Camouflage tanks of the Red Army westward
Before the war, after long experiments, a camouflage system was finally developed for the armored vehicles of the Red Army, consisting of yellow-green (7K) and dark brown (6К) spots on a green (4BO) background. But such a camouflage scheme has not been widely adopted.
The system of protective coloration, camouflage and tactical symbols used by the armored units of the Red Army in this theater of operations was quite monotonous, being closest to the requirements of the regulations and underwent its most minor changes over the entire period described above.
This situation was due to a number of factors. First of all, this is the fact that the main hostilities on the Soviet-German front (until mid-spring 1942) took place precisely in the western direction. Consequently, new formations and products tank factories entered primarily this theater to compensate for the high "natural" loss of material. Secondly, in the face of intense battles and the rapid replacement of material, the crews did not have much motivation to create additional camouflage patterns and complex tactical designations. Thirdly, the main green paint of the Soviet 4BO armored formations was developed specifically for the color landscape of mixed deciduous-coniferous forests of Belarus and Central Russia, so green-painted tanks and armored vehicles did not require additional camouflage in the summer. The winter camouflage system developed by the military specialists of the Red Army was also most suitable for landscape changes caused by the climatic conditions of the winter of Central Russia.
By 22, June 1942, the Western Special Military District, which was deployed to the Western Front, had 6 mechanized corps of the Red Army (6, 11, 13, 14, 17, 20 micron) of which 4 (6, 11, 13, 14, 2, 17, micron), of which 20 (100, 22, 23, 1941, XNUMX, XNUMX, NNUMX), of which XNUMX (XNUMX, XNUMX, XNUMX, XNUMX, XNUMX, XNUMX, XNUMX u) were located ) were fully combat-ready, and XNUMX (XNUMX, XNUMX MK) had only a combat training tank fleet, whose composition varied within XNUMX machines for each mechanized corps. During XNUMX-XNUMX June XNUMX, most of the above units were forced to engage the German forces, reducing the duration of the mobilization measures to the maximum.
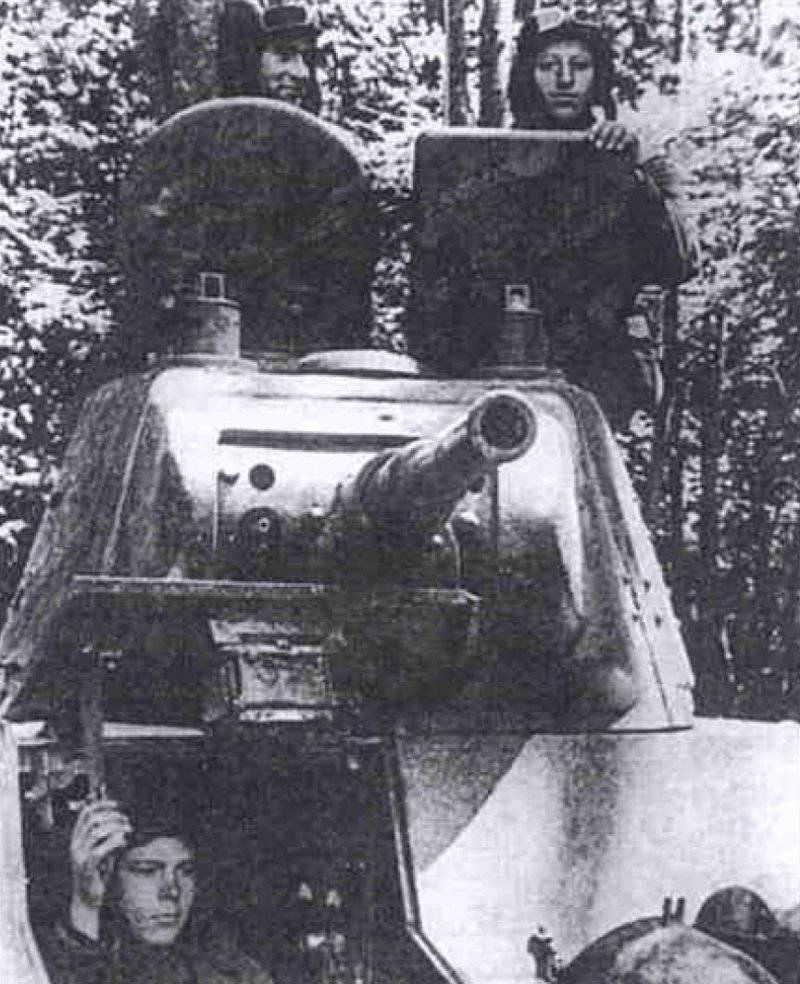
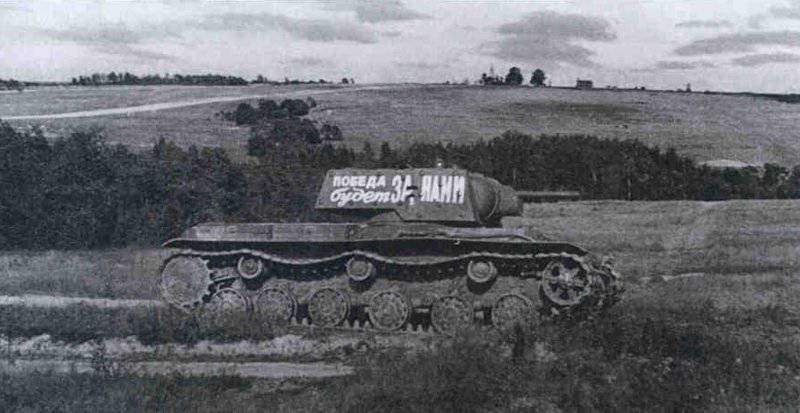
Tanks mechanized corps SOVOOVA were painted in green 4BO. A tactical designation system was not envisaged, however, old-issue armored vehicles, previously held in tank and cavalry units deployed in Belarus, had a tactical designation of the 1939 model of the year from solid and intermittent stripes, colored squares and numbers until 1932. On the sides of the towers of some cars were red stars.
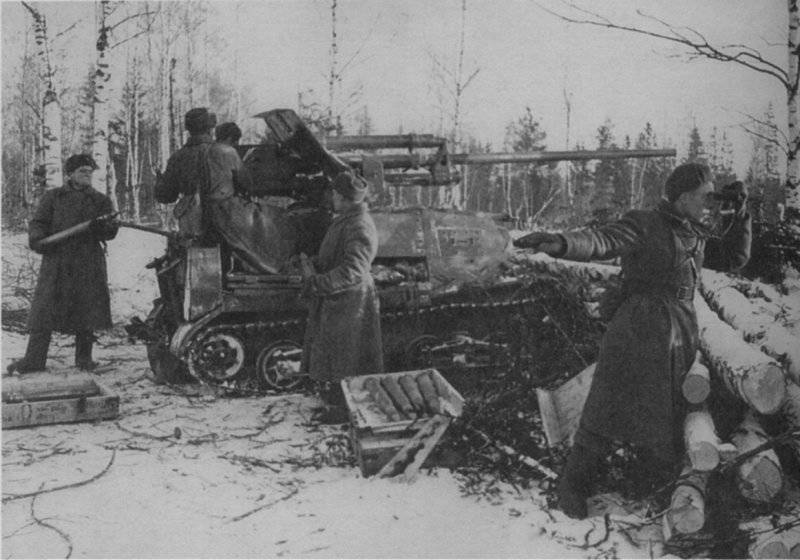
The most prepared for battles from the mechanized corps of the Western Front was 6 micron. He entered the battle of the day 23 June 1941 of the year, fulfilling the task of preventing the flank coverage of the Soviet group on the territory of Belarus. Some tanks, first of all commanders, still received tactical numbers. They were applied in white on the back of the tower, or in some cases on the sides of the tower or turret box.
The remaining tank formations and units (except for the above mechanized corps, armored units were in the 6 th and 36 th cavalry divisions of the 6 th cavalry corps as part of the tank regiments of the 64 BT tank in each, as well as in a separate tank company (BT tanks) 7, BA-10 armored vehicles of the 1-th separate motorized rifle regiment of the NKVD, which was transferred to Belarus from Lithuania 23 on June 1941 of the year - most of them had no tactical designations.
By the end of June 1941, the overwhelming majority of the tanks of the mechanized corps of the Western Front were lost in the battles and surroundings, in which the 3 and 10 army of the Red Army were trapped in Minsk. The front, where the 4 and 13 armies remained, essentially had to be rebuilt. In order to deploy the 19, 20, 21, and 22 armies arriving at the front, it was necessary to delay the German offensive for at least several days. This task was assigned to the 5 and 7 th mechanized corps of the Red Army, which arrived at the front in early July of the 1941 year.
The 7 th mechanized corps of the Moscow Military District was one of the most powerful connections of the Red Army. By the beginning of the war there were 715 tanks and armored cars of various brands in two tank (14, 18 etc.) and well-known motorized (1-th Moscow Proletarian Motorized Rifle Division) divisions. But only serviceable, combat-ready machines were transferred to the front, and even taking into account the material part arriving directly from the factories, the number of tanks participating in the battles did not exceed 500.
The 14 Panzer Division on the 6 July 1941 of the year included the 192 tank: the 176 BT-7 and 16 flamethrower vehicles based on the T-26.
18 Tank Division on 6 July 1941 of the year included 236 tanks: 178 T-26, 47 flamethrower tanks based on T-26 and 11 BT-7.
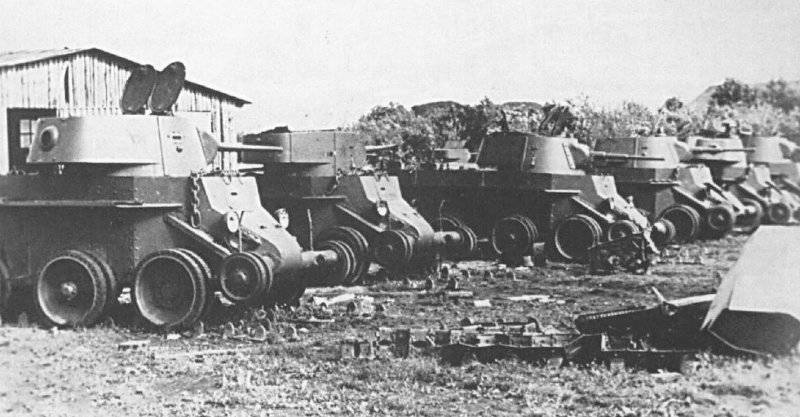

The 1-I Moscow Proletarian Motorized Rifle Division, an elite formation of the Red Army, demonstrated the might of the ground forces at parades in Moscow and had up to 100 tanks, of which around 50 BT-7М and 40 T-34 and KV.
