Automated control system of troops "Andromeda-D"
According to the results of the successful military operation of the Polet-K, which was conducted by the Airborne Assault Division (Pskov) in 76, it was decided to further develop the ACCS system, but this time - with coverage of all units of the airborne troops control airborne combat vehicle and a separate soldier. Experimental design, open to the solution of this problem, received the name "Andromeda-D."
The work was based on system-engineering solutions adopted and implemented in the framework of Polet-K. As the practice of several years of troop exploitation has shown, these decisions, in their essence, turned out to be correct. As part of the project, the principle of maximum unification of the devices being created with hardware and software already developed in the framework of Polet-K was applied, as well as the principle of modularity of the control tools created, which are intended for staffing control points at all levels of the military hierarchy - as tactical, and operational management.
In view of this, the project has become considerably less costly in financial terms than the complex ESU TZ (created in the “M2 Constellation” tactical unit) created in the “Constellation” concern. And this, despite the relatively greater number of levels of control included in the system (Airborne Forces Command - division - regiment - battalion - company - platoon - detachment - soldier), which is envisaged in the system of ESU-TZ (team - battalion - company - platoon - department - soldier).
Total: eight to six.
In addition, the Andromeda-D development project took into account the experience of creating and operating the Maneuver automated command and control system, as well as international experience in creating similar automated control system. As a result, a unified management system was created not just for tactical but for operational-tactical level!
In 2010, deliveries of sets of the complex began in 76 SDS, and in 2011 - to the command of the Airborne Forces, in 7 SDN (g) and 98 airborne divisions.
The first, the “installation” party of the Andromeda-D system was operated during the combat training activities in the same 76 SDA.
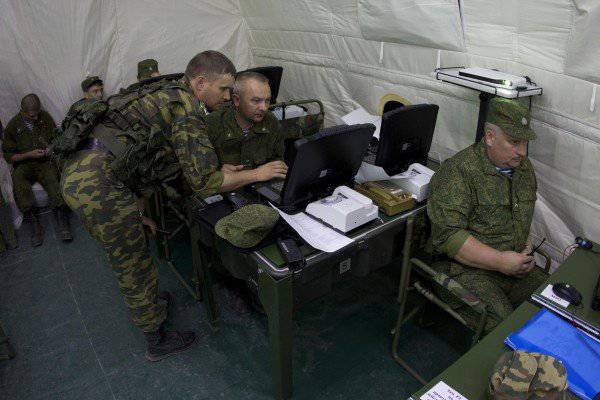
As a result of this operation, significant changes and improvements were made to the composition of the set of hardware and software and equipment. Officials of the Airborne Forces Command, divisions and regiments, for work in the field, received new automated workplaces (AWP) created on the basis of protected EC-1866 PCs with 17-inch monitor and built-in video cameras.
The ergonomics were also improved and the overall weight of the equipment included in the field control points was reduced. Significant processing has undergone software products used in the system. And all this was done fairly quickly - during the spring and summer of the 2011 year.
And, finally, in August - September, it was possible to "try" the operation of the complex with the participation of the whole "vertical of power" from the commander of the airborne forces to the detachment and the soldier.
Iron…
A feature of equipping mobile control points of the system is the ability of the operational (combat) personnel to choose how to organize work, depending on the conditions of the situation.

