We will break through: Russian supercomputers

According to open data, the most powerful supercomputer in Russia is Yandex's Chervonenkis. Source: wikiwand.com
Strategic technologies
States claiming technological sovereignty must be able to build supercomputers on their own. Or for the first time at least buy from others. Efficient and extremely expensive computers are the engines of progress in the country and in the world. Literally. Among the most important destinations of "super" is a complex three-dimensional modeling of various processes. For example, in the aircraft industry, computer systems can significantly speed up the aerodynamic calculations of the fuselage and other critical systems.
Supercomputers even got into a number of government programs. For example, in 2017, the government issued an instruction “On the development of high-tech and promising military equipment products only using modern computer design technologies, electronic mathematical modeling.” The Logos software package was written directly for supercomputers. As the developers write, one of the modules of the Logos-TMP software allows "calculating the flow of viscous compressible and incompressible gas, taking into account turbulence using all modern approaches."
The second module - Logos-Strength "models the processes of static and dynamic elastic-plastic deformation, gas dynamics, destruction, contact interaction, thermal conductivity, kinematics, analysis of frequencies and vibration modes." The software package, in particular, was widely used for calculations on the topic of the fifth generation Su-57 fighter.
From open sources it is known that they worked on solving the problems of a safe separation aviation means of destruction from the aircraft, analyzed the resource of new structural materials, evaluated the gas-dynamic effect of the cannon installation and calculated the spread of the fire-extinguishing mixture in the power plant compartment. Virtual simulation makes it possible to significantly simplify further full-scale tests, without which, of course, not a single design work can do.
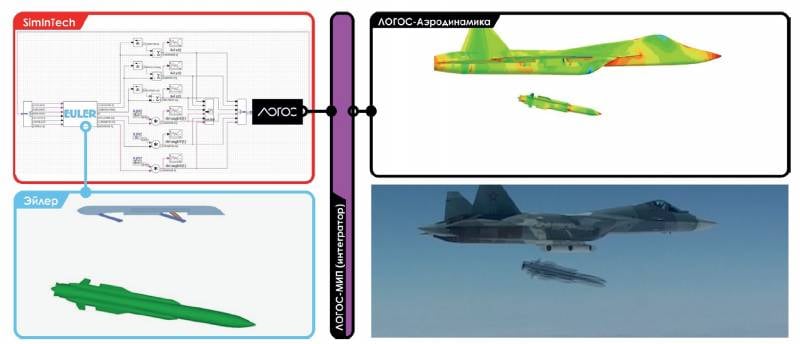
An example of providing high-precision three-dimensional models with initial and boundary conditions from functional models. Source: A. V. Kornev "Application of domestic supercomputer technologies for the creation of advanced aircraft models"
To understand what data arrays a supercomputer has to calculate, let's give an example for a machine with a capacity of 1 Pflop / s.
For reference, 1 petaflops means that a computer can perform one quadrillion floating point operations per second. Approximately 50 thousand ordinary personal computers are capable of this.
The petaflops supercomputer is trusted to calculate the aerodynamic characteristics of aircraft in various flight modes. For example, fighter models at speeds before and after overcoming the Mach number. A supercomputer with a performance of 1 Pflop / s creates a model in each mode for at least 12 months! At the same time, a tenfold increase in supercomputer performance does not give a corresponding acceleration - the duration of the calculation is reduced to 2–3 months.
The use of high-precision models of combustion and fire extinguishing processes on board an aircraft is even more resource-intensive, by one or two orders of magnitude. From the foregoing, it is clear how critical it is for modern Russia to have advanced supercomputers. Especially taking into account the literally revolutionary breakthrough that the civil aircraft industry should make in the next seven to eight years. By 2030, almost all the needs of domestic transportation should be covered by domestic aircraft, and these are several hundred aircraft, some of which have not even taken to the skies.
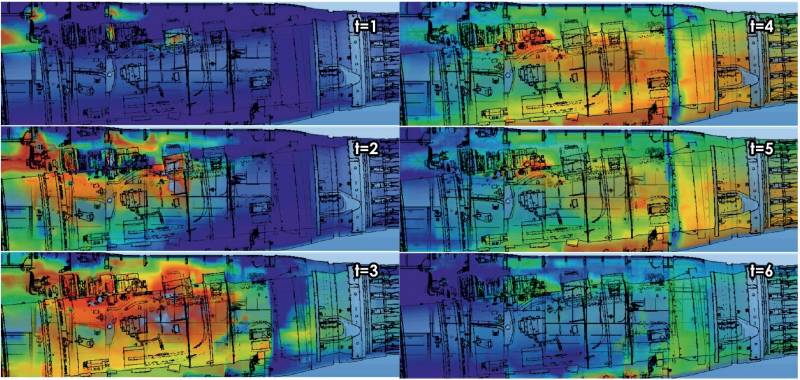
The results of the calculation of the spread of the fire extinguishing mixture in the compartment of the power plant. Source: A. V. Kornev "Application of domestic supercomputer technologies for the creation of advanced aircraft models"
No less powerful "super" is needed in the automotive industry. Especially given the large-scale import substitution program that has yet to be launched. High-performance computers, among other things, are trusted to calculate aerodynamics and simulate virtual crash tests.
In pharmacology, molecular modeling methods are widely used, for example, docking - a description of the interaction of target proteins and low molecular weight molecules of future drugs that block the work of these proteins. The supercomputer sorts through thousands of ready-made molecules and selects the most promising of them.
