Space debris
The size of the garbage fragments that are in Earth orbit varies widely: from microparticles to the size of a school bus. The same can be said for the mass of this garbage. Large fragments can weigh up to 6 tons, while the weight of small particles is only a few grams. All these objects move in space in different orbits and at different speeds: from 10 thousand km / h to 25 thousand km / h. Moreover, in the event of collision of such parts of space debris with each other or with any satellite moving in opposite directions, their speed can reach 50 thousand km / h.
According to Alexander Bagrov, a senior researcher at the Research Institute of Astronomy of the Russian Academy of Sciences, today there is a paradoxical situation. The more vehicles mankind launches into space, the less suitable it becomes for use. Spacecraft fail every year with an enviable regularity, the result of this is that the amount of garbage on Earth’s orbit increases annually by 4%. Currently, the Earth’s orbit rotates to 150 thousands of different objects, ranging in size from 1 to 10, see, but particles that are smaller than 1 and see in diameter are just millions. At the same time, if in low orbits up to 400 km, space debris is decelerated by the upper layers of the planet’s atmosphere and falls to the Earth after a certain time, then in geostationary orbits it can be for an infinitely long amount of time.
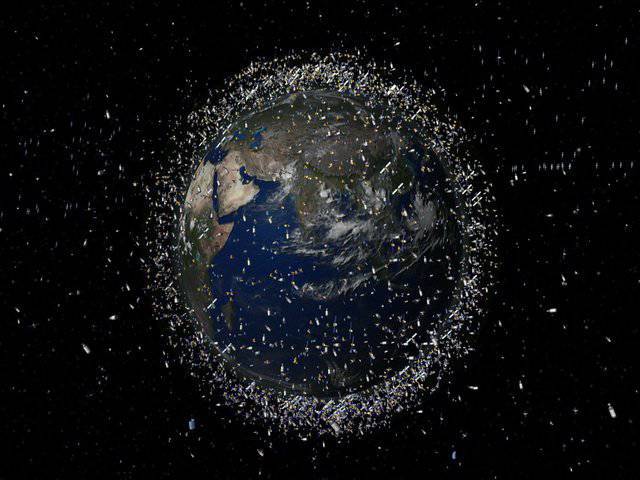

Their contribution to the cause of increasing space debris is made by accelerating rockets, with the help of which satellites are launched into Earth orbit. In their tanks, there remains about 5-10% fuel, which is very volatile and easily turns into steam, which often leads to quite powerful explosions. After a number of years of being in space, the missile stages that have served their time explode into pieces, scattering a kind of “shrapnel” around them from small fragments. Over the past few years, 182-like explosions have been noted in near-Earth space. Thus, only one explosion of the Indian rocket stage caused the formation of large debris at once by 300, as well as countless smaller, but no less dangerous space objects. Today the world already has the first victims of space debris.
So in July, 1996, at an altitude of about 660 km. the French satellite collided with a fragment of the 3-th stage of the French launch vehicle Arian, which was launched into space much earlier. The relative speed at the time of the collision was about 15 km / s or 50 thousand km / h. Needless to say, the French specialists, who missed the approach of their own large object, after this story, bit their elbows for a long time. This incident did not turn into a major international scandal, since both objects colliding in space had French origin.
That is why the problem with space debris in our days does not need additional spreading. You just have to keep in mind the fact that a substantial part of the Earth's orbit will not be the safest place for spacecraft at the existing rates very soon. Understanding this, researcher Jonathan Missel, who is a member of Texas A & M University, believes that all existing methods for collecting space debris have at least one of two common diseases. They either assume the holding of missions “One piece of space debris - one garbage man” (and this is very expensive), or they suggest the creation of technologies that will take more than a decade to finish. Meanwhile, the number of victims of space junk is only growing.

Understanding this, Jonathan Missel suggests upgrading the concept of “One piece of space debris - one scavenger” to reusable use. A system called TAMU Space Sweeper with a Sling-Sat satellite (satellite sling), developed by him and his colleagues, is equipped with special customizable “hands”. Such a satellite, after its approach to space debris, captures it with a special manipulator. At the same time, due to the different motion vectors, Sling-Sat begins to twist, but thanks to the adjustable tilt and length of the arms, this maneuver is fully controllable, which allows rotating like a soccer ball to intelligently change its own trajectory, sending the satellite through the opposite direction. space debris.
At that moment, when the satellite is on the trajectory of movement to the second space object, the first element of space debris is released by it during rotation. And it will happen at such an angle that a sample of space debris is guaranteed to crash into the atmosphere of our planet, burnt in it. Having reached the second space debris object, this satellite will repeat the operation and will do so every time, while receiving additional charge of kinetic energy from space debris and at the same time sending it back to Earth to the planet that originated it.
It is worth noting that this concept is somewhat reminiscent of the method of ancient Greek long jumpers, who did this with a drop of dumbbells (for additional acceleration). However, in this particular case, the objects of space debris will have to be caught and thrown on the fly, whether TAMU Space Sweeper can cope with this is an open question.
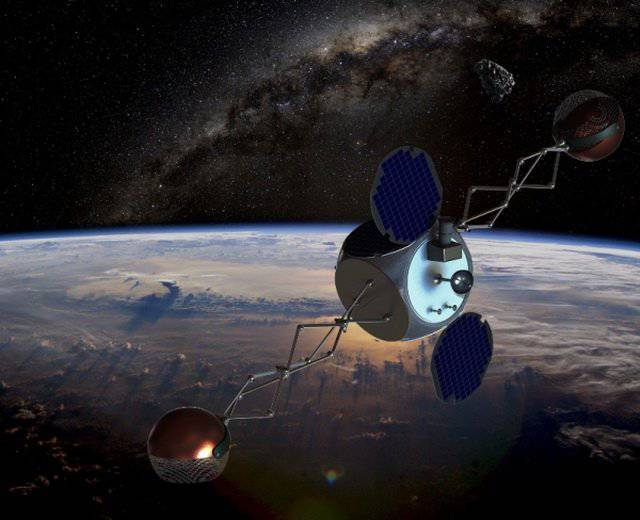
Conducted computer simulation shows that the proposed scheme has a high theoretical fuel efficiency. And this is understandable: in the case of “satellite sling”, energy is supposed to be taken from the pieces of satellites and rockets that were already overclocked to the 1 space velocity for a long time and not from the fuel that would have been delivered to our garbage collector from Earth.
Of course, the concept presented by Missel has quite narrow places. It should be noted that none of the pieces of space debris, of course, is not adapted for the manipulator trap and, most importantly, for high accelerations during intensive rotation. In the event that a piece is too large and heavy, its energy during rotation may be sufficient to destroy itself, as well as the manipulator. At the same time, the creation of a large number of others instead of a single space debris object is unlikely to improve the situation in space in low near-earth orbits. In this case, of course, the idea seems interesting, and in the case of an adequate technical implementation - effective.
Information sources:
-http: //science.compulenta.ru/739126
-http: //www.popmech.ru/article/479-kosmicheskiy-musor
-http: //dev.actualcomment.ru/idea/996
-http: //cometasite.ru/kosmicheskiy_musor
Information