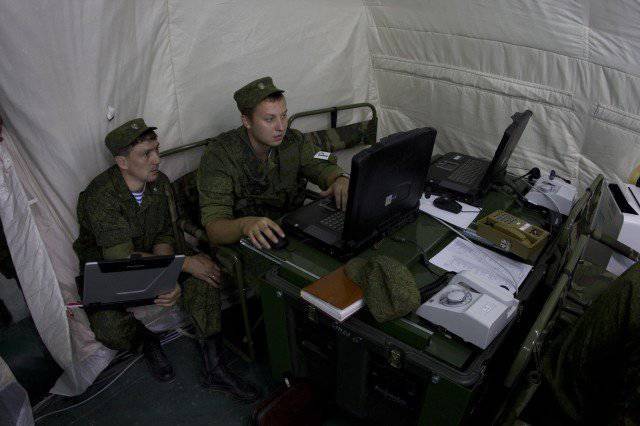
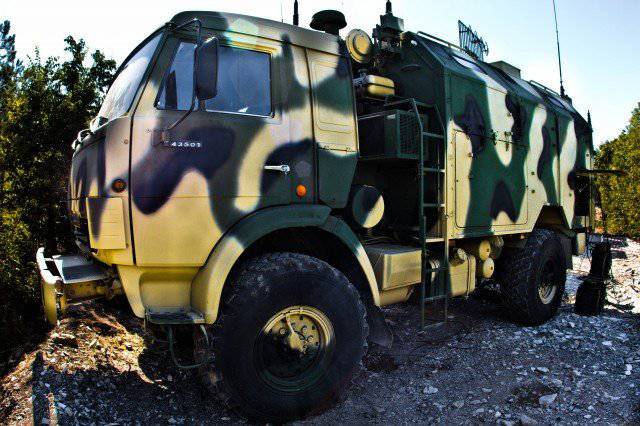
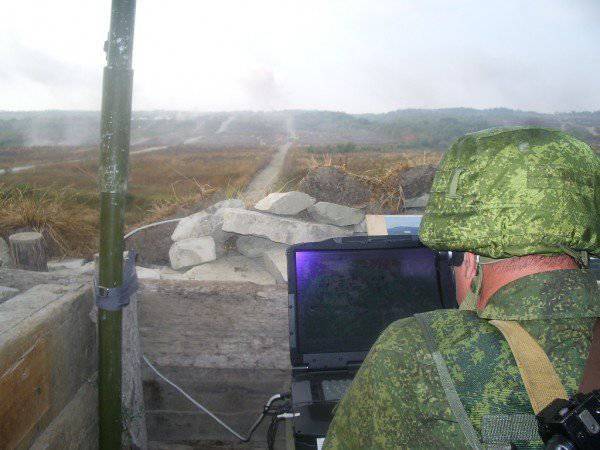
The main management tool for each official in the system is a commander (command and staff) machine based on the BMD-2 (BTR-D), equipped with an automated workplace (in the BTR-D - several places) and communication facilities that transmit information on various channels.

Each such vehicle, up to and including the squad leader, is equipped with GLONASS equipment, and duplicate inertial coordinate determination equipment, which allows the positioning of the armored object, reads the direction and speed of movement on the battlefield and passes this data to the higher-level commander on his “one-time” request, or periodically, there is discrete (in automatic mode at specified intervals). The coordinates, speed and directions of movement obtained from the machines can be displayed in the form of symbols (tactical signs) on the electronic map of any official authorized to receive such data.

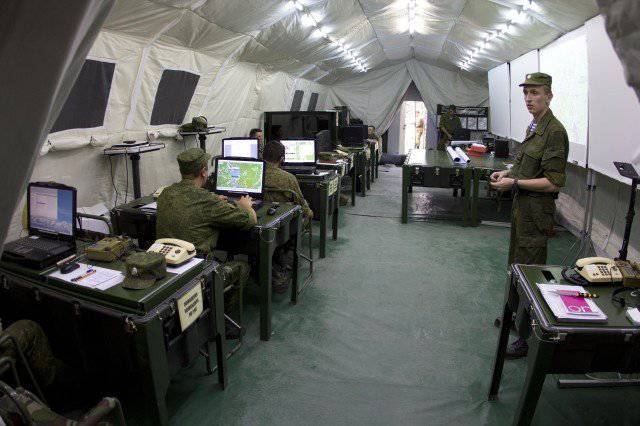
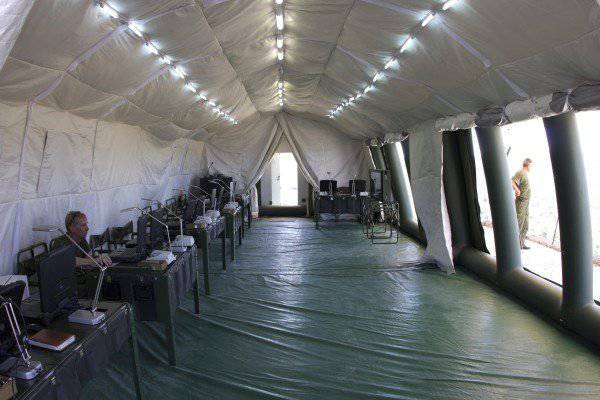
In addition to commander and command-staff machines, the kit of each divisional and regimental command and control centers (PU) includes the required number of modules for organizing collective work (tents on a pneumoframe), which are equipped with everything necessary to ensure comfortable work of the operational (combat) personnel in conditions when the impact of the enemy by means of fire destruction is excluded, or it is extremely unlikely.
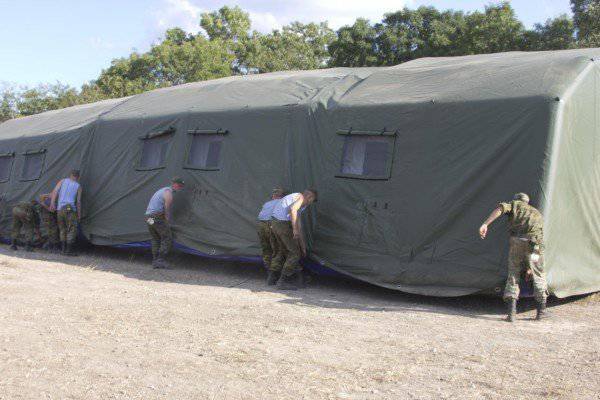

