He conquered the Soviet Union
The most interesting thing is that at this moment, unexpectedly for the Germans, the Soviet tracked artillery tractors of the Stalinets type C-65, STZ-5 NATI and Komsomolets, which were initially ignored by representatives of the Ground Forces Armaments, showed themselves well, as they did not differ in speed indicators and were not suitable for a “blitzkrieg”. But already in winter, “Russian type” tractors increasingly showed their advantages in cross-country conditions in the absence of good roads.
***
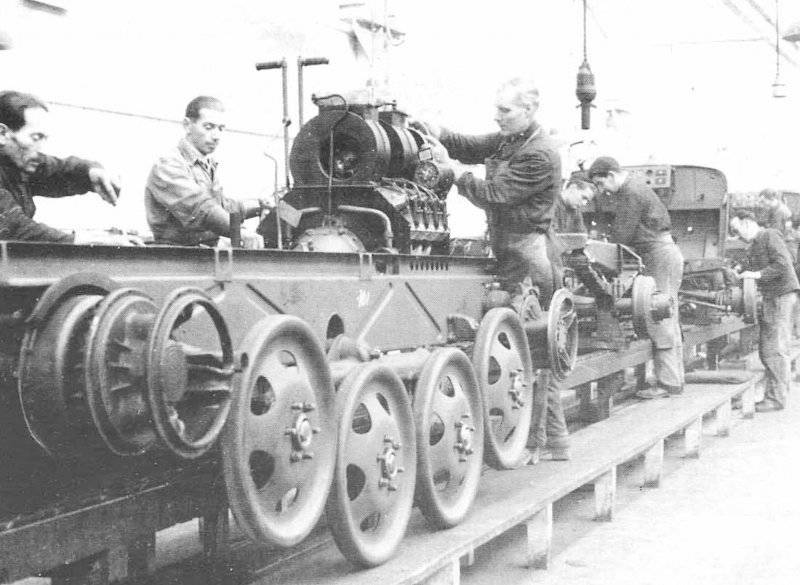
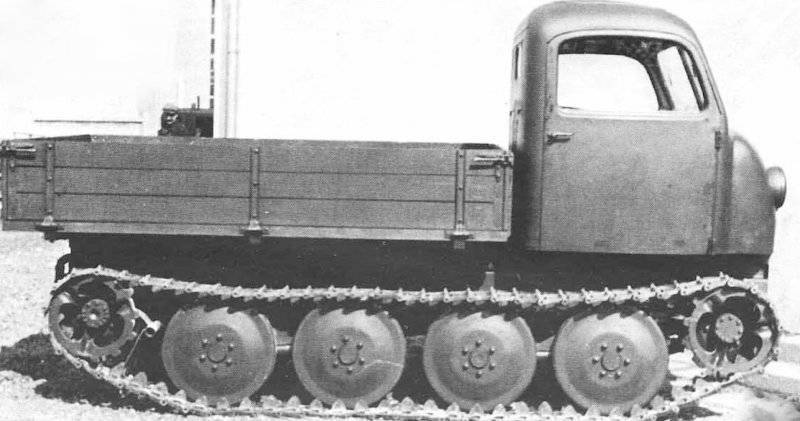
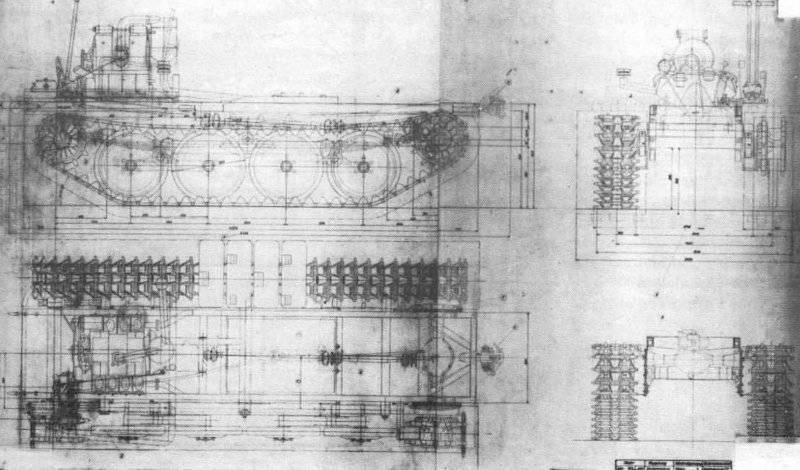
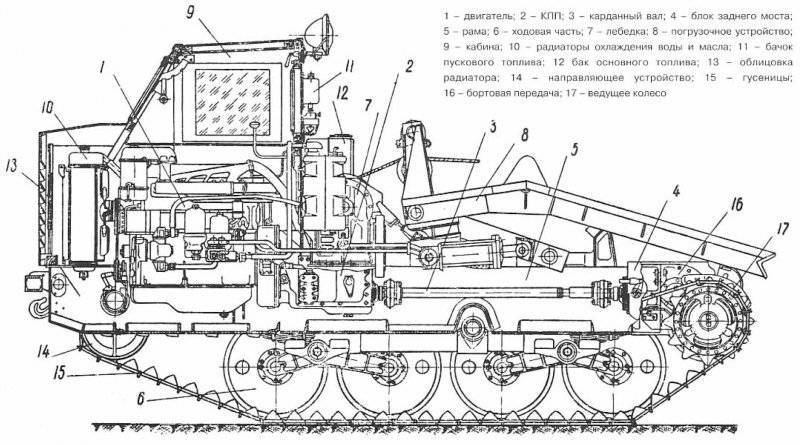
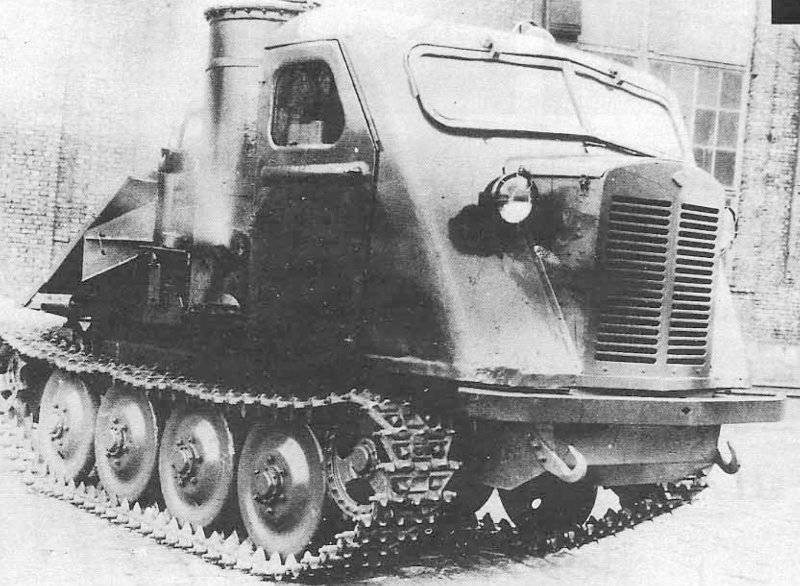
After the battle for Moscow was over, the Wehrmacht command made it clear that the German army urgently needed cheap and easy-to-maintain tracked off-road tractors. "Tank The commission ”of the Reichs Ministry of Armaments and Ammunition, chaired by Professor F. Porsche, completed a preliminary design of such a tractor together with the engineers of the concern“ Steyr-Daimler-Puch ”(Syeyr-Dainler-Puch), and the project was completed without the participation of specialists from the Armed Forces Directorate. It is difficult to say how the planned litigation between these departments could have ended if Hitler had not suddenly spoken out in defense of the concept of a “Russian type” caterpillar tractor with high ground clearance for use in Russian snow conditions. According to some researchers, it was Hitler who gave the new tractor the nickname “Raupen-schlepper Ost” (RSO for short), which meant something like “a tractor heading east”. All the main parts of the new tractor were borrowed from the well-developed truck Steyr 1500/02. The heart of the tractor was an 8-cylinder 3,5-liter V-shaped gasoline engine. and with a maximum power of up to 85 hp, the suspension of a simple design seemed to be conceived for production only in wartime conditions.
Basic rollers were supposed to be made by stamping from sheet steel and did not have rubber bands. Tracked tracks 340 mm wide (type Kgs 66 / 340 / 120) also did not have rubber pads (like the half-tracks) and could even be made from unalloyed steel. The decoration of the cabin was different Spartan rigor. All this reduced, undoubtedly, the speed characteristics of the tractor, but made it cheap in mass production and maintenance. But the main thing - the tractor had a very large ground clearance, which could not be better affected its patency in mud and snow.
