Modern Japanese anti-aircraft missile systems
By the time the Cold War ended, Japan had a scientific and technical potential that made it possible to independently create quite modern short and medium-range anti-aircraft missile systems. Currently, the Japanese Self-Defense Forces are mainly equipped with air defense systems developed in Japan. The exception is the American Patriot long-range complexes, but they were purchased for political reasons and a desire to save time. In case of urgent need, the leading Japanese corporations working in the field of electronics, aircraft and rocketry could create an air defense system of this class on their own.
Due to the fact that Japanese law does not allow the sale of weapons abroad, Japanese-made anti-aircraft systems were not supplied to foreign buyers. In the event that legislative restrictions are lifted, Japanese short- and medium-range air defense systems can create intense competition in the world arms market to other sellers offering goods of this kind.
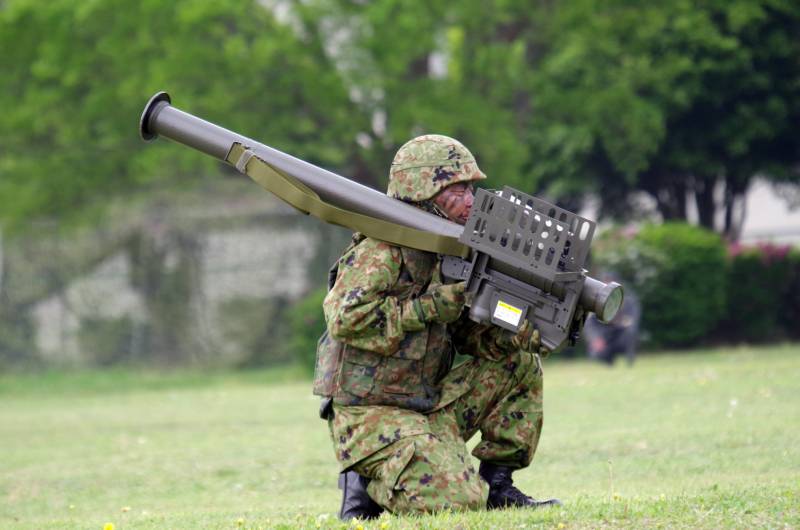
MANPADS Tour 91
In 1979, when the issue of the delivery of FIM-92A Stinger MANPADS to Japan had not yet been resolved, the Japanese government initiated a competition to create its own portable anti-aircraft complex. In 1980, Kawasaki Heavy Industries and Toshiba Electric presented their projects to the military-technical commission created by the Self-Defense Forces. As a result, preference was given to the Toshiba project. But, in connection with a positive decision on the delivery of American "Stigers" to Japan, the development of its own MANPADS was officially postponed for 7 years. However, all these years, Toshiba has been conducting research on a proactive basis. In 1988, practical tests of prototypes began, and in 1990, several copies of MANPADS were transferred to military trials.

MANPADS Tour 91
In 1991, the Japanese Tour 91 MANPADS officially entered service. To speed up the work and reduce the cost of development, some minor parts were borrowed from the Stinger, but in general, despite the external resemblance to the American MANPADS, the Japanese Tour 91 is an original, independently created complex. In the Japanese Self-Defense Forces, the Tour 91 MANPADS has the military designation SAM-2.

In 1993, three combatant anti-aircraft units, which received a total of 39 portable complexes, were declared fully combat-ready.
The mass of the complex ready for use is 17 kg. The length of the launcher is 1470 mm. The rocket diameter is 80 mm. The mass of the rocket is 9 kg. Launch tube weight - 2,5 kg. The mass of the launcher with a radar interrogator and a sight is 5,5 kg. The maximum flight speed of the rocket is 650 m / s. The maximum firing range is 5 km.
The rocket arrives at the troops equipped with a disposable fiberglass launch tube, on which removable equipment is mounted: a friend or foe radar interrogator, a trigger with a coolant bottle and a sight.
The cooled Ture 91 homing head, unlike the FIM-92A Stinger MANPADS used in the Self-Defense Forces, from the very beginning had a combined guidance system: infrared and photocontrast.
Since 2007, the Type 91 Kai MANPADS (military designation SAM-2В) with an improved homing head and an optoelectronic sight has been mass-produced. The new modification is better protected from thermal interference and can be used in conditions of poor visibility, the minimum height of the defeat is also reduced.
In the period from 1991 to 2010, the Self-Defense Forces received 356 sets of removable equipment for the Tour 91 and Tour 91 Kai MANPADS. About 1000 anti-aircraft missiles have been delivered.
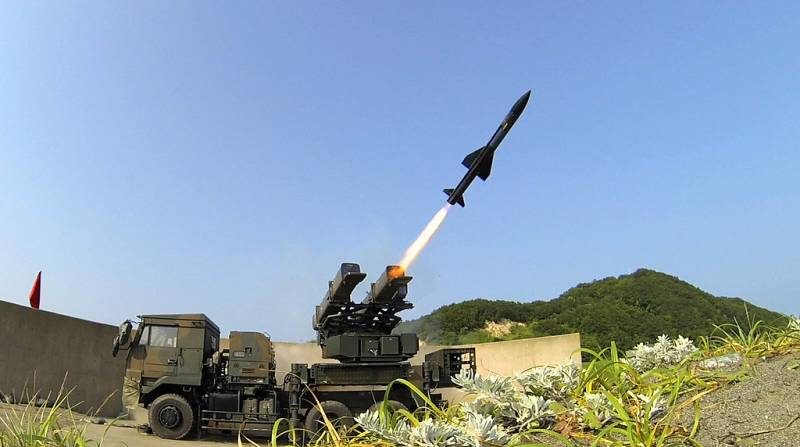
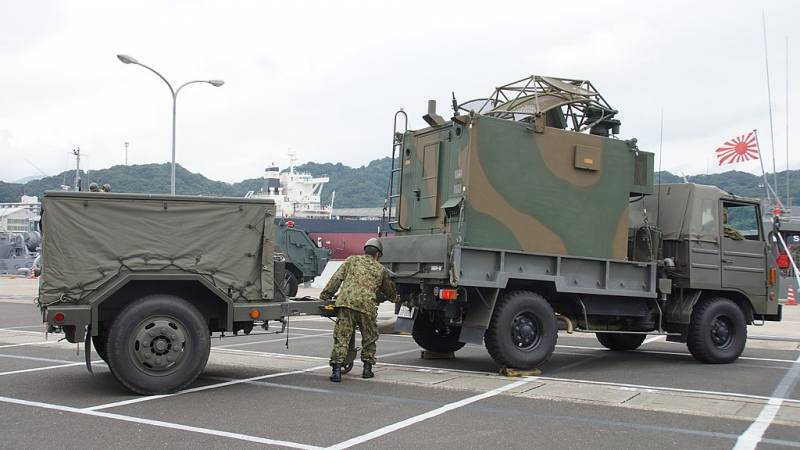
Ture 93 short-range mobile air defense system
Even before the Ture 91 MANPADS was adopted, a self-propelled version was being developed. Serial production of the complex, known as the Tour 93 (military designation SAM-3), began in 1993. Until 2009, 113 self-propelled complexes Ture 93 were built. The manufacturer of the hardware and missiles was Toshiba Electric.
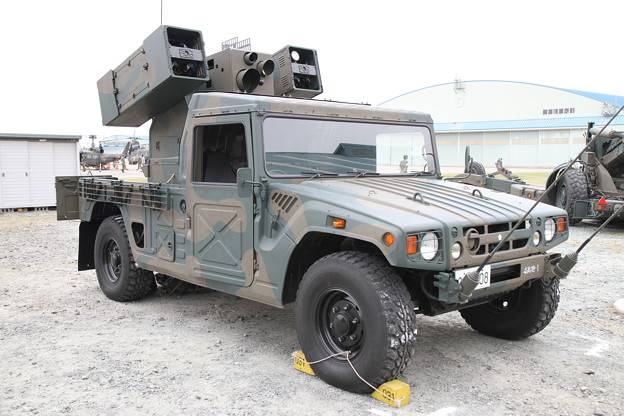

