Misuse: firefighter armor
Tank humanitarian mission
When a tank joins the fire department, there are several reasons.
Firstly, tracked vehicles are often indispensable in the fight against forest fires due to their cross-country ability and the ability to deliver the extinguishing mixture directly to the front of the fire. The ignition temperature of rubber does not allow wheeled vehicles to rake burning debris and come close to the flame.
Secondly, the armor protects not only from extreme temperatures, but also from shrapnel and even direct hits from shells when artillery warehouses catch fire. This is why firefighters Tanks first appeared in the military.
In the Soviet Union, the Lviv Armored Plant (17th Repair Plant) was responsible for the production of armored vehicles for firefighters, which to this day converts tanks into fire engines.
The first order for unusual tracked vehicles came to Lviv in 1978 from the Main Missile and Artillery Directorate of the USSR Ministry of Defense. By that time, the production documentation for the fire tank had been developed and prepared by the engineers of the Kiev 482nd KTC of the USSR Ministry of Defense.
Please note that fire armor was needed not by tankmen, but by artillerymen. This is largely due to the Siberian ammunition depots, which regularly suffer from forest fires.
For a while, the gunners made do with homemade products based on the decommissioned T-34s, but by the 70s, this technique was morally outdated. The military made serious demands on the developers - at least 10 tons of water on board, 2 tons of foam concentrate and the presence of a fire monitor with a water supply capacity of 40 liters per second.
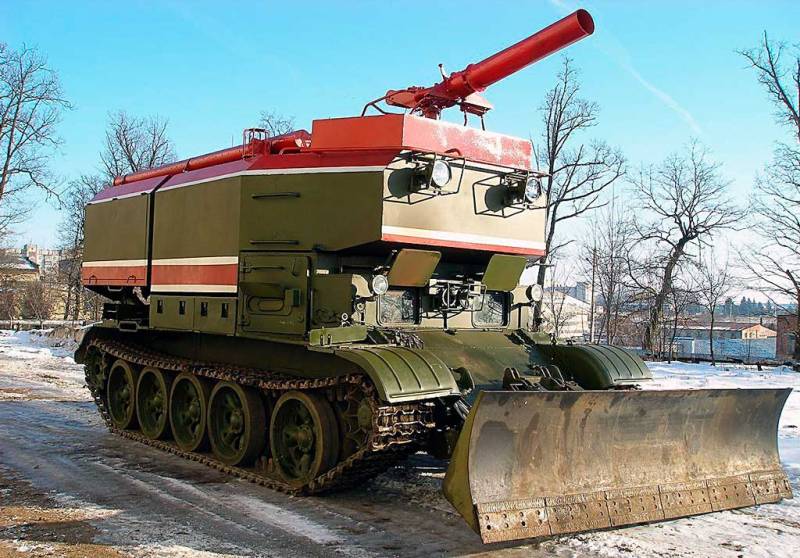
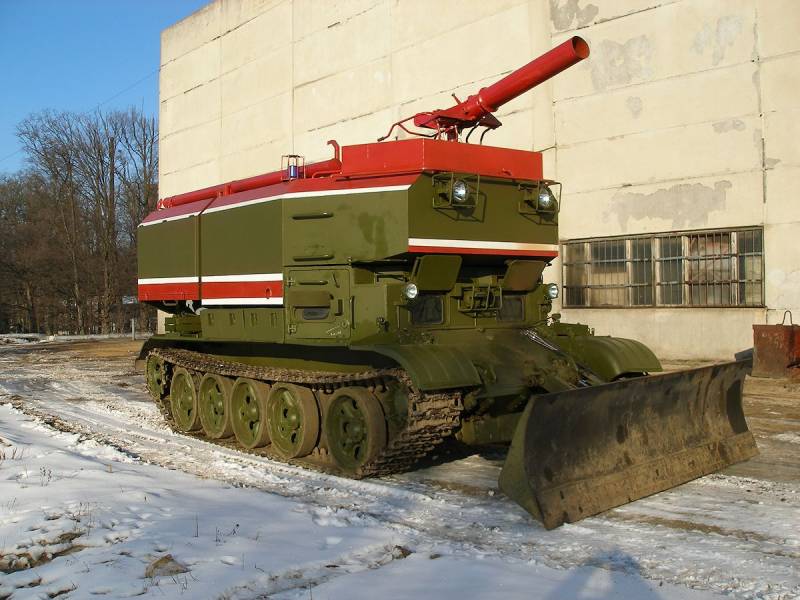