Before being sent to the front of the vehicle, the 7 mechanized corps was painted in tricolor camouflage in accordance with the requirements of the instructions. And apparently they were in a hurry: they gave the team the camouflage, they provided them with paints, and they did not familiarize them with the standard paint schemes, relying on the ability of the crews. Therefore, depending on the specific units, the tanks had a different camouflage pattern: from paint colors striped in 3 (green-yellow-brown or in some cases brown, light and dark green colors) to spotty cars. Tactical symbols on the 7 MK armored vehicle were absent.
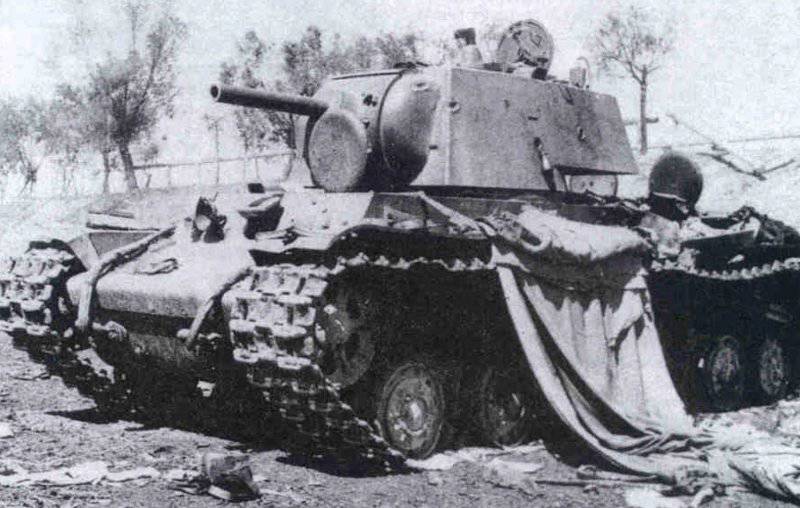
It should be noted that the material part of the tank regiments of the 7 th mechanized corps from 6 July was replenished daily with new tanks KB and T-34 that arrived from the factories and repair bases, which were immediately distributed among the units. These tanks were painted in green 4B0, camouflage was not applied to them.
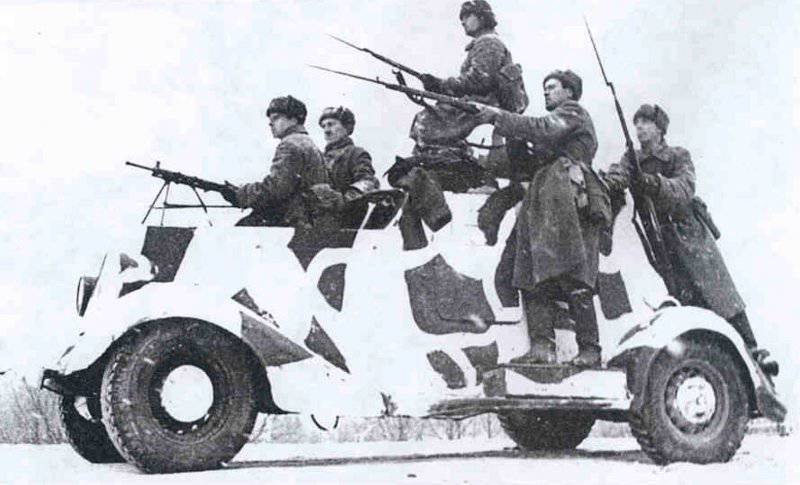
The 5 th mechanized corps, which arrived in the western part of the USSR from the Trans-Baikal Military District, was originally intended for the South-Western Front (the 109-I motorized division of the 5-th mechanized corps even managed to fight on it. - Comments of the author), however, due to the complicated position in Belarus 5 MK was transferred to the Western Front. In the three tank and one motorized divisions of the corps (except for the 2 regular tank divisions 5 MK, the 57-I separate Red Banner Tank Division ZabVO. - Prim. Aut.) Was operating the 924 tank. This technique was painted green with 4BO, without the use of sophisticated camouflage. In the 109 th motorized division, large tactical white three-digit numbers were used, which were applied to the sides of the BT-5 tank turrets.
On July 5 and 7, they joined the battle on July 6, trying to defeat the enemy group in the area of Lepel-Senno settlements. The 1st Proletarian Moscow Motorized Rifle Division conducted combat operations independently in the Orsha area. Despite the fact that our tankers fought bravely and even advanced slightly to the west, the counterattack of mechanized corps was not developed. Under continuous enemy strikes aviationsuffering heavy losses, the mechanized corps covered the withdrawal of combined arms armies to new frontiers of defense.
From the second decade of July to mid-September, the battle of Smolensk unfolded on the Western Front for the defense of the Soviet armies (July 1941 - September 10 10 of the year. - Note by author). Fearing new surroundings, the Red Army command insistently sought to seize the initiative in the theater of operations. However, counterstrikes needed fresh armored formations that were formed in the rear on the basis of the 1941 mechanized corps from the Kharkov Military District, the 25 mechanized corps from the Oryol Military District and the 23 mechanized corps of the Central Asian Military District. After arriving at the front, the control of these mechanized corps was disbanded, and on the basis of the most equipped tank divisions (in 27 MK there were only old worn-out tanks of the training and combat fleet. - Ed.) New armored formations were formed: 23,25,27 (from 104 etc. 9 micron), 27-th (from 105 td 53 micron), 27-th (from 110 td 51 micron), 23-th (50 micron), 25-th (55 micron). 25-I and 101-Panzer Division, which is also formed on the basis of 102-rd and 52-Panzer Divisions 56-Mechanized Corps of the North Caucasus Military District, 26-Panzer Division, renamed from 107-th Motorized Division, 69-I a tank division (formerly 108, etc. of the Far Eastern District) appeared on the Western Front as separate forces in the middle of July, 59.
109-I separate tank division appeared on the Western front a little later - August 30 1941. The very typical individual tank division according to staff No. 010 / 44 from 6 July 1941 of the year included 215 tanks, of which 20 KB, 42 T-34, 153 T-26 and BT.
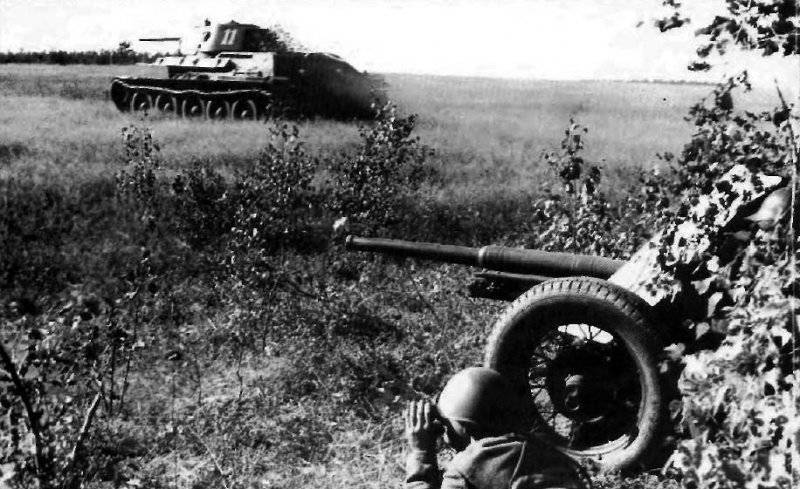
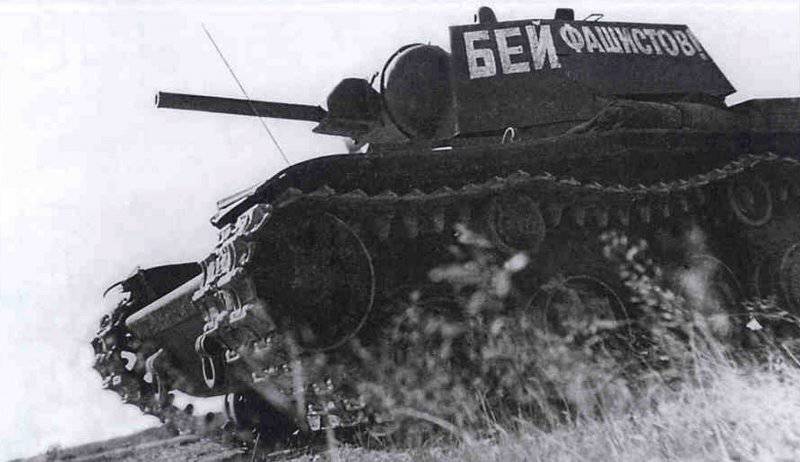
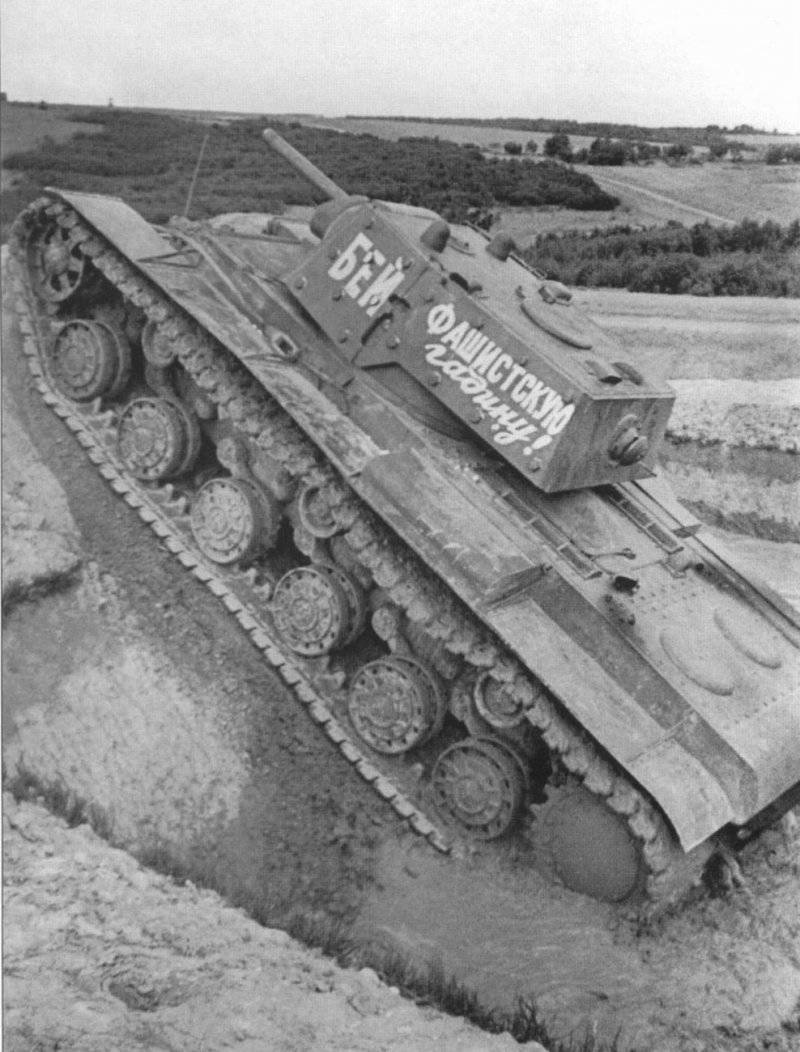
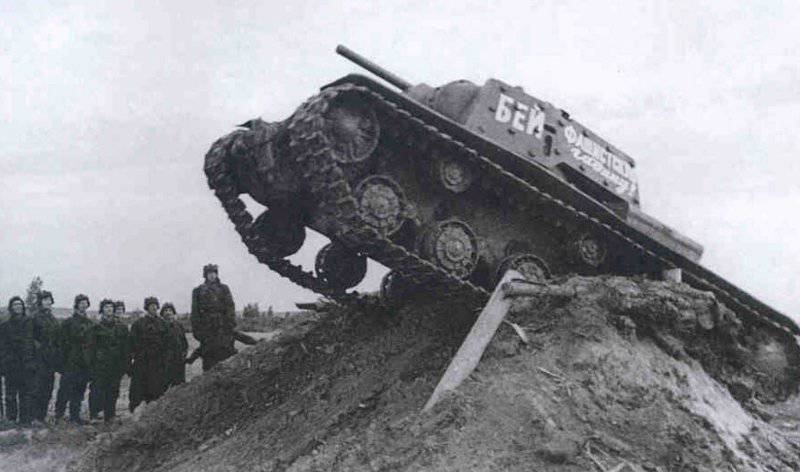
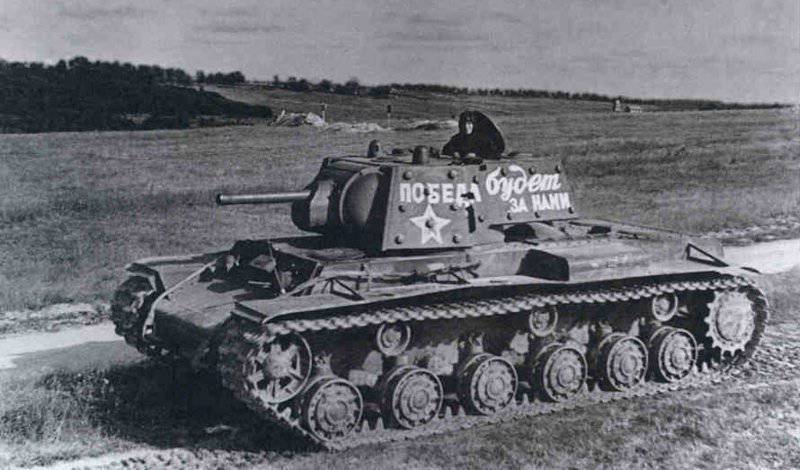