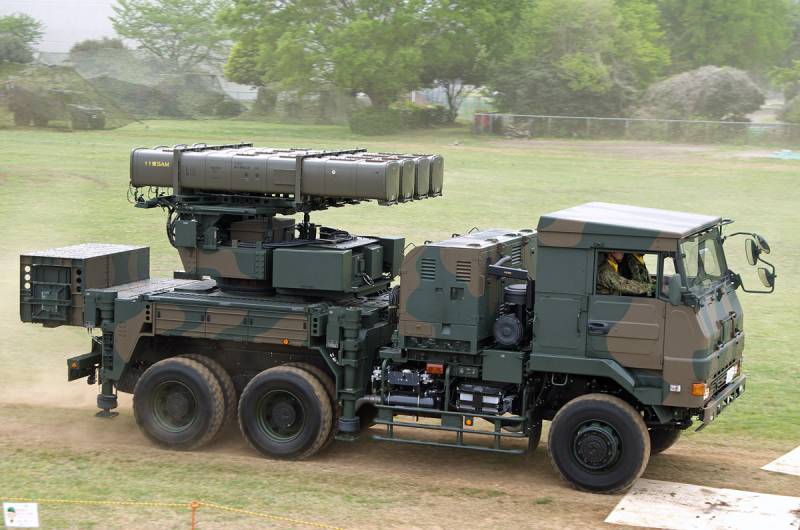
SAM Tour 93
The chassis of Toyota Mega Cruiser was used as a base. The maximum speed is 125 km / h. The power reserve is 440 km. Although the Tour 93 is conceptually similar and outwardly strongly resembles the American self-propelled complex AN / TWQ-1 Avenger, the Japanese air defense system does not have a 12,7-mm anti-aircraft machine gun.
The rotating platform houses two containers for four Type 91 missiles in each. Between them is a block with sighting and search equipment.
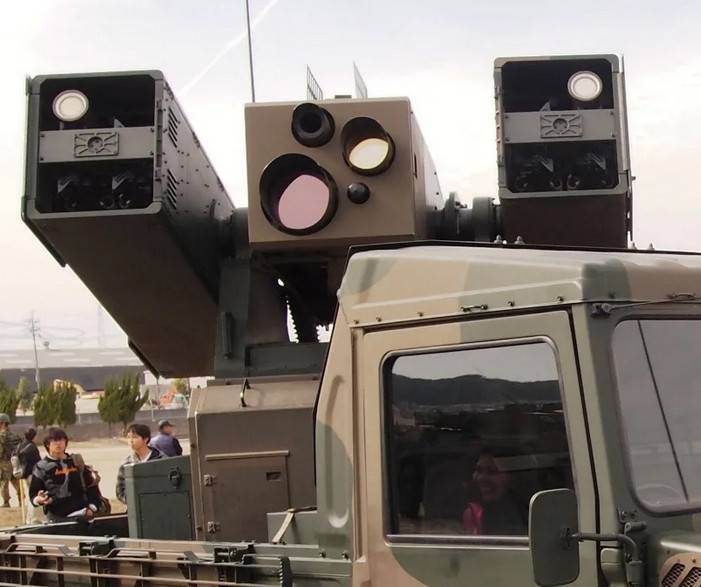

To search for and capture an air target on the Tura 93 air defense system, a thermal imager and a television camera are used, capable of working in low light conditions.

After capturing the target, it is taken for tracking, the distance is measured with a laser rangefinder. The search and firing of the target is carried out by the operator from the cockpit. The crew includes: commander, operator and driver.
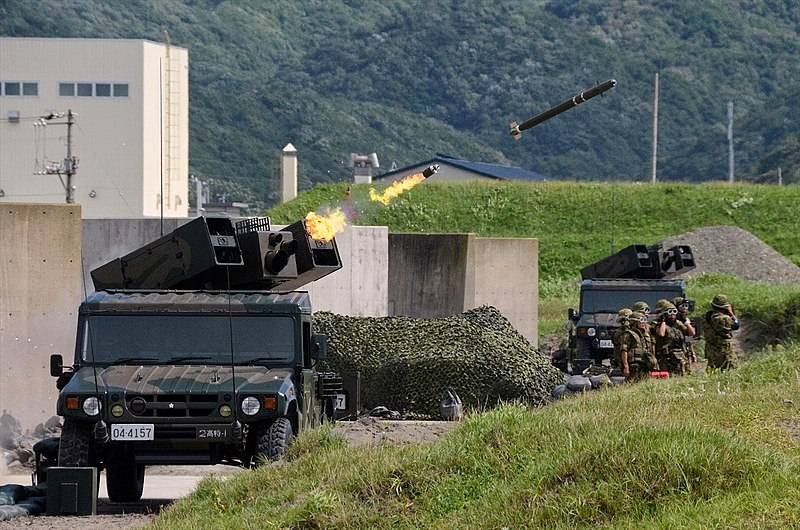
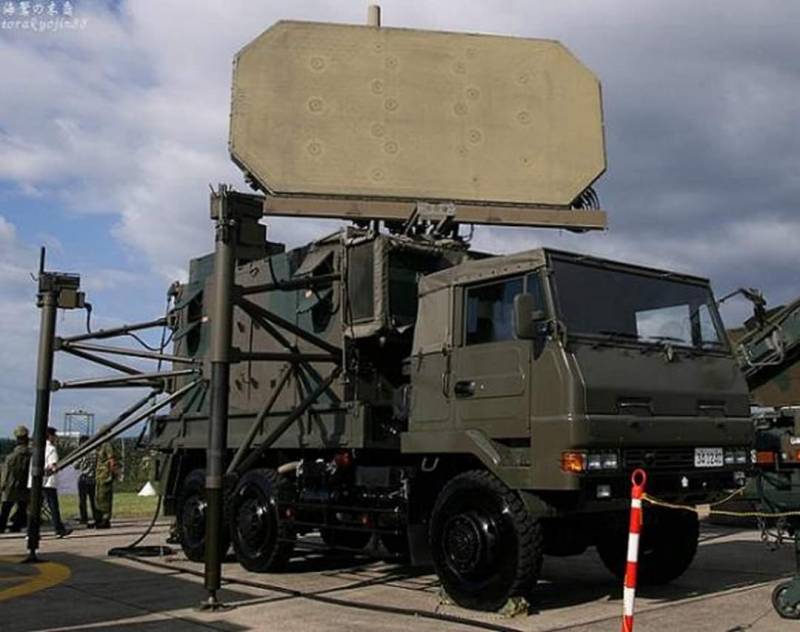
Upgraded short-range air defense system Ture 81 Kai
In 1995, tests of the modernized air defense system Tour 81 Kai, developed by Toshiba Electric, began. In connection with the need to increase the firing range, the radar of the command post has undergone significant modernization. Judging by the materials available in the Japanese press, thanks to the improved energy performance, the detection range of the radar reaches 50 km. To detect air targets without the inclusion of a radar, a passive thermal imaging sight combined with a wide-format video camera was introduced into the equipment of the combat control point and self-propelled launchers. The absence of unmasking radar radiation makes it possible to increase the secrecy of actions and reduce the vulnerability of the complex.
In addition to the updated electronic blocks of the computing complex, communication facilities and information display, new Ture 81S missiles with a combined anti-jamming seeker (IR + photocontrast) were introduced into the SPU ammunition. The mass of the rocket increased to 105 kg. Warhead weight - 9 kg. Length - 2710 mm. Thanks to the use of a new, more energy-intensive jet fuel with a burning time of 5,5 s, the maximum speed has increased from 780 to 800 m / s. Firing range - up to 9000 m. Altitude reach - 3000 m.
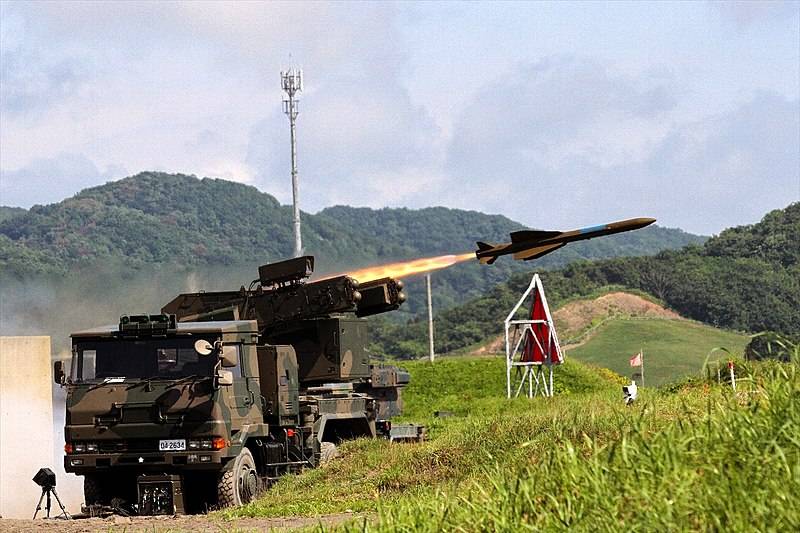