Further, the experimenters in the laboratories only have to check the solution of the superbrain in full-scale experiments. Giant time and tens of millions of rubles are saved. Similar work is being done at the Research Computing Center of Moscow State University at the 1,7-petaflop Lomonosov. By the way, he was once one of the five hundred most powerful supercomputers in the world.
"Chervonenkis" and others
The last time the top 500 most powerful computers in the world was updated in November last year, and it was marked by the appearance of the first ektaflops device. This is the Frontier machine from the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in the United States. Its exact maximum power is 1 Pflop/s or 102 Eflop/s. This is a thousand times more powerful than the supercomputer mentioned above for calculating the aerodynamic characteristics of an aircraft.
Most likely, Frontier will build similar models for the Su fighters in a matter of days. The peak power of the American product can reach 1,685 Eflop / s. At the same time, it consumes energy like several high-rise buildings on a frosty winter evening - up to 21 kW. Until November 100, the Japanese Fugaku supercomputer with a performance of 2022 Pflop / s was in first place, while it consumed noticeably more energy - almost 442 thousand kW.
There are two trends - an increase in the power of supercomputers with a simultaneous decrease in energy consumption.
Where are Russian cars in the top 500? In 25th place is the "super" from "Yandex" - "Chervonenkis" with a performance of 21,53 Pflop / s, used by the company mainly for the needs of neural networks. The device is named after Alexei Chervonenkis, one of the greatest theorists of machine learning.
Of course, all the filling is imported - NVIDIA A100 GPUs paired with AMD EPYC 7702. At the time of its appearance in 2021, the supercomputer ranked 19th in the world ranking.
Also in the world ranking are two more machines from Yandex - the 16-petaflop Galushkin (44th place) and the 12,8-petaflop Lyapunov (47th in the ranking). The first one is named after Alexander Galushkin, one of the main researchers of neural networks, the second - in honor of Alexei Lyapunov, the author of the works underlying computer science. All machines appeared relatively recently and therefore did not have time to critically become outdated.
Sber also has supercomputers, such as Christofari and Christofari Neo, built in 2019 and 2021, respectively. Neo is 50th in the world rankings, while his older brother is 87th.
How much the construction of such units costs can be judged by the costs of the Lomonosov-2 supercomputer, for which almost 2009 billion rubles were spent by 2. Fugaku mentioned above cost billions of dollars. Supercomputers are expensive but highly sought-after toys.
At the moment, the world leaders, both in terms of power and the number of cars, are China (about 170 cars) and the USA (almost 150), followed by Japan, Germany, France and the Netherlands. Until November last year, the top 500 included the Lomonosov-2 mentioned above with 1,3 Pflop / s, but now it is outside the elite club. But Thunder from MTS with a capacity of 2,26 Pflop / s in November last year stopped the fall at 352nd place.
The rating of the most productive computers in the world is based on a voluntary principle - if the applicant has a desire to stand out, then the parameters of the supercomputer are included in the top 500. A large part of powerful computers passes by, as it is used in the interests of national security.
In Russia, of course, the most famous and most powerful of these is the “super” of the National Defense Control Center. There is not much open information about this machine, but it is claimed that the performance is about 16 Pflop / s. If this is true, then the computer is among the fifty most powerful in the world. The computing potential of the machine on Frunzenskaya Embankment is more than three times higher than the capabilities of a similar supercomputer in the Pentagon.
One of the purposes of the supercomputer of the Russian Ministry of Defense is modeling and forecasting the development of military conflicts. The machine's algorithms are said to have reported a government crisis in Venezuela weeks in advance. One can only guess what predictions the 16-petaflops computer makes about the outcome of the special operation in Ukraine. And what models did she generate before February 24, 2022.
Despite all the seeming positive picture, in the near future Russia will have certain difficulties with the creation of new supercomputers. As can be seen from the material, dependence on foreign components is approaching absolute - in Russia there is no production base for graphics processors, on the basis of which "super" ones are built. That is why last fall the Americans banned the import of Nvidia chips to Russia, and at the same time to China. First of all, products of the A100 and H100 series, on which the entire supercomputer industry is based.
If everything is left as it is, then in five or six years Russia's backlog in computing power from Western countries may become critical. This, of course, will not cause a momentary and total collapse, but it will slow down many design and technological processes. In enemy countries, on the contrary, the development and adoption processes in the series will accelerate.
The NVIDIA A100 graphics accelerator is the basis of most Russian commercial supers. Expectedly fell under Western restrictions. Source: i2hard.ru
Work on import substitution of supercomputer stuffing is certainly underway. Money is allocated for the development of a domestic photolithograph, the main component in the microelectronics production chain. This will theoretically allow the production of graphics chips by 2030.
Of course, not world-class, but quite their own. The fact is that the key parameter of the modern development of "super" is energy efficiency. Recall that the world's most powerful Frontier consumes about 21 kW, and the less powerful Fugaku almost 100 kW. For Russia, honestly, this parameter is not so critical. Moreover, our country is the best in the world for organizing supercomputing.
Firstly, we have very inexpensive electricity, and secondly, a cold climate, which greatly simplifies the cooling of hot supercomputers. Therefore, for some time, it is possible to increase the power of existing machines and build new ones on frankly outdated graphic processors. Such giants will simply take up space and generate more heat.
If we exaggerate completely, then a small power plant will have to be assigned to each computer center. What to do, technological sovereignty has never been cheap.
Information