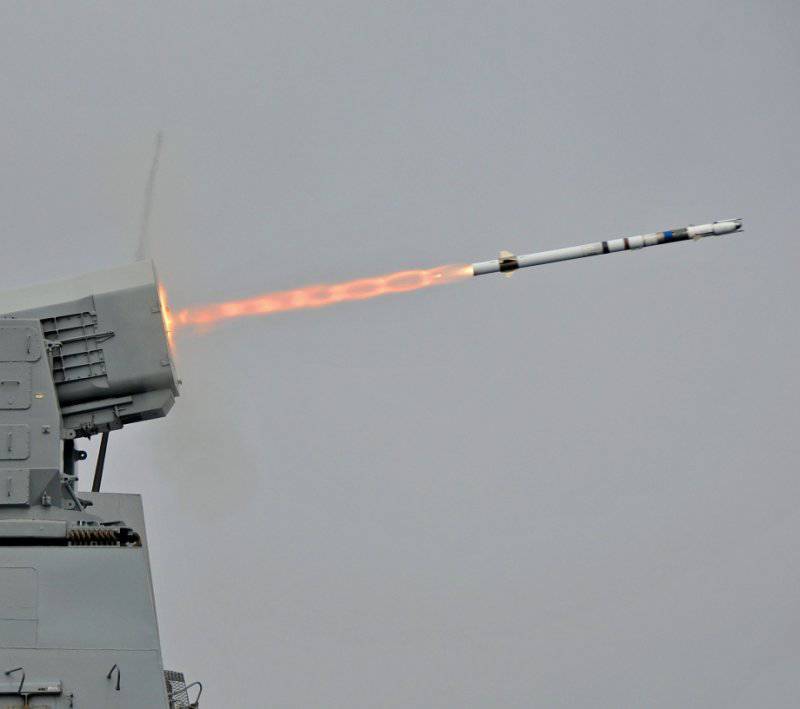
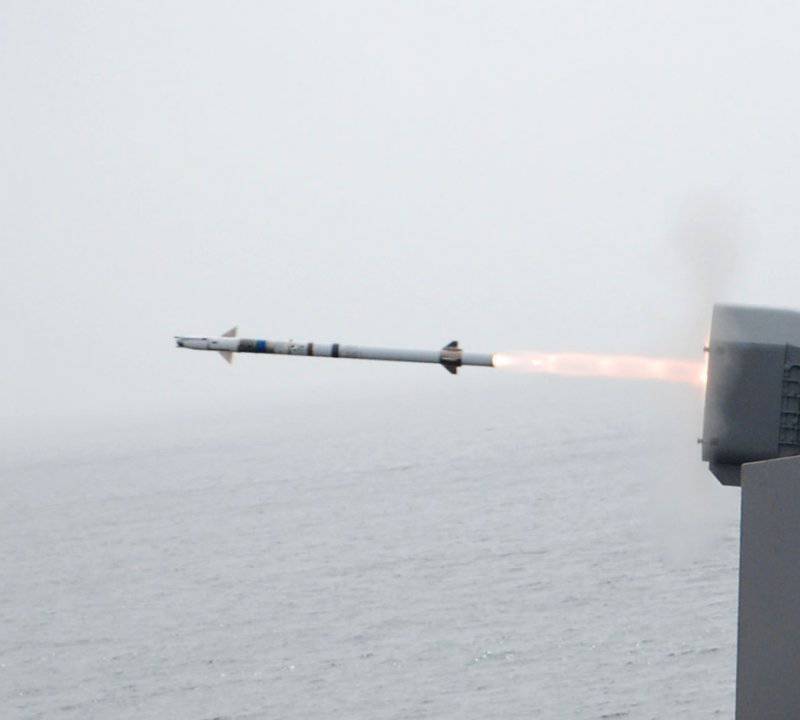
RAM anti-aircraft missile (RIM-116A)
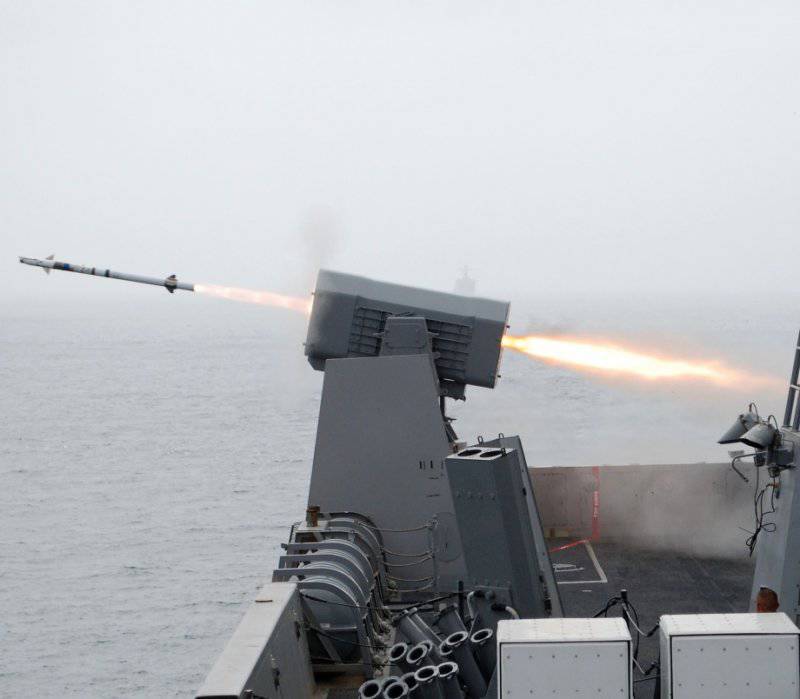
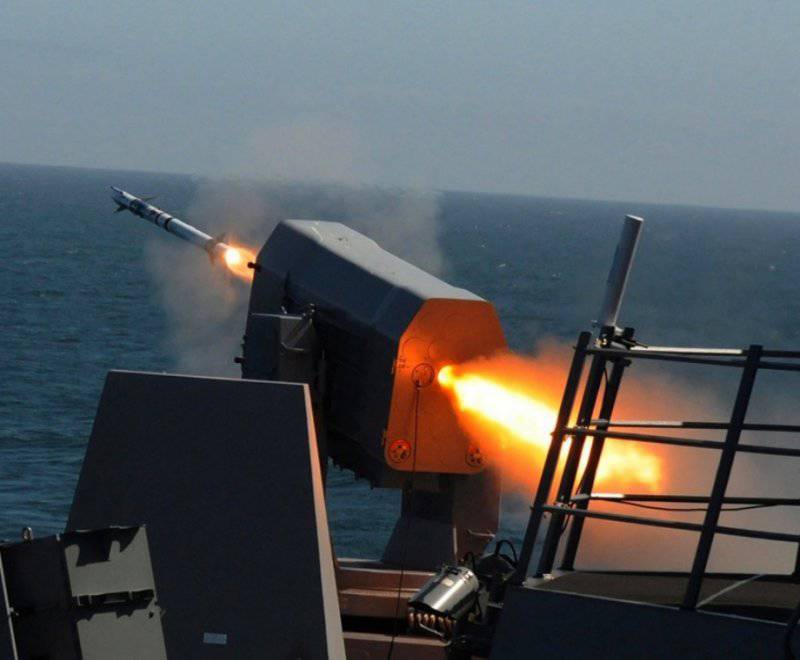
Raytheon, together with the German company RAMSYS, developed the RAM (RIM-116A) anti-aircraft missile. RAM was created as a rocket designed