History of domestic combat diving
In 1931, the submarine No. 9 of the Baltic sank fleet, and in the same year the workshops of Epron received an order for the development and production (1932-1938) of five types of breathing apparatus "Epron-1, 2, 3, 4, 5". The latter two types were later used on the Navy submarines.
In 1938, the Military Council of the Fleet decided to urgently organize training in diving and the construction of training pools in order to work out the skills of working in diving equipment from the personnel of submarines. This decision was made after checking the status of the Pacific Fleet on the introduction of underwater vehicles.
October 24 1938, by order of the Pacific Fleet Commander flagship 2 Rank Kuznetsov N.G., a pilot exercise was held, involving the landing of light divers from the submarine Shch-122 and their subsequent return.
This is the first in stories Navy training landing from a submarine during the dive of an armed group of light divers. The exercises ended in success, demonstrating new opportunities for the use of light divers in solving special combat missions. But until 1941 of the year, even after a positive decision of the Military Council of the fleet, there was practically no implementation of these undertakings in the process of combat and organizational training of the fleet.
At the end of July, 1941 from the city of Vyborg to the city of Leningrad was evacuated a diving school. During the report on this, the head of the EPRON, Rear Admiral F. Krylov. He informed the representative of the Supreme Commander-in-Chief, Deputy People's Commissar of the Navy, Admiral I.S. about the need to create a special squad of scout divers, which would include the best divers of the school.
Deputy Commissar of the Navy quickly realized that such a unit was really necessary in the light of the blockade ring, which closed around the city. In the archive of the fleet you can find a signed order under the number 72 from 11 in August 1941 of the year, which provided for the formation of a special purpose company (RON) at the reconnaissance unit of the Red Banner Baltic Fleet headquarters (Roshbf). She was manned by fighters of the Marine Corps and Red Navy divers.
In 1949, the captain of the 2 rank I. Prokhvatilov requested the creation of an experimental research group consisting of light divers. The order of the 4 Navy Commander from 18 July 1949 of the year contained the following: “In order to improve the combat training of the fleet divers and the creation of new instruments and devices that facilitate the work of the light divers, form a special research group during the ADF. From the ASO states for these purposes, select 12 diving specialists. To appoint Captain 2 of the rank IV Prokvpilov as the group leader. Report on the work submit to 15 December 1949 of the year "
In December 1949, Prokhvadilov presented a report on the work done. Attached were designed and tested samples of an individual inflatable rubber boat, an advanced hydro-overalls for multiple dives and ascent, an advanced breathing apparatus ISM-M, special diving goods, a buoy, packing bags and folding oars.


The work carried out by the group, together with the results of research carried out at the Institute for the development of special equipment for light divers, became a good foundation for the development and creation of special purpose diving equipment (VSON).
In January, 1952 completed the development of two types of breathing apparatus: C-1, developed by Captain 1 Engineer, Soldatenko OM, and BAP-52, developed by Captain 2, IV Prokhvatilov.
In August 1952, their comparative laboratory tests were carried out. The best results showed apparatus VAR-52.

The next step was the September 1953 test of the year at one of the experimental exercises. They ended successfully, but the equipment had significant flaws. I had to rework TK in accordance with them. The order to create a batch of prototypes was received by SKB-KDA.

The first experimental batch of equipment was made only in 1955 year. And since the end of 1957, the SBON began to enter into service with special units in the required quantities. The chief designer of the equipment under the name of the SAN-55 was Sapogov S. V.).
In the future, this equipment was refined according to the results of trial operation. In 1961, the ARMS-61 kit was introduced into service, which included a whole set of diving tools. Among them, besides the breathing apparatus, the inflatable boat and the hydro-overalls, there were also a compass, a wrist depth gauge, a clock, a knife, a diving periscope, packing bags, a tablet and other devices.
The development of the first samples of diving equipment and its subsequent tests in military units greatly influenced the path of further development in this area. In addition, it was identified the need to use technical means of movement of divers, which maintained their performance.

