US increases constellation of GSSAP inspector satellites
The US Space Force continues to strengthen its orbital constellation. On January 21, they launched two new spacecraft of the GSSAP series. They should complement the four already operating satellites of this type and expand the capabilities of such a "constellation". At the same time, the devices have a number of important features that make them a convenient observation tool and attract increased attention.
Two new satellites
Deployment of GSSAP (Geosynchronous Space Situational Awareness Program) spacecraft in orbit began in 2014 with the launch of the first two products. In the fall of the following year, they took up duty. Two more satellites were launched in 2016 and put into operation in 2017. The third launch with the GSSAP-5 and GSSAP-6 vehicles was scheduled for 2020, but then it was postponed indefinitely. The reasons for the transfer were not named.
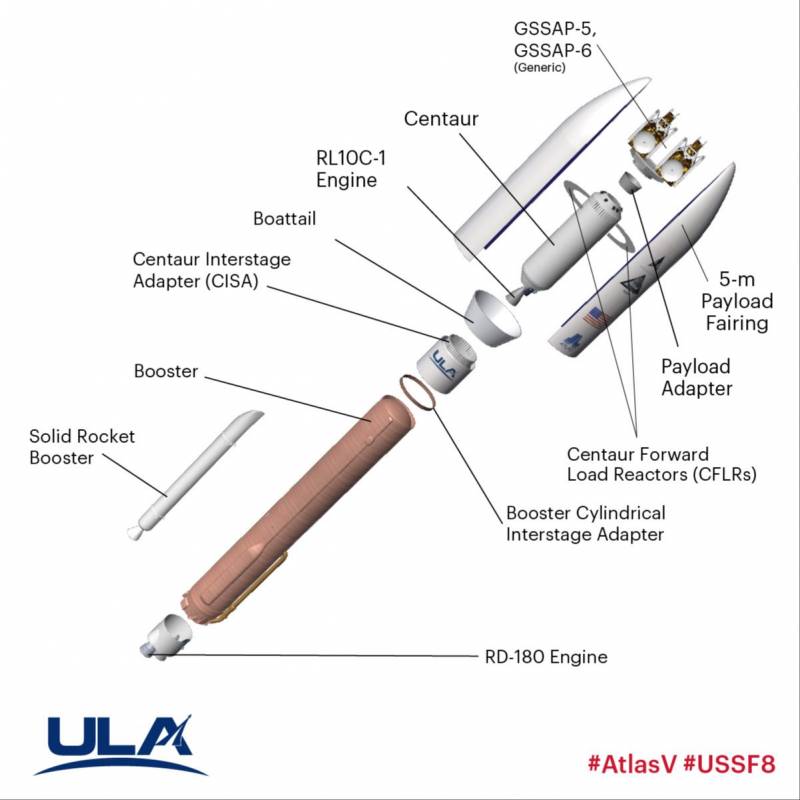
Apparently, there were serious difficulties, because of which the preparations for the launch were significantly delayed, and it was possible to complete it only in recent weeks. Northrop Grumman reportedly delivered both new satellites to the customer, and ULA provided the Atlas V 511 launch vehicle with the Centaur upper stage. The rocket was supposed to launch from the spaceport at Cape Canaveral. The launch was designated United States Space Force-8 (USSF-8).
