Czech super cannons. How did the Škoda company arm both Germans and Russians

In the summer of 1937, a commission of prominent Soviet gunners visited the Skoda factory in Czechoslovakia. There she was presented with projects 210-mm gun and 305-mm howitzers. The barrel of the gun was lined, and howitzers - bonded. The gates of both systems are wedge horizontal, loading is separate-sleeve.
I will not restrain myself from the author's remark - on the report of the commission, some “smart guy” from Arthurvolvement stressed “separate-cartridge case” and boldly wrote: “This is a minus - you need a cap”. At the end of 1930's "Caps" began another campaign against the separate-cartridge loading.
As a result, the Soviet side proposed a number of changes to Skoda. According to the results of negotiations, the company finalized the project. Barrels of guns and howitzers got free liners. The wedge valves were changed to piston ones, the loading became cap type.
According to the X / NUMX D / 7782 contract of April 6 entered into by the People's Commissariat of Foreign Trade with Skoda, the latter undertook to produce for the USSR a 1938-mm cannon and an 210-mm howitzer with a set of ammunition and accessories for the USSR using one prototype. The date of delivery of the prototypes was set 305 December 1 g. In addition to the prototypes had to be transferred sets of working drawings and other documentation for the manufacture of these artillery systems. The total cost of the order was $ 1939 million (about 2,37 million crowns).

The deliveries of prototype instruments and technical documentation were not affected by the capture of Czechoslovakia by the Germans. The firm Skoda regularly fulfilled all clauses of the agreement with the USSR.
Skoda presented for testing the swinging parts of the 210-mm gun and 305-mm howitzers instead of June (as planned) in October 1939 of the city. The tests were carried out in Slovakia in the presence of the Soviet selection committee. Factory tests of the 210-mm guns were completed on November 20 1939, and 305-mm howitzers - December 22 1939.
The acceptance tests (delivery of the USSR) of both systems took place from April 22 to May 10 on 1940 at the test site in Gylbok in the territory occupied by the Germans.
The Skoda report says that the 210-mm gun is stable when firing a small charge at angles from 0 to + 50 degrees, and with a full charge from + 16 to + 50 degrees. It is worth noting that the instability of the gun at small elevation angles was associated not with the design of the gun itself, but with the weakness of the soil on which the foundation stood. Thus, the Br-17 could be used in the coastal defense for direct fire, but for this it would be necessary to concrete the base of the gun.
At the end of the tests, in accordance with the terms of the contract, the gun and the howitzer in its complete form, together with the ammunition, were accepted by the commission and sent to the USSR for further tests.
In October, 1940 from the USA produced pneumatic tires for Skoda wheels in the number of 54 units (48 complete and 6 spare). Temporarily, before the domestic industry mastered the 12x24, 210-mm and 305-mm tires, it was decided to complete the wheels with 12-X20 wheels.