In 1955, a batch of sports balloon breathing apparatus manufactured by Zibe-Germa (FRG) and AGA (Sweden) was purchased abroad.
In one of the special laboratories of the SRW, a set of equipment was developed, which included the breathing apparatus ABM-1 and the wetsuit GKP-4. In 1957, the research and development work developed TZ, according to which the SKM-KDA created modifications of the ABM-1, AVM-2, and AVM-3 devices.
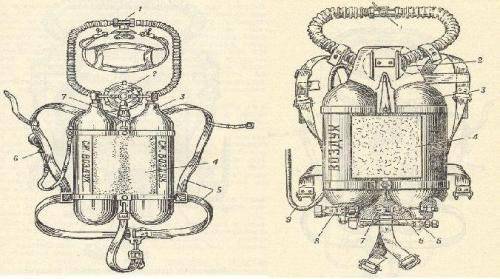
In 1958, these devices entered the training dive units.

It also developed and issued to the SKB a technical assignment for an underwater combat equipment kit.
In SKB-KDA developed a regenerative unit for navigation on the design and estimate documentation, as well as exit from submarines. For the device used the cipher "TP" - tactical navigation. The chief designer of the "TP" apparatus was Semenov M. Ya. Tests were carried out by employees and divers of the special laboratory Shklyar, Kurochkin, Kondratenko, Batyushko and Karpenko. Testing dives were guided by a diving specialist Ivanov B.A., and the physiologist Lieutenant Colonel Tyurin was responsible for the maintenance. Tests continued until August, and already in September, the "TP" apparatus accepted for the supply of special units of the Navy.
In 1956, the 2 division of the General Staff of the Navy ordered the development and creation of diving equipment in special laboratories, allowing jumps from aircraft to be carried out. In the technical assignment there was a special bib overalls with an individual breathing apparatus and a parachute suspension system. The task was divided into several parts.
Since January, 1957 has been working in the laboratory together with the Institute of the Navy Number 15 on R & D (IT-72-40) - "Research and development of diver equipment for diving from a float plane, for going out of submarines, free swimming and walking on the ground." TK and thematic card were developed. In April, the 1958 of the Year at SKB-KDA performs the R & D "Isolating breathing apparatus for a diver with a parachute."
At the same time, the development of GK-TO and GK-U special hydromyzones, which is operated by plant number 151 in Yaroslavl, is under development. All work is carried out under the supervision of special laboratory supervisors. In August, 1969, successful flight tests of the created equipment are carried out: a GK-TO hydro-overalls, a suspended parachute system and an IDAP vehicle.
And in January, 1960, Maksimikhin, Pleskov, Ivanov, Kudrin and Tyurin, are working on research to modernize the way out of a submarine. 130 outputs are analyzed, and then 50 outputs are conducted. As a result, a new breathing apparatus IDA-59P was created, which was included in the equipment of divers-paratroopers SVP-1, receiving a new diving suit GK-5.