Inside the tents, autonomous lighting, air-conditioning and heating systems, officials' automated workplaces and folding plastic furniture for their deployment are deployed. Tents and their internal equipment are unified and interchangeable both “vertically” and “horizontally”, the hierarchical structure of the Airborne Forces. Each module can be deployed to 20 workstations.
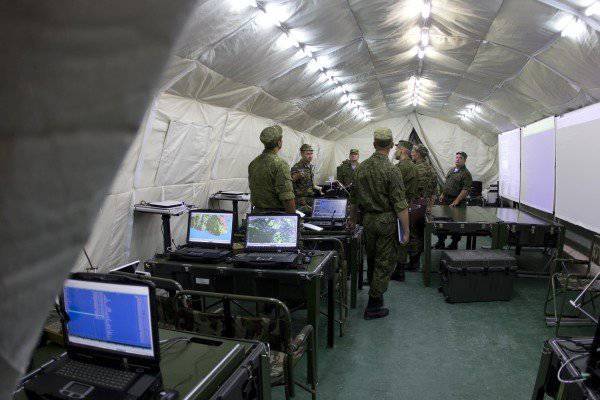

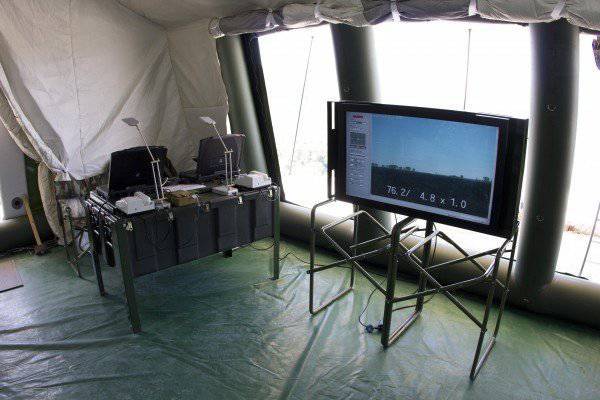
Each tent (module) is equipped with systems that provide local network operation with uninterruptible power supply devices, a speakerphone, four multimedia projectors and screens, an 24-inch plotter, a scanner, a laser printer. Each module has its own units for providing autonomous power supply.
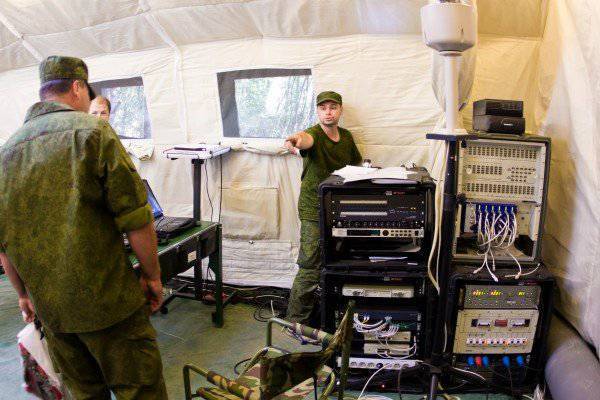