In December, Steyr received an order for the production of an experimental batch of 1941 tractor RSO in 50. Already in the spring of 1942, the tractor was subjected to minor alterations, aimed at a somewhat simplified release. But, despite the improvements made, the output of the tractor was largely constrained by the fact that tractors were manufactured on the same assembly lines as the truck, which was very necessary for the Wehrmacht. In addition, it became clear that some of the shortcomings of the high-speed gasoline engine when it is working on the tractor.
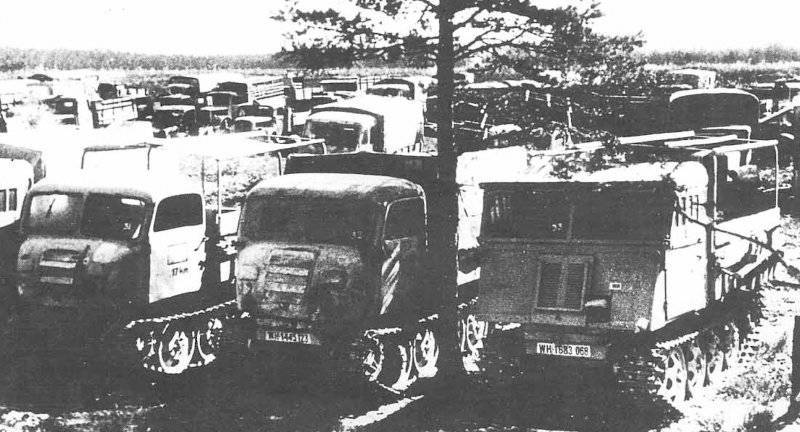
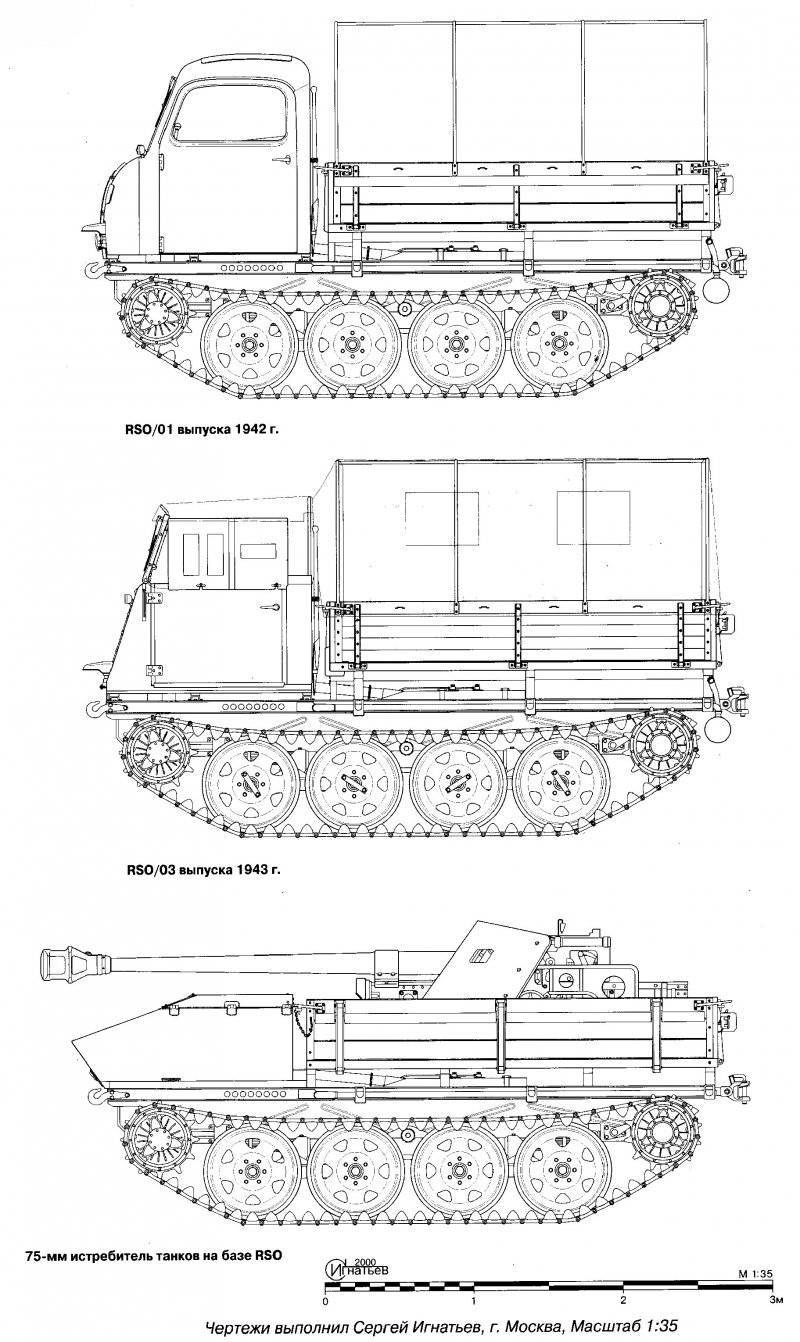
In the summer of 1942, the Klöckner-Humboldt-Deutz company (Kloeckner-Humboldt-Deutz), connected to the serial production, offered its version of this tractor, which had a place for a successful four-cylinder diesel engine (KHD F4L 514), which provided the same, more had the same number of engines. in severe operating conditions. In the autumn of 1942, it was decided to further increase the production of tracked tractors, which by January 1943 should