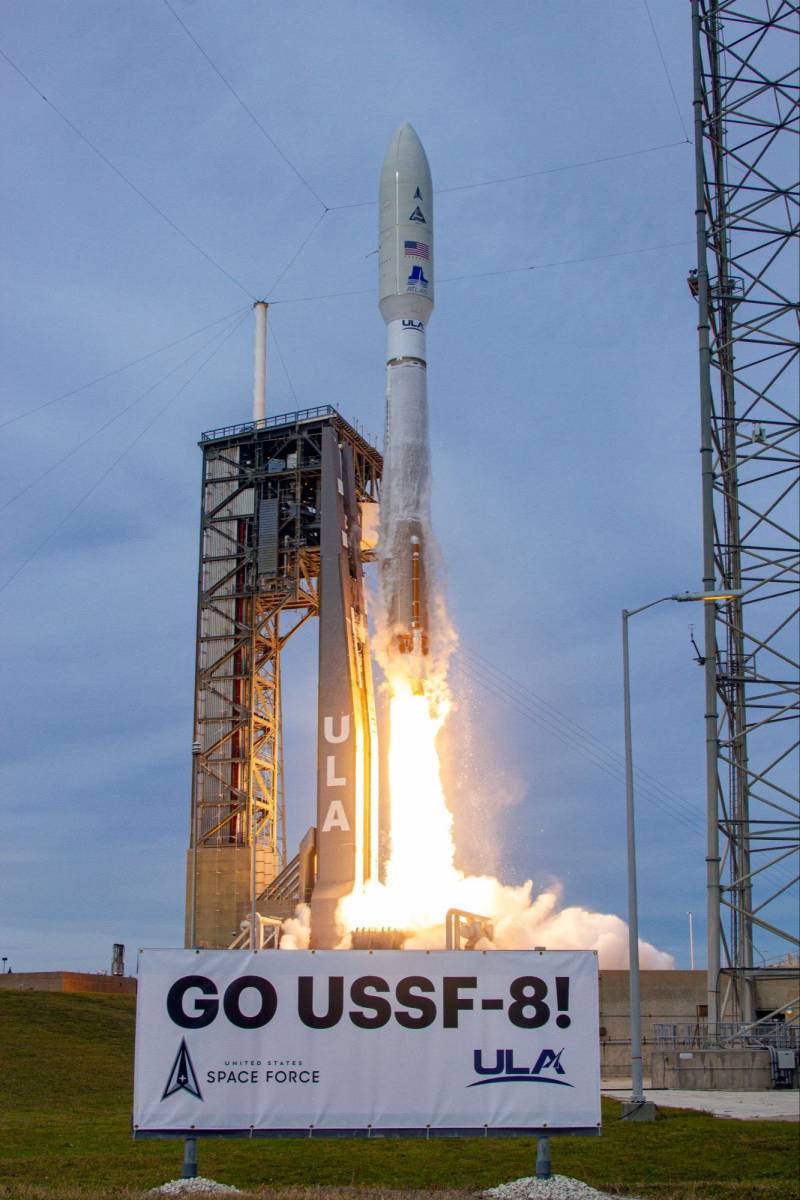
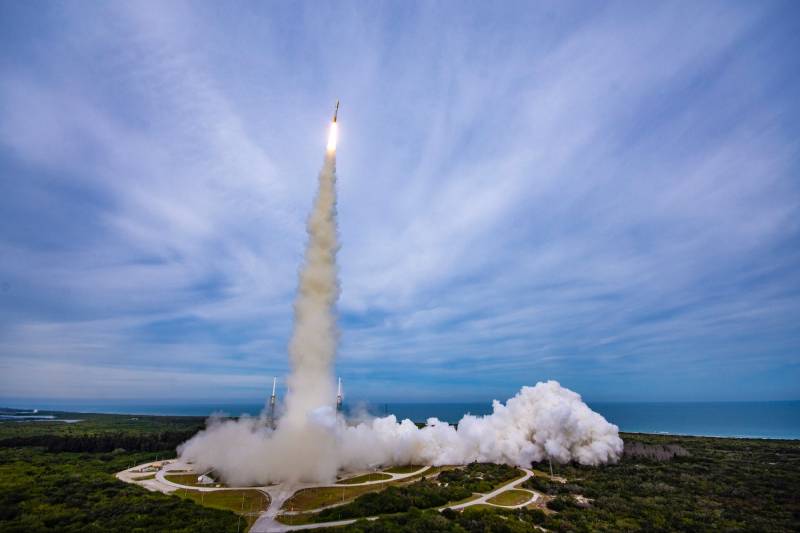
The USSF-8 mission launched on January 21 at 22:00 local time. The rocket rose from the launch pad and went into space. After 13 minutes, the carrier reached low Earth orbit, after which the work of the upper stage began. With the help of several engine starts, the Centaurus with satellites entered the calculated trajectory.
After 6 hours, 35 minutes. and 45 sec. after the launch, the GSSAP-5 spacecraft separated from the upper stage. Almost 10 minutes later, the separation of the second satellite took place. Less than an hour later, ULA announced the successful entry of both products into their calculated geosynchronous orbits. The launch is declared a complete success.
In the coming months, the Space Force will conduct the necessary tests and other activities, as a result of which the two satellites will be ready for operation. It is possible that already this year they will take up combat duty and fully begin to solve the assigned tasks. However, such plans are not specified.
Special Features
According to official data, the GSSAP satellite constellation is designed to monitor the situation in geosynchronous orbits and track various space objects. Information from its devices enters the general control and data processing circuits of the Space Forces. Together with data from other means of observation, they are used to track orbiting objects, incl. potentially dangerous and other tasks.