In reality, the composition of the newly formed formations varied within 180-220 tanks and armored vehicles for each armored division. They were tanks of both old and new brands. For example, in 109 30 etc. on August 1941 7 KB Download now, it was, 20T-34, 82-26T, 13HT-130, 22 BT-2-5-7, 10 T-40, 10-10 AD 13 and light armored vehicles. Most of the equipment was painted with green 4BO paint, occasionally tactical numbers were put on tanks or armored vehicles with white paint (for example, "11" or "365") or inscriptions-slogans: "Beat the Fascists!", "Beat the Fascist reptile!", "Victory will be over us!" etc. There were also unsolved tactical systems in the form of two vertical rectangles (maybe the 2 Battalion), painted on each side of the turret of the tank with white paint ...
In August, 1941, some tank units due to heavy losses began to be transferred to the states of motorized rifle divisions. The tank regiment of such a division, according to the abbreviated staff of 6 in July, 1941 of the year had an 93 tank: 7 KB, 22 T-34, 64 BT and T-26. 1-I Moscow Proletarian Division, 101-X and 107-I Tank Divisions became motorized rifle troops. The 82-i motorized rifle division of the pre-war formation, which was not composed of a tank regiment, and the tank battalion arrived in the western direction in September 1941 of the year.
Also at the end of August 1941, the first separate tank brigades began to form, which, according to state No. 010 / 78, had a separate tank regiment of three battalions: 7 KB, 22 T-34, 64 T-26, BT. And if only separate tank divisions took part in the initial phase of the Smolensk battle, then at the beginning of September 1941 joined the Bryansk front armored group, which along with the Western and Reserve fronts from the 16 of August acted against the Germans in the western direction, included the 108-I tank division The 141 Tank Brigade and the 113 Tank Brigade of the 3 Army, as well as the 50 Tank Division and 43 Tank Brigade in the 13 Army. This group was tasked with smashing the 2 th tank group (tank army) of the "scoundrel Guderian", which could break through to the rear of the troops of the South-Western Front. But the strength and ability were clearly not enough - Guderian’s tank divisions managed to withstand the blow and outflank the troops of the vast Southwestern Front. The first victory came to the Soviet troops in another sector - 30 August 24-I and 43-I armies of the Reserve Front resumed the offensive on the Yelnitsky direction. The 24 Army 102, 105-I tank divisions and 103-I motorized division, and the 43-I army - 104-I and 109-I tank divisions. On September 5, the enemy, unable to withstand the blows of the Soviet troops, began a hasty retreat. The 24 Army of the Red Army liberated Yelnya and, by 8 September, eliminated the dangerous Yelnytsky bulge. September 10 troops of the Western, Reserve and Bryansk fronts went on the defensive. Smolensk battle ended, both sides began to prepare for the battle for Moscow.
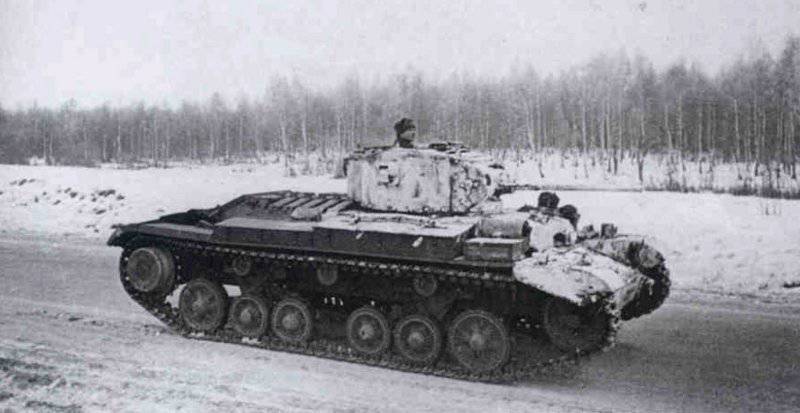
Despite the grandeur of the operations carried out, the tanks and armored cars of the Red Army during the battle for Moscow (October 2, 1942) were painted quite monotonously. And this fact has an explanation - the high dynamics of current events.
The main armored compound used during the Battle of Moscow was a tank brigade. Part of such armored brigades (17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 25 tbr) was formed according to staff number 010 / 87, according to which the tank regiment consisted of two tank battalions and had an 61 tank: 7 KB, 300, 22, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X, X. 34 T-32, BT-26 / 5, T-7. But there was a catastrophic shortage of tanks, so October 40 9 appeared new staff number 1941 / 010, according to which the brigade consisted of two tank, motorized rifle battalion and 306 individual mouths, all 4 tanks: 46 KB, 10 T-16, 34 T-XNUM , BT, T-20. According to such a structure, the famous 26-I tank brigade (later 40-I Guards tank brigade. - Approx. Ed.) Under the command of Colonel M.Ye. Katukov. On 4 of October 1, a brigade tank regiment formed in September 3 (staff No. 1941 / 1941) had an 010 battalion and a total of 87 tanks (approximately to staff No. 2 / 49?) KB, T-010, T-306, BT-34? . Such discrepancies between staff and reality were present in many armored brigades, which makes it difficult to establish consistency in tactical and identifying marks.