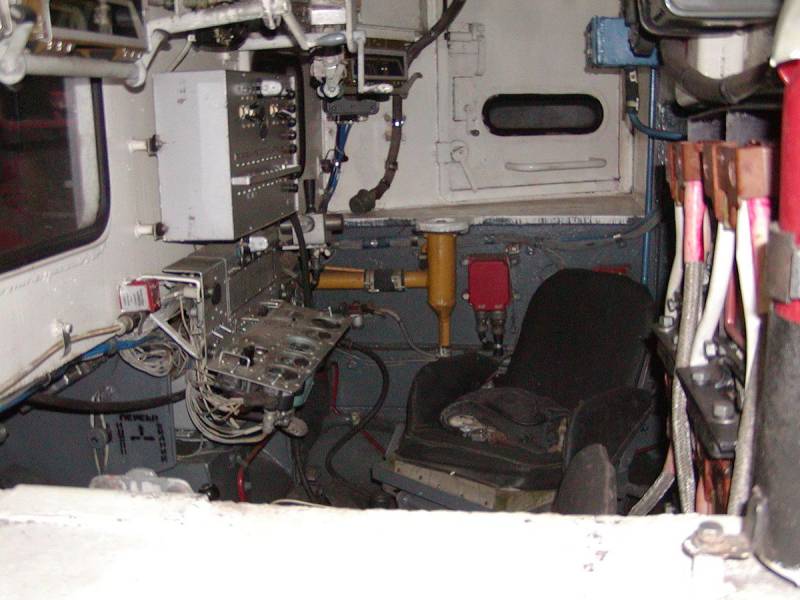
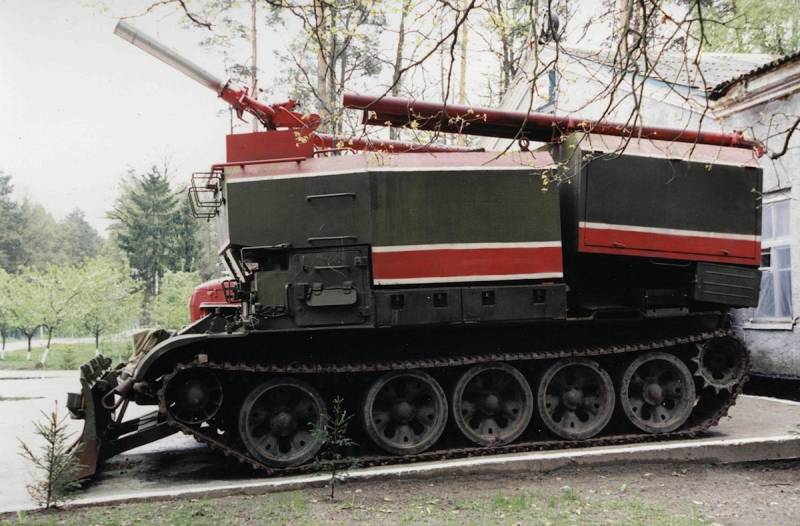
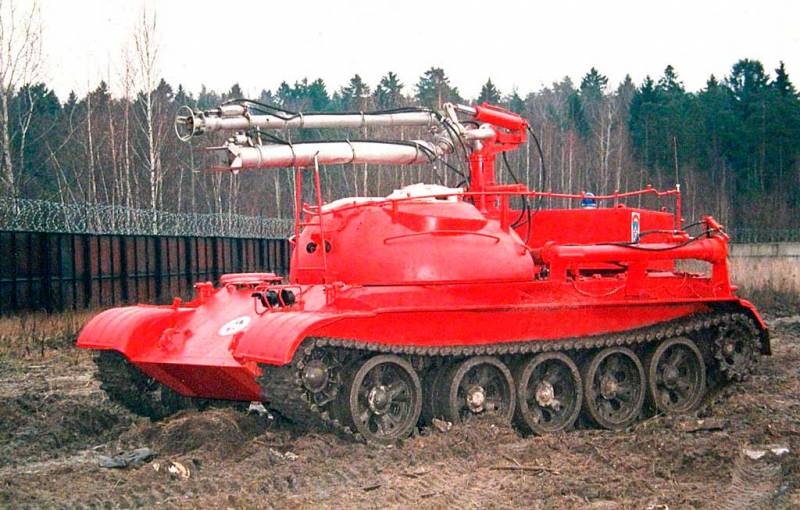
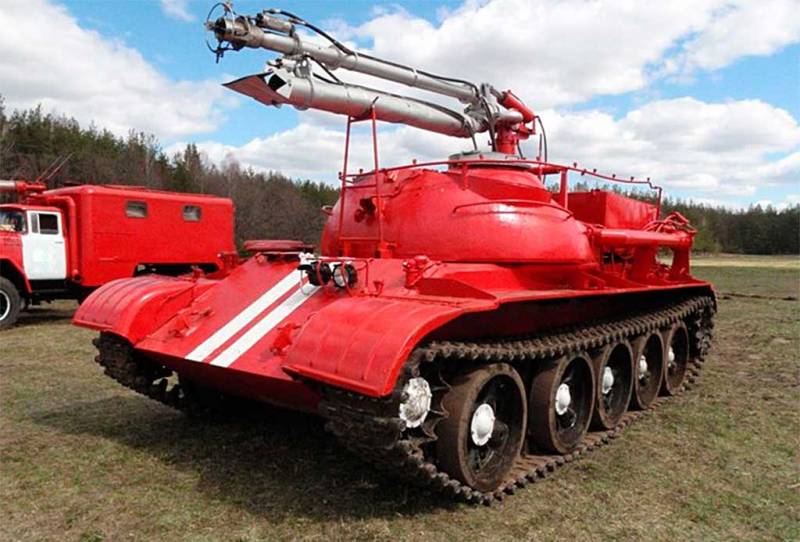
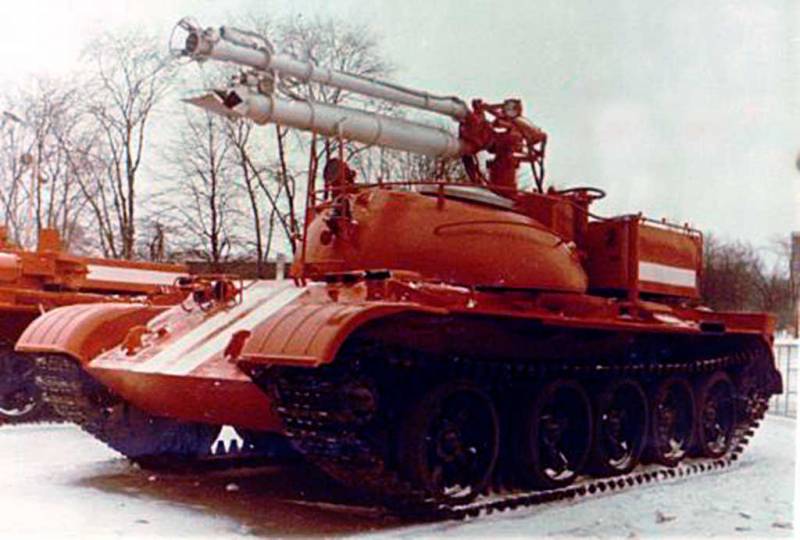
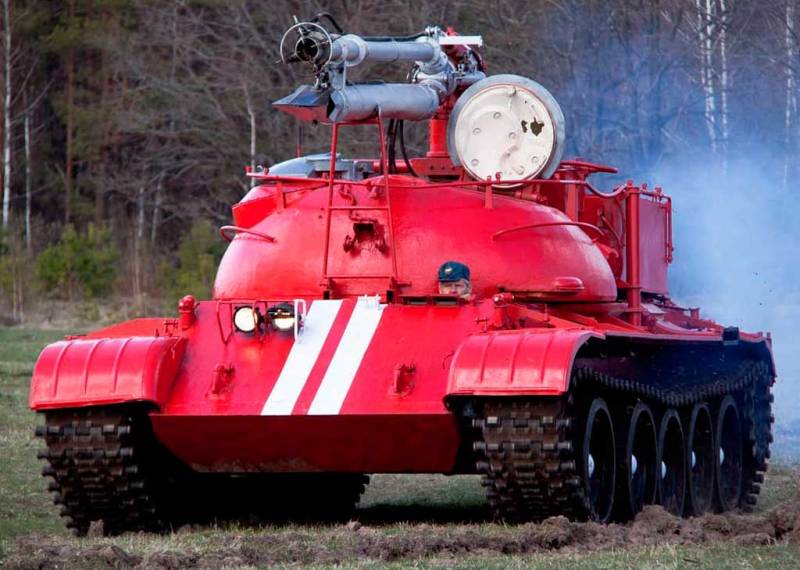
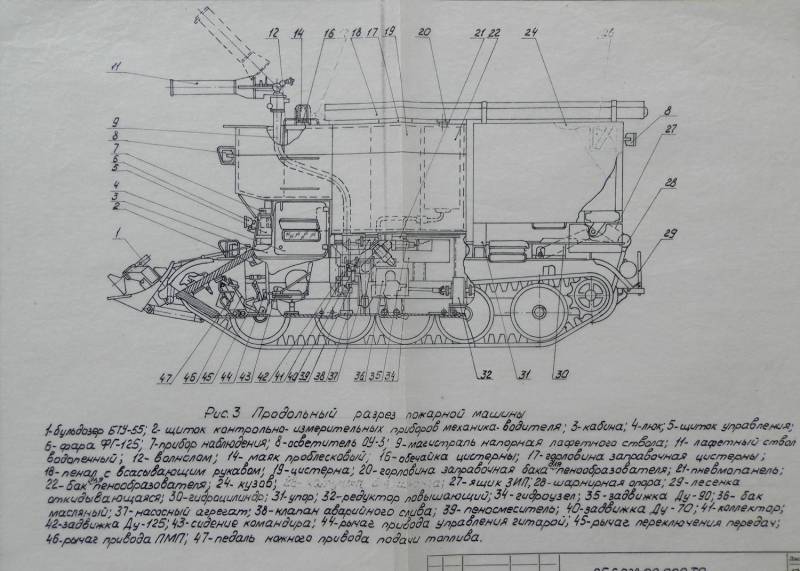
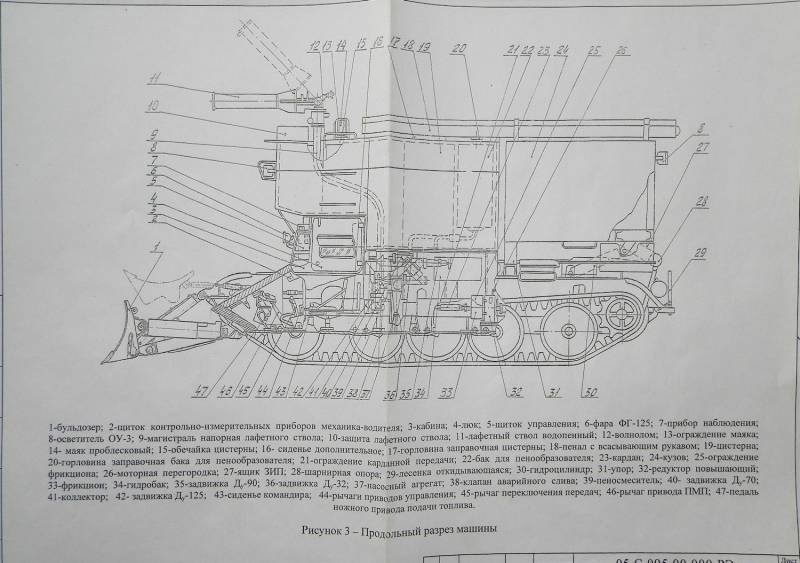
The T-54 was chosen as a platform, from which the turret was removed by hoisting a giant tank. Fortunately, there were a lot of tanks written off from service by that time. The new product was named accordingly - GPM-54 (tracked fire engine).
