Capella Space's All-Seeing Eye: Harbinger of the Satellite Intelligence Revolution
More recently, we have considered the capabilities of space-based reconnaissance assets to detect aircraft carrier strike groups. In particular, the author put forward the assumption of the creation in the near future of "constellations" of compact and inexpensive reconnaissance satellites placed in low orbits and capable of replacing existing large and expensive reconnaissance satellites. Something similar is already happening with communications satellites thanks to Space X and its Starlink global high-speed satellite Internet project.
According to the author's assumption, the technologies used for large-scale construction and deployment of Starlink satellites could subsequently be used for the construction of reconnaissance satellites. Some opponents have objected to this that reconnaissance satellites will be much larger, more complex and more expensive. And this is especially true for active radar reconnaissance satellites, which are of the greatest interest, since they can operate at any time of the day and in any weather.
Well, the future comes earlier than the author assumed. But, unfortunately, this future does not come for everyone.
Capella space
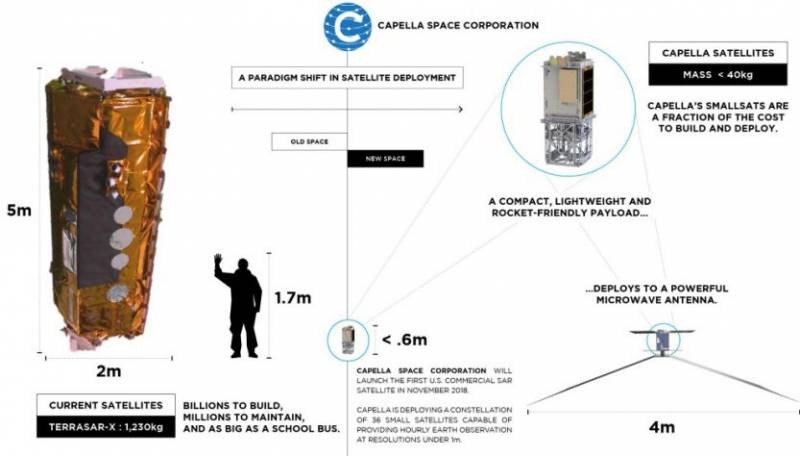
Founded in 2016, the American company Capella Space, based in San Francisco, California, aims to provide users around the world with the ability to obtain high-resolution commercial radar images of the planet's surface.
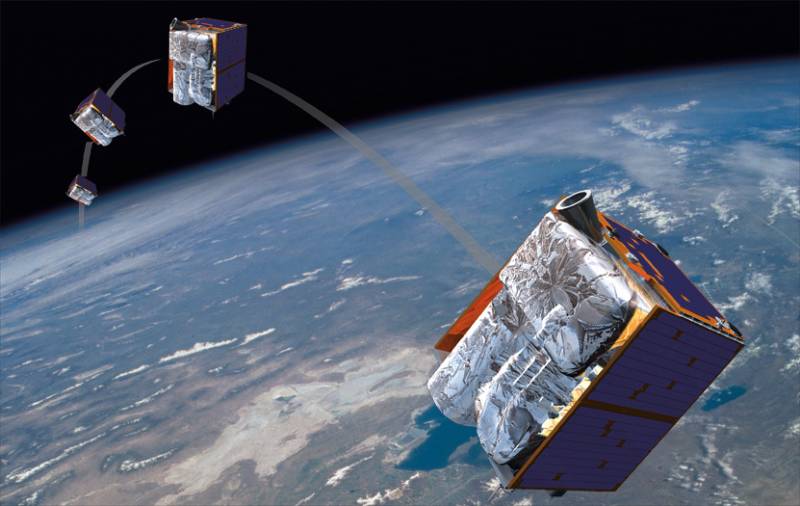
Capella Space plans to deploy 36 satellites equipped with synthetic aperture radar (radar). It was assumed that the mass of one satellite would be about 40 kilograms. The system should allow obtaining radar (RL) images of the earth's surface with a resolution of 50 centimeters.
Moreover, presumably the system is capable of receiving images with a resolution of 25 centimeters and higher, but this opportunity for civilian consumers is still blocked by US law.
