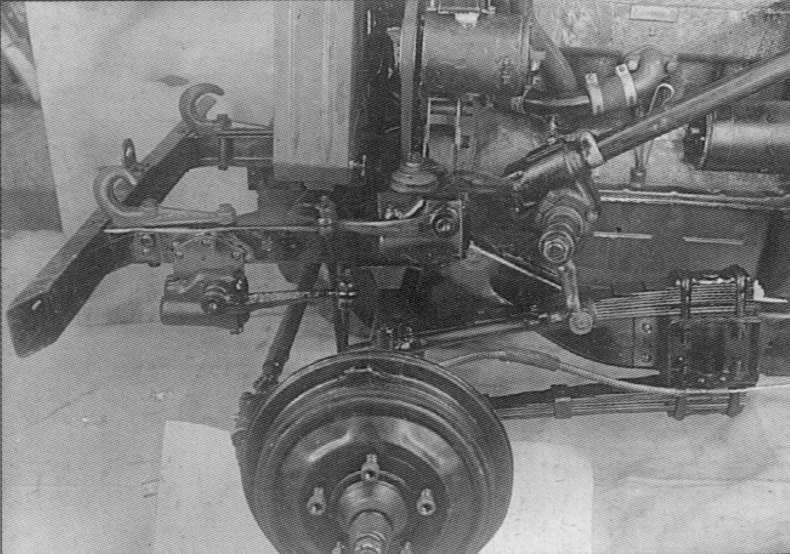
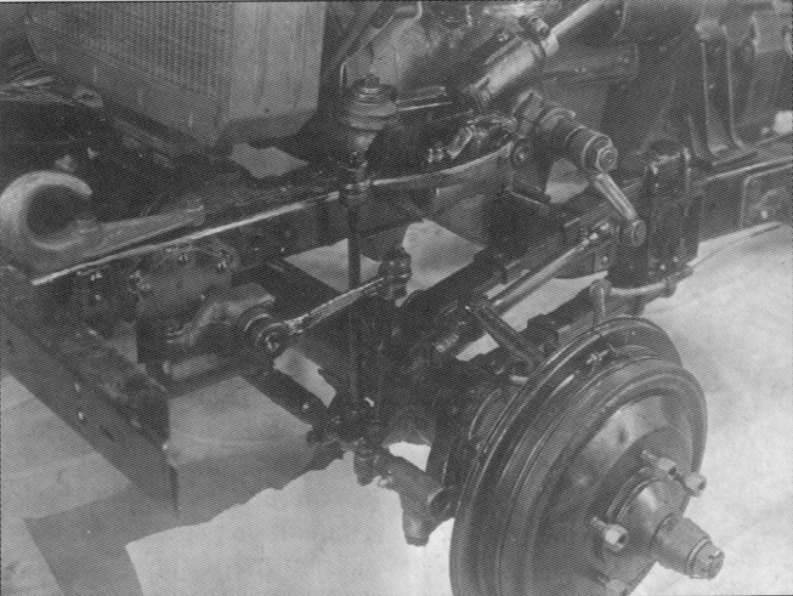
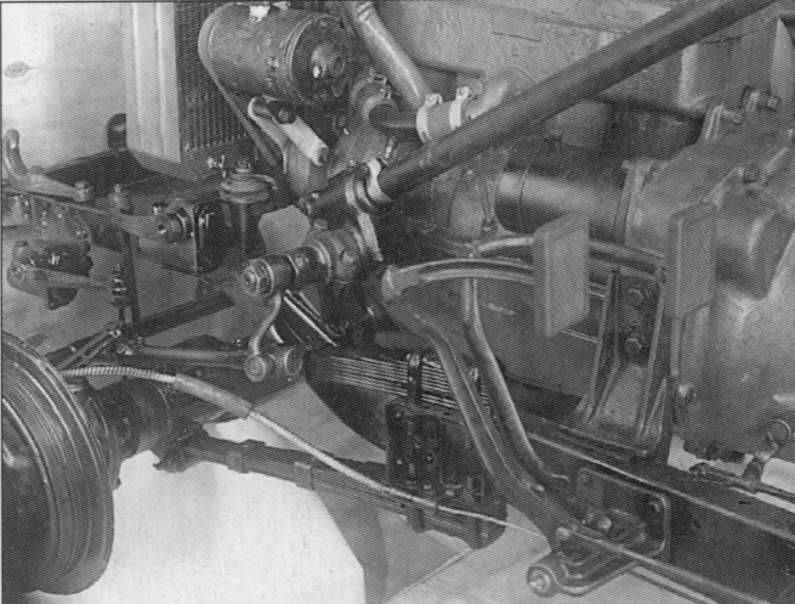
For the implementation of the rotation of the front, leading, wheels in the drive introduced special hinges constant angular velocity, which allow the transfer of power and rotation of the wheels at a considerable angle.