The very first tests showed that the T-54 is not the best suited for the role of a fire fighter, largely due to its large mass. The huge fuel consumption reduced the operating time of the fire tank, and the problem was solved by replacing the projectile armor with 20 mm steel sheets.
However, even in the deserted state, the curb weight of the car was excessive - it had to be reduced to 43 tons by reducing the stock of transported water to 9 tons.
The crew consisted of two people: a driver-mechanic and a fire-barrel operator, concurrently as a tank commander. The key disadvantage of the GPM-54 was the gear drive of the water pump, which did not allow the machine to simultaneously move and spray the flame with a fire-extinguishing mixture.
The power plant maintenance procedure also added complications. Directly above the tank diesel engine, a body with tanks raised on hydraulic cylinders was placed. Despite a sufficiently powerful pump, the firefighters lacked the speed of the water supply. In order to extinguish the flaming ammunition piles, a high flow rate of water was required. The range of the fire barrel was about 60 meters, the crew of the GPM-54 nevertheless had to approach the flame by 10 meters - only then the fire extinguishing efficiency was sufficient.
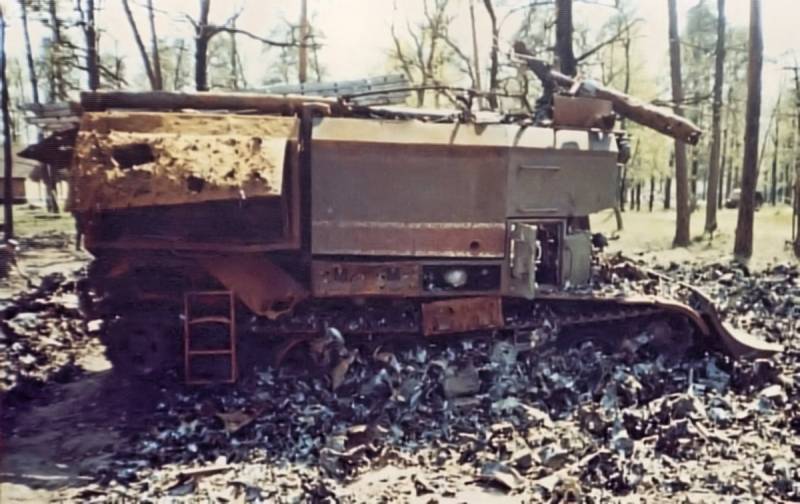
First of all, diesel engines that were out of order from overheating suffered from the extreme heat. The fire intensively burned out oxygen in the area, abundantly saturating the air with combustion products, which also caused the engines to stop. A fire tank that has died out in front of a burning arsenal is almost certainly a mass grave. The temperature around GPM-54 did not even allow the crew to get out of the car. Unfortunately, such tragedies happened ...
Best of all, the Lviv fire tank coped with forest fires - for this it had a bulldozer blade. GPM-54 was capable of making passages and clearing burning rubble. In 2005, the Ukrainian tank was modernized, adding index 01 and new bulldozer equipment TBS-86. Another seat was added to the cockpit - the duties of the fire barrel operator could be removed from the vehicle commander.