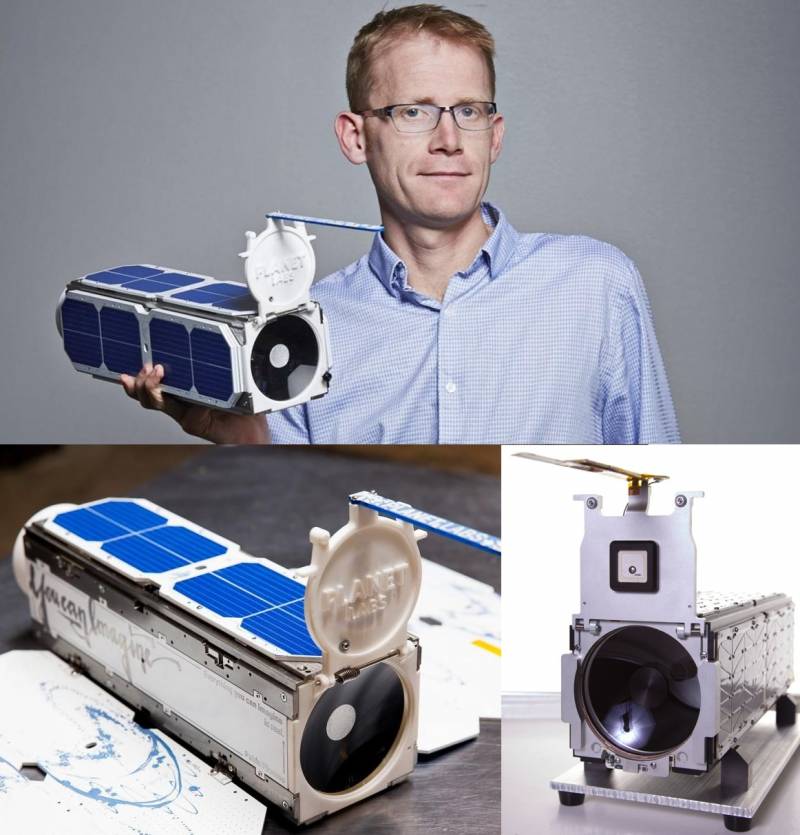
In December 2018, Capella Space launched its first test satellite, Denali, into orbit. The launch was carried out using a SpaceX Falcon 9 launch vehicle from Vandenberg Air Force Base (California).
The Denali satellite is designed to test design and technology. RL images from it were not sold. But they were used for internal testing and attracting investors and potential customers. After launch, the Denali satellite deployed a flexible antenna web covering an area of about 8 meters.
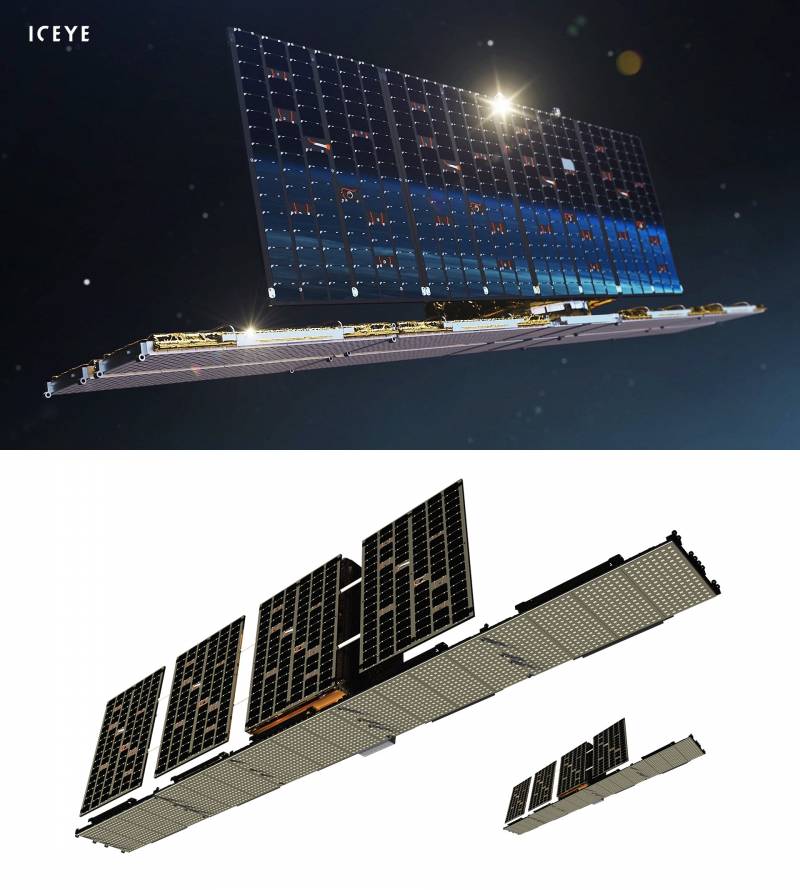
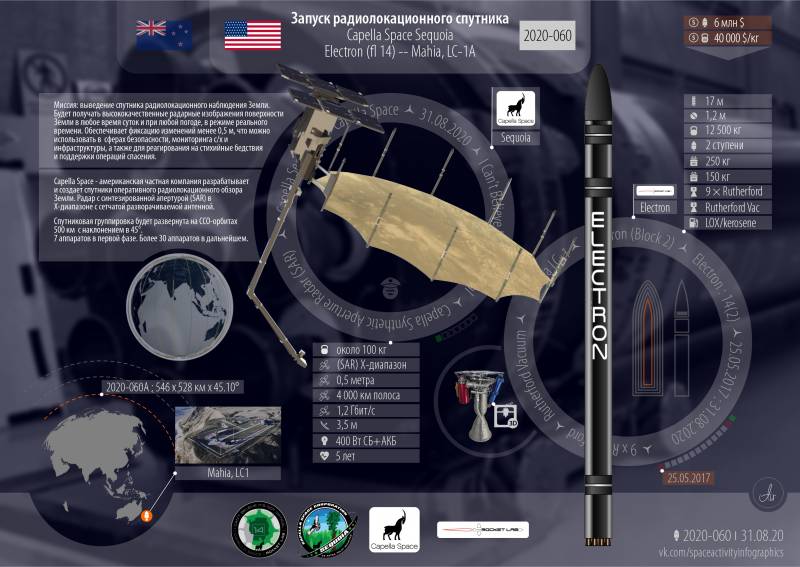
In August 2020, the first serial operational satellite, Sequoia, was launched, which is already capable of providing radar images of the earth's surface to commercial customers. The launch into orbit was carried out by the RN Electron of the private American aerospace company Rocket Lab.
The Sequoia satellite weighs 107 kilograms. It contains 400 meters of cables and wires connecting over a hundred electronic modules. The software includes over 250 lines of C code, over 000 lines of Python code, and over 10 lines of FPGA code.
With an orbital altitude of 525 kilometers and an orbital inclination of 45 degrees, Sequoia satellite provides customers with access to radar imagery in regions such as the Middle East, Korea, Japan, Europe, Southeast Asia, Africa and the United States.
By the end of 2020, it is planned to launch into orbit two more Sequoia RN Falcon 9 satellites from SpaceX. In total, it is planned to launch at least seven satellites of this type.
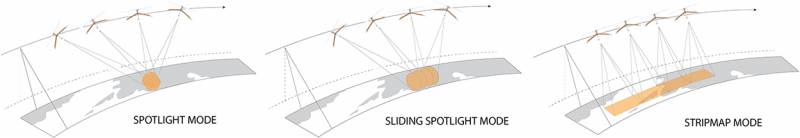
It should be understood that the maximum resolution of the area selected for the survey is provided when the radar image is exposed for about 60 seconds, for which the Sequoia satellites are equipped with a system of mechanical orientation of the antenna web. In-flight clearance will be lower. Synthetic aperture mode allows accurate 3D topography and surface features.
It is assumed that the final constellation of 36 satellites will provide an image of any part of the planet with an interval of no more than one hour.