to provide surface ships with an effective, inexpensive, easy self-defense system capable of attacking attacking anti-ship cruise missiles. RAM is a joint project of the United States and Germany and is part of an autonomous, self-guided (shot-forgotten) shipboard anti-aircraft missile system directly protecting the ship.
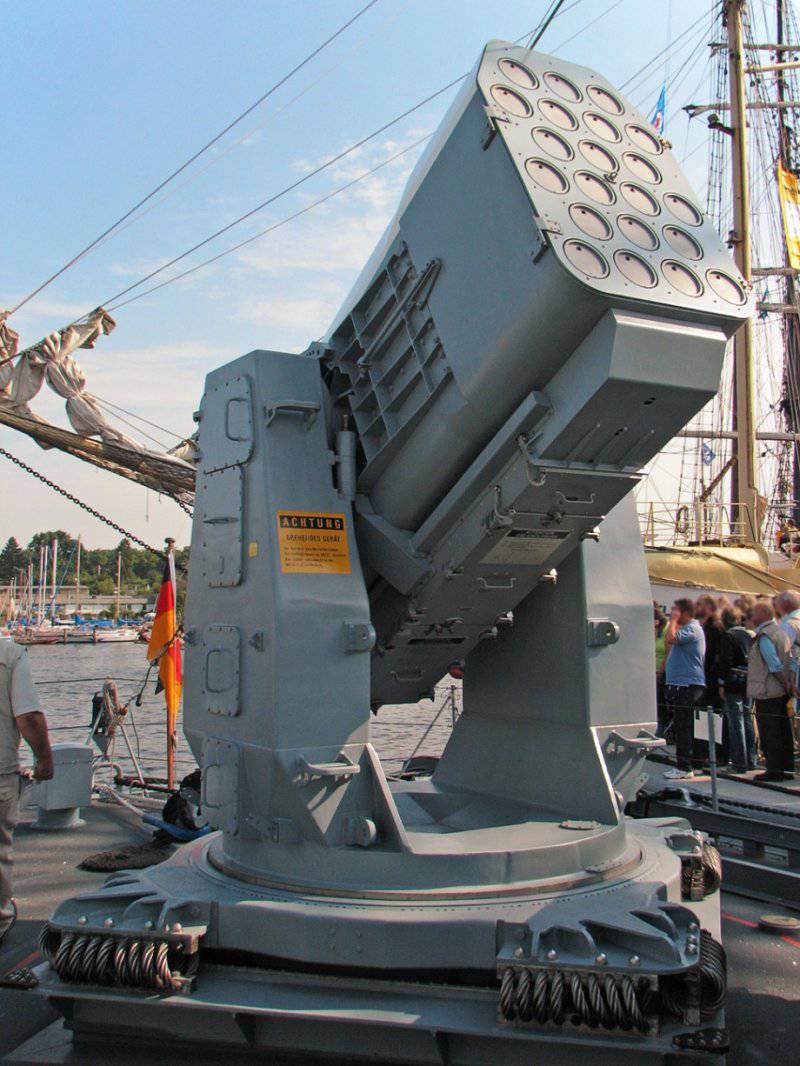
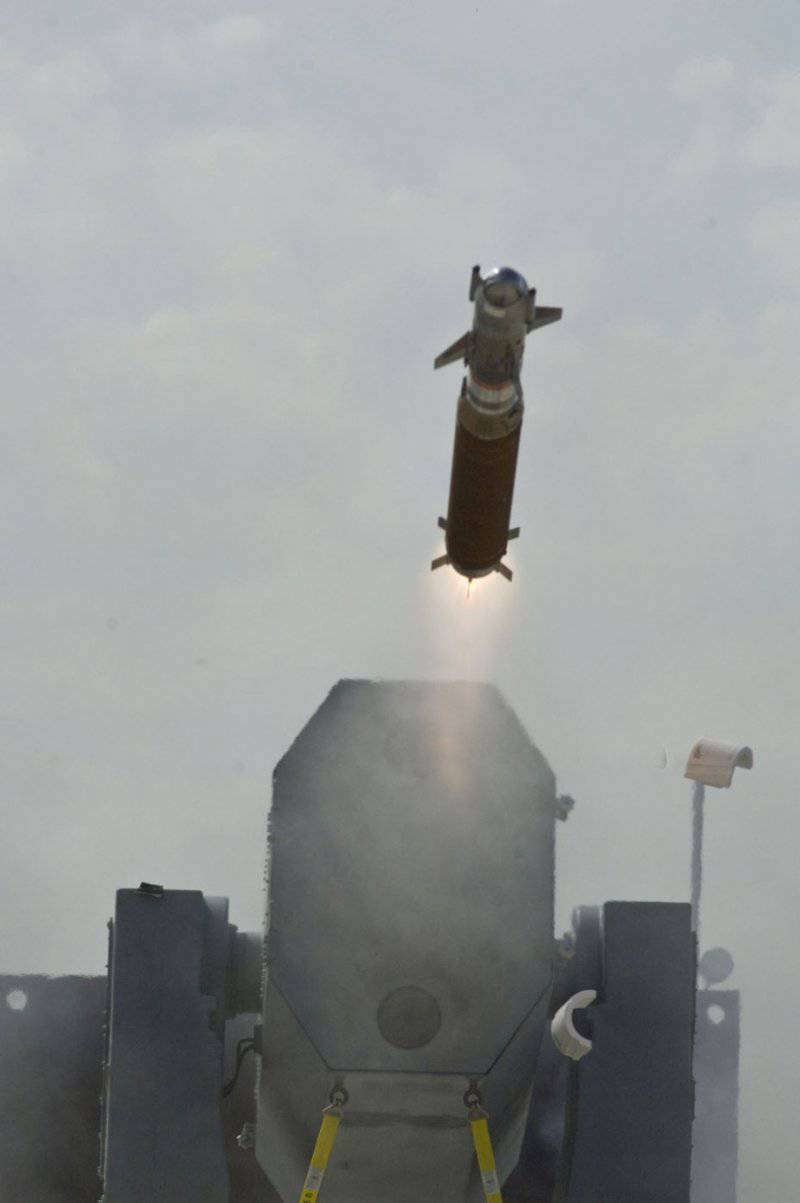
To reduce the cost of creating RAM, some of the existing components were used, including the Chaparral MIM-72 rocket engine, the Sidewinder AIM-9 warhead, and the Stinger FIM-92 infrared homing system. The rocket can be launched from the launcher on 21-s or 11 missiles.