have been 2000 machines. For this, the design has undergone another wave of simplifications, which have found a place in the RSO / 02 products (and in 1943 and RSO / 03). The main external difference of this modification was the ersatz-cabin of a simplified form made of wood and sheet steel. However, the plan for 2000 machines could not be completed by the end of the year, and the 1943 tractor was released until January 1452.
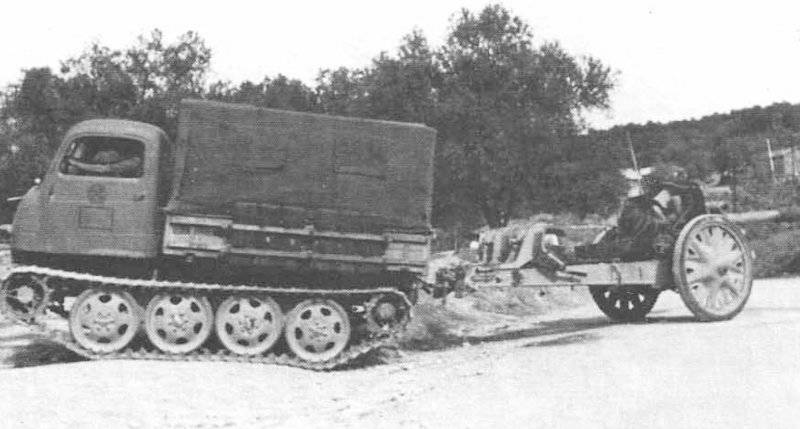
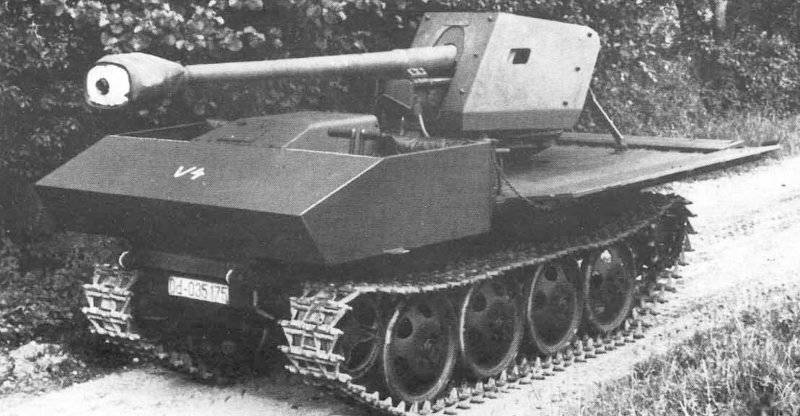
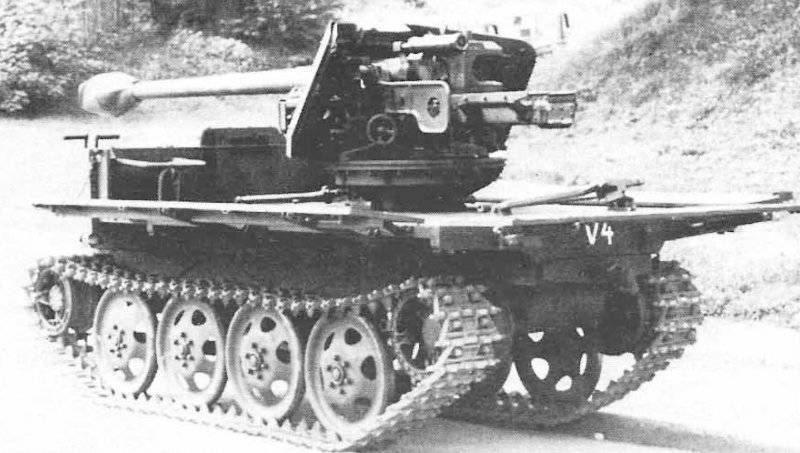
In the spring of the summer of 1943, the question of using the RSO chassis as a carrier of various weapon systems, mainly anti-tank and anti-aircraft, was considered. But it was not so easy because of the small size of the chassis and its cargo platform. In August, the 1943 was tested on a tank destroyer, carrying an X-NUMX anti-tank Cannon on the 75-2 cargo platform. At the same time to accommodate the long barrel of the gun in the car, the covered cabin had to be abandoned, although the remaining lower part of it was protected by splinter armor.