Another significant innovation was the missile with active radar guidance. The mass of this missile is 115 kg. Length - 2850 mm. Firing range - 13000 m. Altitude reach - 3500 m.
The use of two types of missiles with different homing heads made it possible to expand the tactical flexibility of the modernized self-propelled complex, increase noise immunity and increase the range. Serial construction of the Ture 81 Kai air defense system was completed in 2014.
Currently, in the Ground Self-Defense Forces, eight separate anti-aircraft battalions and four brigades are armed with complexes of the Ture 81 family. In the Air Self-Defense Forces, they are in service with four anti-aircraft groups covering air bases.
SAM MIM-23 Hawk
Since the first half of the 1970s, low-altitude air defense systems "Hawk" of various modifications in peacetime provided protection against air attacks from large Japanese military bases, and in a threatened period and in wartime they had to cover places of concentration of troops, headquarters, warehouses and strategically important objects ... More details about the Japanese air defense systems "Hawk" are described: here.
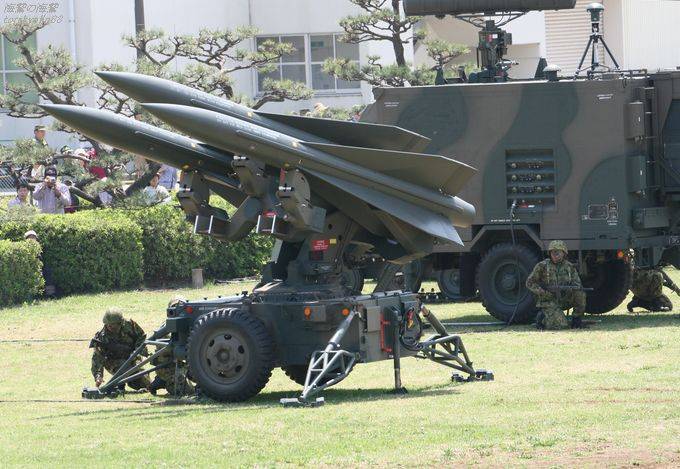

Until 2018, on an ongoing basis, three anti-aircraft missile divisions equipped with Hawk Type III modification complexes (Japanese production) were on alert at stationary positions in the central part of Japan.

Satellite image of Google Earth: the position of the Hawk anti-aircraft missile battalion at the Shimoshizu military base in the city of Chiba
At present, all Hawk complexes in the central and southern parts of Japan are concentrated in storage bases and are not on alert.
Three Hawk Type III batteries, deployed in the vicinity of the Chitose airbase on the island of Hokkaido, remained on alert. The Hawk air defense missile system launchers in the area are protected by quick-detachable dome-shaped shelters that protect against adverse meteorological factors.
It should be expected that the Hawk Type III air defense systems, which are in reserve and are on alert in Hokkaido, will soon be replaced by modern Japanese-made complexes.
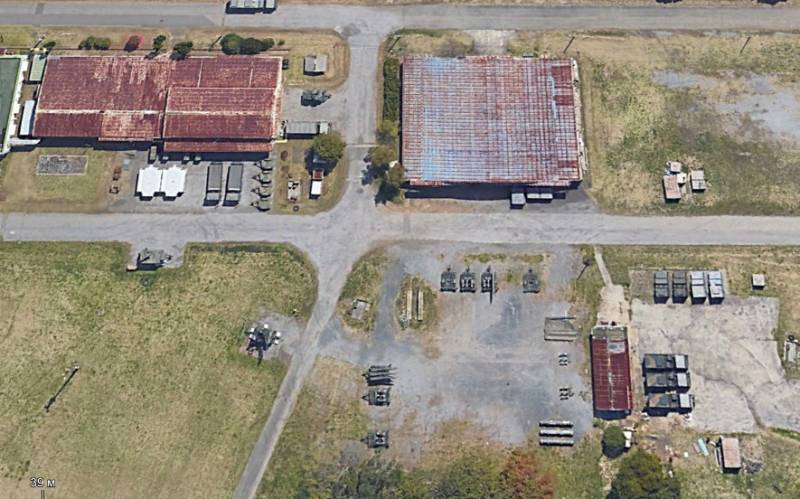