The RAM Block 0 rocket has a 12.7 cm (non-stabilized roll) body rotating in flight and is equipped with a dual-mode passive radio frequency / infrared (RF / IR) homing head. The initial capture of a target is made by the rocket in the radio frequency mode, induced by the radar of the attacking missile, after which the target is captured in the infrared mode.
The operational evaluation of the RAM Block 0 was conducted from January to April of the 1990 year. Potential operational effectiveness was tested in all climatic and tactical conditions and possible weaknesses and ways to eliminate them. Based on an analysis of the deficiencies that emerged during the operational assessment, in April 1993 of the year, it was decided to upgrade the rocket to the level of RAM Block 1.
To improve efficiency against a wide range of existing threats, the upgrade of the RAM Block 1 included a new infrared GOS operating throughout the rocket’s entire trajectory. This helped to improve the ability to intercept cruise missiles with new passive and active GOS. Thus, the Block 1 rocket retained all the capabilities of the Block 0 rocket, while possessing two new targeting modes: only infrared and dual modes including infrared (Dual Mode Enable, IRDM). In the IR mode, the GOS is induced by the thermal signature of the CRP. In IRDM mode, the rocket is aimed at the IR of the RCC signature while still retaining the possibility of using radio frequency guidance in the case when the radar of the attacking rocket allows this. The RAM Block 1 rocket can be launched in the mode when the infrared GOS is operating throughout its movement along the entire rocket trajectory, as well as in dual mode (passive radar-guided RCC, and then passive IR) used on Block 0.
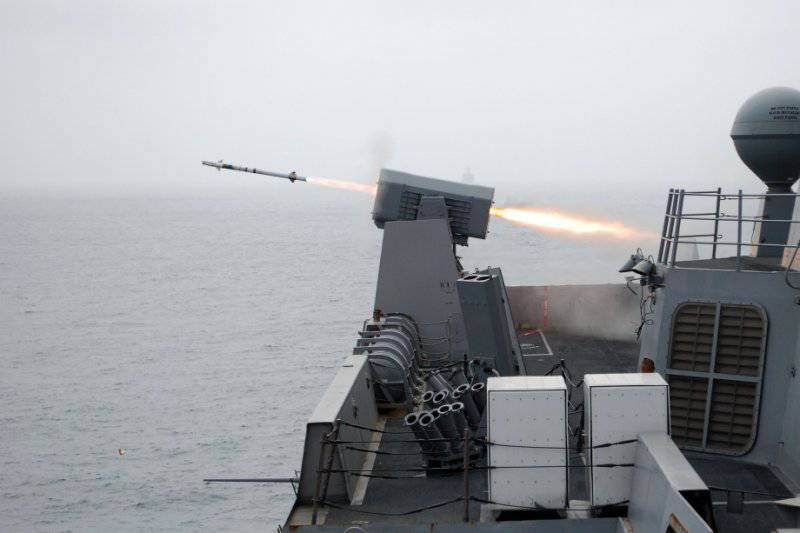
The Block 1 retrofit program was successfully completed in August 1999 of the year with a series of field trials to demonstrate its readiness for adoption. In 10 different scenarios, real anti-ship missiles and Vandal supersonic missile targets (developing speeds up to 2.5 Mach) were successfully intercepted and destroyed in actual conditions. The RAM Block 1 system from the first shot hit all the targets, including those flying at extremely low altitude above the sea, diving and highly manoeuvrable targets during single and group attacks.
On these firing RAM showed its unique ability to intercept the most complex of modern threats. To date, a total of more than 180 missiles have been fired on anti-ship missiles and other targets, having achieved success in more than 95% of cases.
RAM entered production in the 1989 year and now it is deployed on more than 80 ships of the American and 30 ships of the German fleets. South Korea installed them on its destroyers KDX-II and KDX-III, amphibious assault ships of the class LPX Dokdo. To the rocket also showed interest or have already acquired it Greece, Egypt, Japan, Turkey and the UAE / Dubai.
Based on the results of the pilot operation conducted on board the USS GUNSTON HALL (LSD 44) landing craft in January 1999, and tests conducted from March to August 1999, RAM Block 1 was found to be effective against various cruise missiles and recommended for adoption fleet. Block 1 missile managed to successfully intercept in 23 of the 24 attacking missiles. Serial production was approved in January 2000.
