Iron fist of the Red Army. Tank park on the eve of the war
Major-General LG Ivashov ("VIZH" №11'89) calls the number of 23457 tanks, of which 30% is combat ready. The publication of the General Staff "The neck of the secrecy was lifted ..." (M., 1993) determines their number in 22600 units (heavy - 500, medium - 900, light - 21200). These data are doubtful in some respects: first, for many years the number of KB tanks at the beginning of the war was 636, and there were still heavy T-35 tanks that were released around 60. In total, the number of heavy tanks results in significantly more 500. Secondly, 1225 T-34 (also a well-established figure) plus a few hundred T-28 (in 3, etc., 38, in 8, 68, in 10, 61, etc.) are not equal 900. The percentage of serviceable tanks is defined in 27. But in general, we can say that in this book the security classification has not been removed.
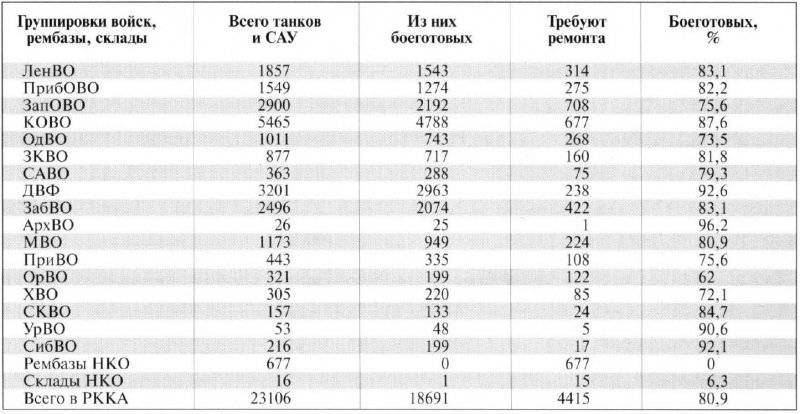
The greatest confidence is caused by the "Summary list of the quantitative and qualitative composition of tanks and self-propelled guns located in military districts, at rembazas and warehouses of NGOs as of 1 June 1941 g." N.P.Zolotova and S.I.Isaeva ("VIZH" №1 G93). According to her, the Red Army was armed with 23106 tanks and SPGs. Of these, combat-ready - 18691 or 80,9%. But this number is not final - from 31 May to 21 June 1941, 206 new tanks were shipped from the factories (KB - 41, T-34 - 138, T-40-27). Here, tanks belonging to 1 and 2 categories are classified as combat vehicles, according to the Manual on Accounting and Reporting in the Red Army:
1-I category is a new, not being in operation, meeting the requirements of technical conditions and completely usable property for its intended purpose;
2-I category - the former (being) in operation, it is completely serviceable and usable for its intended purpose. This also includes property that requires troop repair (routine repairs carried out by the forces of the unit itself).
The authors stipulate that there is no reliable information revealing the state of the Red Army tank park on June 22. But of all the data encountered, these appear to be the most plausible, although they contradict many well-established indicators, especially the quality status of Soviet tanks (agree that the difference between 27% good and 80,9% is quite large).
The total number of tanks here included machines of mechanized corps, tank regiments of cavalry divisions, tank battalions of airborne corps and rifle divisions. Evaluating the number of cars in the western direction, it should be borne in mind that the tank forces of KOVO, PribOVO, OdVO, LenVO and ZapVO with the beginning of the war were replenished with equipment transferred from rear districts.
Table No. 4. Quantitative and qualitative composition of the Red Army Tank Park to 1 June 1941
And how did the German command assess the state of the ABTA of the Red Army? Before the war, the main command of the Wehrmacht determined the number of tank divisions in 7, plus 38 tank (mechanized) brigades. The inaccuracy of this information was caused by the fact that the formation of the mechanized corps continued, and the regular material part was missing. Already after the start of the war, German Army Chief of the General Staff of the Ground Forces G. Halder made the following entry in his service diary: “The number of tanks available to the enemy is assumed to be 15000 vehicles. This corresponds to 35 tank divisions. Of these, 22 was detected on the front. the enemy was greater than expected "(25.07.1941). On the whole, the Germans' ideas about the number of tank forces opposing them in the western districts were quite reliable, and it remains to be surprised how they risked starting a war by putting their 3329 tanks, most of them light, against this armada.
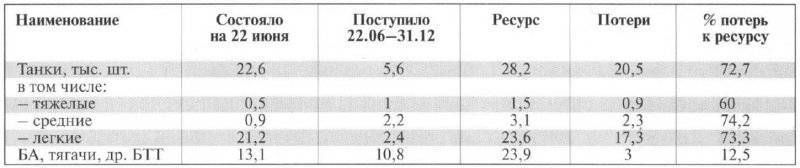
Almost all of our huge tank fleet (see tab. 5) was lost in the battles of summer-autumn 1941. The total losses of Soviet tanks also remain in question. Figures from various sources, including reports of parts and formations submitted in the confusion of retreat, vary considerably, so here are the official data of the General Staff, published in 1993 g .:
Table No. 5. Loss of armored and mechanized troops in 1941
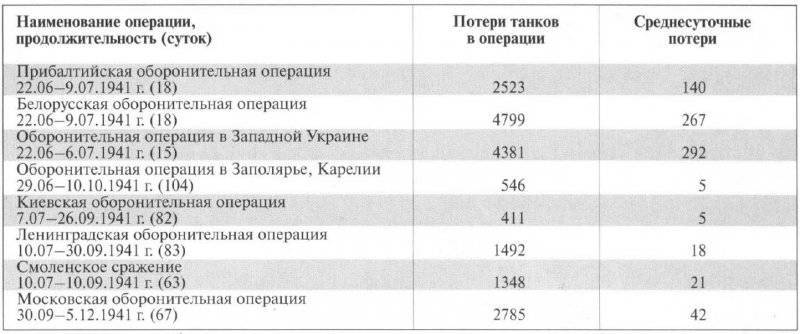
Table No. 6. Loss of armored vehicles in 1941 operations
A large amount of equipment was simply abandoned during the withdrawal of Soviet troops. So, only in a warehouse in Dubno, German troops seized 215 tanks, 50 anti-tank guns and a lot of other property. In the 10 Tank Division of the 15, the MK was abandoned during the retreat of 140 tanks (for comparison, combat losses amounted to 110 vehicles). In the 8 tank division of the 4, the crews destroyed 107 tanks, 10 went missing, 6 got stuck in the swamp and was abandoned. Knowing all this, it is already possible not to be surprised at the average daily loss of the SWF in an 292 tank. There was no such level of losses even in the largest tank battles of the war, for example, in the Battle of Kursk, this figure ranged from 68 (in the Oryol offensive operation) to 89 (in the Belgorod-Kharkiv offensive operation).










Information