Satellite image of Google Earth: elements of the "Hawk" air defense system stored at the Shimoshizu military base
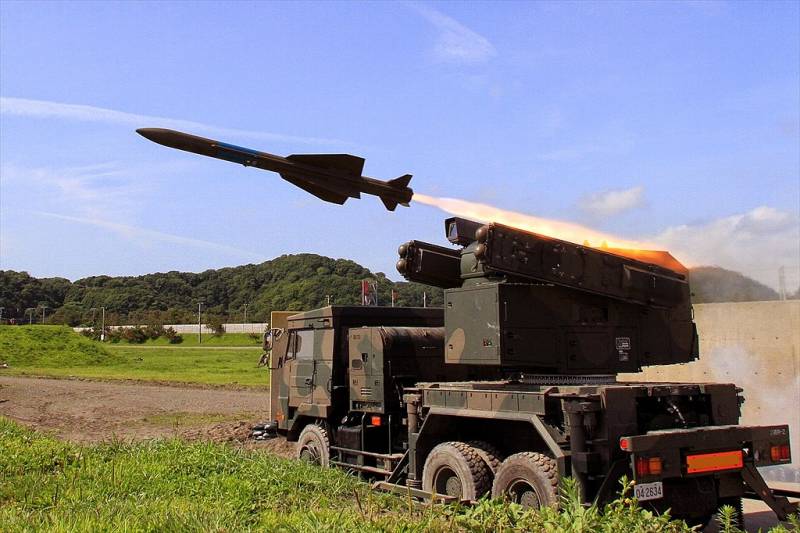
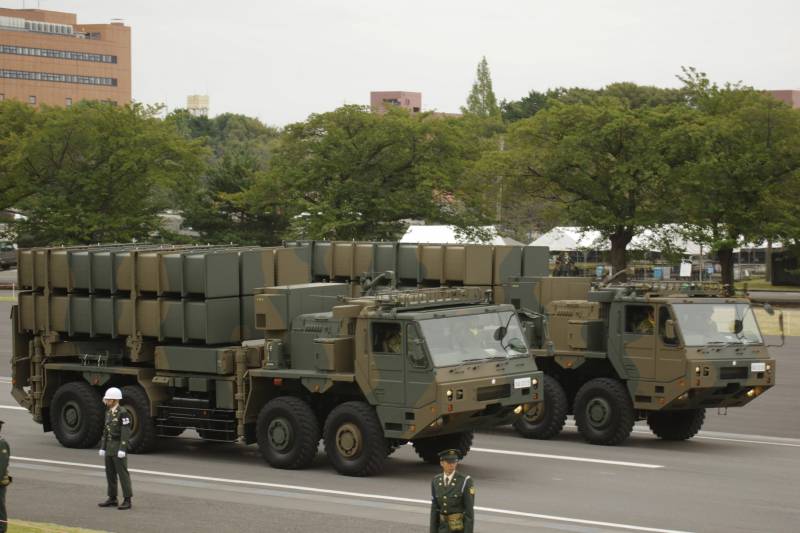
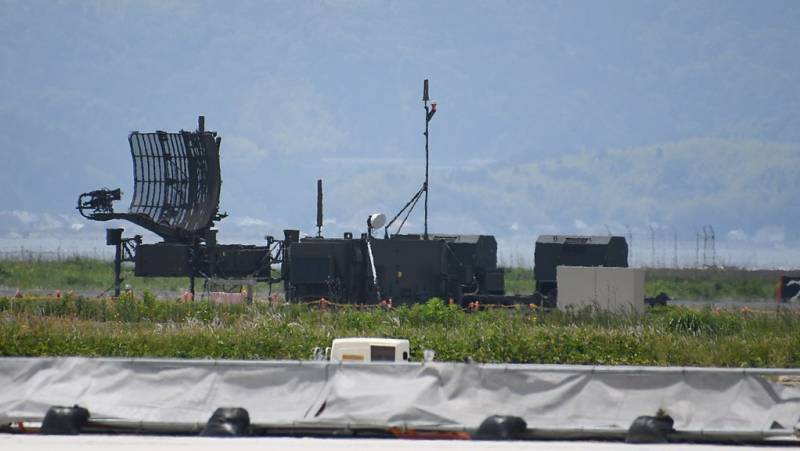
Medium-range air defense missile system Type 03
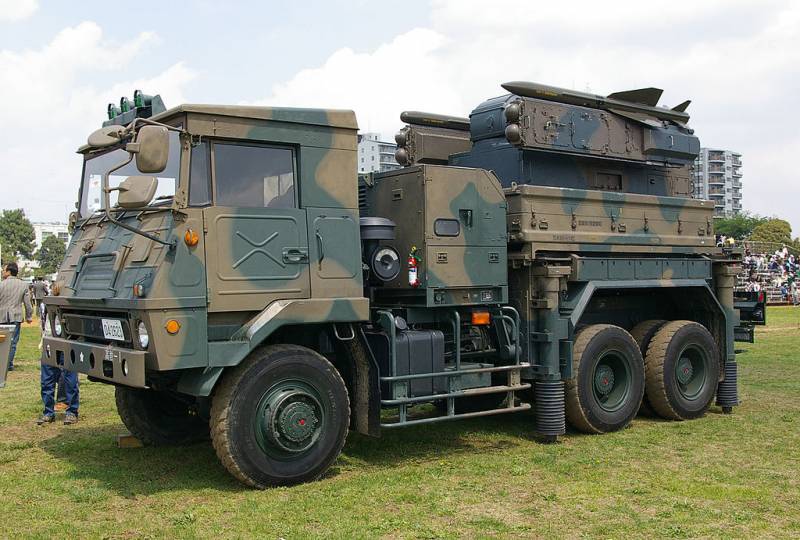
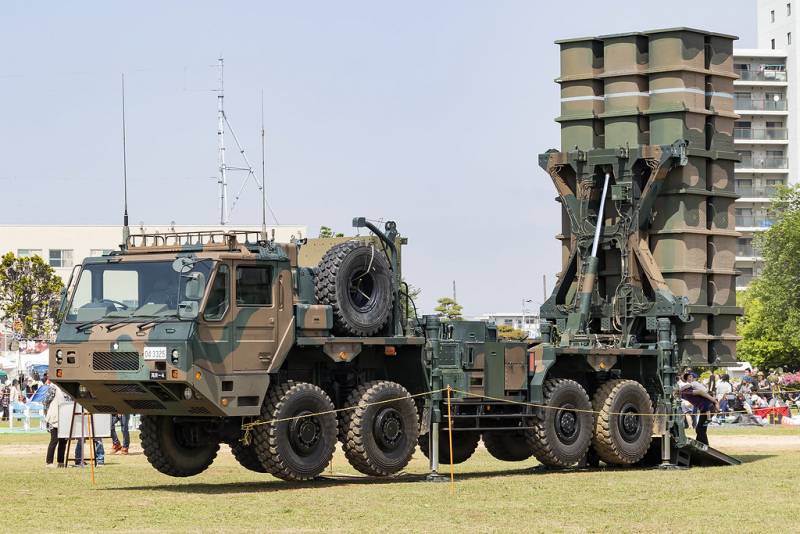
In 1990, Mitsubishi Electronics, together with the TRDI (Technical Research and Development Institute) of the Japanese defense agency, began to create an air defense system that was supposed to replace the Hawk family complexes. It was assumed that no more than 10 years will pass from the start of work to adoption. However, the difficulties that arose in the process of fine-tuning the complex required additional tests carried out from 2001 to 2003 at the American White Sands test site (New Mexico). Officially, the new medium-range air defense system, designated Type 03 (military designation SAM-4), was put into service in the 2005 year.
The anti-aircraft missile battery includes three launchers, transport-charging vehicles, a fire control point, a communications point, a multifunctional radar and a mobile diesel power plant.
The self-propelled launcher, multifunctional radar, diesel generator and TZM used as part of the Type 03 air defense system are located on a four-axle all-wheel drive Kato Works chassis. Unified container modules of the command post and communication vehicles are installed on the Toyota Mega Cruiser off-road vehicle.
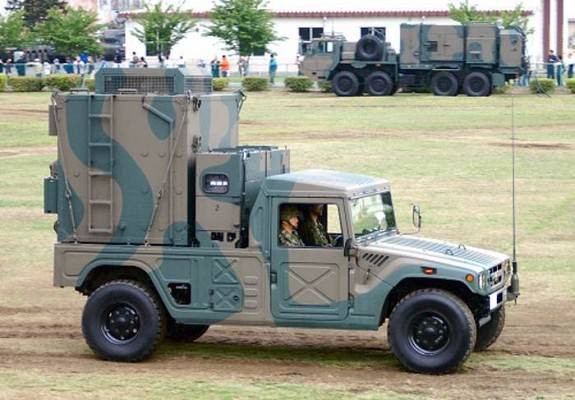