In March, 2000 of the year of the Block 1's RAM were installed on two LSD-class landing ships and were expected to be installed on two more LSD 41, LHD 7 and CVN 76 class ships. In the period between 2001 and 2006, the US Navy installed Block 1 on 8 and LSD class ships 41 / 49, 3-x DD 963, 12-1 CV / CVN, LHD 7, and also decided to deploy them on 12 LPD 17 under construction. In addition, in the 2007 year, RAM Block 1 was installed on all five LHA class ships.
In November 1998, the United States and Germany amended the Block 1 program, which indicated the scope of work and funding for the development of a version against helicopters, airplanes, surface ships (HAS). To accomplish these tasks, only a software change of the 1 RAM Block rocket was required. Upgrading to the RAM Block 1A level included additional signal processing capabilities for intercepting helicopters, airplanes, and surface ships.
The first US combat shooting of RAM took place in October of the 1995 of the year on the landing ship USS Peleliu (LHA-5). March 21 The USS Kitty Hawk 2002 (63 CV) was the first aircraft carrier in the United States to execute firing RAM.
The RAM system on some ships is integrated with the AN / SWY-2 combat system and as a Ship Self Defense System (SSDS) on other ships of the LSD-41 type. AN / SWY-2 consists of a weapon system and a combat control system. The combat control system uses the existing 23 Mk target detection radar and the AN / SLQ-32 (V) auxiliary electronic