The current state of combat training of ground forces and the requirements for its provision with technical training aids
Tactical training
Analysis of the results of tactical training shows that the level of training units has increased slightly. The Ground Forces managed to increase the number of classes conducted at night. For tactical training, the commanders began to plan the necessary number of vehicles.
At the same time, there are shortcomings in the course of conducting tactical exercises, where, as before, the leaders focus on the stages of live firing, leaving behind the scenes the organization of combat and the training of subunits to carry out the tasks ahead. Issues of the electronic impact of the enemy, as well as complex radiation, chemical, and bacteriological conditions are not always addressed.
In addition, it is problematic to create the required combat situation in the training conditions for testing modern forms and methods of using troops due to the limited space of training tactical fields. In this regard, it is more effective to conduct classes first on a tactical simulator. For example, on a simulator of a motorized rifle company with dowry tank a platoon and a supporting mortar (artillery) battery, bringing all actions to automaticity, followed by exit to the landfills. This simulator should teach commanders of all degrees the correct decision-making, on which either victory or defeat will depend, reflecting the real losses of personnel and equipment.
Such a comprehensive class tactical simulator for training tactical managers is currently being developed and plans to have crews of combat vehicles, a simulator for a motorized infantry unit, simulators of attached and supporting units, united by a single information-modeling environment, which will allow to work as a single preparation and coordination of units to the company (battery), inclusive. The simulator allows you to simulate any terrain for training in special conditions (in the city, forest, desert, in the winter or in the northern regions), which is extremely important, since it is almost impossible to create similar conditions on real test sites.
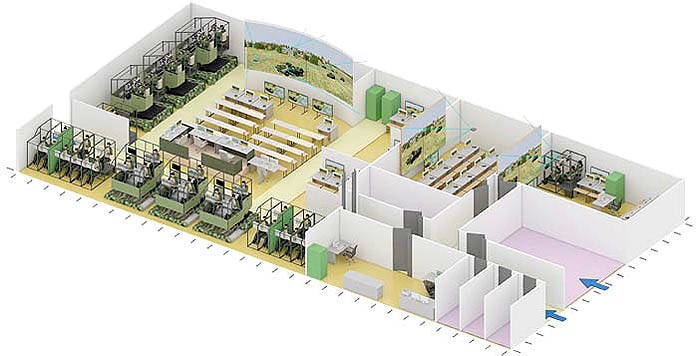
At present, within the framework of the R & D, the Brigade-U is developing a tactical simulator for a reinforced motorized rifle (tank) battalion, which will be installed in the newly created training center of the new generation Mulino in the village of the same name in the Nizhny Novgorod region.
To ensure the readiness of the units to conduct a lesson on such a simulator, it is planned to equip each combined-arms team with tactical simulators for a reinforced company.
In addition, it is planned to create interactive computer classes in the training buildings of the formations for training specialists of all categories of the armed forces of the Ground Forces, which will improve the efficiency of conducting classes through the use of universal software. This will eliminate the need to attract additional material resources (posters, mock-ups, samples, etc.), which, due to their wear and aging, need to be constantly updated.
Fire training
Fire training activities are aimed at improving the individual training of military personnel and improving the skills of personnel in actions weaponsarmed with combat vehicles.