In 1972, IDA-59P, TP, IDA-66B for Triton-1М and Sirena-U, ADA-61 chest for walking on the ground, the stationary respiratory system SDO-1 for NV "Triton-2" and STP-2 for NV "Triton-1M" and "Siren-U". But this diversity turned out to be redundant, so in 1971, in the research project “Korsar”, they developed a model of a single respiratory device IDA-71P. Since 1973, they have been replaced by everyone else.
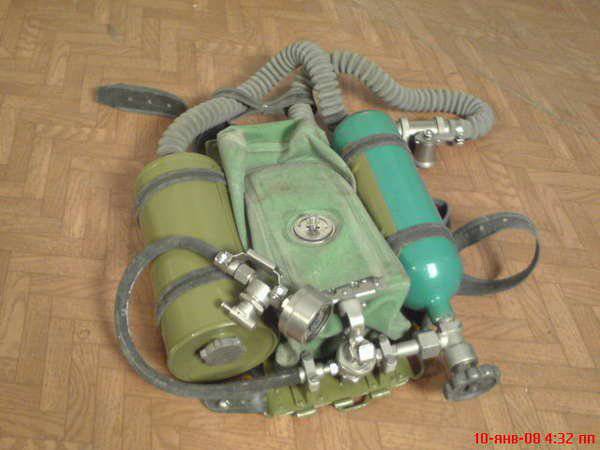
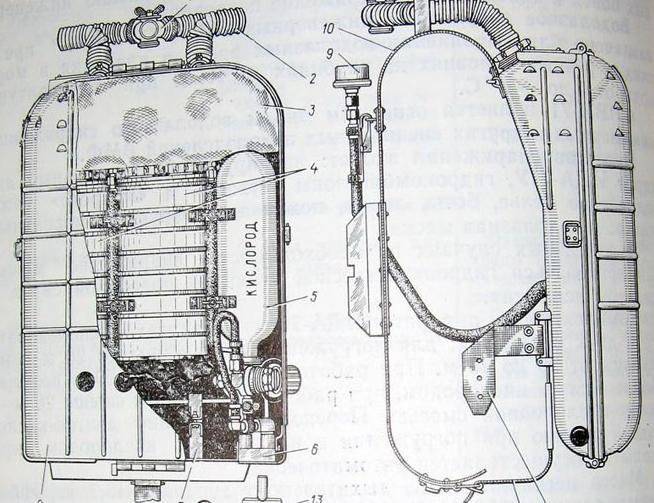

The new device was part of the diving equipment of IEDs, which is the main in special parts of the Navy and at the present time.
Creating underwater means of movement diver
Much more difficult was the situation with the creation of underwater vehicles (PSD). There were reasons for this. In the state there were no design and industrial enterprises and organizations that could create means of such a direction. Also the situation was complicated by a whole range of versatile research, which was necessary for the development and creation of the design and estimate documentation.
Essentially, the design and estimate documentation is a miniature submarine, which, like an ordinary submarine, must possess all the systems and mechanisms for its normal operation. In this case, all equipment should be compact. For the production of such products required completely new technologies, equipment and specialists.
One of the difficult moments in the operation of the design and estimate documentation is that the driver was placed in an open space for water, so it was difficult to maintain its performance in such conditions. The problem was aggravated by a small number of ordered devices, which was economically unprofitable.
In 1958, the fleet headquarters sent a request to the torpedo department weapons LCI (now it is St. Petersburg State Maritime Technical University). It was necessary to develop self-propelled vehicles - double carriers of torpedo design and single towers for divers.
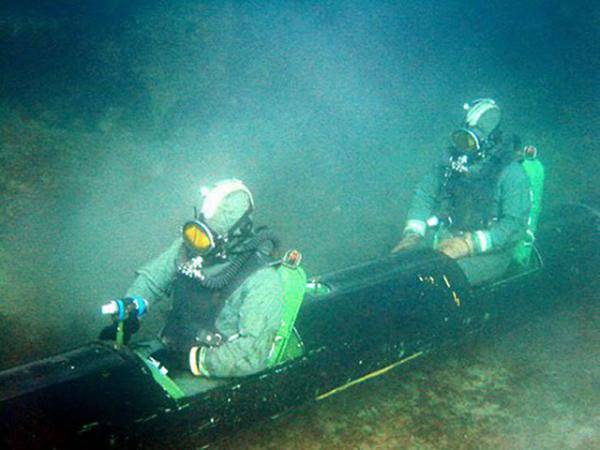
Already in September 1959, the university specialists completed the development, testing and began to produce domestic models of tugs "Proteus-1 and 2" One of their dignity - mounted on the body of a diver - the first "Proteus" on the chest, and the second - on the back.
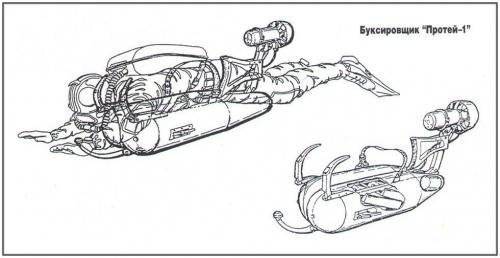
The Protey 1 towing vehicle was 1830 mm in length, 650 mm in width, and 465 mm in height. Its mass reached 95 kilogram, and the speed of movement - 2.5 nodes. The range of the device was ten miles with a depth of 32 meters.
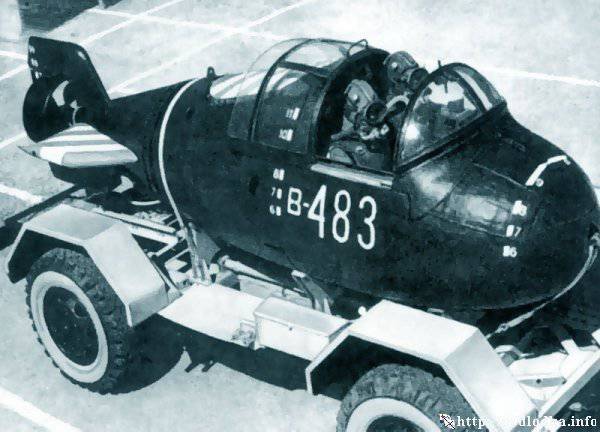
The development of a double transporter using a torpedo caliber 533 mm was also completed. He was named "Siren", was tested and put into production.