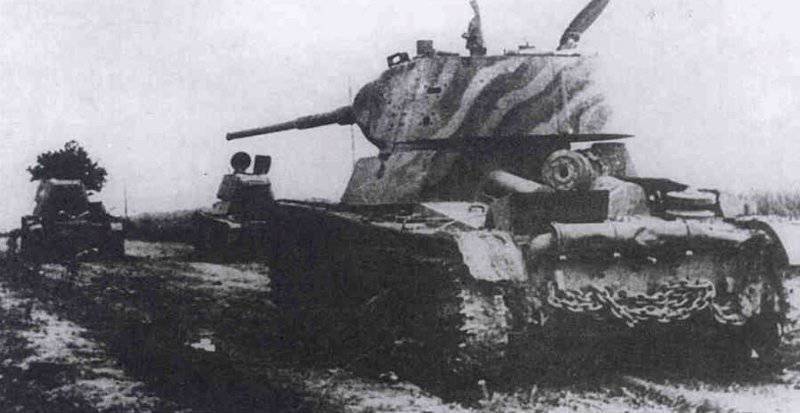
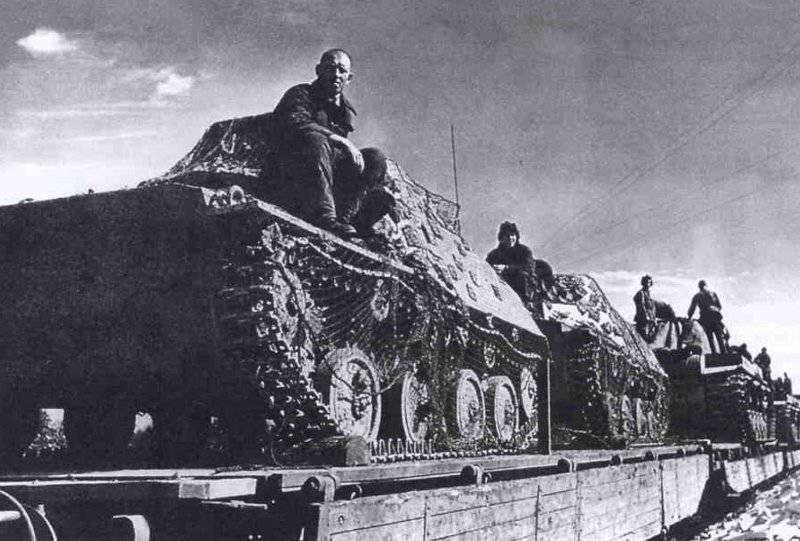
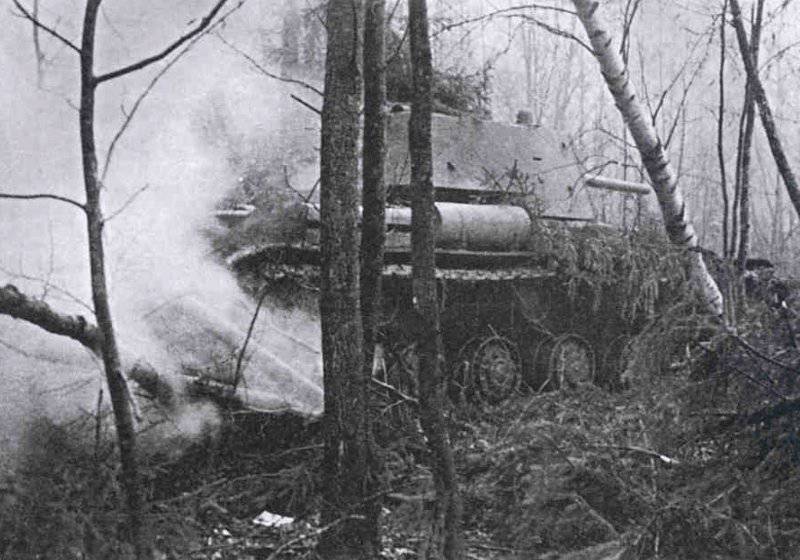
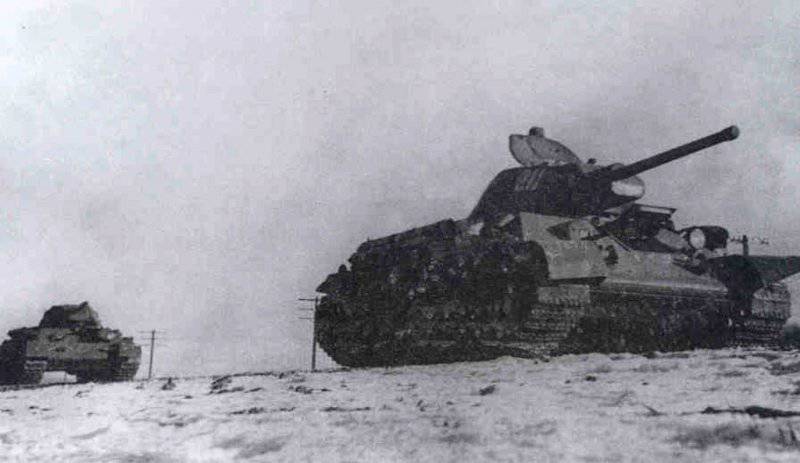
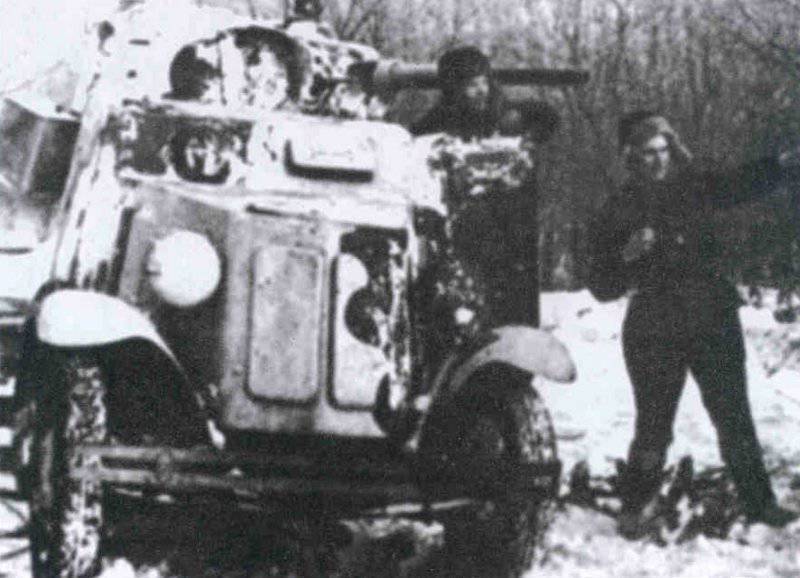
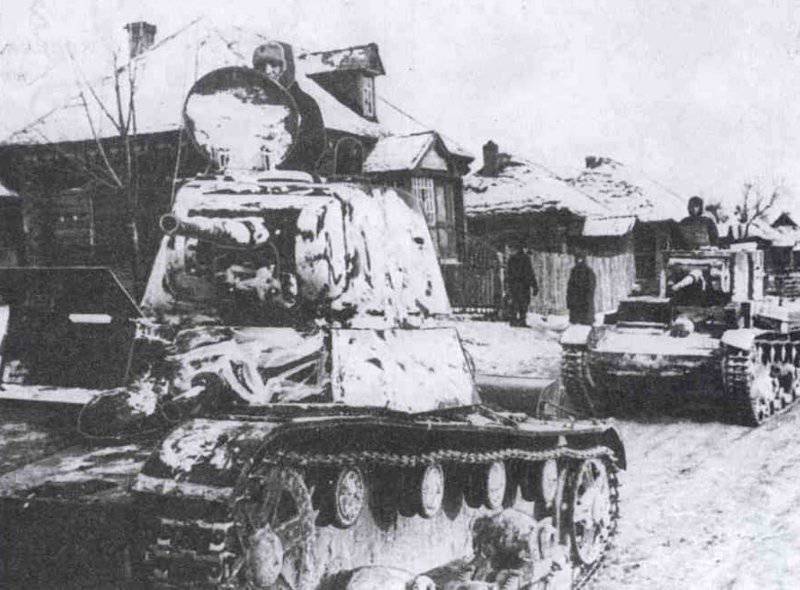
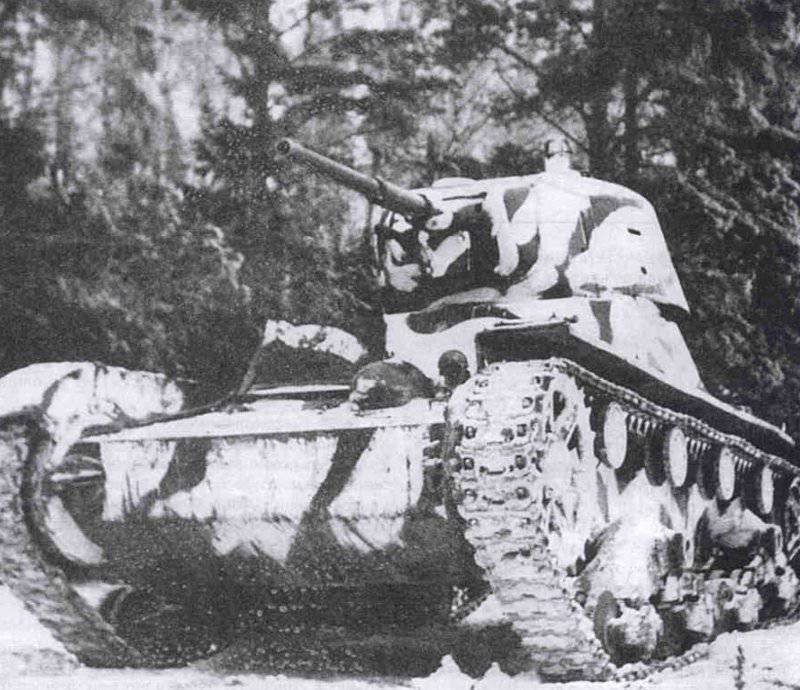
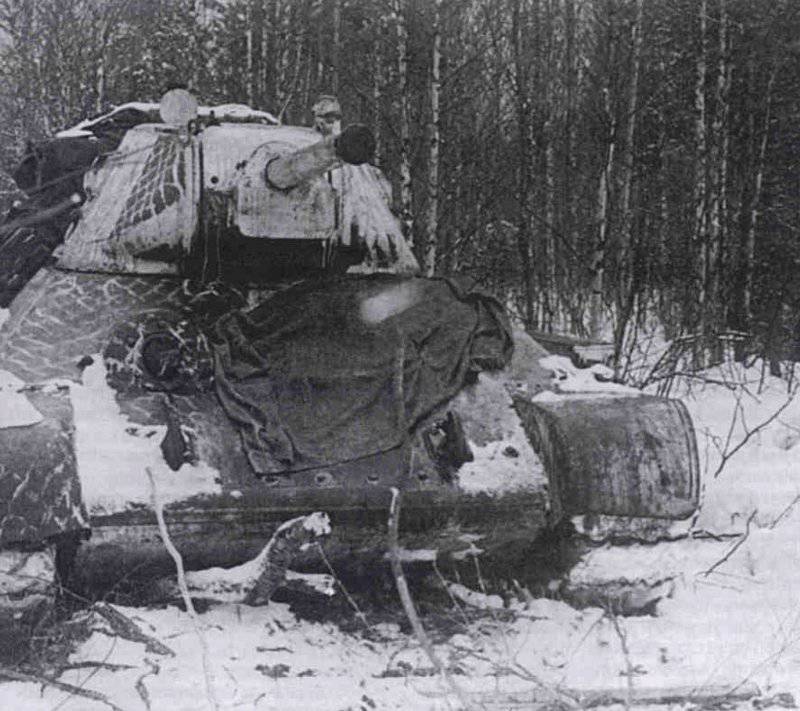
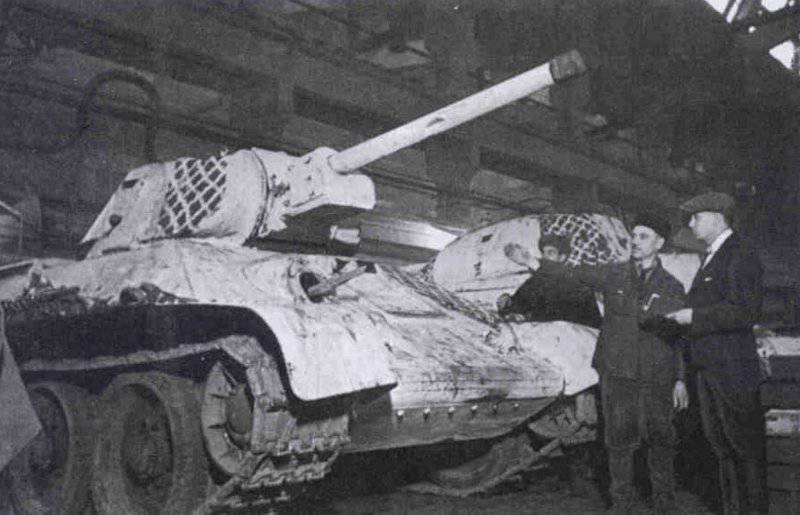
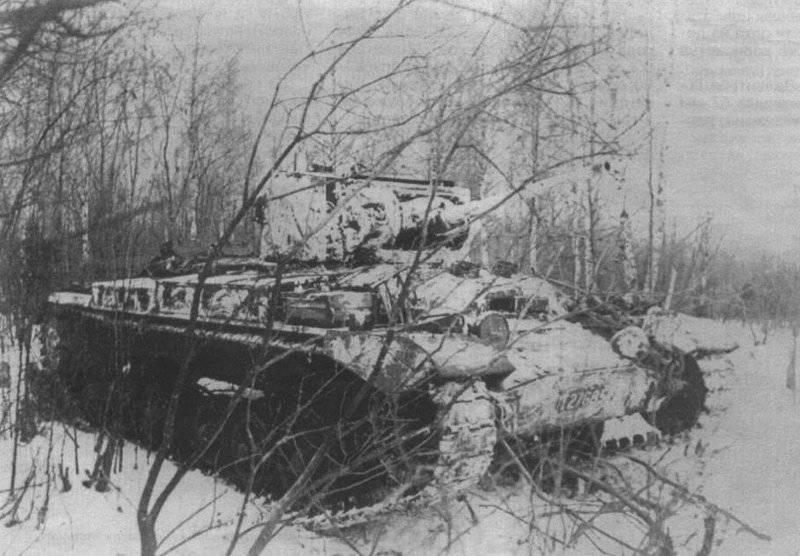
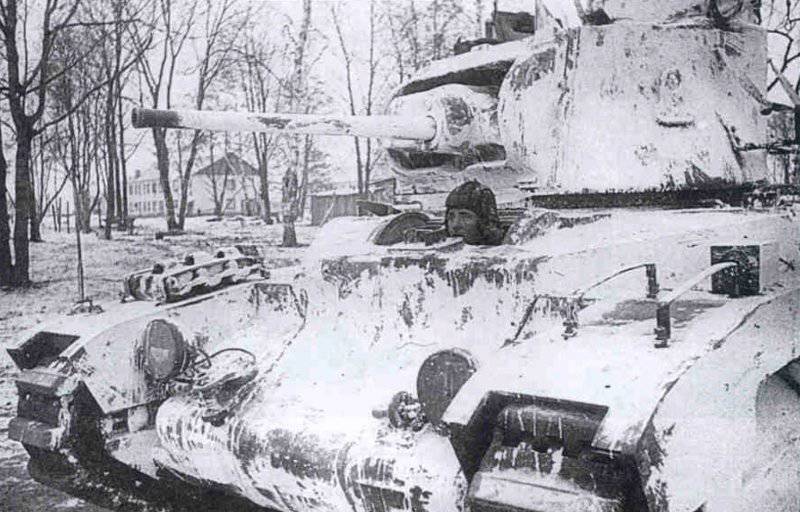
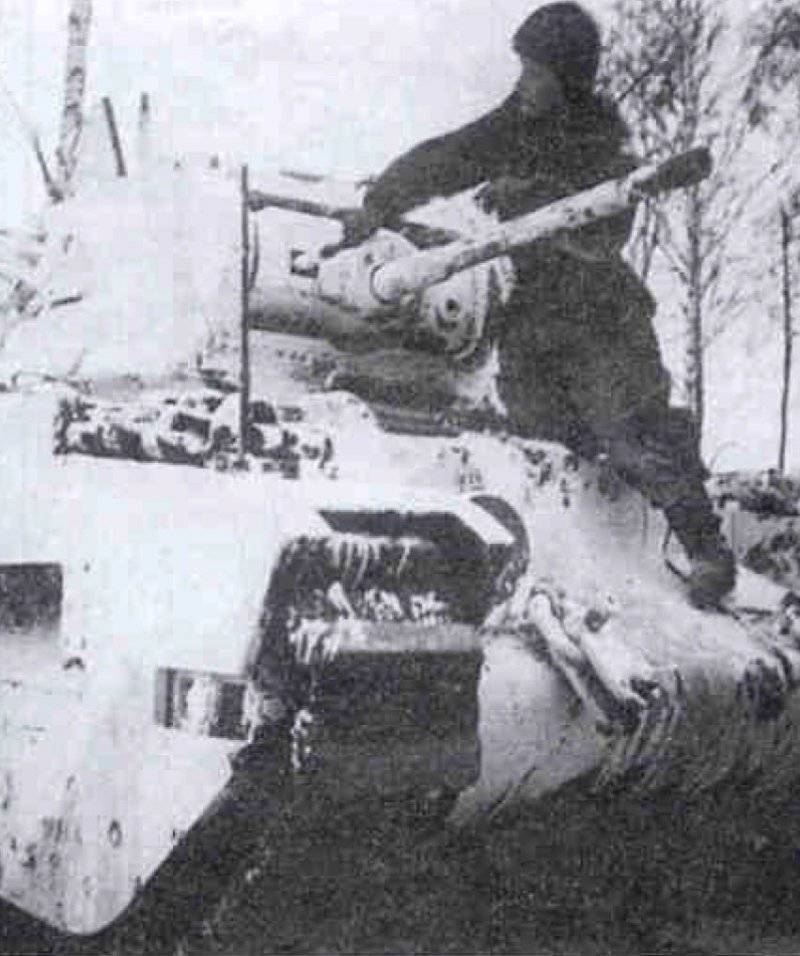
Most of the material parts of the individual tank brigades that fought on the Western, Reserve and Bryansk fronts, and later on the Western, Bryansk and Kalininsky (created October 19 1941 of the year. - Approx. Ed.) The fronts were painted in green 4BO and had no camouflage, except three color 57-mm ACS ZIS-ZO. Winter in the western theater theater came unusually early. Already in mid-October, the first snow fell, and at the end of the month, due to stable snow cover, it became necessary to paint armored vehicles in white or to apply special winter camouflage.
Spots and patterns with winter camouflage paint applied, following the following rules.
In the winter camouflage painting on the previously camouflaged surface, all the green spots were evenly painted over with white paint, and on the yellow-earthy and dark brown spots were applied with a white paint a diamond-shaped net. The direction of the white stripes forming the grid should have been varied: it was impossible to apply only vertical or horizontal stripes, mainly inclined stripes were applied.
The distances between the white stripes of the diamond mesh were provided by the following standards (see table 1):