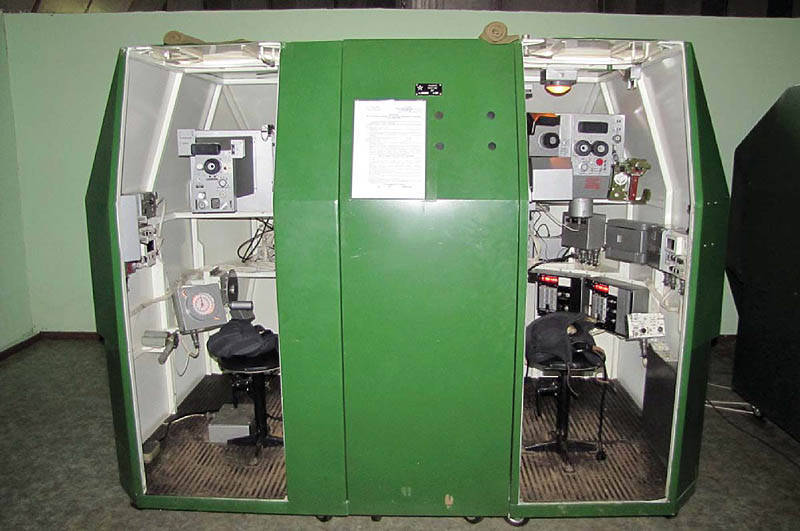

Analysis of the results of the implementation of fire training measures allows us to conclude that at the present time during the training sessions there are systemic flaws that significantly affect the quality of training.
Not all commanders can put into practice the requirements of the Course of Shooting and Combat Training Programs, as a result of which the volume, content and sequence of practicing fire training exercises are not respected.
The leaders of the classes, in most cases, cannot conduct a qualitative analysis of the actions of the trainees and the results of the shooting. Some officers, especially graduates of schools, as a result of low personal professional training do not see shortcomings in the actions of subordinates and do not take measures to eliminate them.

Therefore, it is necessary to devote more time to classes at modern training facilities. All initial and preparatory exercises must be performed on simulators (which reduces the time for training, saves resources and eliminates the serious consequences caused by the violation of safety requirements), and then go out into the field and engage in military equipment, performing training and control shooting.
In addition, a modern tactical simulator allows you to work out exercises for managing fire units, which is not always performed during fire training.
Taking into account the experience of the ground forces of major foreign countries, it is advisable to equip tactical and fire training facilities with laser imitation systems for shooting and defeat, transferring them into the category of the command and training base, which will lower the costs for purchasing ammunition and restoring (repair) equipment (weapons).
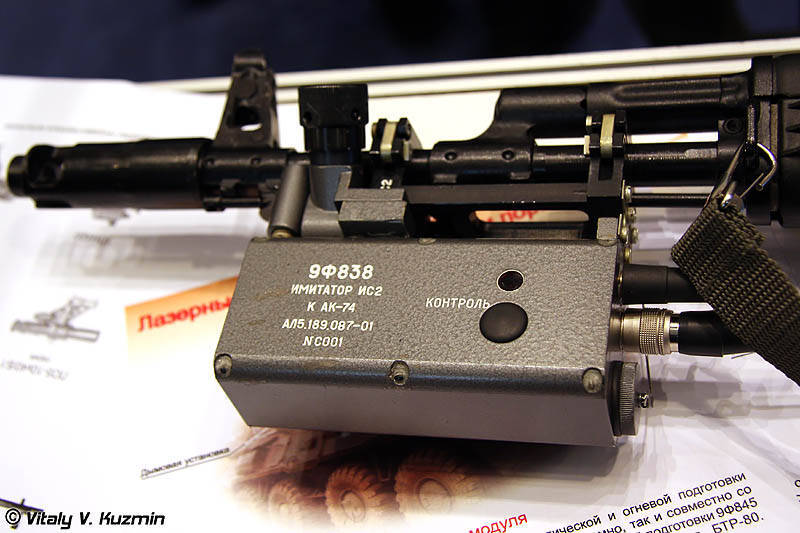

It is planned to create laser shooting and destruction simulators (LISPs) of the main modern combat simulation tools, providing for simulating fire from armored weapons, artillery systems, air defense systems, simulating the use of mine clearance systems, the entire line of small arms and grenade launchers, which are armed with a motorized rifle brigade.
To date, this system LISP is the most effective compared to analogues of domestic and foreign manufacturers. The LISP system being developed provides for conducting bilateral tactical exercises on a battalion scale per battalion, as well as objective control over the actions of the trained units and the preparation of materials for the analysis of tactical exercises.