Also, the structure of each module includes external (internal) review video cameras, which allow to conduct video surveillance both inside the tent and on the approaches to the location of the PU.
The total number of modules in each control center may be different and is determined by the needs of the corresponding control center in the workplace.
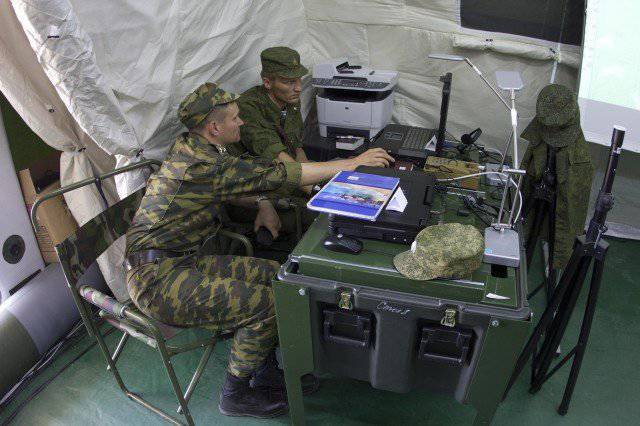
At the same time, each official (DL) of the division management (regiment) has two personal computers (AWPs) - one as part of a module for working in a tent, and the other is installed on a mobile armor base (with the possibility of its remote removal for working on the ground, or remote connection to the local network organized inside the PU module).
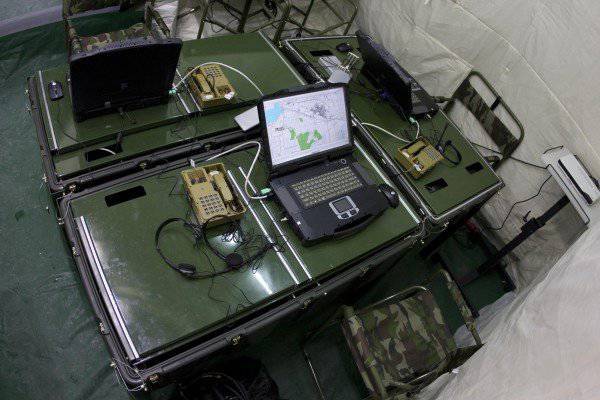


Therefore, depending on the conditions of the situation, management can work in the following ways:
- collectively (all PU officials are in modules). For transmission of information using cable communication channels);
- in distributed mode (each official is on his “armor”, while the module (tent with equipment) does not unfold). Radio channels are used to transmit information;
- in the combined mode (module + armored objects) with the ability to exchange information with all DLs over the network (for data transmission, both cable and radio channels are used).

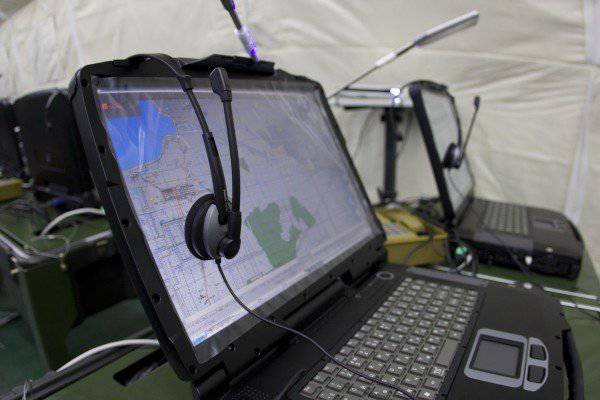
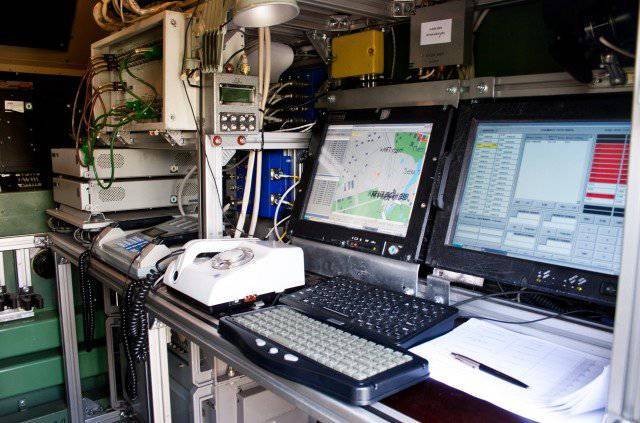
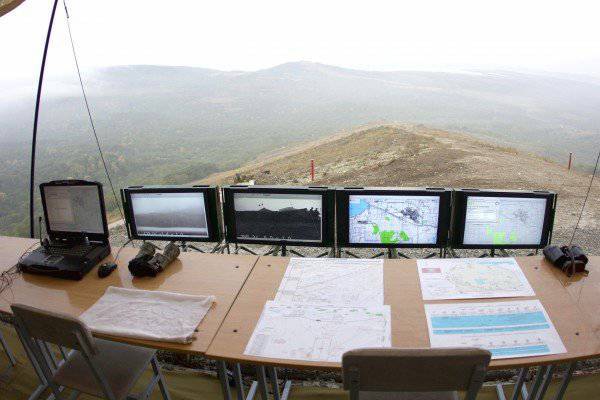
Each ARM official, made on the basis of a protected PC EC-1866 with 17-inch screen, includes a built-in WEB-camera and headset, providing communication between DL and PU in video conferencing mode.
In addition, the commander’s AWP (senior module) is connected to an interactive whiteboard and has the appropriate software components to ensure quick input of graphic information to an electronic card “by hand”, that is, without using a graphic editor.