Later, the apparatus was modernized by the specialists of the Dvigatel plant together with a number of shipbuilding, aviation and electrical industrial enterprises. A highly efficient and reliable sample called "Sirena-UME" was created.

The diameter of the device was 532 mm, length - 8600 mm, weight - 1367 kilogram. The speed reached 4 nodes. The duration of the autonomous course was two hours, during which the unit could go eight miles at a depth of up to forty meters.
To launch the apparatus, it was possible to use any surface ship or boat equipped with a lifting device up to two tons. Also for this purpose it was possible to use submarines belonging to the type of "Piranha". After the development of a special mechanical push rod, it became possible to launch the device from submarines 877EKM and 877EK.
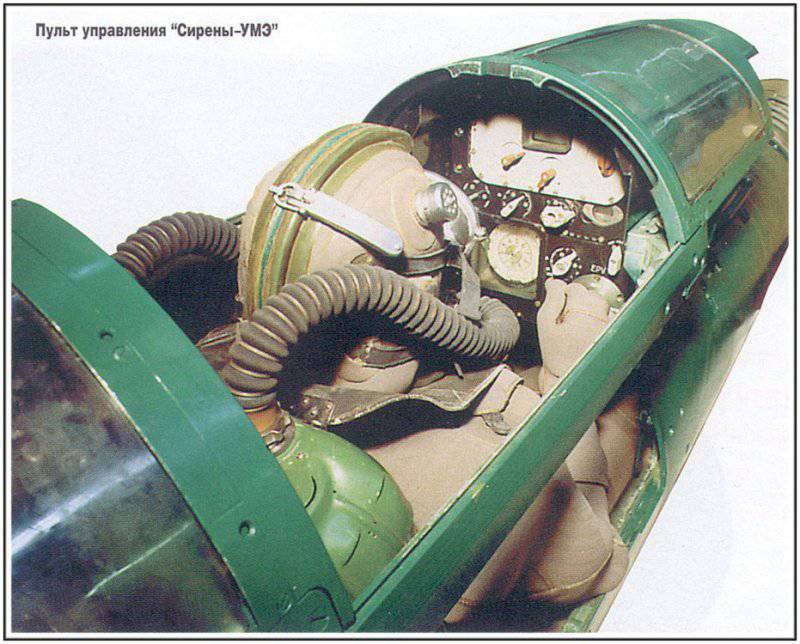
Structurally, as part of the "Siren-VME" is the head, flow and feed compartment. To connect the cargo container to the head mechanism, a high-speed mechanism is used. Also the head compartment is used to store nickel-cadmium batteries.