Driving combat vehicles
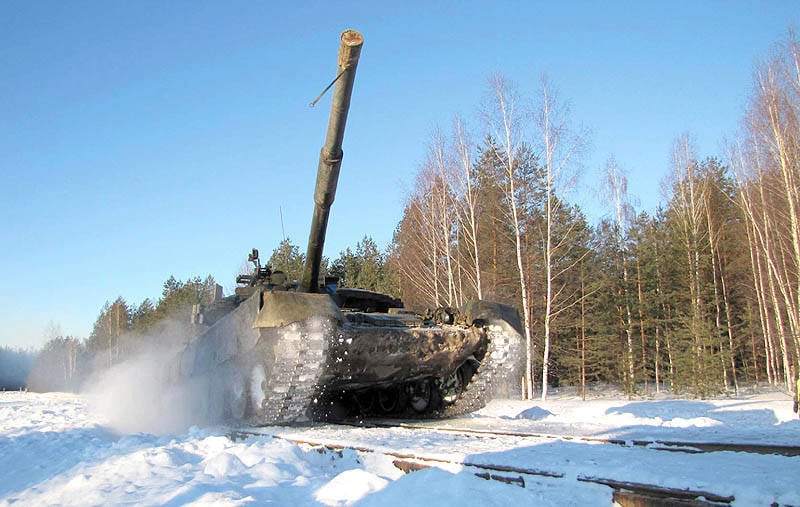

Conducted classes in driving combat vehicles are aimed at improving the level of training of driver mechanics, to coherent and professional actions in crews, platoons, companies, in solving various tactical tasks on the battlefield, as well as during marches and overcoming water obstacles afloat and under water.
An analysis of the measures taken in the Ground Forces for the training of driver mechanics shows that the unit commanders do not pay due attention to classes using the available training means.
One of the reasons for this is the large depreciation of the driving simulators available to the troops, both in terms of resource development and in terms of service life, which are often more than 15 years. Technical maintenance of simulators was not conducted in the Ground Forces since 2010, therefore their condition does not allow to conduct high-quality driving lessons in class conditions.
At present, a complex of polygon equipment is being created for objective monitoring of the results of driving combat vehicles and tanks at the tankodrome. The planned completion of works and the delivery of polygon equipment complexes is 2013 year.
Technical training
The Main Directorate of Combat Training of the Ground Forces to determine the actual state of the simulators available to the troops, at the initiative of JSC Training Systems, together with the Western, Southern and Central Military Districts conducted their inspection and technical examination.
The results of the inventory allow not only to assess the security of combat training of military units and training centers, but also to identify specific measures for organizing maintenance and rehabilitation of simulators, carrying out repairs, writing off obsolete or developed technical equipment simulators.
It has been established that military units are equipped with practically on 100% simulators in accordance with the timesheets to the states, and also have a significant number of simulators in excess of the standard requirement.
At the same time, in the units of constant readiness, there is an almost complete absence in the report cards to the states and in the presence of crew simulators for armored vehicles (tanks, infantry fighting vehicles, BMD, and armored personnel carriers), artillery and anti-aircraft armament complexes that are needed to co-ordinate crews after the arrival of military specialists (driver, gunner, operator, commander, etc.) from the district training centers.

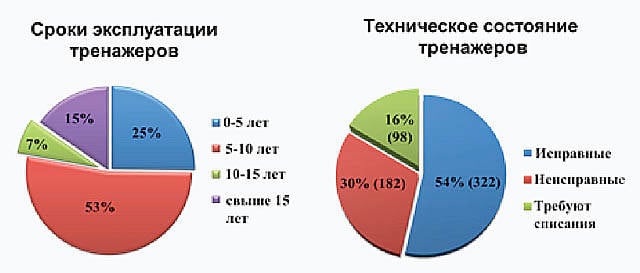
The presented diagram of the distribution of simulators over the service life shows that 15% of simulators have worked over 15 years. At the same time, it was found that only about 54% of simulators are in good condition and are actively used in the training of military specialists in military units.