Workplaces (AWPs), including those installed directly on combat vehicles, are unified in software from the detachment commander to the commander of the Airborne Forces and differ only in the level of access to the corresponding programs and database sections.
The exercises with 7 dshd were notable for the fact that, along with the control points of the division, regiments, battalions of the battalions, companies and platoons equipped with automated workplaces, the command headquarters of the exercise also had similar automated controls at its point. Unlike earlier exercises, this item was deployed at a considerable distance from the trained authorities. And he worked with the management of the division remotely, carrying out the completion of combat missions, the delivery of introductory and controlling the actions of the trainees practically on-line.

The network routing scheme provided an opportunity for each management staff officer to automatically “directly” contact any control object (up to and including platoon), bypassing numerous “manual” connections at intermediate communication nodes. In order to send a message, for example, to the commander of the artillery battalion of the airborne assault regiment, it was enough to select the appropriate line in the electronic address book, the same for all workstations.
In addition to mobile components, the Andromeda-D system in the future will also include stationary command and control points (for the command levels of the Airborne Forces Command, division, regiment), which will ensure control of the daily activities of the troops, as well as solving management tasks with individual units (formations) without deployment of field control points of higher levels of government.
For example, the division commander conducts a bilateral command and staff regimental tactical exercise with the regiments of the division. Permanent dislocation points (RPMs) and polygons of these regiments are located at a considerable distance from each other. In the presence of stationary components of the system in the RPM regiments and divisions, he will be able to hear the decisions of the trained commanders, without diminishing anywhere from his headquarters. Video conferencing will provide him with “live” communication with regimental commanders, intermediaries and other officials, and on the next screen he will be able to see a graphical display of any elements of the tactical situation, including decisions made by students, transmitted to him over the network.
Some stationary elements of the complex were already mounted at the point of permanent deployment of the Airborne Forces Command and during the exercise, the leadership staff was provided with the opportunity to contact the operational duty officer of the Airborne Forces practically from any automated workplace. Including - using video conferencing.
Algorithms
It should be noted that the use of hardware-software complexes of the automated process control system initially implies that officials have a certain level of theoretical knowledge, practical skills and abilities.

That is, it is impossible, for example, to teach a person to satisfactorily display a tactical situation on an electronic map, or to make operational and tactical calculations, if he did not have previous skills in working with a paper map, or does not know the methodology for carrying out such calculations.

In addition, the level of coherence of the military command body, the knowledge of each military personnel of the headquarters and the management of their place and role in the collective work to develop a decision, as well as the order and organization of the commander and staff with the receipt of the combat mission is of considerable importance.
And here another problem arises that directly follows from the law of the dependence of control methods on the means of control used.
As the preparation for the teaching showed, attempts to combine the use of the old, “manual method” designed algorithms of the commander and headquarters, while simultaneously using new automated management tools, not only do not give the desired effect of gain in time, but often are inferior to methods of solving similar managerial tasks in a purely "manual" mode of operation.

Therefore, a characteristic feature of the work of commanders and staffs at all levels, not only during training, but also during the exercise itself, was the search for ways of organizing work that would be optimal in terms of shortening the combat command cycle.
It should be understood that automated systems themselves are not “accelerators” of solving managerial tasks. In any case, the algorithms of the work of commanders and staffs with or without the use of such systems are determined by people.

However, despite the experience gained during the exercise, the operation of the system (both positive and negative), it is worth noting that the development of algorithms for the work of the military command body in preparation for the battle and in the performance of combat missions is still the prerogative of the commander and the staff of the division .
Work
From the point of view of any official, the hardware and software systems of the system should provide the solution of eight basic management (information) tasks in an automated mode.

According to the results of the exercise, it can be argued that the use of an automated command and control system during the preparation and control of the battle ensured the achievement of a real, rather than declared, acceleration of the fulfillment of the specified information tasks.
Speaking about the system as a whole, it is worth mentioning the fact that it provided automation of the most laborious and unproductive work of staff officers in collecting, processing, displaying and exchanging information.