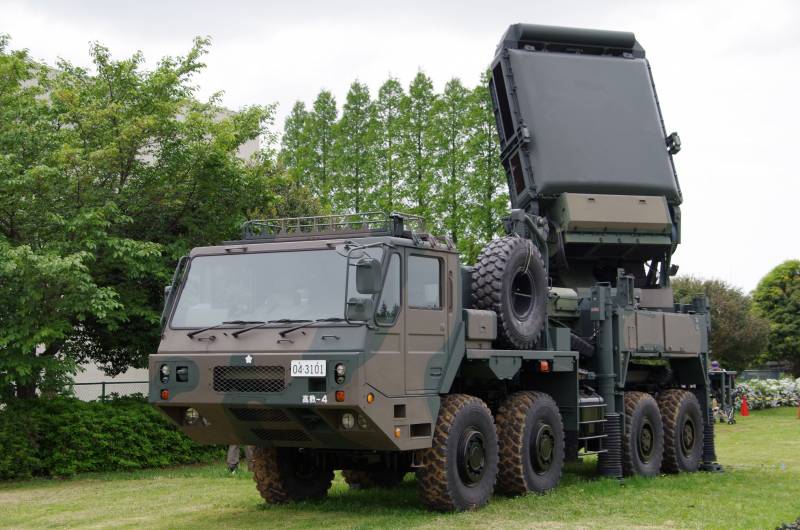
Command post SAM Type 03
Multifunctional radar with AFAR is capable of tracking up to 100 air targets and providing simultaneous shelling of 12 of them. Information about the air situation, the technical condition of the complex elements and the presence of missiles ready for launch is displayed on the displays of the fire control point. The complex is equipped with equipment for interfacing with the JADGE automated air defense control system of Japan, which makes it possible to quickly distribute targets between different batteries.
The ammunition load of each launcher is 6 missiles located in the TPK. In the firing position, the SPU is leveled using four hydraulic jacks, the TPK package is installed vertically.
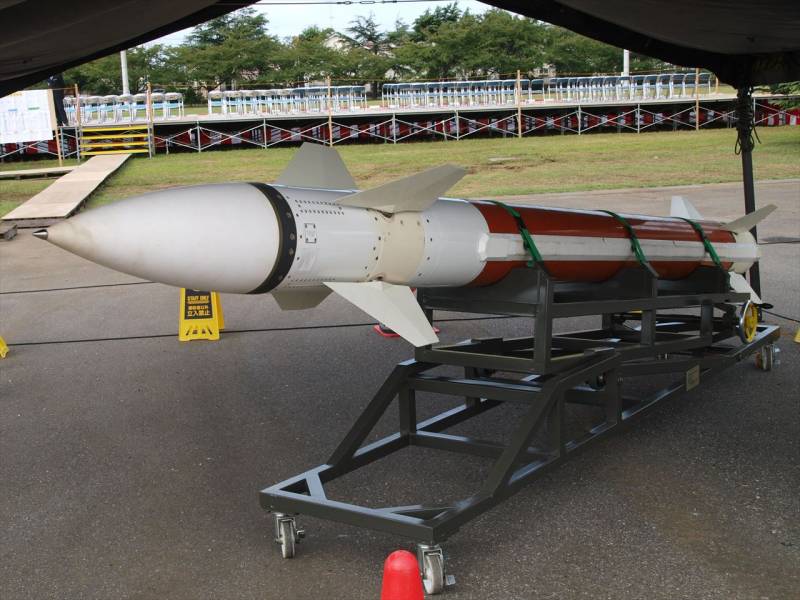
To defeat air targets, the Type 03 air defense missile system uses a missile defense system with an active radar homing head borrowed from the AAM-4 air-to-air missile. The mass of the anti-aircraft missile is 570 kg, the length is 4900 mm, the body diameter is 310 mm. Warhead weight - 73 kg. The maximum speed is 850 m / s. The firing range is 50 km. Height reach - 10 km.
The presence of a thrust vector control system and developed all-turning front and rear aerodynamic steering surfaces provide the missile defense system with high maneuverability.
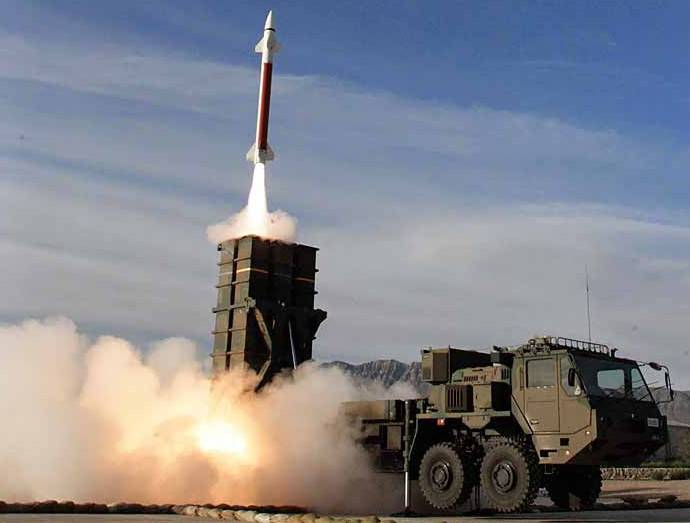

The rocket is launched vertically, after which it is directed towards the target. At the initial stage of the trajectory, the rocket is controlled by an inertial control system, according to the data loaded before launch. The data line is used to transmit correction commands in the middle segment of the trajectory until the target is captured by the seeker.
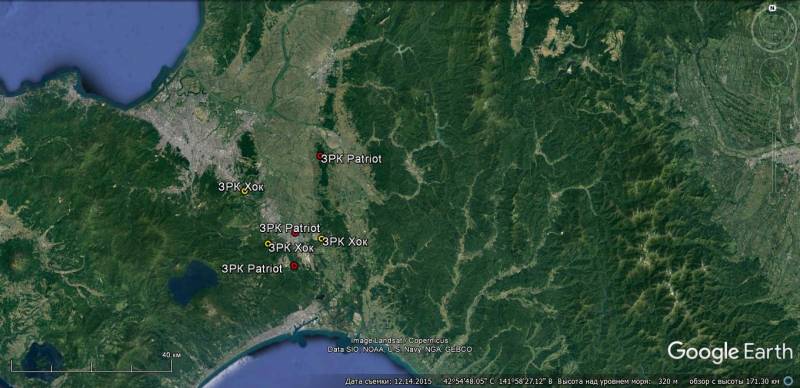
In 2003, even before the official acceptance into service, the first Type 03 battery was delivered to the Air Defense Training Center of the Ground Self-Defense Forces, located at the Shimoshizu base in the city of Chiba (about 40 km east of central Tokyo).

Satellite image of Google Earth: elements of the Type 03 air defense system at the Shimoshizu military base, belonging to the Air Defense Training Center of the Ground Self-Defense Forces
In 2007, the 2nd anti-aircraft group of the Eastern Army reached the required level of combat readiness. The anti-aircraft missile battery of this unit is also on alert at the Shimoshizu base. Earlier, an anti-aircraft battery of the Hawk air defense missile system was deployed at this position.

Satellite image of Google Earth: the position of the Type 03 air defense system at the Shimoshizu military base
In 2008, rearmament began from the Hawk air defense system to the Type 03 of the 8th anti-aircraft group from the Central Army stationed at the Aonohara base, 5 km north of the city of Ono, Hyogo Prefecture.

Satellite image of Google Earth: the position of the Type 03 air defense system at the Aonohara military base, the SPU and the multifunctional radar are in a combat position
In 2014, the Ground Self-Defense Forces began testing the upgraded Type 03 Kai complex. In the summer of 2015, 10 rockets were fired at the White Sands training ground in the United States. The real characteristics of the upgraded complex are not disclosed. It is known that thanks to the use of a more powerful radar and new missiles, the firing range exceeded 70 km and it became possible to combat ballistic targets. Thus, the Type 03 Kai received anti-missile capabilities. However, plans for the mass purchase of the modernized complexes have not yet been made public. According to information published in open sources, as of 2020, 16 Type 03 air defense systems of all modifications were released.
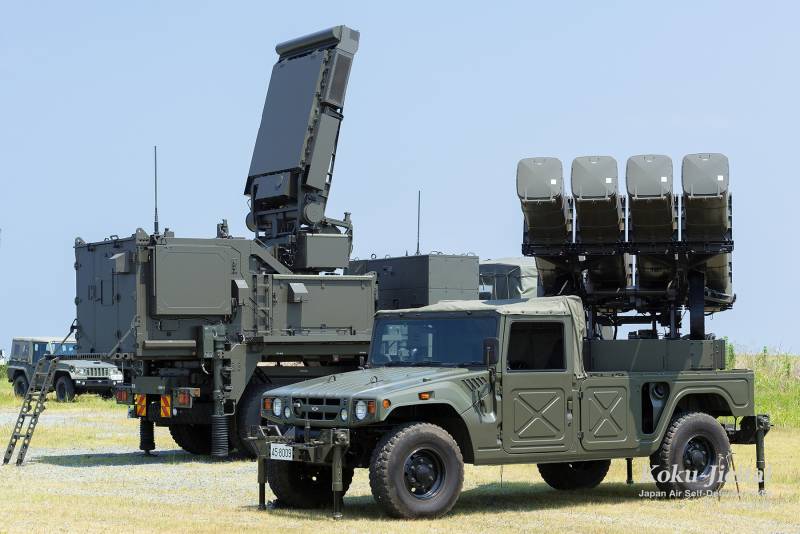
Type 11 short-range mobile air defense system
In 2005, Toshiba Electric began to create a short-range mobile air defense system, which was supposed to replace the aging Ture 81 complexes. Thanks to the existing developments, already in 2011 a prototype was presented for testing. After fine-tuning, the complex was put into service in 2014 under the designation Type 11.
Unlike the Type 81 air defense system, the new complex uses only missiles with active radar guidance. The rest of the structure of the fire battery of the Type 11 air defense system is similar to the Type 81. The air defense system includes a command post equipped with a radar with AFAR, and two self-propelled launchers with four missiles.
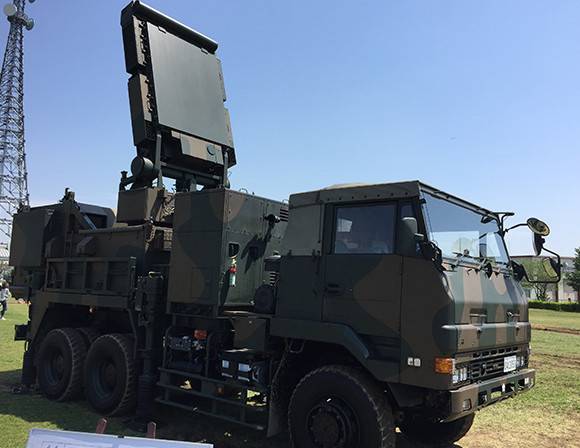