The flow compartment contains cabins for divers, an onboard life support system, as well as a control panel and a device for conducting vertical maneuvers. Cabins are equipped with retractable covers that protect divers from the flow that occurs when driving under water.
The aft department received a navigation complex, communication units, control devices and engine speed control and steering cars. All units, propellers and devices are designed for low noise operation.
Since 1969, design and development work on Tritor-1М, Protey-X and Triton-2 has been carried out by the design organization Malachite. Production was launched at the facilities of the plant LAO.
It is worth noting that the creation of these devices took quite a lot of time. Triton-1M was developed by 12 for years from 1966 to 1978. Specially equipped surface ships belonging to the project A-1824: "Anemometer" and "Gyro" were chosen as carriers of the vehicles.
In 1971, the Novo-Admiralteisky Shipyard in St. Petersburg built the first two underwater vehicles, the Triton-1M. These were prototypes for a comprehensive study of the operation of the new submarines. In July, 1972, the tests of two SMPLs were completed, after which the “tritons” went to the Black Sea for testing at the Gidropribor enterprise.


Total 32 apparatus was built, which entered service in 1973-1980's. The main purpose of the device is to transport light divers to a depth of forty meters.
In the case of the device were impenetrable and durable volumes: the driver’s remote control, as well as the electromotive and battery compartments. The installed power of the electric motor was 3.4 kW. The device could remain on the ground without moving for up to ten days. Its equipment included a compass, hydroacoustic station, a radio station, as well as an automatic course movement system.
The length of the device is 5 meters, width - 1.35 meters, height - 1.38 meters, draft - 1 meters. Cruising speed reached 6 nodes, cruising range 35 miles at depths up to 40 meters. The crew consisted of two divers.
In 1966, the Navy Emergency Rescue Service prepared the task of designing and building an experienced submarine carrier for divers “Triton-2”. The development was headed by the chief designer Sinyakov V.I. under the supervision of the scientific research institute number 40 of the Gatchina Metalworker plant. In the same year, the work on the "Triton-2" was transferred to the Volga Center. Yevgrafova Y. Ye. Evgrafova was appointed to lead the project under the code number 908.
The main purpose of the "Triton-2" - hidden underwater transportation of a group of six light divers to the place of performance of underwater tasks in coastal areas.
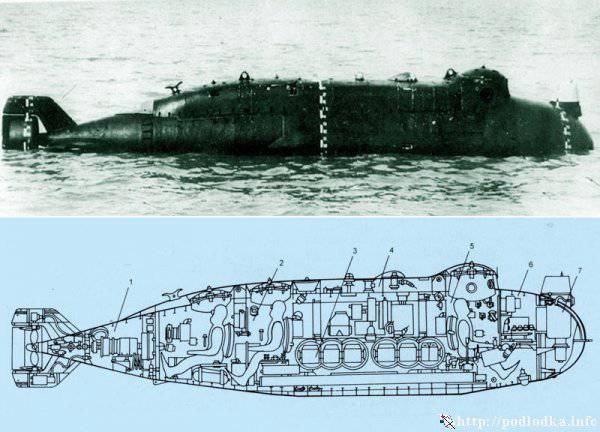
A total of 12 vehicles were built, which entered service in 1975 - 1985. The length of the device - 9.5 meters, width - 1.8 meters, draft - 1.6 meters. The duration of autonomous navigation is 12 hours at a speed of 5.5 nodes at a depth of up to 40 meters.
Over time, the fleet faced more and more complex tasks, and the requirements for combat effectiveness and quality of equipment increased. Therefore, there was a need to develop new scientific approaches and the training of scientific personnel. 24 July 1963, the directive of the General Staff, which provided for the study of combat effectiveness and economic evaluation of the developed systems in the further work on this area.