Such a low percentage of the presence of serviceable simulators in the troops is primarily due to the almost complete absence of maintenance and rehabilitation of simulators in the Ground Forces in 2010-2011.
It should be noted in general, the low supply of troops with modern simulators. The simulators developed by 10-20 years ago and still operated by the troops do not meet the current level of technology and modern requirements for the organization of combat training, which necessitates their profound modernization or replacement.
The problems of providing troops with simulators, including their maintenance, rehabilitation and repair, are aggravated by the low level of unification of simulators of the same type for the armament complexes of the Ground Forces.
This is especially noticeable in the armor simulators available in the troops, which were supplied by eight different enterprises of the national defense industry in the period from 1980 to 2010. Raznunifikation creates certain difficulties in training military personnel of training platoons of proper operation and ensuring the efficiency of simulators, when training unit commanders to work on simulators and methods of training military personnel using simulators, while solving military issues of ensuring simulator operability in warranty, and especially in the post-warranty period in full lack of group and repair spare parts, as well as the necessary funds for the restoration of their work ability as well as the formation of the military districts in exchange nodes funds, units and assemblies for the restoration of health trainers.
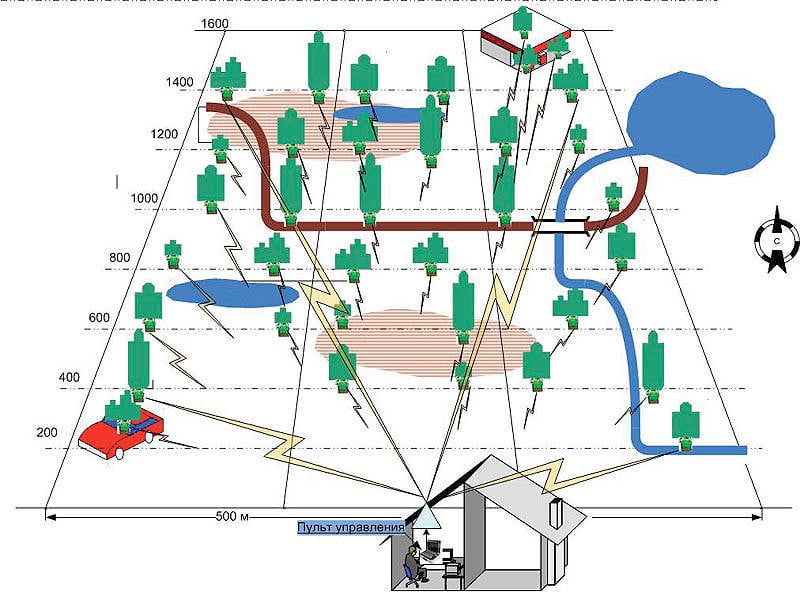
Currently, development work is being carried out by the Brigade-U (2011-2013) and the Connection-OVF (2012-2014) to establish the Center for Combat Training of the Ground Forces (Mulino), it was decided to create Interspecific training ground of the Southern Military District in Ashuluk.
The software-modeling environment created within these ROCs, a unified system of visualization of virtual space, complex simulators and other TCBs should be the basis for the training and training of the paratroop base of constant readiness units and training centers of the Ground Forces to prepare units at the level of platoon, company, battery, battalion, division, etc.
This will not only improve the quality of training brigades in locations, but also facilitate the adaptation of personnel and units to the training and material base of the Ground Forces Combat Training Centers during the training of military personnel in brigades and battalions.
Brigade training and material base, based on world experience in organizing combat training of troops, should rationally combine two forms of training:
• traditional (in the field) associated with the use of existing directresses, fire towns and polygons;
• computer (classroom training), which includes simulation and modeling complexes, computer simulators, simulators for training and control of the level of training, etc.