A prototype 210-mm cannon Br-17, manufactured by factory No. 221, was presented to the customer 26 August 1940. After factory testing, this September 9 sample arrived at the Artillery Research Experimental Test Site (ANIOP) for conducting field testing. The shooting took place from September 21 to December 11 1940. In total, 110 shots were fired. Initially, there was a mechanical rammer on the loading farm. But it turned out to be inconvenient and was replaced by a hand-held “dosylnik” from collapsible rods of the barnik, and the head of the “towing” was made in ANIOP workshops. "Dunker" usually operated 6-7 people.
The first 305-mm howitzer Br-18, made at the plant number 221, arrived at the ANIOP 21 September 1940 g. Shooting was conducted from October 2 to November 27 1940. Total 108 shots were made. During the shooting, three liners were tested, of which two were with normal cutting (one from Plant No. XXUMX, the other from Skoda) and one with deep cutting.
The management was in a hurry and announced that the tests of the experimental samples of the Br-17 were not field tests, but field test forces, and according to the results their Br-17 cannon and a concrete-hammering shot were recommended for use. The high-explosive projectile failed the test.
As is known, based on Czech guns at the Barricades factory in Stalingrad in the 1940-1941. Nine 210-mm Br-17 cannons and three 305-mm howitzers Br-18 were manufactured.
In total, there were nine 210-mm Br-17 guns in the Red Army. They were put into combat readiness only in 1944. Then the firing tables were published for them for the first time and thousands of shells were made for 4,2.
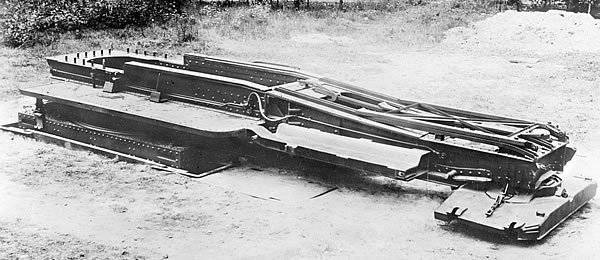
In December, 1944 based on four separate battalions of 152-mm cannon Br-2 and four separate batteries of 210-mm cannon Br-17, three separate special power regiments were formed (18-th Guards, 1-th and 2-th). They included three Br-2 two-gun batteries and one 210-mm cannon two-gun battery. By the end of 1944, these three regiments were descending to the front, and the formation of the fourth (No. 20) began only in 1945, and it did not hit the front.
In 1945, the 1 th gun regiment of special power was part of the 8 th Guards Army of the 1 Belorussian Front. During the battle for the Seelow Heights and in the battle for Berlin, 930 210-mm shells manufactured in 1944 were spent.
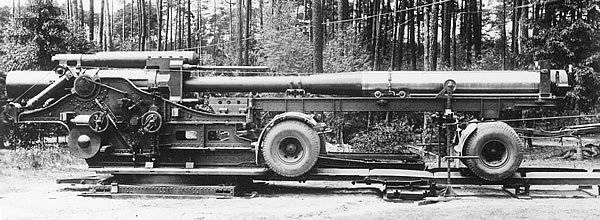
305-mm howitzers arr. 1939 G. (Br-18) was made only three pieces. They went on to form an 233 separate artillery division of special power, located at the end of the war in the Moscow Military District. Apparently, howitzers were incapacitated.
Well, Skoda firmly supplied heavy-duty Wehrmacht 210-cm caliber K.21, 52 cm K.21 / 39 during the war. Curiously, in the second 40 cm. K.21 / 39 retrofit, the barrel was extended and the muzzle brake was set.

In 1944, for 21-cm of the Czech guns K.52 “converted”, heavy 232-kilogram fired projectiles were created. For them, Skoda manufactured smooth trunks.
In 1944-1947 based on the experience of the war, Skoda created a unique X-NUMX-mm V-210 cannon, equipped with a powerful muzzle brake. Naturally, the company offered its products to the Soviet Union.
The prototype was thoroughly tested in the USSR. For a time, several samples were in service in the Soviet army. But the document on its adoption by the author was not found. It is possible that the V-3 were listed "on supply". In 1950, the V-3 service manual was published in Russian. By the way, in the domestic documentation the gun was called both V-3 and B-3.

In addition, the Czechs offered the USSR the X-NUMX-mm howitzer V-305, created on the carriage of the V-4 gun. The 3-mm howitzer barrel also had a muzzle brake.
However, neither V-3 nor V-4 were launched in the USSR. Originally it was associated with the work of Vasily Grabin on a large duplex - 210-mm C-72 cannon and 305-mm C-73 howitzer. Well, by 1960, because of the voluntarism of Khrushchev, who believed that the artillery of a large and special power of the Soviet army was not needed, work was also stopped on the Grabin guns and on the modernization of the V-3.
The barrel of the V-3 consisted of a free pipe, a casing, a breech and a muzzle brake. The breech is screwed onto the casing. The casing is mounted on the pipe with a gap. Muzzle brake dvukhkamorny, on both sides of it there are two windows. The slope is constant.
Push-pull piston shutter with Bange-type plate obturator. Manual action only.
A distinctive feature of the swinging part was the combination of a cylindrical cradle of the overwhelming type with rolling cylinders of recoil devices. Two gear sectors of the mechanism of vertical guidance are attached to the cradle. The horizontal guidance mechanism had two speeds. The mechanism for the rapid drive of the trunk in the loading position was not. The recoil brake is hydraulic, located at the bottom of the rolling away part, the nakatnik is hydropneumatic, located at the top of the rolling part. Rollback length is variable. Balancing mechanism of hydropneumatic type with two symmetrical columns.