The next work is the research work of the research work 40-08-71КФ "Justification of requirements for the design and estimate documentation used by the WG, RGSN, RUSN in the enemy's rear" (code "Vyun"). This was the first substantiation of the carrier of Sirena-K divers - caliber 650 mm. Immediately, work began on the NGS Directive of the Navy No. 729 \ 001057 - operational-tactical (OT) and military-economic justification (VEO) PLM Ave. 08650 (cipher "Piranha").
In July, the 1984 was the Leningrad Admiralty Association laid the first experimental submarine with a titanium hull, which could dive to a depth of 200 meters. The device belongs to the NATO two-body class - LOSOS. Its length is 28.2 meters, width is 4.74 meters, height is 5.1 meters, and the draft is 3.9 meters. The duration of autonomous navigation is ten days with a maximum depth of immersion in 200 meters and an underwater speed in the 6.7 node. The submarine crew included a 3 man, as well as a group of light divers of six.
The boat was armed with two torpedoes in caliber 533-mm or min.
The weapon complex was located in the middle part of the superstructure, including two cargo containers used to transport equipment. Usually there are four Proton towers or two Sirena-UME transporters and two mine devices in 4 high-level bottom mines, including those with nuclear charges. The cargo container was filled with seawater. This is a cylindrical design, the length of which is 12 meters, and the diameter of 62 cm. For loading and unloading works, a sliding tray with a drive and controls located inside the housing was used.

Making special weapons
In 1968, a technical task was transferred to the Central Research Institute of Precision Engineering (TsNIITOCHMASH), which envisages the development of underwater systems of small arms - a pistol, an automatic rifle and ammunition for them. It is the leading domestic scientific center for the development, research and testing of small-arms sporting and hunting weapons, as well as ammunition and accessories, means of individual weapons and protection for special units.
In 1968, a task emerged involving the development of an underwater pistol complex. TsNIITOCHMASH and TOZ developed a pistol and an 4.5-mm cartridge, which were put into service in the 1971 year, giving the designation SPP-1 - a special underwater pistol. This system was successfully tested in the 1970 year, and was transferred to the units as personal weapons for divers.
4.5-mm SPP-1 is a common four-barreled pistol that opens from the breech. It had four smooth trunks that were attached to the frame with hinges and rotated around its trunnions. For reloading, they had to be folded down, and a latch and lower hook were used for locking.

Caliber barrel pistol - 4.5 mm. Its length is 244 mm, with the barrel 203 mm. Weight without ammunition - 950 grams. SPP-1 allowed to conduct effective shooting at a distance from 5 to 17 meters at a depth from 6 to 40 meters. In the air, this figure reached 50 meters. The initial speed of the bullet was 250 m / s.
Positive experience in solving the problems of the underwater pistol system allowed TsNIITOCHMASH to receive another order in 1970 year. Now it was necessary to develop an underwater automatic small arms, which were supposed to equip the underwater vehicles "Triton-1M", as well as divers-fighters.
At the beginning of the 1970-s, V.V. Simonov began designing a special automatic underwater complex as part of an AG-022 underwater submachine gun in 5.66 caliber mm. This type of weapon had a system of cruel locking of the bore, as well as original structural elements, including a gas engine for an automatic fire system in water and in air. The machine shop had 26 cartridges with high efficiency in various conditions.

The length of the machine without a stock was 615 mm, width - 65 mm, height - 187 mm. Curb machine weighed kilogram 3.4.
Until 70-ies did not develop the development of navigation tools for the design and estimate documentation and divers. At the first "Protei", "Sirens" and "Tritons" put waterproof aircraft magnetic compasses KI-13.
A little later, the Siren and Triton carriers received the Gyropolukompas GIC-52 aircraft gyro. It had small dimensions and allowed to enter information about the course into the automatic control system for design and estimate documentation.
Purposeful development of the navigation system for design and estimate documentation and divers began in the 70-s, when she took up the 9-th SRI MO. In 1972, the development of the navigation instrument for divers NIP-2, consisting of a watch, a depth gauge, a spinner lag and a magnetic compass, was completed at the Dolphin Scientific Research Institute.
The instruments were equipped with all types of towers. The NPS-2 had a special platform for locating the direction finder and a tablet with a map.
The first navigation complex (NC), developed for the "Triton-2", was the system "Samur". Its main task is to ensure the driving of the ship and the transfer of navigation parameters to the automatic control system. The “Samur” consisted of: the Volkhov remote compass, the GKU-2 gyro indicator, the Yaz-S echo sounder, and the Terek induction lag, the Amur gasket and numbering system.
The auto pager used a roll-up map on which the route was previously laid. The whole complex weighed 136 kilogram.
In 1983, the development and creation of a second generation of navigation tools was completed. The basic “Vozchik” navigation complex has appeared in service. It was used not only in PSD SPECNAZ, but in a number of other submarines of the navy. The complex was the first to receive a digital data processing system based on the Salyut-3 digital computer.