Many participants of the exercise noted that the implementation in the system of such features as:
- organization of multi-user access from various workstations to the commander's file of graphic settings;
- the ability to quickly scale the environment and link it to the displayed scale of the topographic base;
- allowing the user to continue to work offline in case of disconnection from the local network without data loss;
These are the means that, to a significant degree, exempt officers from performing non-creative work, mainly related to copying the graphic data of the situation and transferring it from one scale of maps to another.
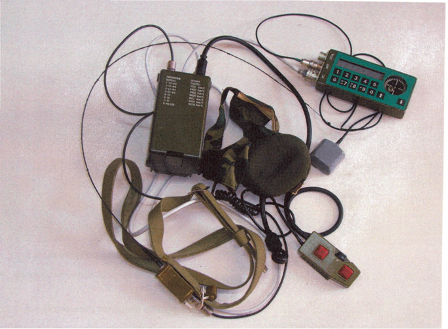
In terms of reducing the “reconnaissance-defeat” cycle, as applied to the fire weapons available in the amphibious divisions, it is worth mentioning the wearable complex NPTK.
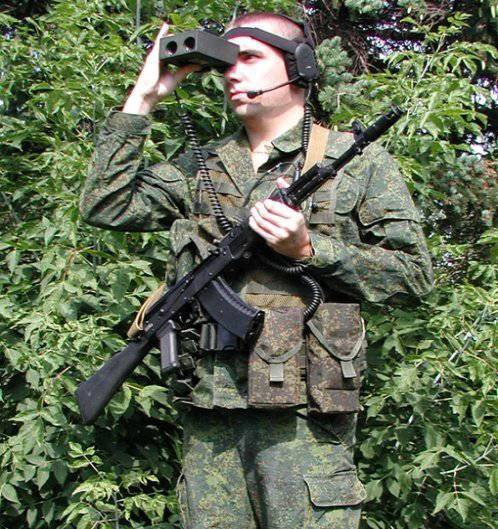

This complex includes means of GLONASS communications, communications, a laser range finder and a protected PC.


Any soldier who has such a kit can automatically give accurate target designation in a single data format used by both the intelligence subsystem and the artillery control sub-system. And also to transfer this data to the commander to make a decision about hitting the target, while simultaneously sending it to the artillery control subsystem to calculate the initial settings for firing.

Further, as they say, - the matter of technology. Target data, falling into the Rheostat artillery fire control subsystem, are automatically calculated for batteries, platoons and guns and are given to them automatically in the form of initial settings for firing. With the receipt of a command for defeat from the corresponding commander, the battery (division) immediately opens fire on the specified target.
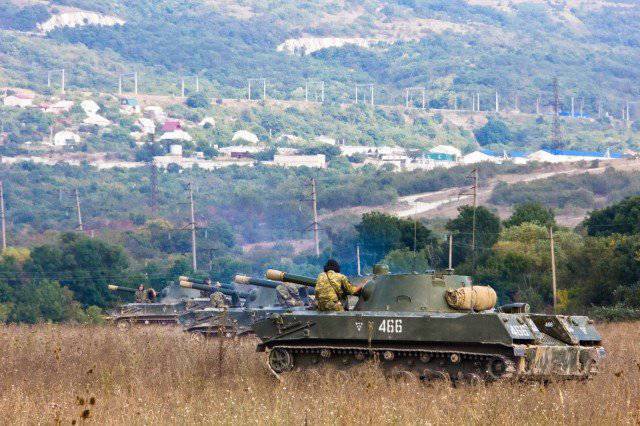