The experience of extinguishing fires at arsenals in the 70s and 80s showed new vectors for the development of technology for such extreme conditions.
Firstly, it is very desirable to have a much larger one-time mass of "water shot" or at least a supply of fire-extinguishing mixture.
Second, high temperatures require remote control systems for fire tanks.
"Jay" and others
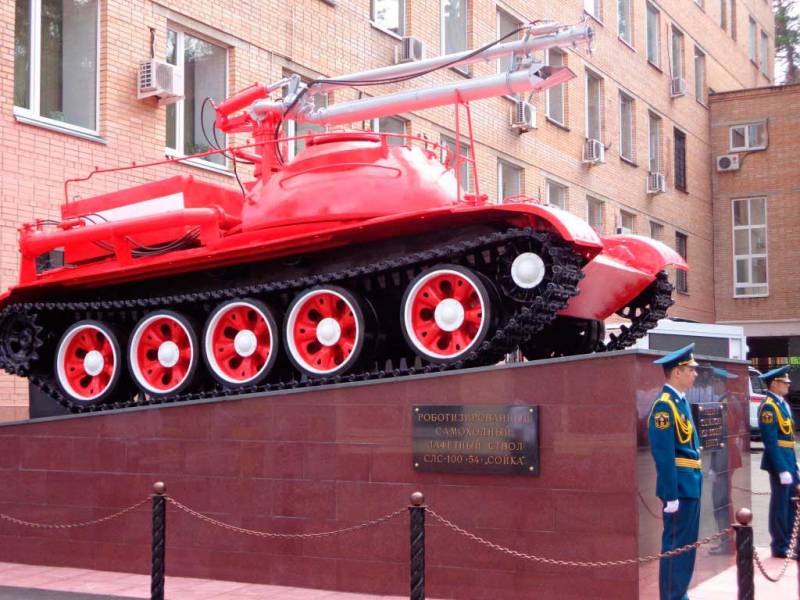
The next hero stories will become a tracked vehicle with a long name - a robotic self-propelled fire monitor SLS-100 "Jay".
A firebird appeared in response to the Chernobyl accident, but numerous difficulties made it possible to assemble the first prototype only by the end of the 90s. The base for the SLS-100 was the T-54/55, equipped with a remote control system and capable of operating near sources of radioactive and chemical contamination. When conditions permitted, the self-propelled carriage was operated by a crew of two inside an armored hull.
There was no need to lighten the Jay - the armor absorbed ionizing radiation quite effectively.
The self-propelled fire monitor did not have a supply of water on board, but pulled a 100-meter fire hose with it.
Developers from the All-Russian Order of the Badge of Honor of the Institute of Fire Protection (VNIIPO) and the Pozhmashina Design Bureau took into account the errors of the GPM-54 tank and equipped the Jay with a more powerful pump. Now water can be supplied to the hearth at a distance of 100 meters, and foam - from 70 meters.
By the way, "Jay" is installed on a pedestal near the main entrance of VNIIPO in Balashikha near Moscow. The production of a small series of a self-propelled gun carriage was established at the 61st repair plant in Petrodvorets.