Depending on the installation object, the dimensions and equipment of the complex varied. Fully equipped “Carter-01” was to be installed on the HB “Triton-3” with a dry diver's cabin. "Carter-02" was intended for "Siren-K". "Carter-3" - for "Siren-M". The complex used for the first time the absolute lag of LA-3.
The aviation magnetic compass KI-13 in 1982 was replaced with an improved version of the KM-48P Neva, which was used as a backup on all diving carriers.
The best example of small-sized navigation aids of the end of 80's is the Anchar complex, which was intended for the Piranha submarine. It included the satellite navigation system ADK-3M. Successful tests of the complex were carried out, and in 1991 it was put into service.
The complex received a lot of components that could later be installed on the NC PDS. In particular, a small Doppler log LA-51, a magnetic compass KM-69P and other equipment.
Creation of hydroacoustic tools for divers and design and estimate documentation
In 1964, work began on the creation of hydro-acoustic diving facilities. Then the ROC "Nerei" was created to develop direction-finding and drive equipment for design and estimate documentation and divers.
During this period, military equipment was actively equipped with semiconductor devices: transistors, diodes, which quickly replaced energy-intensive and bulky electronic tubes. The set of SJC "Nerey" were: integrated GAS of the carrier of divers "Triton-2", light diver device (LV), as well as anchor acoustic beacon-answering machine (GM).
Integrated GAS VGM-459 installed on the layout of the HB "Triton-2" in 1969 year. But the model failed to pass the test, so the creation of the GUS VGM-459 was delayed. In 1976, it was tested on two Triton-2 prototypes developed by the Malachite SPMBM.
The Navy received the diver's direction finder and hydroacoustic beacon GAS VGM-459 in 1978 year under the code MGV-11. During the tests, it turned out that it was also necessary to develop a device for negotiations within the apparatus, a sonar and a sonar communication station.
For communication "Triton-2" and providing a boat used VHF radio "Falcon" P-352. The antenna was placed on a foam plastic buoy, and a sixty-meter coaxial cable was used to connect it and the radio station.
The station itself was placed in a sealed iron box, which had one handle to switch between reception and transmission. However, the cable did not allow to plunge to a full depth of forty meters, since there was no possibility of hermetic locking of the cover of the HB
The development of GAS communications for Eel divers began in 1970. In 1973, they were completed. The range of the station was one kilometer, weight - 4.5 kilogram, and the place of its initial placement was the space under the breathing apparatus.
A small induction headset jack and remote control were placed on the diver’s chest.
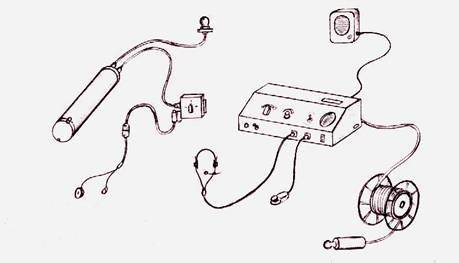
In 1974, the GAS MHT-6В was installed on two prototypes of Triton-2, which were tested on the territory of a torpedo test site in the village of Ordzhonikidze. This device was designed for seven divers, working, like a regular telephone, in duplex mode. Later it was installed on the Piranha PLM project.
Sources:
http://www.baltika-diving.ru/index.php?page=41&item=76
http://www.padelt-online.de/doc666/index1.html
http://www.arms-expo.ru
http://www.navy.su


Information