warfare sensor, together with software, to conduct threat assessments and allocate weapons on the Mk 23. RAM along with SSDS are part of the ship's defense system. For example, RAM, the Phalanx Block 41A melee system and the bait launch system are included in the typical defense system of the LSD 1 class amphibious assault ships. The self-defense system (SSDS), in turn, includes radar AN / SPS-49 (V) 1, AN / SPS-67, AN / SLQ-32 (V) and CIWS.
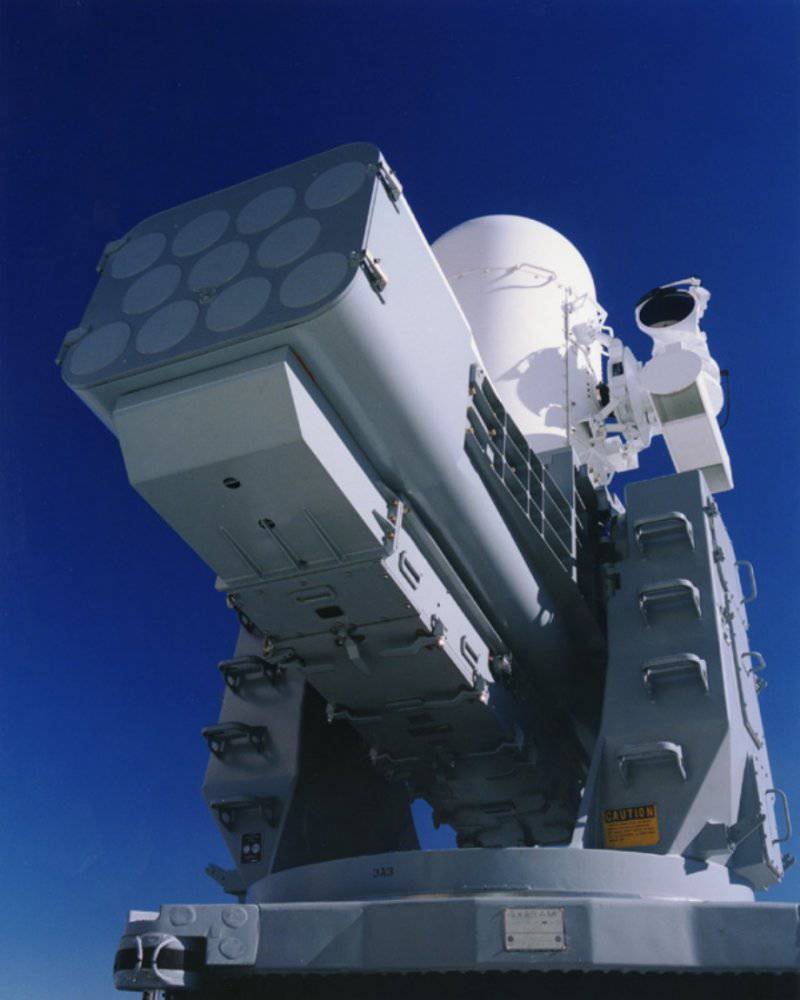
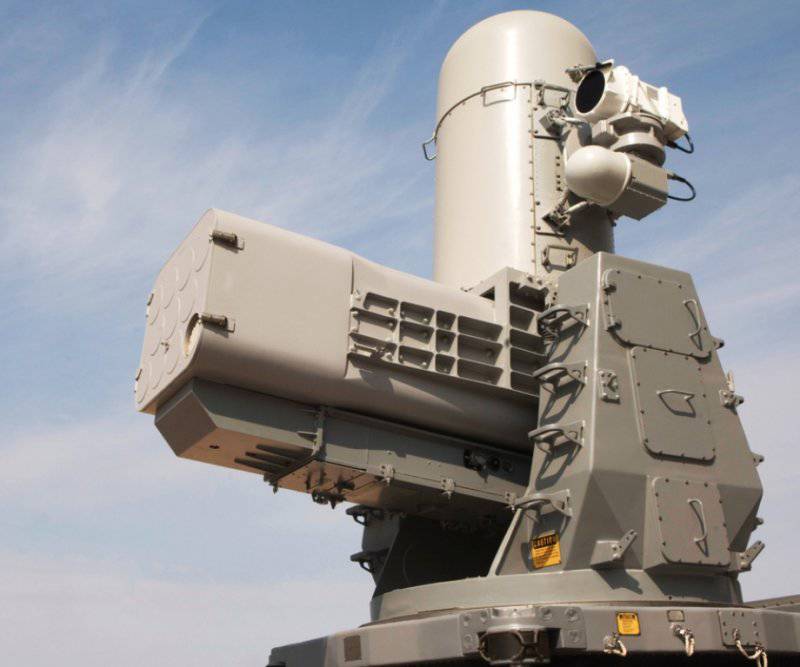
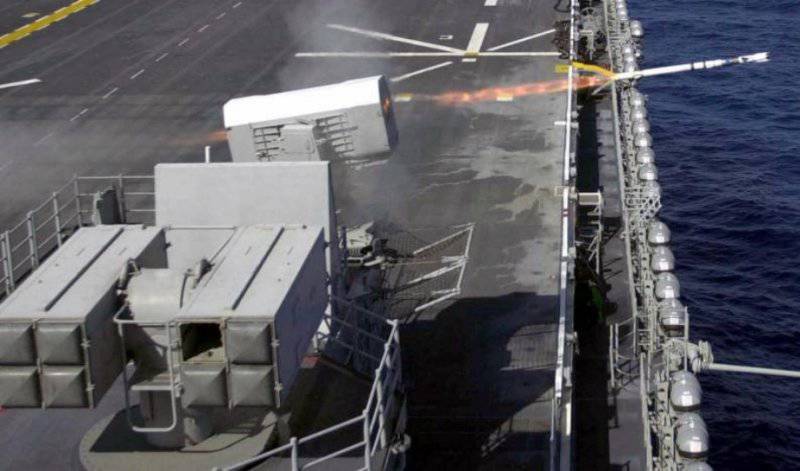
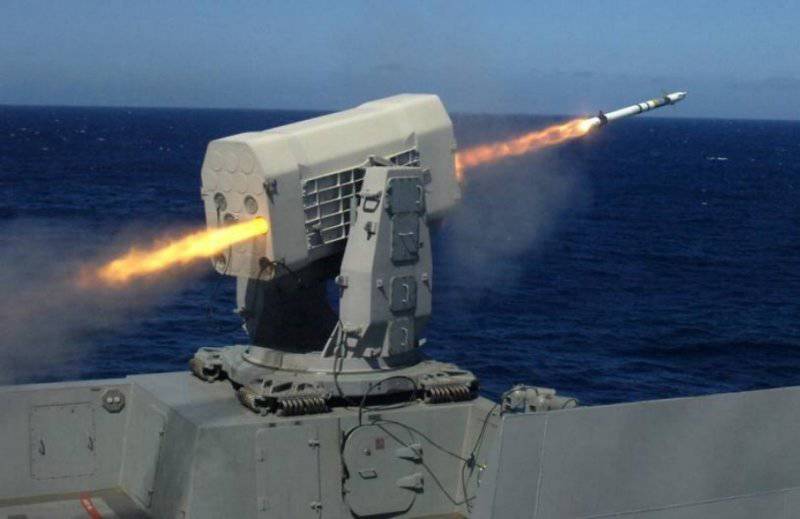
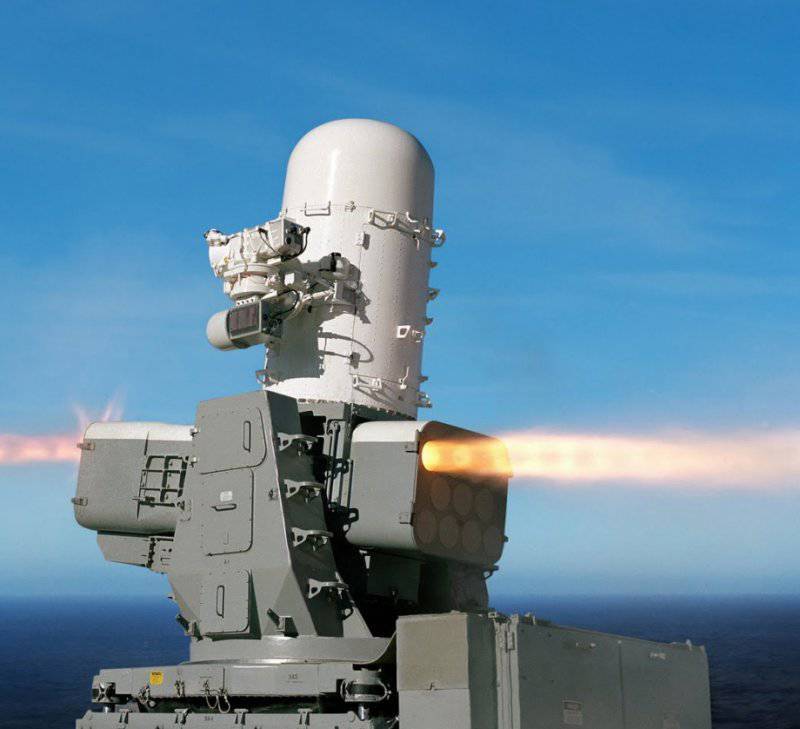
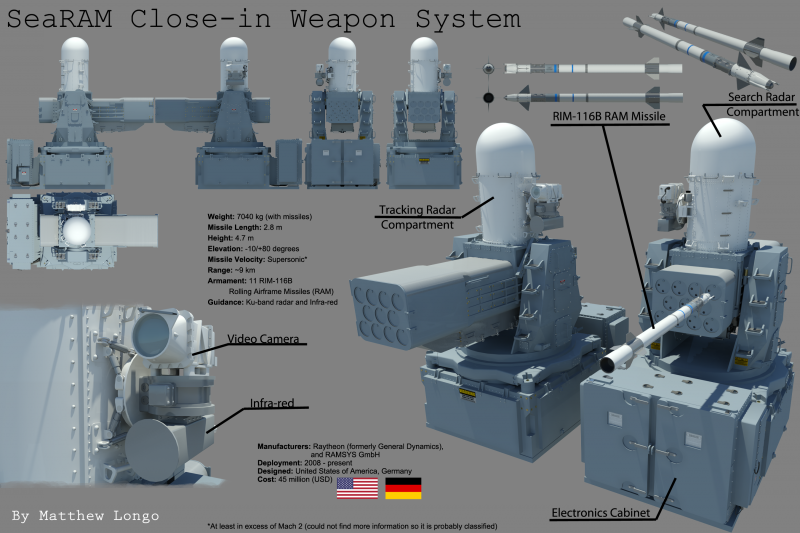
For the defense of ships in the near zone of air defense from massive attacks of low-flying cruise missiles, the system SEA RAM was developed. It combines elements of the system weapons Phalanx melee and ram missiles. This approach extends the range of the melee weapon system and allows the ship to operate effectively on several targets simultaneously. For this purpose, a launcher with 20-x RAM block 11 missile launchers is installed on the modified 1-mm ZAK Phalanx quick-mount paw. As a result, SEA RAM combines high accuracy, long-range interception and high maneuverability of RAM along with a high resolution search and tracking system, and a quick and reliable response from Phalanx Block 1B. 1 February The 2001 of the year SEA RAM was deployed for testing aboard the destroyer of the royal fleet HMS YORK.
8 On May 2007, the United States Navy and Raytheon signed a contract for $ 105 million to develop RAM Block 2. In May, the 2013 of the year, the company Raytheon announced the holding of successful combat firing of the RAM Block 2 rocket during which the missiles hit two high-speed, maneuvering, subsonic targets, successfully confirming the incorporated characteristics.
"The success of the RAM Block 2 tests followed a series of successful tests of the guidance system," said Rick Nelson, vice president of sea missile systems and defense systems at Raytheon. RAM Block 2 increases the rocket’s kinematic capabilities, which, along with its advanced guidance system will continue to provide the fleet with a significant advantage in battle. "
Raytheon and her German partner RAMSYS received an order for the production of the 61-th RAM Block 2 in December 2012. At the beginning of the current 2013, the company received an order for the production of RAM Block 2 for the German fleet in the amount of $ 155.6 million. The United States intends to acquire 2093 RAM Block 2 rockets.
The upgrade of the RAM Block 2 includes a four-axis independent power drive of the control surfaces and a more powerful sustainer engine, increasing the missile's effective interception range by about half and its maneuverability almost three times. The passive radiofrequency homing head, the digital autopilot and the individual components of the infrared HOS were also upgraded.