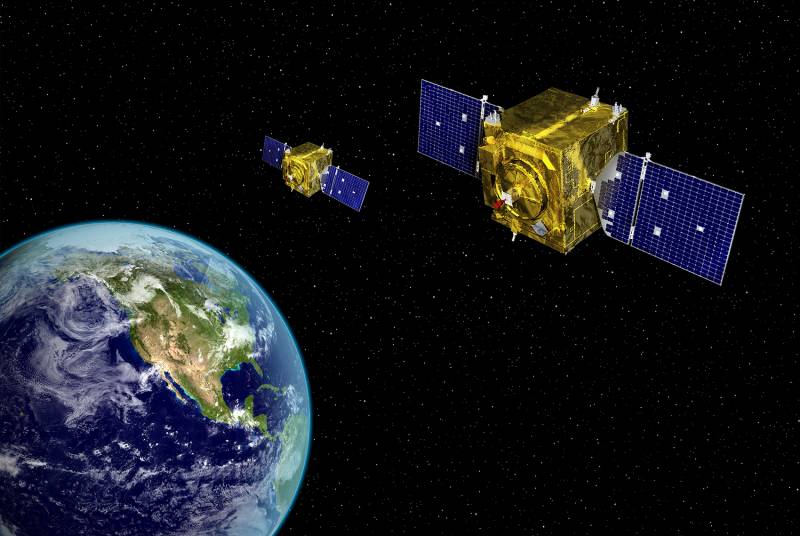
The design features and principles of operation of GSSAP satellites are unknown. The Space Force has released only one official image, making it impossible to establish an accurate picture. According to this drawing, the spacecraft is made in a cubic body, equipped with a pair of solar panels and does not have obvious external features that indicate the characteristics, capabilities and principles of operation. Space Force reports that the GSSAP system is being deployed in geosynchronous orbits with an altitude of approx. 22,3 thousand miles - almost 36 thousand km.
According to unofficial data, the satellites of the GSSAP system are equipped with optical-electronic equipment. They are able to literally observe a large number of space objects, form routes and transmit data to ground complexes for further processing.
GSSAPs are not "space telescopes" but inspector satellites. Space forces report that they are able to actively maneuver and change the trajectory of movement. If necessary, such an inspector can approach a given object and survey from a minimum distance. Perhaps there are other unknown functions.
Shortly before the launch of USSF-8, a spokesman for the Space Force said that the two new satellites would be a more effective means of collecting information. With their help, they will improve the safety of the space constellation in all orbits, up to geosynchronous and geostationary.
From these statements it follows that the GSSAP-5 and GSSAP-6 satellites were made by Northrop Grumman according to a modernized project. However, this information is neither confirmed nor denied. The nature of the renewal of the design and units of the devices is also unknown. Probably, the target equipment responsible for the search and detection of objects fell under the replacement.
Companions at work
The first spacecraft of the GSSAP system began operation in 2014, and since then the number of such equipment in orbit has gradually increased. Four “active” satellites are currently in operation, and two more will come into operation in the near future. Despite the general secrecy, some details of the work of the existing "constellation" have become known in the recent past. It is noteworthy that such data confirm the known capabilities of the satellites.
GSSAP satellites participate in the overall space tracking system, but precise data on their role and contribution, for obvious reasons, are not available. It is likely that they provide the bulk of the data on the situation in geosynchronous orbits.
In August 2016, the US Air Force, which at that time included the Space Force, publicly announced the GSSAP inspection mission for the first time. One of these devices changed its trajectory and approached another American satellite. Having carried out the necessary shooting, he again changed the orbit and moved away from his "target". Apparently, these were tests of one of the key functions of the satellite.
Later it became known that such events became regular, but were already held in "combat mode". According to foreign organizations monitoring outer space, in 2016-18. four available GSSAP satellites approached foreign vehicles eight times. These actions did not have negative consequences, but naturally drew attention to themselves.
In the future, such satellite activity continued, and right now four GSSAP products are monitoring certain objects in orbit or are waiting for an order to perform a task. In the coming months, the grouping will increase by one and a half times. Whether the next construction and launch of new satellites is planned is unknown. Due to the secrecy of the program, news on this account may appear only in a few years, when the next devices will be ready for launch.
Secret Targets
The US Space Force is constantly updating and improving its orbital constellation. With the recent launch of USSF-8, they plan to improve and expand the capabilities of the satellite surveillance system. Moreover, the two new GSSAP satellites, like their predecessors, have special features, and secret capabilities may not be limited to the ability to maneuver and rendezvous.
Obviously, the main objects of observation for GSSAP, old and new, are the spacecraft of a potential adversary - Russia and China. Accordingly, the new American system may pose a danger to our satellite constellation, as well as to other components of the military forces that benefit from its support. Probably, these risks have already received the necessary assessment and were taken into account in planning.






Information