When equipping the training and material base of the formations and the Combat Training Centers, priority is given to the creation and supply of technical training aids for the training of high-tech military personnel.
This primarily relates to the calculations of modern artillery systems such as the 2C19 "Msta-S" and 2C25 "Sprut", the newest salvo-fire systems such as the Tornado-S and the Uragan-1M, and the Iskander missile system, as well as line of samples of military air defense.
Experience in the operation and maintenance of simulators in the troops showed that without organizing a system for training specialists to ensure the operation of simulators in the troops, it is impossible to ensure the necessary intensity and effectiveness of training the Ground Forces.
First of all, it is required to ensure that officers are trained to work on simulators for the chosen specialty (armored vehicles, artillery, anti-aircraft complexes, etc.) in higher education institutions or in advanced training courses, which will allow them to properly organize the training of their units.
The platoon simulators available in brigades and training centers (full-time 14 personnel) cannot ensure the proper operation of the simulators, since the training of the commanders of such platoons (contract servicemen) is not carried out, and the rest of the military platoon troops serve by the call of 1 a year.
Modern combat training provides for the intensive use of simulators in the army during the school year (8-16 hours daily), which requires the recovery of the simulators from working for 24-48 hours.
At the same time, the Order of the Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation on 2010, No. XXUMX, approved the “Provisional Regulation on the Basics of Organizing Servicing of Armament and Military Equipment in the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation”, which provides for maintenance, rehabilitation and repair of simulators at different stages. At the same time, according to the existing experience of work organization, troubleshooting is planned for 1919 years, i.e. in general, the first year is the troubleshooting of products, the second year is the restoration.
An important factor in the provision of combat training is the presence in the troops of modern ground equipment, its ability to quickly create and manage a diverse target environment with the provision of objective information about target destruction and equipment operability in real time.
In 2009, the PSO-P radio-controlled firing equipment on the 40 target installations was adopted for the supply of the Armed Forces. On state tests set showed good results. But, unfortunately, due to the limited budget allocations for these purposes, over the past years only a few sets have been purchased.
The above problems with the maintenance and operation of simulators, as well as simulator repair, fully applies to field equipment, taking into account the fact that it works at all times of the year, in all weather conditions and time of day in the field.
The rifle and small artillery polygons are morally and physically outdated and no longer provide, with due quality, training for the rocket forces and artillery. Today, it is necessary to widely use in the training of artillery officers modeling and visualization systems, to create technical means of training such as the 9ФХNUMX simulator for training the command personnel of the artillery unit (division battery).
Requirements for advanced TCB
Changes are taking place in the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation related to the reform of the Ground Forces, the formation of military units according to the mixed principle of recruitment: by contract and conscription, by reducing the service life of conscription to 1 year. The officer training system has undergone a change, and combat training is being improved in line with the existing threats to the country's security.
Each of these changes in the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation has an impact on the assessment of the technical means of training available today in the Ground Forces and imposes new, increased requirements on the training means newly developed and delivered to the troops, to ensure their reliable and uninterrupted work during combat training, to reduce cost of production and the cost of their operation. Prospective TCB should include:
• unified software;
• creation of a unified visualization system for the formation of a fono target environment;
• use of three-dimensional digital space;
• a unified system of imitation of dynamic loads on students;
• single workplace instructor;
• the maximum possible unification of design and technological solutions (nodes, blocks, monitors, computers, etc.);
• modularity of construction to ensure different versions of the exercise of simulators (dynamic, static);
• the possibility of combining crew simulators into complex simulators for training units (platoon, company).
Providing the Ground Forces with new technical means of training, as well as introducing new forms of training for troops (forces), tactical echelons of the Ground Forces, Airborne Forces and Coastal Forces of the Navy, will allow to qualitatively increase the level of combat readiness of troops (forces) at the present stage and in the future.

Information