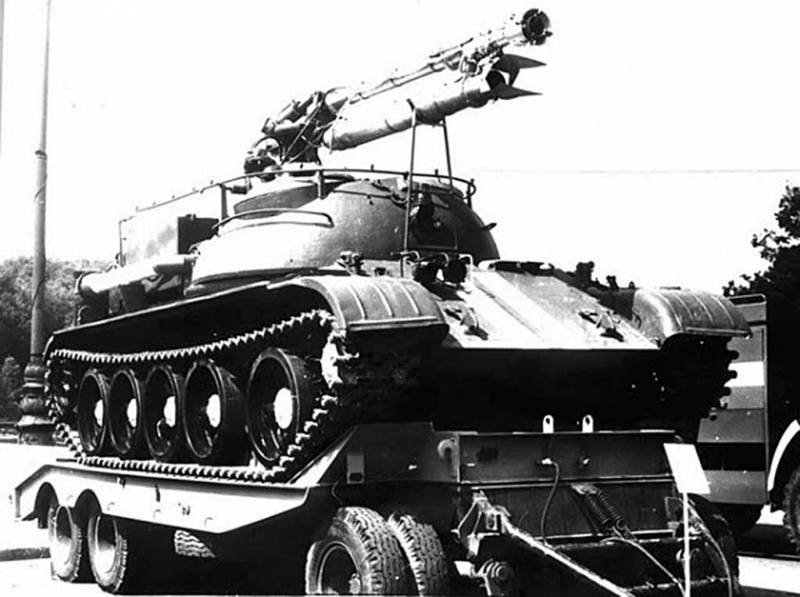
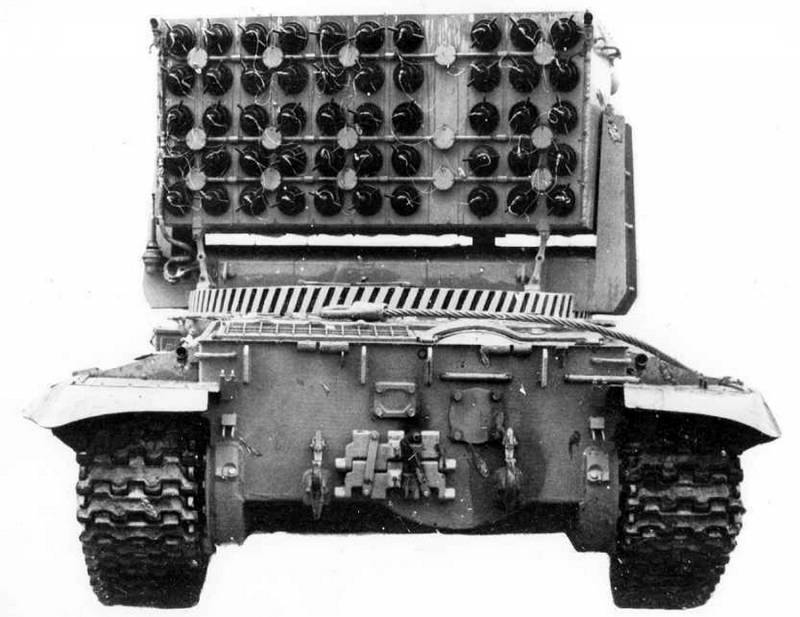
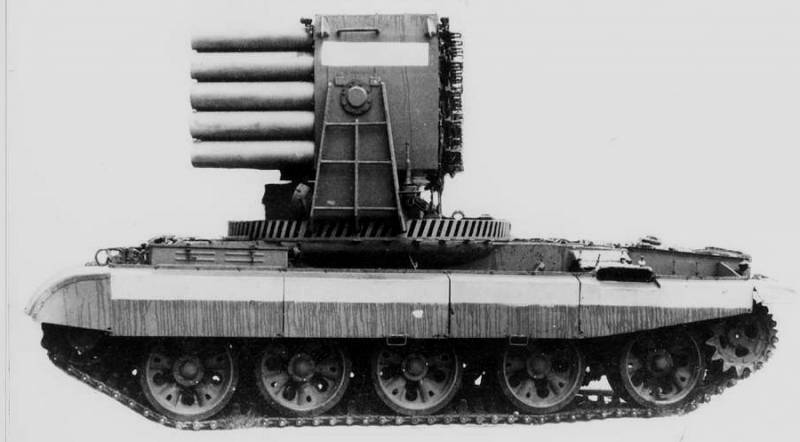
The issue of remote control of fire tanks was resolved only in the late 90s. The problem of the volume of the fire-extinguishing salvo was overcome much earlier - in 1988, with the advent of the unique Impulse-2M vehicle. Experimental work in the direction received the characteristic name of the ROC "Braking", and the tracked vehicle itself at the final stage of revision was designated as "product 054".