Multifunctional radar SAM Type 11
Unlike the Type 81 air defense system, on Type 11 self-propelled launchers, anti-aircraft missiles are located in sealed transport and launch containers, which protects them from adverse environmental influences and allows the use of transport and loading vehicles.
Just like on the Type 81, the SPG has a remote sight that allows, if necessary, to fire at visually observed targets, regardless of the command post.
Officially, the characteristics of the Type 11 air defense system were not announced. But taking into account the external similarity of the SAM with active radar guidance used in the Ture 81 Kai air defense system, it can be assumed that their characteristics are very close. However, a new command post with a more powerful radar and modern means of information processing and communication was introduced into the Type 11 air defense system.
Initially, the air defense missile system was located on the chassis of a three-axle all-wheel drive truck. This modification is used by the Ground Self-Defense Forces. By order of the Air Self-Defense Forces, a version with an SPU on the chassis of a Toyota Mega Cruiser was created, which is mainly intended for air defense of air bases, stationary radar posts and regional air defense command posts.
As of 2020, the Ground Self-Defense Forces had 12 Type 11 air defense systems, which are equipped with 3 anti-aircraft battalions in the Northeast, Central and Western armies.

Satellite image of Google Earth: elements of the Type 11 air defense system in the vicinity of the Naha airbase
In the Air Self-Defense Force, six Type 11 air defense systems are in service with three anti-aircraft groups covering the airbases of Nittakhara, Tsuiki and Naha.
Air target detection radars used in conjunction with Japanese short-range air defense systems
Talking about Japanese short-range air defense systems used in military air defense and to protect airfields, it would be wrong not to mention mobile radars.
Although the command posts of the Japanese Type 11 and Tour 81 air defense systems and the Tour 87 ZSU have their own radars, anti-aircraft missile brigades and divisions (in the Ground Forces) and anti-aircraft groups (in the Air Force) are assigned control companies equipped with communications and radars on a car chassis. The same radars issue preliminary target designation to the calculations of the Ture 91 MANPADS, the Ture 93 mobile air defense systems and the Ture 87 ZSU. It should be noted that these radars are not on constant duty and are not part of the system of constant control of the Japanese airspace.
In 1971, the Ture 71 two-coordinate radar, also known as the JTPS-P5, entered service. This station, created by Mitsubishi Electric, was housed in containers weighing 2400-2600 kg on two trucks and was similar in performance to the American AN / TPS-43 mobile radar. If necessary, the elements of the station, dismantled from the cargo chassis, could be transported by CH-47J helicopters.
A station with a pulse power of 60 kW, operating in the decimeter frequency range, could detect large targets flying at medium altitudes at a distance of more than 250 km. At a distance of 90 km, the accuracy of issuing coordinates was 150 m.
At the first stage, JTPS-P5 radars were assigned to anti-aircraft artillery units, and since 1980, anti-aircraft missile brigades and divisions of Tour 81. Currently, all JTPS-P5 radars have been removed from service of combat anti-aircraft units and are used to control flights in the vicinity of air bases.
Due to the fact that the JTPS-P5 station could not effectively work on low-altitude air targets, in 1979 the two-coordinate radar Ture 79 (JTPS-P9) entered service. Like the previous model, it was created by Mitsubishi Electric.
The main elements of the JTPS-P9 radar were located on the chassis of an all-wheel drive two-axle truck, the motor-generator, which provides autonomous power supply, is located in a towed trailer. In working position, the radar antenna is lifted by a retractable telescopic mast.
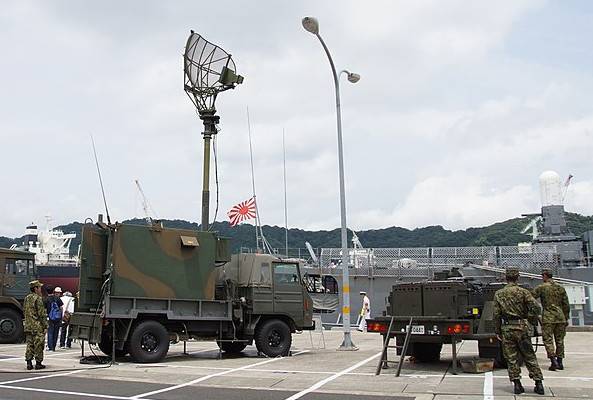

Radar JTPS-P9 in working position
The JTPS-P9 radar operates in the frequency range 0,5–0,7 GHz. At a distance of 56 km, an air target with an RCS of 1 m30 flying at an altitude of 120 m can be detected. The maximum detection range is XNUMX km.
Like the JTPS-P5 radar, the JTPS-P9 stations were part of the radar companies attached to the anti-aircraft artillery and anti-aircraft missile units. But, unlike the JTPS-P5, the JTPS-P9 radar is still actively used by the Japanese Ground Self-Defense Forces.
In 1988, the first three-dimensional radar JTPS-P14 with a phased antenna array entered trial operation. Its manufacturer has traditionally been Mitsubishi Electric.
Despite the fact that the station was adopted for a long time, the exact characteristics of the JTPS-P14 radar have not been disclosed. It is known that the mass of the container with equipment and antenna is about 4000 kg. The radar operates in the decimeter frequency range, the detection range is up to 320 km.
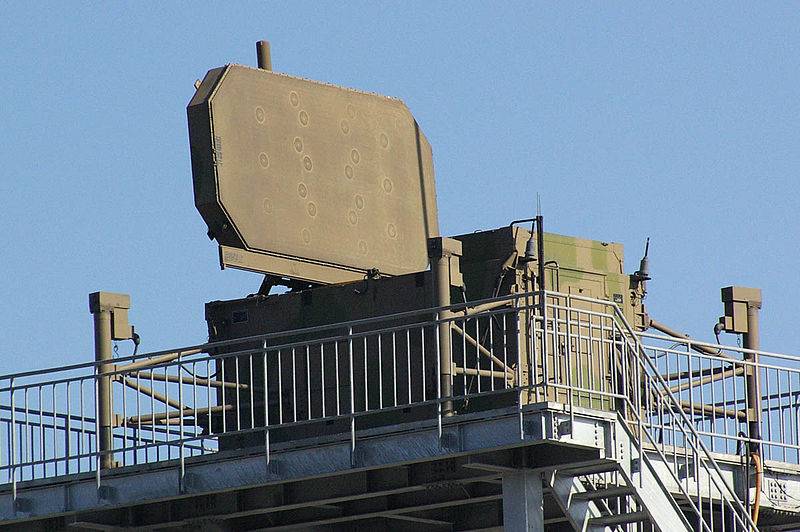