1 TABLE White stripe width in cm | The distance between white stripes in cm | |
On dark brown spots | On yellow earthy spots | |
1 | 6,5 | 3,5 |
1,5 | 10,0 | 5,0 |
With winter camouflage painting on a smoothly painted green surface, when the material part was not managed to paint in 3 colors with summer camouflage colors, they acted as follows.
Marking for the three-color camouflage was applied with chalk on the armor of the tank. Spots that were marked under the green color, painted over with white paint; spots marked for a yellow-sallow color and for dark brown were covered with a white diamond-shaped mesh. The distances between the white stripes of the diamond mesh should have been as follows (see table 2):
2 TABLE Width of white stripes in cm | The distance between the edges of the white stripes in cm | |
On patches intended for dark brown color | On stains intended for yellow-sallow color | |
1 | 8,5 | 2,5 |
1,5 | 13 | 4 |
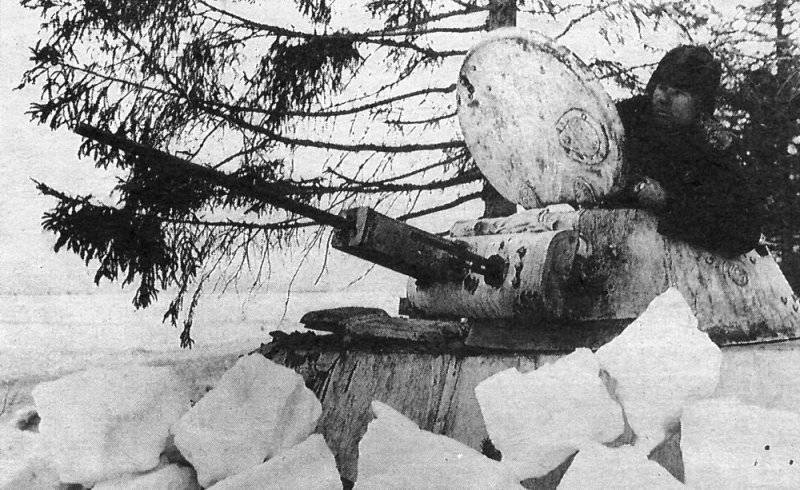
Coloring was made depending on the nature of the area where the fighting took place. If these were open spaces covered with white snow, the object was allowed to be painted in a solid white color or the distance between the white stripes of the diamond mesh was reduced by applying additional stripes.
With the transition of parts from open spaces to closed ones (forest, bushes, settlement), it was planned to remove additionally applied continuous white coating and additionally applied stripes.
With the transition of the parts to the snow-free areas and with the onset of spring (after the snow melted), the white paint was completely removed by wiping it with rags moistened with water or kerosene.