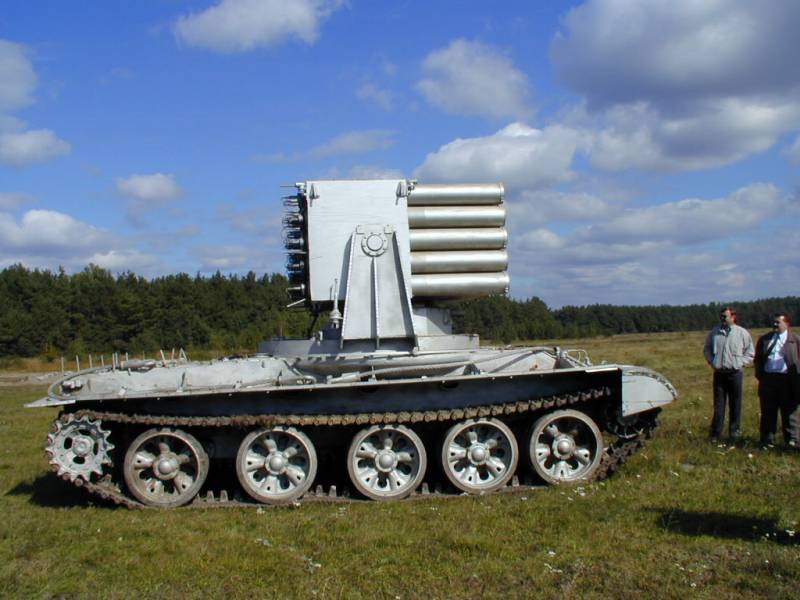
The first experiments were carried out on the well-deserved T-55 chassis under the name "Impulse-1". The fire tank, which later became serial, was dispatched to the T-62 tank leaving the army and put on the roof ... a multiple launch rocket system! If you do not take into account the characteristic color of the car, then "Impulse - 2M" can be confused with TOS "Buratino".
The so-called multi-barrel module consists of 50 barrels, from which you can fire anything - liquids, gels, sand or powders, in general, anything that does not support combustion. It is worth noting that the fire tank did not fire rocket-propelled grenades, but rather fired at the center of the fire, as if from a cannon.
The T-62 platform made it possible to withstand the recoil of the machine from five consecutive volleys of ten barrels. If the operator cocked more than ten barrels by mistake, the automatics blocked the salvo.
An important feature of the new fire tank was the system for irrigating the armor with water or other insulating substances - the sad experience of the burnt-out GPM-54 was not in vain.
The mechanics of extinguishing the burning artillery depots were simple.
Unlike its predecessor GPM-54, "Impulse" did not need to approach the fire at a distance of 10 meters - 70-100 meters was enough. Further, the operator pointed the launch module with 200-mm barrels and fired a single shot, or immediately a volley. The flame was extinguished by the projected substance (water, sand, and so on), and was also knocked down by the shock wave, blocked by the explosion products and crushed into small, not so dangerous, foci.
In each barrel of "Impulse-2M" it was possible to drive up to 30 kg of substance. It was a real Soviet know-how, the author of which was Vladimir Dmitrievich Zakhmatov, a junior researcher at the Explosion Geodynamics Department of the Institute of Geophysics of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine. The scientist not only proposed to extinguish the fire with an explosion, but also successfully tested his extinguishing bombs in Chernobyl in 1986.
The fire tank demonstrated impressive performance in practice.
For example, once the developers filled a 30-meter ravine 2 meters deep with rubber tires, filled everything with a ton of diesel fuel and 150 liters of gasoline. They set fire to and sent to investigate the crew on the "Impulse-2M". The tank suppressed the fire with eight volleys from 10 barrels from a distance of 10 meters.
To be continued ...













Information