Despite the mass of "childhood diseases", this ACS, being shown to Hitler, made a very favorable impression on him, since it theoretically combined a high power of a shot, good maneuverability and low cost. Immediately followed by an order for the manufacture of 50 machines for carrying out military tests and an order to prepare in 1944 for the mass production of 400 such SAUs monthly.
Back in the fall, 1943 in the back of an unarmored tractor in the army began to openly install an 20-mm anti-aircraft gun FlaK 38. True, in the zenith version this tractor was unsuccessful, since its center of gravity was located quite high and did not gain widespread experience. In total, 12 (according to other sources - 20) machines that took part in the battles of the final period of the Second World War were redone.
In January, 1944 passed the 75-mm Cannon 40 / 4 RSO gun tests and approved the following production schedule for March - 50, April - 100, May - 150, June - 200, July - 400. But most likely this plan was not fulfilled, since 75-mm anti-tank guns were required, among other things, for organizing the mass production of the light fighter of the Hetzer tanks, which had significantly greater combat capabilities and a relatively low price.
In 1943-44 a reduced version of the RSO for mountain parts was released and tested, and work was carried out to create a floating version of the tractor, which was built in several prototypes that were tested in various conditions, but did not go into series.
But the most interesting thing is that, having actually finished life on the fronts of the Second World War, the RSO, like the mythical bird Phoenix, was revived ... in the national economy of the USSR. History This revival is no less interesting than that in Nazi Germany. Back in 1943, trophy RSOs were studied by representatives of the artillery department and received very high marks. The following advantages of the tractor were highlighted:
- unpretentiousness;
- high permeability;
- the presence of successful broad snowmobile plates;
- ease of maintenance;
- not critical to the type of fuel (gasoline of higher and lower grades).
By order of the WGC NKTP artillery directorate, under the leadership of V. Bera, he conducted a draft design of a similar product with a pull of about 3,5 tons under the ZIS-5М engine (75-77 hp) for use in divisional and corps artillery. However, this product was late, as the tractor with similar characteristics was already produced in the USSR serially.
It was Yaroslavl I-12 / I-13 and therefore the order for the RSO replica for the needs of the artillery control in 1944 was canceled.
However, 1946 returned to the tractor when specialists from the Leningrad Forestry Academy arrived at the General Machine Building Bureau under the direction of B.Kaspersky in Leningrad with technical requirements for developing a special tractor for logging, which was urgently needed to restore the destroyed industry and build housing.
An analysis of the available chassis for the tractor showed that the RSO chassis, which has a large ground clearance and a simple design, had the greatest suitability for hauling, and from the design bureau they requested a draft design of an artillery tractor developed by 1944 in OGK NKTP.