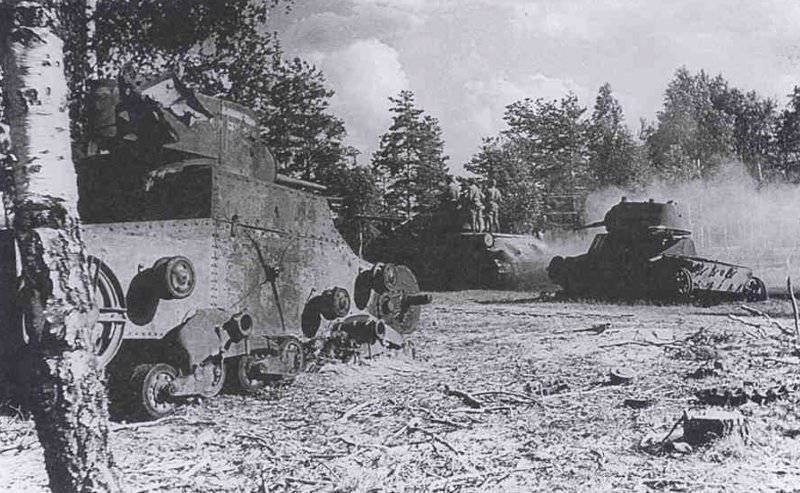
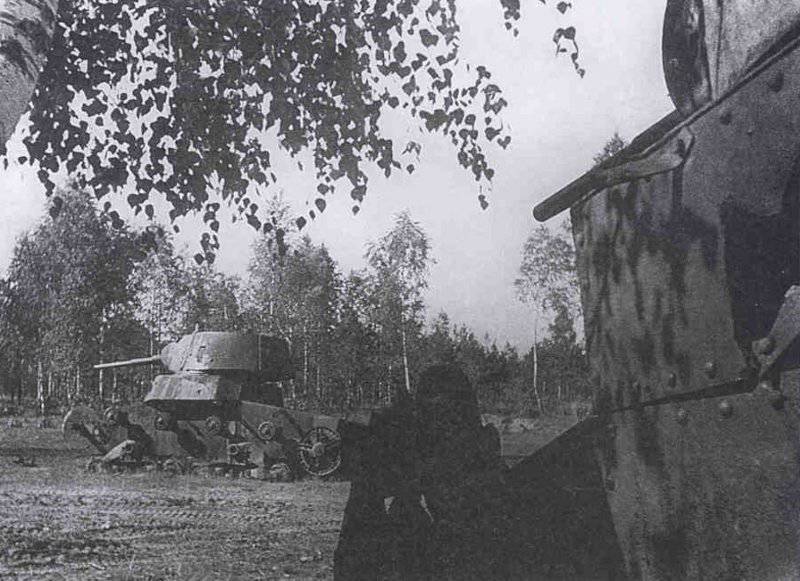
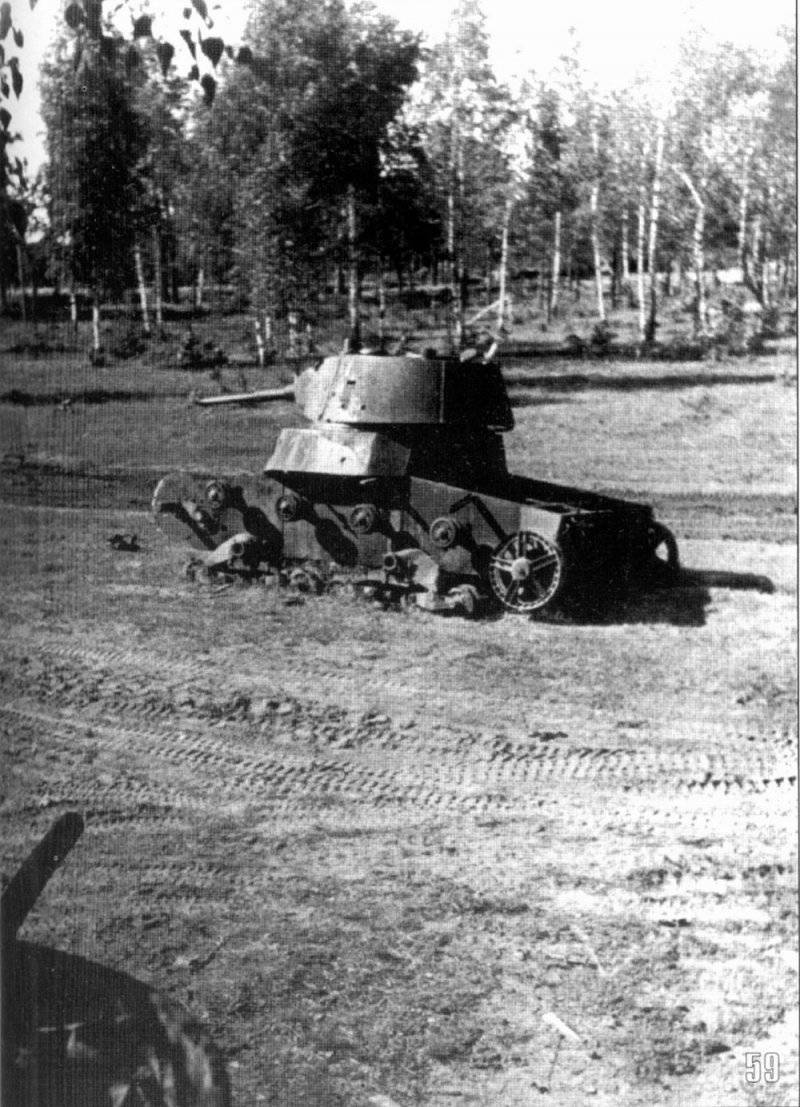
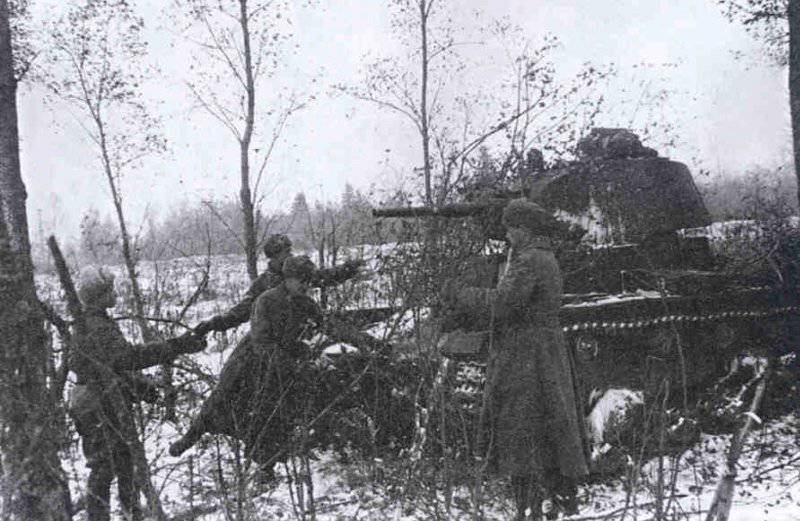
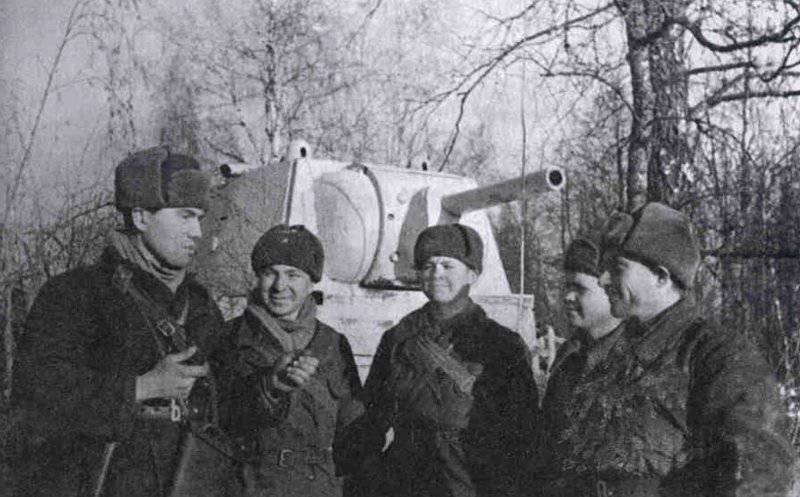
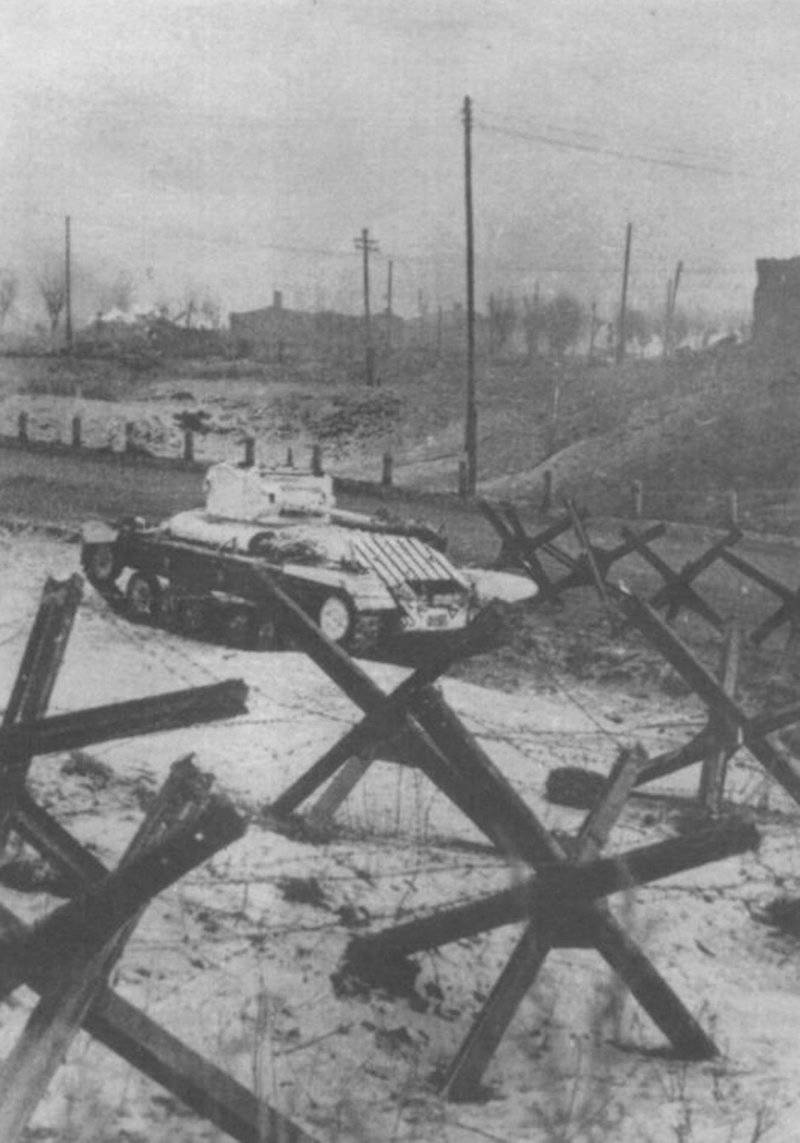
In reality, with the onset of winter, only part of the tanks painted white or winter camouflage. Most of the photographs are available about the 1-th Guards Tank Brigade, known for its exploits and tankers-aces (Lavrinenko, Burda, Lyubushkin) compound.