The increase in the transmission ratio in the transmission reached the setting of the gearbox of the GAZ-MM truck with some design changes caused by the installation of the transfer case. The first gear and the reverse gear in the box were switched on when the front axle was engaged, since working on these gears of the rear axle only leads to a load.
Electrical equipment and instruments from GAZ-M1 and GAZ-MM. In the design of their number reduced to the limit. In particular, oil pressure and coolant temperature indicators were not installed.
At the beginning of the Great Patriotic War, workers on the GAZ-64 chassis quickly built a light machine-gun armored vehicle, designated BA-64. The armored car was produced in parallel with the GAZ-64 since May 1942. He was the only armored vehicle produced in the USSR throughout the war.
The cross-country vehicle GAZ-64 had some drawbacks. The main one was the lack of lateral stability (which was also characteristic of "Willis"), caused by narrowed ruts. Insufficient lateral stability was especially felt by the crew of the armored car. This made the designers go back to the original track. September 26 1942 approved a plan for its radical modernization. However, only 15 February 1943 began to implement this program.
The organization of production of the GAZ-67 car began in accordance with the Decree of the State Defense Committee of the USSR No. 3106с from 01.04.1943.
The body was slightly widened, front and rear fenders installed, an extra gas tank was placed under the driver’s seat. The frame of the car strengthened and slightly modified the suspension. On the car were put tires with lugs, increasing the grip on the wheels and significantly reducing their slip on slippery (snowy or muddy) sections of the road.
As a result of all the improvements, the length of the GAZ-67, in comparison with the GAZ-64, increased slightly and amounted to 3345 mm, but the width increased to 172 centimeters. This greatly improved the lateral stability of the all-terrain vehicle.
In the process of mastering the production, the weight in the equipped state decreased to 1342 kg. Due to the increase in width, body drag has increased. The combination of these two reasons, led to the fact that, despite the increase in power, the maximum speed dropped to 88 km / h.
GAZ-67 received a kind of business card - 4-spoke steering wheel having a bent wooden rim with a diameter of 385 mm. The production of such a steering wheel was forced to be mastered in one day due to the failure of the supplier of carbolite parts - the factory producing these products was bombed. Despite the inconspicuous appearance, the drivers loved the wooden steering wheel, because it was possible even to work without gloves in winter.
The first GAZ-67 went off the 23 of September of the 1943 of the year off the assembly line, and the 2 of October already produced at least 10 vehicles every day. Until the end of 1943, 718 vehicles were produced, in 1944, 2419 was produced, and the 1945 year was 6068.
The upgraded command or army headquarters vehicle GAZ-67B replaced the previous version at the end of 1944. The modification was developed back in January 1944. GAZ-67B was equipped with the same engine and 4-speed gearbox. True, a new carburetor, an ignition distributor and a gasoline filter were used on the new car, the front axle was reinforced, new needle bearings were used in it, the driveshaft and suspension were modernized.
In 1948, the welded grille was replaced with a characteristic stamped lining with seven air intake slots arranged vertically in the style of the American Willis-MV. In both jeep suspensions in 1951, double-acting hydraulic shock absorbers were introduced. In 1953, the shape of the vents on the hood was changed.
Production of GAZ-67B lasted for nine years, thus becoming the most famous post-war multi-purpose all-wheel drive car, but in peacetime it was mainly used as a means of motorization of agriculture. With 1950, that is, during the active development of GAZ-69, the further modernization of GAZ-67B was stopped.
In the army, the all-terrain vehicle received a large number of nicknames, among them: “pygmy”, “goat”, “flea warrior”, HBV (I want to be “Willis),“ Ivan-Willis ”. During the war, the production of GAZ-67 and GAZ-67B were very small - only the 4851 unit was produced, since the main focus was on the production of the BA-64B armored car. Until the end of the war, 3137 all-terrain vehicles GAZ-67 and 1714 GAZ-67B were launched. In total, until the end of production (1953 year) released 92843 car of this type.
Specifications:
Wheel formula - 4x4;
Weight - 1320 kg;
Length - 3350 mm;
Width - 1685 mm;
Height - mm 1700;
Engine power - HP 54 .;
Maximum speed on the highway - 90 km / h;
Cruising on the highway - 500 km;
Gradeability - 38 degrees;
Number of seats in the cabin - 4.
Prepared by materials;
http://www.weltkrieg.ru
http://www.retro-car.ru
http://avtocollection.com
http://retrobazar.com
http://www.opoccuu.com



Information