The base consisted of a fixed and rotating part. In the combat position, the base fell into the pit 600 depth mm. Inside the base was placed a ball epaulet, which allowed for the possibility of turning the gun by 360 degrees. The turntable, which with its upper plane connected to the machine tool, rested on the ball tackle of the base. On both sides of the turntable there was a platform for calculation.
The back of the turntable (trunk support) is removable with a support plate at the end. On top of the trunk support attached iron rails, which was rolled on a trolley for loading.
The turning mechanism had two speeds of guidance, the drive was manual — the system had no electric motors at all. With horizontal hovering, it was necessary to first lift the base plate and lower it again before firing.
Charging devices included a rail track located on the turntable of the base and a trolley for loading. A projectile and one half charge were placed on the trolley by hand. When firing a full charge, the second half charge was brought to the gun with a single calculation number. Five numbers of calculation rolled a cart with a projectile to the gun on the track. On the final section of the path, the slope of the trolley corresponded to the angle of loading of the implement, that is, was 7 degrees. At the last moment of rolling the cart, its support entered into the gate of the barrel. To speed up the loading, two trolleys were attached to the gun. 6-7 people were manually sent to the chamber with a piper.
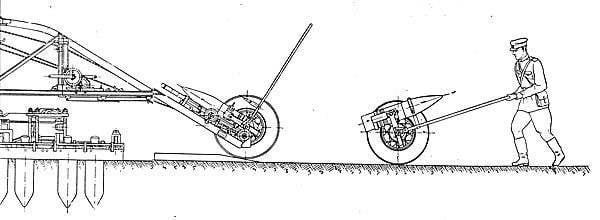
Gun firing rate - 2 shot in 3 minutes. The design of the barrel allowed such a pace for 30 minutes. Next, the rate of fire was necessary to reduce to one shot in 3-5 minutes. When firing a full charge, the barrel survivability was 600 shots. With a charge of No. XXUMX - 2 shots, and with a charge of No. XXUMX - 1300 shots. Shooting without a muzzle brake was allowed only by charge # 1. I note that the Czechs, like the Germans, the charge weight increased with increasing charge number, and the maximum charge was the last charge, and the lowest charge was # XXUMX. In the Red Army it was all the opposite: the most powerful was the full charge, then the charge # 2400, and then with the increase in the number the charge decreased.
The system in the stowed position consisted of three special carts: trunk carriages, machine tool carriages, and base carts. The barrel had a special wagon, and the machine and the base had only wheel travels and made up the hulls themselves. The carriage was attached by the pivot paw of the forward boom to the towing vehicle.
In Czechoslovakia, a three-axle all-terrain vehicle served as a full-time tractor. In the USSR, tracked tractor Voroshilov or AT-T were used for transportation.
Each wagon was transported by a separate tractor with the necessary devices to transfer the system from the traveling position to the combat position, with the tool and accessories for disassembling and assembling individual system groups and spare parts. Devices, tools and accessories could be transported on separate vehicles.
The carriage casing is equipped with pneumatic tires. The carts had independent suspension on leaf springs.
In the USSR, a new shot with a high-explosive projectile was designed for the V-3. The work on it was discontinued 15 February 1961
The latest salvos of Br-17
The final chord in the fate of Czech cannons in the USSR was quite unexpected. Experienced 210-mm Czechoslovak cannon from the 1960-s. kept in the backyard of the Artillery Museum in Leningrad. He was remembered during the shooting of the movie “Moonzund” based on the novel of the same name by Valentin Pikul. In 1987, a cannon was installed on an abandoned fort No.3 in Liepaja (Libau), where it “played the role” of an 305 / 52-mm open-shore battery installation at Cape Tserel. On the set, the gun even fired with reduced charges. The maid was taken entirely from the Rzhev polygon. After the shooting, the gun was sent back to the Art Museum, but this time it was installed in an open exhibition in front of the museum building. Now, in addition to St. Petersburg, this is far from the most common weapon in Moscow in the open area of the Central Museum of the Armed Forces and in Verkhnyaya Pyshma in the Museum of Military Equipment, created by the Ural Mining and Metallurgical Company.


Information