In March, 2013, the German government signed a contract for $ 343.6 million with Raytheon and RAMSYS GmbH for the production of 445 missiles RIM-116 2 unit. Deliveries must be completed by January 2019.
General system characteristics RAM (RIM-116A Mod 0,1.)
Classification: surface-to-air missile.
It is intended against anti-ship cruise missiles, surface ships, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles and aircraft of all types.
Manufacturer: Hughes Missile Systems Company and RAM Systems Germany
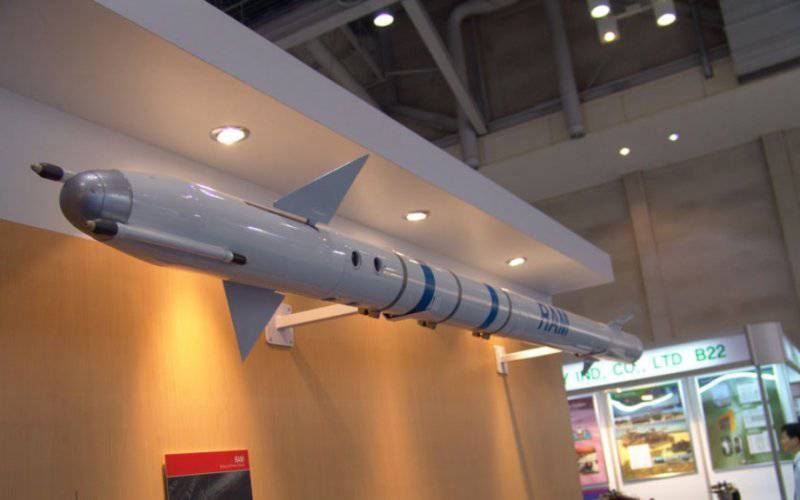
Rocket diameter, cm: 12.7
Rocket length, m: 2.82
Wingspan, cm: 44.5
Rocket Speed: Over 2's Mach
Range: about 5.6 miles
GOS: two mode
Warhead weight, kg: 10
Total rocket weight, kg: 73.6
The cost of the rocket: Block 0- $ 273'000, Block 1- $ 444'000
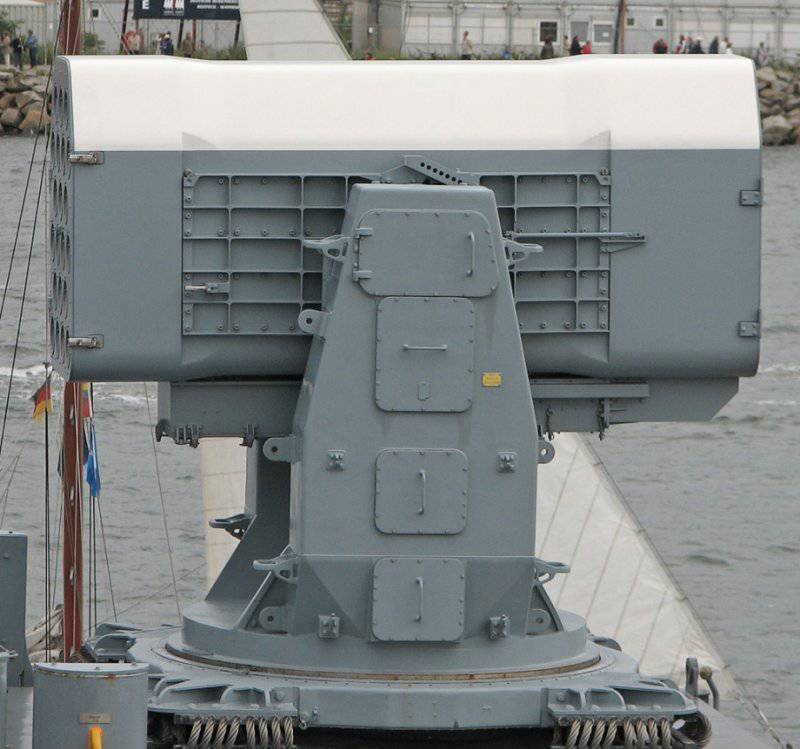
Launcher: MK-43 (basic version) or modified MK-29
Search Radar: Ku-band, digital
Tracking radar: Ku-band, pulse-Doppler
Infrared guidance station: LWIR (7.5-9.5 µm)
Lifting angle PU: –10 ° to + 80 °
Weight above deck, kg: 7000 (including rockets)
Angle of rotation: ± 155 °
Weight below deck, kg: 714
Ammunition missile: 11
















Information