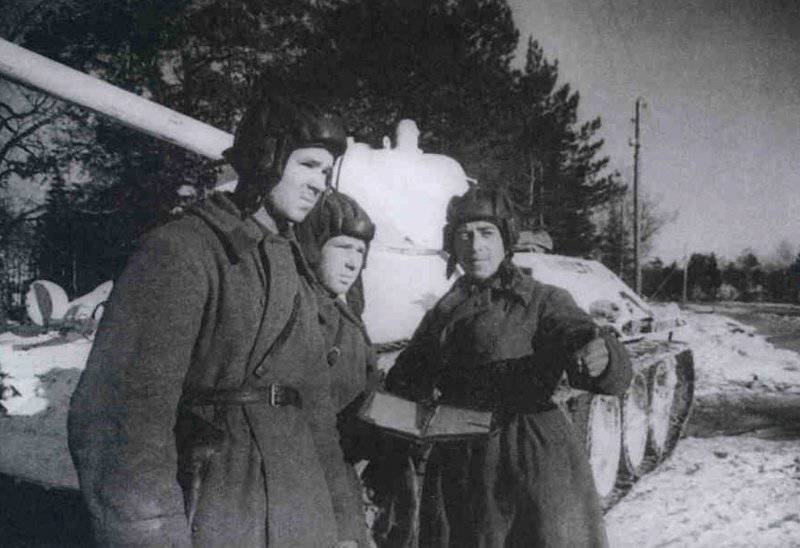
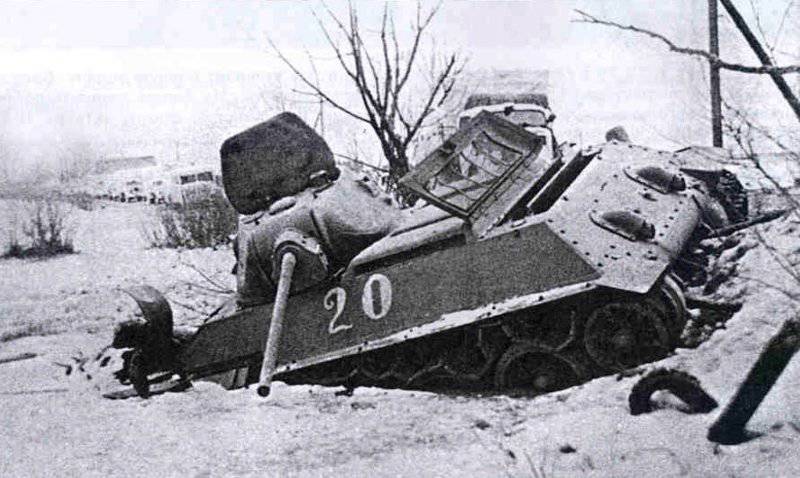
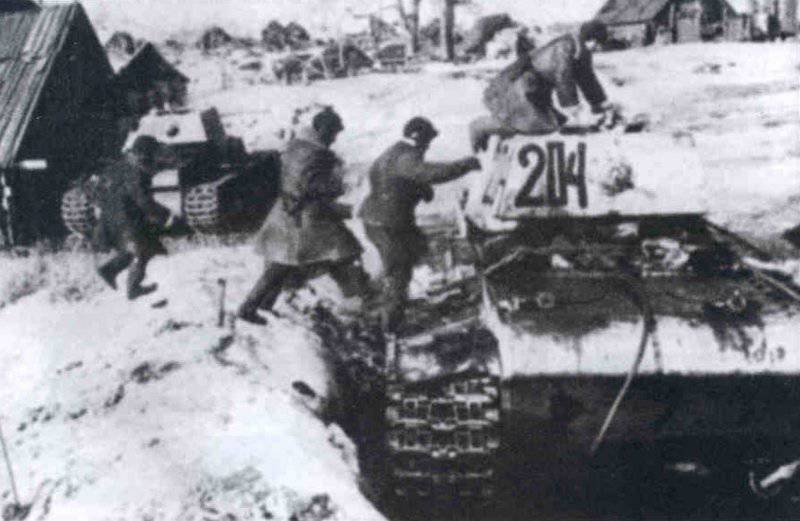
In the same period, 1 of the winter painting type was fixed in the 3 Guards Tank Brigade: according to the instruction, white and “mesh” spots (most T-34 tanks were painted this way), white (KB tanks) and dark green vehicles (armored reconnaissance vehicle BA-10). In particular, on the BA-10 unpainted in white camouflage, tactical symbols are visible that are specific to the 1 Guards Tank Brigade, and subsequently deployed on its base the 1 Guards Tank Corps and 1 of the Guards Tank Army. This sign was a diamond divided into 2 triangles. In the upper part of such a “fraction” there was a figure designating the number of the battalion, company or platoon (in the reconnaissance of the brigade there were 6-7 armored cars), and in the bottom - the tactical number of the tank. Thus, the BA-10 pictured in the photograph was probably the 2-th vehicle of the 3-th reconnaissance armored platoon. Also on this armored car, a white rectangle is visible on the roof of the tower - a sign of air recognition. In other brigades, for example, in the 5 tank, the air mark was a triangle, a circle was used less often. On the green car, the air identification marks were applied in white paint, and on white, on the contrary, they were left green or painted in red. Red paint was also used in the 1 Guards Tank Brigade; sometimes tactical symbols were applied to it on the sides of the towers painted in the winter camouflage of tanks. In other armored units tactical numbers of white, yellow or red colors were used. For example, on fighter tanks (T-34 with a long-barreled 57-mm ZiS-4 gun. - Auth. Note) T-34 / 57 from the 21-Tank Brigade applied double-digit tactical numbers in white paint to the sides of the tank hull. The machine commander of the tank regiment 21 tbr Major Lukin had a tactical number "20".
Of the three tank divisions that fought near Moscow (58, 108, 112, etc.), the most photographs are available from the 112 armored division.
The 112 Panzer Division was formed in the Far East in August 1941. The 112 Tank Regiment of the 239 th Motorized Division of the 30 Th Mechanized Corps of the Far Eastern Front served as the basis for the formation of this compound (this was despite the absence of war called the unification of the Soviet troops in the Far East. - Ed.). In October, 1941 of the year, along with the 58 Tank Division, the 112 Tank Division was sent to the Western Front near Moscow. November 5 1941, having X-NUMX tanks T-210, as well as armored BA-26, BA-10 and BA-6, the division began hostilities in the Podolsk region as part of the Western Front mobile group. She transferred a part of her equipment to other parts and connections. Subsequently, she fought in the Tula area, striking the Wehrmacht’s 20 Panzer Division, as part of the 17 Army, participated in the Soviet offensive near Moscow, and on December 50, her first tanks broke into Kaluga. In early January, 21, along with other tank divisions operating on the Western Front, was reorganized into the 1942 Tank Brigade.
T-26 tanks and BA-20 armored cars had camouflage of green and white spots, most likely these strip-like spots were applied with a brush upon arrival at the front.
The BA-10 armored cars were roughly covered with white paint entirely, with brush strokes clearly visible on them. The T-34 / 76 tanks, which arrived for replenishment, were painted with green 4B0 paint and had three-digit tactical numbers, painted in white paint on the sides of the tower.
In addition to armored formations, the 4 motorized rifle divisions 1 (later 1-I Guards) and 82-I pre-war formation, 101-I and 107-I, reorganized from reduced-size tank formations participated in the Battle of Moscow. As mentioned above, their structure also had armored units and subunits.
As part of separate motorized rifle brigades, the tank battalion had an 32 tank - 12 T-34 and 20 T-26, BT, T-40. 3 participated in such brigades in the Battle of Moscow: 151, 152, and a separate motorized rifle.
Separate tank battalions (Soviet-made tanks) were formed according to staff No. 010 / 85, approved by 23 on August 1941, and had 3 tank companies and three separate platoons, total 29 tanks: 9 T-34 and 20 light various brands. In addition, in the structure of some rifle divisions, there were separate tank guard companies of the headquarters, which consisted of X-NUMX T-15, T-37, less often T-38, T-27 or armored vehicles. Similar companies were part of the battalions of the defense headquarters of the armies, but they had a little more equipment - 26-17 tank or armored car.
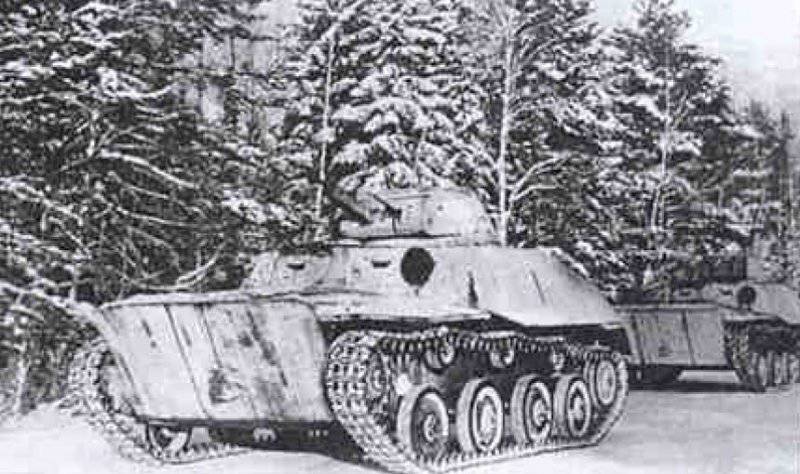
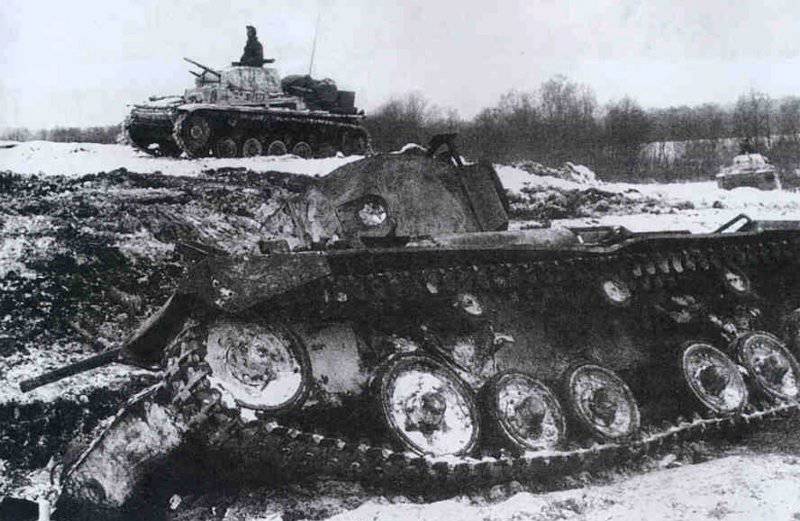
As for the materiel of tank units, its composition was quite variegated. During the fighting, the whole range of armored vehicles produced in the USSR before the start of the war was used: all types of T-26, BT-2, BT-5, BT-7, T-37, T-38, T-40, T-27 ( as tractors for 45-mm guns), T-28 (in small quantities), T-50, T-34, KB, BA-3, BA-6, BA-10, BA-20, FAI, armored tractors T -20 "Komsomol member" and even such "rare books" as MS-1 tanks and BA-27 armored cars. In general, everything that could go and shoot went into action, even prototypes of tanks located at the Kubinka range, for example, A-20 and T-29. In addition, the battles near Moscow were the first to use new models of tanks created in wartime conditions - these are T-30 and T-60. Moreover, if the T-60 tanks were subsequently used in large quantities on other fronts, then the number of T-30s participating in the battles (and its floating counterpart T-40) in the battle for Moscow were not equal. In August-November 1941 of the year, at least 40% T-40 and 80% T-30 from among all manufactured were sent to the Red Army tank units operating in the Moscow sector.
On the eve of the December counterattack of the Soviet troops near Moscow, English-made armored vehicles appeared on the fronts: 145 tanks MK II "Matilda II", 216 MK III "Valentine II / 1V", and also 330 light armored personnel carriers MK I "Universal". The first cars (no more 50 tanks. - Approx. Ed.) Went into battle in November 1941 of the year, and later the British tanks were widely used in battles in this theater. So on the Western Front on 31 December 1941, British tanks were part of the 146 (2 T-34, 10 T-60, 4 MK III), 20 (1 T-34, 1 T-26, 1 T) 60, 2 MK III, 1 BA-20), 23 (1 T-34, 5 MK III) of tank brigades operating in 16 combat formations. 49-th and 3-th armies, as well as in the 112-th tank division (1 KB, 8 T-26, 6 MK III), attached to the 50-th army. MK II Tanks "Matilda" were in the 136-m separate tank battalion.