If necessary, the container with the radar can be dismantled from the cargo chassis and promptly delivered by a CH-47J heavy transport helicopter to an area inaccessible to wheeled vehicles. It is known that some of the existing JTPS-P14 radars are installed on the hills in the vicinity of Japanese air bases.
Currently, Mitsubishi Electric manufactures the JTPS-P18 mobile two-coordinate radar, which is designed to replace the JTPS-P9 low-altitude station.
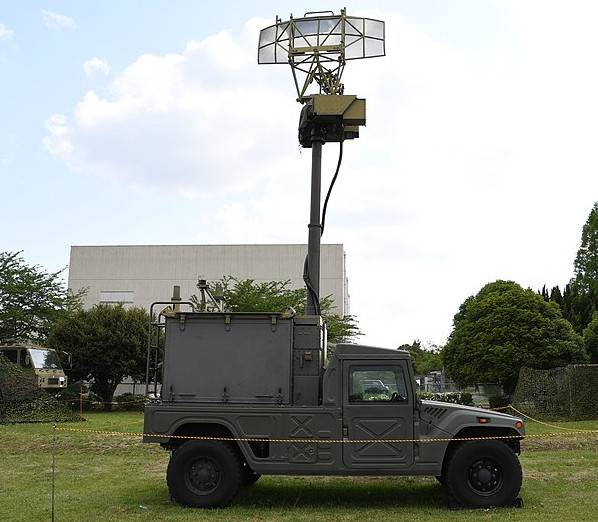

Radar JTPS-P18 in working position
All elements of this radar are located on the chassis of the Toyota Mega Cruiser off-road vehicle. As with the previous generation JTPS-P9 radar, the antenna of the JTPS-P18 radar operating in the centimeter frequency range can be lifted by a special retractable mast. The characteristics of the JTPS-P18 radar are not known, but we must assume that they are at least not worse than that of the old JTPS-P9 radar.
The newest Japanese radar operating in military air defense is the JTPS-P25. This station was officially introduced by Mitsubishi Electric in 2014 and is intended to replace the JTPS-P14. Deliveries to the troops began in 2019.
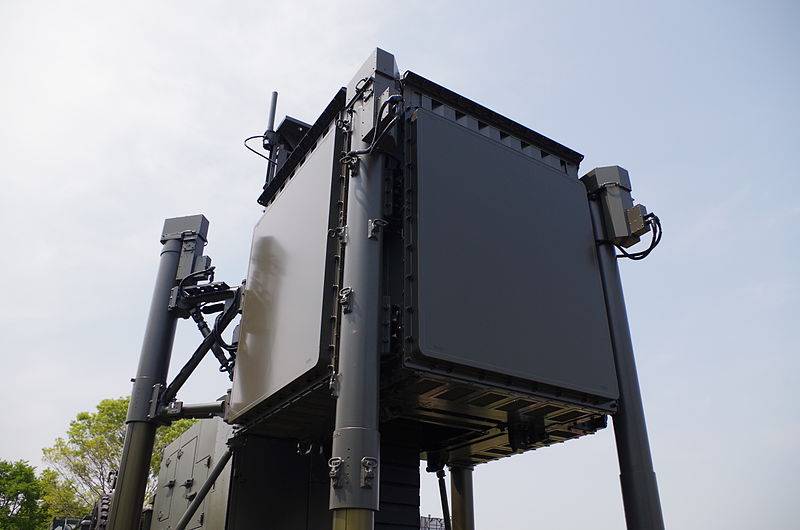

Radar antenna JTPS-P25
The JTPS-P25 radar uses the original scheme with four fixed active phased antenna arrays. All elements of the station are placed on a cargo chassis, unified with the Type 03 air defense missile system. The station mass is about 25 tons.
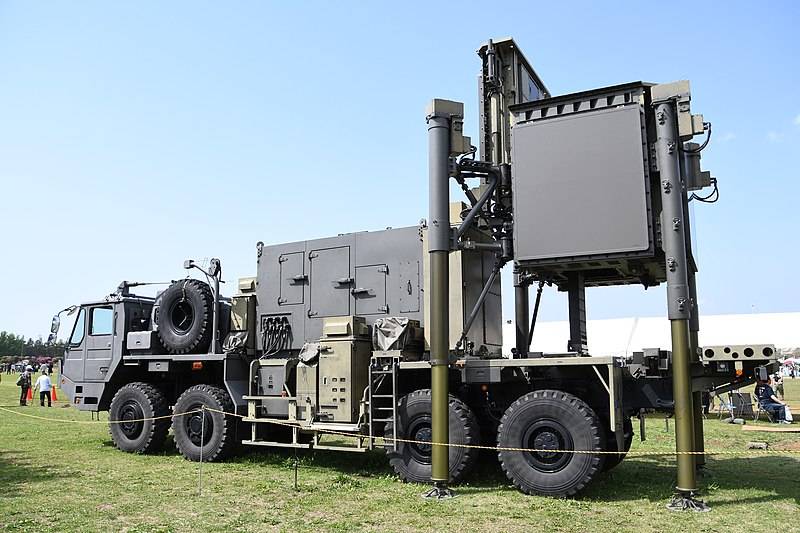

Radar JTPS-P25 in working position
The main purpose of the JTPS-P25 radar is to detect air targets at medium and high altitudes. It is stated that this station, operating in the centimeter frequency range, has improved capabilities when working with targets with a low RCS. The detection range of high-altitude targets is about 300 km.
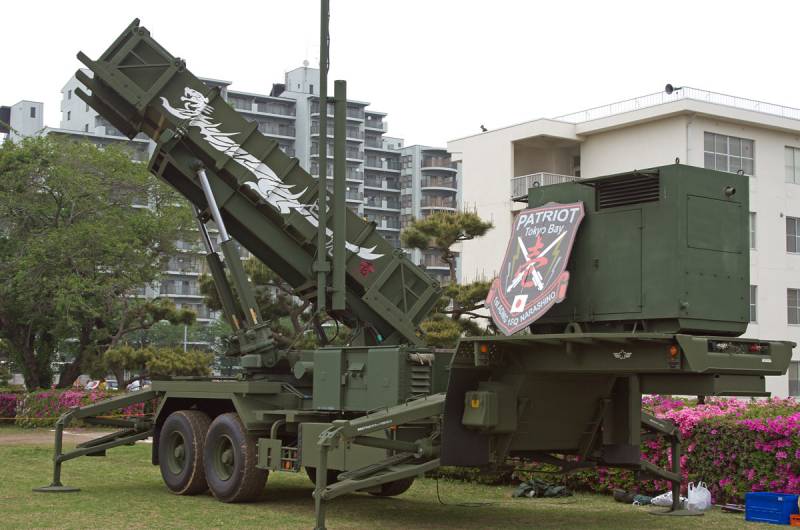
Long-range air defense missile system Patriot PAC-2 / PAC-3
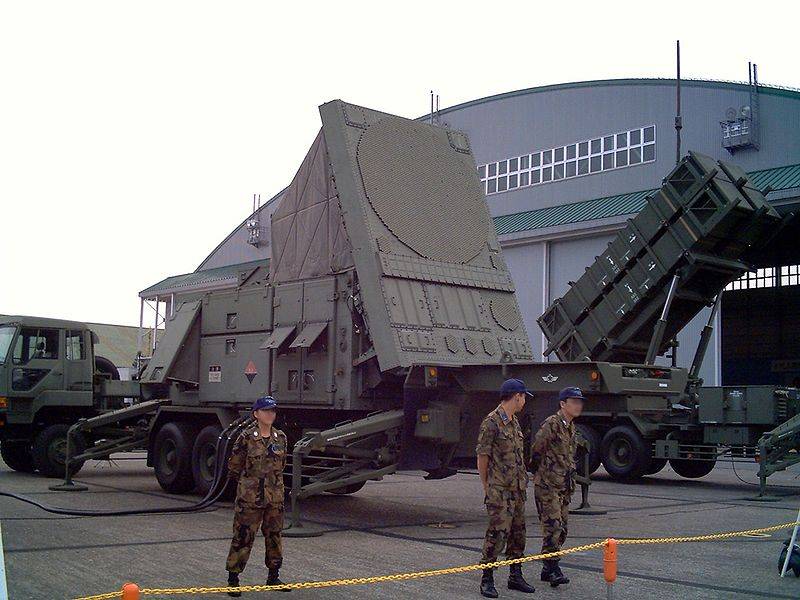

In the period from 1990 to 1996, the Patriot PAC-2 air defense system was deployed in Japan, which replaced the outdated Nike-J long-range single-channel anti-aircraft missile system.
In 2004, an agreement was reached with the United States on the supply of three Patriot PAC-3 air defense systems, but, in connection with the North Korean tests of ballistic missiles, 3 more complexes were subsequently purchased.