By the way, at the Raevskaya test site, this method of target designation (using the bundle of Andromeda-D systems - “Rheostat”) was first used with real fire at the defeat of the chosen target. The automatic transmission of information was carried out as part of the “complete chain” from the reconnaissance platoon of the paratrooper battalion to the calculation of the gun of the artillery division of the 120-mm SAO Nona.
At present, only reconnaissance paratroop and air assault battalion reconnaissance platoons, as well as reconnaissance company platoons of reconnaissance companies of regiments are equipped with NPTK complexes, but all parachute (airborne assault) platoons of battalions will be provided with these complexes in the future.
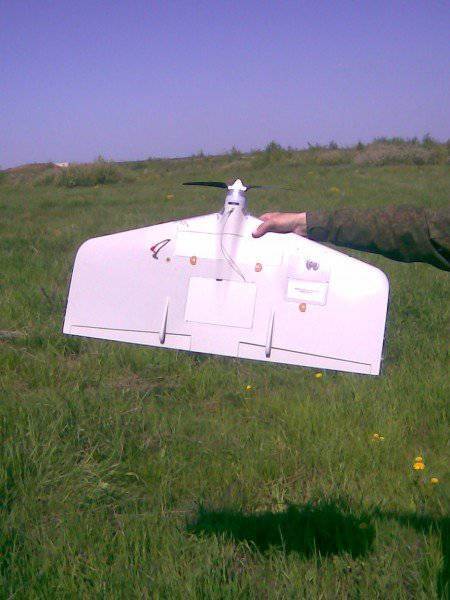
In the future, using a single format of target data, it is also planned to use unmanned aircraft of various classes, adding to the reconnaissance functions that they perform now, also the function of targeting and adjusting artillery fire.
The fulfillment of the need for information arising from the airborne units and individual servicemen in the performance of such a specific task as collecting after landing and searching for combat vehicles (goods) landed by parachute also did not go unheeded.
Back in the period of work on the creation of the Polet-K system, a wearable complex of paratrooper controls (SPAC) and a paratrooper collection unit (DDD) were created, which ensured that each crew member could quickly search for his own car after landing, especially in reduced visibility conditions.

A transmitter is installed on each landed vehicle, which turns on when the parachute system is triggered when landing.
Crew members who have a wearable part of the complex receive a radio signal from their combat vehicle, which is converted and issued to the paratrooper in a sound and visual form (direction to the vehicle).
Did not work out.
As they say in official reports: “despite the progress achieved ...”,
There are disadvantages in the system.
Where in the army without them?
From the point of view of users, the main disadvantages of the system lie in the software. Basically, this is reflected in the complexity of the software interfaces and the absence of software components of the system, allowing to automate the solution of computational and analytical tasks.
In addition, due to the use of an outdated version of GIS “Integration” in the system with very limited functionality, the functions of differentiating access rights when working with a map of the situation in multi-user mode cannot be implemented, which makes the use of such a mode extremely difficult and unsafe.
The problem of the speed of putting tactical signs on the map in acceptable time parameters remains unsolved.
Does not provide "Integration" and the display of electronic maps in three-dimensional form. And, meanwhile, volume visualization of mountainous terrain is a necessary task, based on the specifics of 7 dsd, which has the word "mountain" in the title.
There are also issues related to the integration of automated workplaces with the latest printing tools for displaying and recognizing graphic information, since the 3,0 operating system does not include the appropriate drivers.
The possibilities of using commander interactive whiteboards have not yet been fully realized yet. The reason is the same - the obsolete operating system of the WSWS, which does not allow full use of their functionality.
In addition, there is still a lot of work to be done in automating and completing the integration into a single information space of all the systems that are the “providers” of the environment data for displaying them in the commander and headquarters subsystem.

Including - data obtained by the means available in the subsystems of intelligence, engineering troops, radiation, chemical and biological protection, electronic warfare, communications, as well as in the subsystem of management of material and technical support.