On the North-Western Front, which acted within the framework of a single operation during the counteroffensive of the Soviet troops near Moscow, were the 170 and 171-th separate tank battalions, also equipped with English-made armored vehicles.
170 off (10 T-60, 13 MK II) was given to 3-th Shock Army, and 171 off (10 T-60, 12 MK-II and 9 MK III) - from the end of February were transferred in the Kalinin front. MK I “Universal” armored personnel carriers were distributed to the reconnaissance companies of tank brigades (including those equipped only with Soviet equipment) at the rate of 4-2 vehicles per brigade.
On the Soviet-German front, the British technique was painted with white paint (whitened) in two ways: completely, with painting the British registration marks and partially, when the upper part of the hull and the tower were painted to save paint. Sometimes during winter whitewash, British license plates were covered with a rectangular stencil. As for the green paint Bronze Green, which was painted by British tanks, it was quite satisfying to the Soviet military - the 1-I motorized rifle division, October-November, the repainting on 4BO was carried out only with a major overhaul.
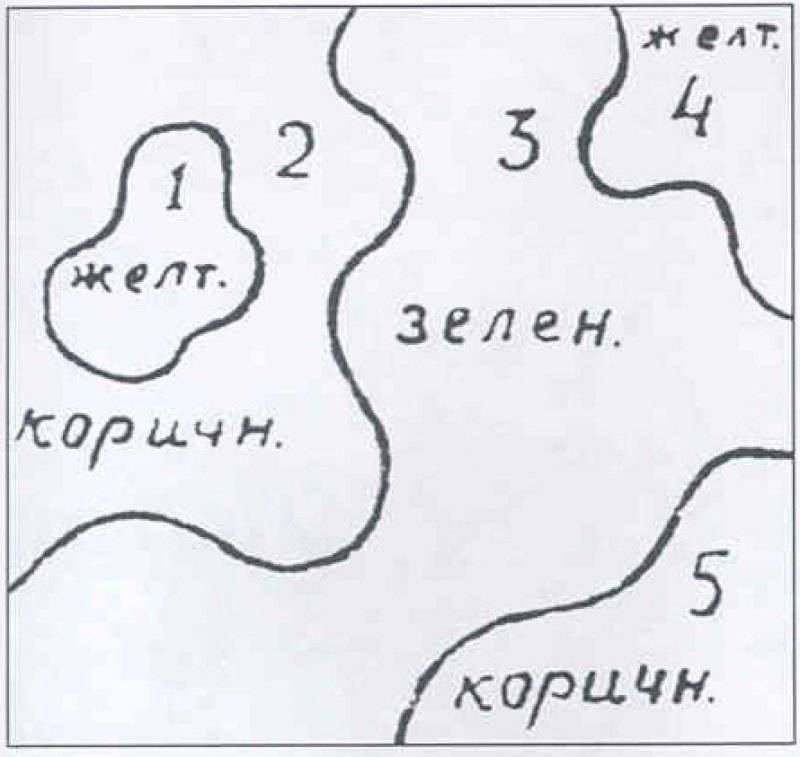
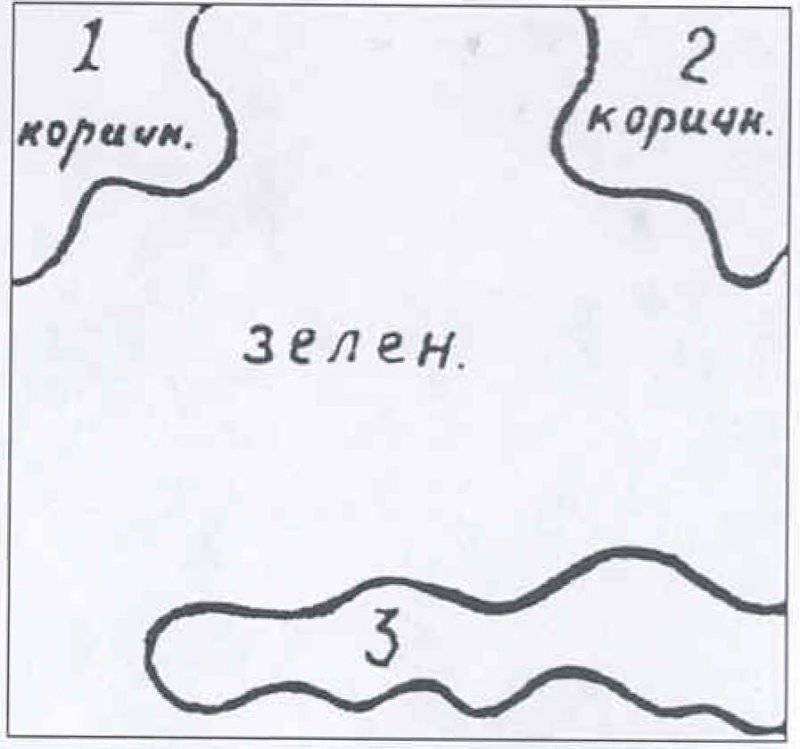
Regarding the application of stains, they should have a winding contour and be diverse in their outlines and sizes, distorting the most familiar look of the material part.
The ratio of color spots: green (4BO) - 45-55% of the total area of the painted object, yellow and earthy (7K) - 15-30% of the total surface area of the object, dark brown (6К) - 15-30% of the object's surface.
The characteristic parts of the tank are straight lines and angles, tower, hull, gun barrel, rollers, etc. had to be painted with spots of various colors.
The general direction of the spot (elongated) should not be parallel to the contour of the object, but should be a combination of angles with it. Spots of the same color and similar in size or shape should not be arranged symmetrically.
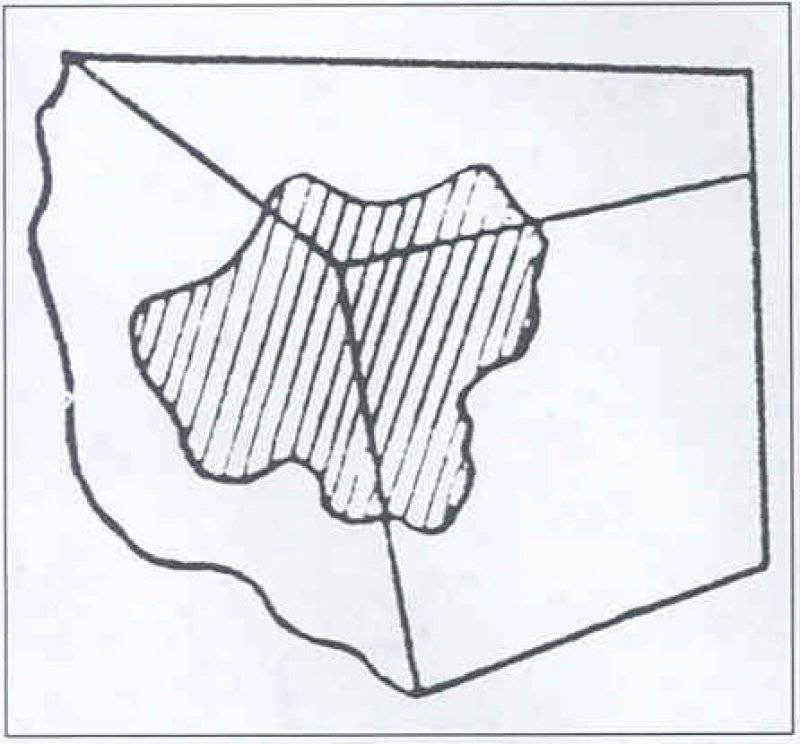
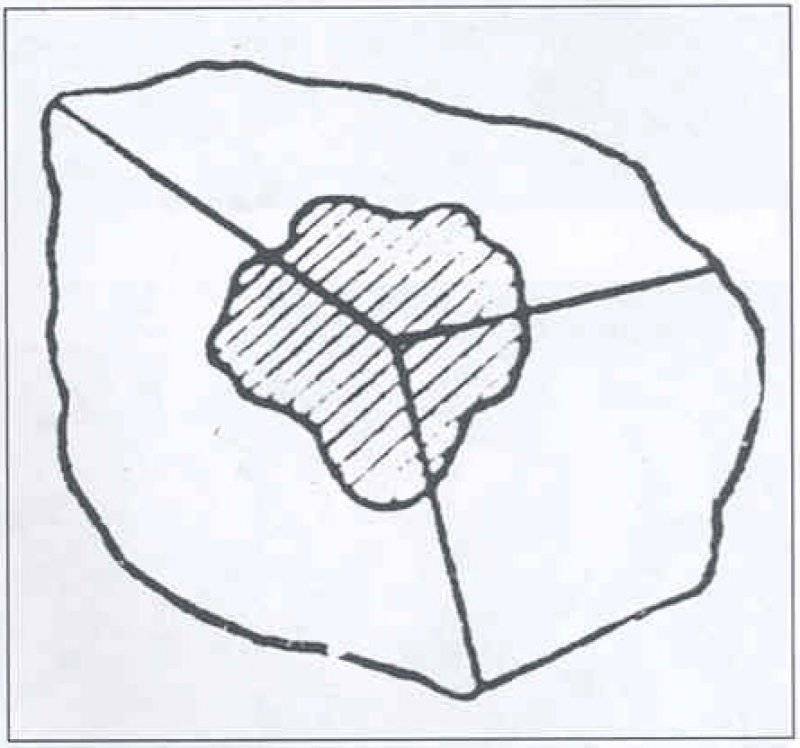
The spots should have been closed, located inside the contour of one face of the object, and open, cut off by the face of the object.
Open spots must necessarily cross adjacent faces of the object, that is, to capture at least two faces. The protruding angles composed of several planes are colored mostly in dark colors for ordinary objects.
The top of the protruding angle should not coincide with the center of the spot.
On the constantly shaded parts of the object, spots of the most contrasting colors are applied - yellow and brown.
When the spot is located on several faces, the center of the spot should not coincide with the top of the spot.
Depending on the estimated range planned in advance (as a rule, from 300 to 1000 m) and the effect of coloring, the size of the spots is determined from the table.
When applying winter camouflage (as mentioned above), all the green spots had to be exactly painted over with white paint, and on the yellow-earthy and dark brown spots "painted over with a white diamond-shaped mesh." The direction of the white stripes forming the grid should have been varied: it was impossible to apply only vertical or horizontal stripes, it was necessary to do mainly inclined stripes.
If the positions of tank units were located in open places covered with pure snow, then it was possible to paint the object in a solid white color or reduce the distance between the white stripes by applying additional stripes.




















































Information