Satellite image of Google Earth: the position of the Patriot PAC-3 air defense system at the Iruma airbase, the AN / MPQ-65 radar is clearly visible on the left side of the image
The deployment of the first Patriot PAC-3 air defense system, belonging to the 1st missile group (which includes 4 PAC-2 and PAC-3 batteries), took place at the Iruma airbase in 2007. Two more PAC-3 batteries by 2009 were deployed at the Kasuga and Gifu bases.
In 2010, a modernization program was launched, during which part of the Patriot PAC-2 air defense system was brought to the PAC-3 level. Since 2014, the Patriot PAC-3 has been gradually upgraded to the PAC-3 MSE.
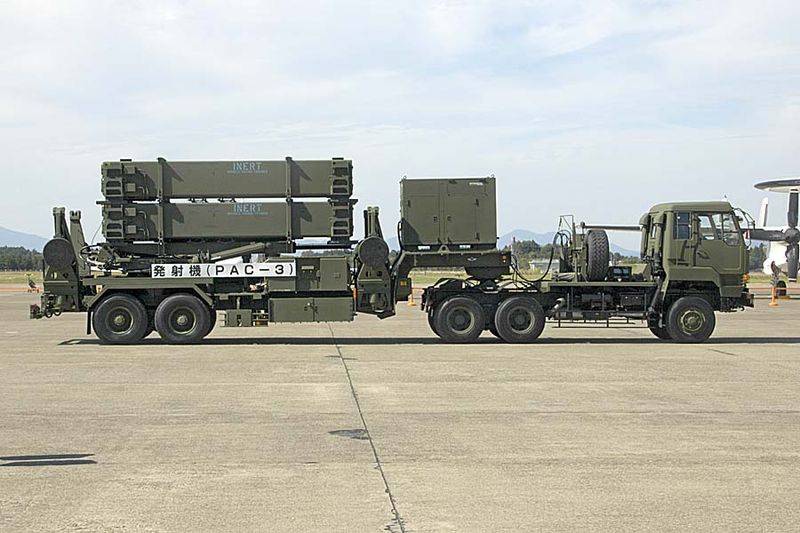

Launcher M902 Japanese air defense system Patriot PAC-3
According to information published in Japanese sources, the six missile groups are armed with 24 PAC-2 / PAC-3 anti-aircraft missile batteries, which include 120 launchers.

Satellite image of Google Earth: the position of the Patriot air defense system based on the Citiura base
However, no more than 20 batteries (10 PAC-2 and 10 PAC-3) are permanently deployed at firing positions. Two air defense systems are being repaired and modernized, two are at the Air Defense Training Center at the Hamamatsu base (one is periodically on duty).

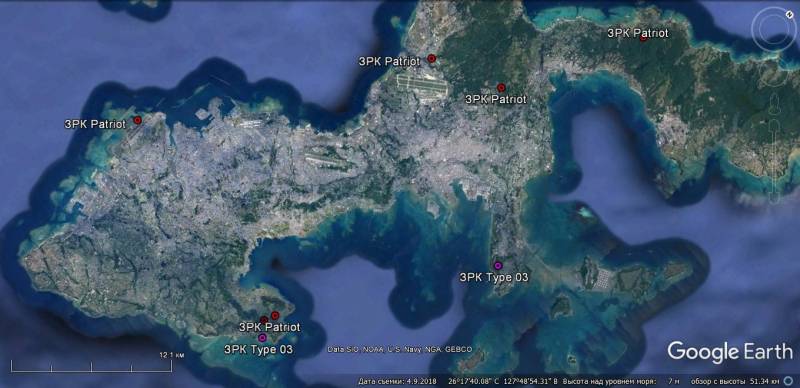
Satellite image of Google Earth: the position of the Patriot air defense system at the Kumure base, about. Okinawa
The publicly available satellite imagery shows that a significant part of the Patriot air defense system is on alert with a truncated composition. Instead of the 5 launchers laid down by the state, there are 3-4 launchers at firing positions.
Apparently, the abnormal number of launchers in positions is due to the fact that the Air Defense Command of the Air Self-Defense Forces prefers to conserve the resource of expensive anti-aircraft missiles and keeps them in warehouses.
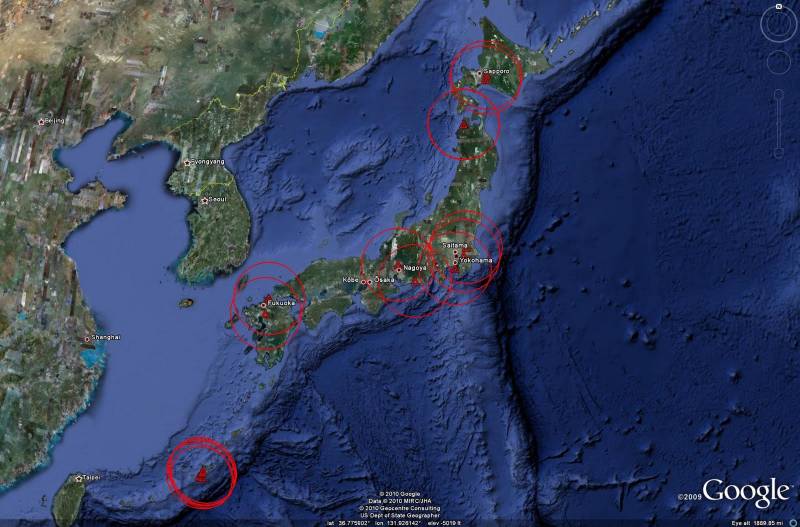
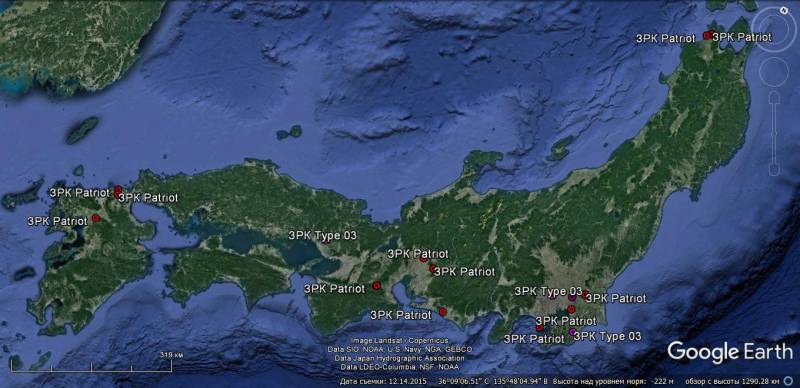
The presented diagrams show that the bulk of Japanese medium and long-range air defense systems are located in the central part of Japan (12 Patriot air defense systems and 4 - Type 03) and on the island of Okinawa (6 - Patriot and 2 - Type 03 ).
On the island of Hokkaido, three batteries of the Patriot air defense missile system and the last three remaining in the ranks of the Hawk air defense missile system batteries cover the northernmost Japanese air base Chitose.
It can be stated that for a country with a relatively small area, Japan has a very developed and very effective air defense system. It is operated by one of the world's best automated control systems and relies on numerous radar posts operating around the clock, providing a multiple overlap radar field. Interception of air targets on long approaches is entrusted to a fairly solid fleet of modern fighters, and the near lines are protected by medium and long-range air defense systems.
Taking into account the covered territory, in terms of the density of the placement of modern air defense systems, Japan occupies one of the first places in the world. In this respect, only Israel and South Korea can compare with the Land of the Rising Sun.
Продолжение следует ...





















Information