For, until the collection and processing of all the situation data necessary for the commander to make an informed decision is not automated, it is too early to talk about the full automation of the control system.
Yes, at this stage of development, the ACCS relieves staff officers from the routine of “redrawing” maps. But in the course of further improvement of the system, first of all, attention should be paid to the automation of the processes of mining, collecting and processing and transmitting information coming to the headquarters from other subsystems.
The main obstacles on this path will be the departmental interests of the producers of individual complexes, which have already completed work on the creation of systems for the production of such data in various subsystems. So - spent the money!
Here are just the display methods and formats of this data used by different manufacturers - each has its own. This leads to the fact that even the data pre-processed in the subsystems cannot be perceived and displayed in the subsystem of the commander and staff without another stage of their processing.
As a result, attempts to automate the extraction and processing of data in individual subsystems without the ability to automatically transfer this data to the subsystem of the commander and headquarters (for which, ultimately, they are extracted!) Makes this work absolutely pointless.
Figuratively speaking, instead of communicating vessels in which information should flow freely, like a liquid, from vessel to vessel, we now have several to the top filled bottles with very narrow necks.
At the same time, attempts to transfuse liquid from one bottle to another (information exchange) are a very lengthy process that requires unreasonably time consuming, unproductive and uncreative work, usually performed manually by officers of the commander and staff subsystems.
One of the organizational reasons for this situation is the lack of a scientific-theoretical basis (concept) for creating an automated command and control system in our Armed Forces, and, as a result, a low level of concreteness, thoughtfulness and priority of the tasks assigned by the ordering authorities of the Ministry of Defense. But this is a topic for another article.
A very serious drawback of the system so far is the need for large amounts of work related to preparing the system for work.
As the experience of preparing for learning has shown, organizing the work of an automated command and control system requires considerable time for organizing communications, as well as for performing practical actions related to setting up and debugging communication facilities and hardware-software complexes. In addition, each such adjustment is carried out in relation to a specific combat mission. When the combat mission changes, or changes in the state (degree of combat effectiveness) of the command and control agencies, and the redistribution of forces and means by elements of the combat order, considerable time is required to make changes to the configuration parameters.
In addition, in the course of the exercise considerable effort while maintaining the specified modes of operation of the means of communication required the performance of monitoring the status of existing channels.
But there are ways to solve this problem. These are the creation of self-organizing information transmission networks using software-controlled radio stations, the use of Mesh technologies (Vibrating Mesh Technology: packet retransmission + dynamic routing), the use of spectrum-analyzers built into the radio to assess the interference environment, and the possible use of UAVs as tactical network repeaters and t .d
In addition to these shortcomings, participants in the exercise, based on the results of their work and operation of the system in field conditions, made a number of proposals aimed at improving both individual elements and the system as a whole, dealing with issues related to the processing and transmission of information, as well as ergonomic characteristics system.
However…
As noted by the officers of the Airborne Troops Command and the participants of the exercise, based on the results of the use of the Andromeda-D automated command and control system by the airborne tactical command and control bodies, a number of conclusions can be drawn:
The use of an automated command and control system in the course of battle planning and control has revealed a number of advantages as compared with the non-automated method of control:

1. Achieved a high efficiency of information exchange (collection, processing and display of information (tactical situation), which increases the speed of performing basic management tasks (information tasks) many times.
2. Due to the constant data collection of the situation in the “on-line” mode, the continuity of the management system is ensured.
3. As a result of using uniform hardware-software complexes, uniform software (including for graphical display of situation data) for all levels of control, from a soldier to the commander of the airborne forces, a high degree of unification of the elements of the control system has been achieved.
4. Due to the ability of the automated process control system to quickly restore its working capacity in the event of failure of a significant part of communication channels (group of hardware-software complexes) or control points in general, the survivability of the control system has been significantly increased.
5. The ability of the commander and headquarters to work in a distributed mode has been implemented, which allows management officials to effectively perform their functions while being at a considerable distance from each other, which significantly increases the survivability of controls and the control system as a whole.

Instead of confinement.
Even during the training period, it became known about the intention of Prime Minister Vladimir Putin to visit the city of Novorossiysk. Moreover, the dates of this visit practically coincided with the period of the active phase of the exercise.

There was a persistent rumor among the participants of the exercise that one of the soldiers, with the humor inherent in the paratroopers, asked his commander the question: “Will the President come to us for training, or is Putin right away?”. Soldier rumor is silent that the officer answered his subordinate, but one of the eight modules of the PU, which was deployed in a place that was most advantageous for a possible show, was even called a “presidential tent”.


However, our commander in chief, during his stay in Novorossiysk, honored his presence by no means with teachings.
At the same time, a biker festival organized by the Night Wolves motor club was held in the city, at which our Prime Minister appeared behind the wheel of a tricycle Harley Davidson, in the company of the motorcycle club leader, biker Alexander Zaldostanov, nicknamed the Surgeon.

After the column arrived at the festival venue, Vladimir Putin went up to the stage and addressed the participants and guests of the show. "You do not just have fun and ride motorcycles, which is not bad in itself, but you combine it with great patriotic events needed by our people, our country."
Let me remind you that in July 2004, by his decree, V. Putin set the task to create a “Unified system of command and control weapons in the tactical level of the Armed Forces "(ESU TZ).
It would be logical and understandable if he took the time to attend the exercise, where, in accordance with his decree, for the first time in the Russian army, on a single hardware and software using uniform data transfer protocols, the tactical link was organized at all levels from division to commander offices inclusive. And which took place just 24 kilometers from Novorossiysk.
It is a pity that this did not happen.
Sources:
http://dragon-first-ru.livejournal.com
http://vpk.name/library/andromeda-d.html
http://rosrep.ru/news/index.php?ELEMENT_ID=7041&SECTION_ID=17
Information