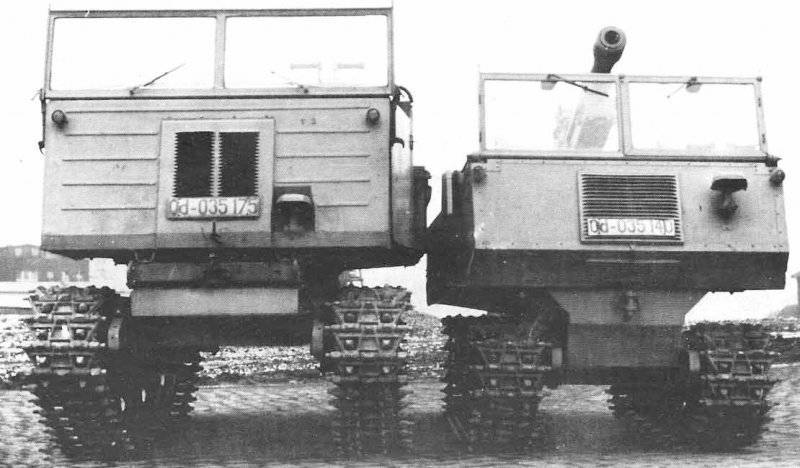
Soon, the work on the tractor was transferred to J. Kotin, who returned from Chelyabinsk as chief designer of the Leningrad Kirov Plant. He headed the work on it in KB N. Kurin, appointed by the head of the "tractor bureau" of OGK LKZ. In 1947, the tractor was registered in terms of pilot work of the LKZ design bureau under the index CT-12 and 5 in March 1947. of the year.
In the summer of 1947, the task for the tractor was corrected. In particular, it was prescribed to supply all “KT tractors” with gas generator sets of the ZIS-21 type. It was very important, as it was difficult to supply the cutting areas with gasoline or diesel fuel at that time, and wooden chumps were not a deficit here. After a long debate, it was decided to supplement the tractor with a winch to facilitate the collection of cut off whips in the package.
In November, the 1947 was the first five experimental KT-12 with the power plant of the gas generator car ZIS-21, power 45 hp at 2300 rpm, were ready and after the November 7 parade, entered the Volosovsky forestry enterprise of the Leningrad region. But what was good at the front did not immediately find its place in peaceful life. Almost a year passed before the modified KT-12 passed all the tests and was found suitable for operation as a tractor for logging and hauling.
1 January 1949. At the Kirov factory began serial production of tractors type CT-12, and in 1950, the design bureau also developed its version with a diesel engine with power 50 hp, but at the time it did not diesel motors.
At the beginning of 1951, the production of the KT-12 skidder was transferred to the Minsk Tractor Works, where it was produced for four years with a gas generator and one year with a diesel engine.
In 1956, the skidder was transferred to the recreated Onega Tractor Works in Petrozavodsk, where he went into production under the symbol TDT-40.
And still in the woods in the expanses of Russia, from its western borders to the Far East, you can find a slightly unusual appearance of the TDT-55М “Onezhets” skidder, which retained many of the features of the unsophisticated RSO, which was to conquer (and in its own way subdued ) the entire Soviet Union until the very last day of its existence. More precisely - the forests of the Soviet Union. However, he conquered his hard work and dependability in our conditions.
TTX RSO | ||
A type | RSO / 01 | RSO / 03 |
Manufacturer | Steyr-Dalmler-Pucri AG | Kloekner-Humboldt-Dcutz AG |
Issue | 1942-1944 | 1944-1945 |
Engine | Sleyr 1500 | KHD F4L514 |
A type | 8 cyl. carb | 4-diesel |
Cylinder volume | 3517 | 5322 |
Revolutions | 2500 / 300С | 2250 |
Power, hp | 70/85 | 70 |
Ignition procedure | 1-3-6-2-7-8-4-5 | 1-3-4-2 |
Compression ratio | 15,75:1 | 13,1:1 |
Driving speed, mate km / h | 17,2 | 18.3 |
Reserve code, km (highway / revenge) | 250/150 | ? |
Dimensions | 4425 * 1090x2530 | 4425x1990x2530 |
Clearance | 550 | 550 |
Track width, mm | 340 340 | |
Expanders, mm | 660 | - |
Curb weight, kg | 5200 | 5500 |
Load capacity, kg | 1500 | 1500 |
Trailer weight, kg | 2000 2000 | |
Landing bridge in the cabin | 2 | 2 |
Fuel consumption | approx.90 l / 100 km | 4-9 n / us |
Volume of fuel, l | 180 | 140 |
Overcoming obstacles | ||
Incline | 30° | 30° |
Ford, mm | 670 | 850 |
Moat mm | 1700 | 1700 |










Information