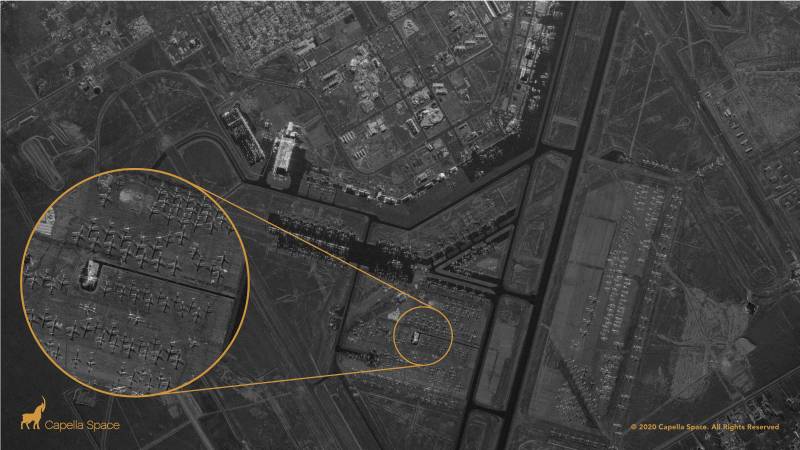

Radar image of McDonnell Douglas MD-80 and Airbus A300-600R aircraft at the Center aviation Roswell in New Mexico.
Capella Space's Sequoia satellite was created in 4 years by a team of 100 people.
Capella Space has already signed contracts for the provision of cartographic information with US government agencies.
In particular, in 2019, an agreement was concluded with the US National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) to integrate commercial radar images obtained by Capella Space satellites with the state-owned NRO observation satellites.
In November 2019, the US Air Force (Air Force) awarded Capella Space a contract to incorporate the company's imagery into Air Force virtual reality software (possibly referring to highly detailed XNUMXD terrain maps for aviation).
On May 13, 2020, a contract was signed with the US Department of Defense to provide airborne synthetic aperture radar data to the US Navy. Capella will also provide the Department of Defense with in-house analytical services to interpret the findings.
And on June 25, 2020 Capella Space announced the signing of the Joint Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) with the US National Geospatial Agency (NGA). The CRADA agreement will provide Capella Space with access to NGA researchers for a deeper understanding of the issues. In return, NGA gets access to Capella Space's imagery and analytics services. This is the first CRADA agreement entered into by NGA with a commercial company providing imagery from synthetic aperture radar satellites.
Of course, Capella Space satellites cannot be considered direct analogues of the sophisticated and expensive reconnaissance satellites launched by the leading military-industrial powers. But something else is important here.
A 100-person company has developed and manufactured satellites capable of receiving high-resolution radar images. This company plans to deploy a constellation of 36 such satellites. The size and mass of these satellites allows them to be launched into orbit in clusters, as is the case with Starlink communication satellites. This makes it possible not only to quickly build up their grouping in orbit, but also to urgently launch them, if necessary, with midget launch vehicles.
If only a private startup company is capable of this? How many such or similar satellites can the US Department of Defense launch, if necessary?
By the way, Capella Space is not the only one working in this direction.
ICEYE
The Finnish company ICEYE was founded in 2014 as a subsidiary of Aalto University, Faculty of Radio Technology.
Since 2019, ICEYE has been offering services for obtaining high-resolution commercial radar images obtained using three proprietary satellites. The first ICEYE-X2 satellite was launched on December 3, 2018 by SpaceX's Falcon 9 launch vehicle, and two more satellites were launched on July 5, 2019.
It is assumed that with the commercial success of the project, several more satellites will be launched annually.
The mass of one satellite is 85 kilograms. It is equipped with ion thrusters for orbit correction. The resolution of the radar images is 0,25x0,5, 1x1 or 3x3 meters, the alignment accuracy is 10 meters, the communication channel speed is 140 megabits per second. The orbital altitude is 570 kilometers, inclination is 97,69 degrees.
Planet Labs
The American company Planet Labs, founded in 2010, develops and manufactures CubeSat-type microsatellites called Dove, which are delivered into orbit as an auxiliary payload for other missions.
Each Dove satellite is equipped with state-of-the-art optical reconnaissance systems programmed to survey different parts of the Earth. Each Dove observation satellite continuously scans the Earth's surface, sending data after passing over the ground station.
The first two experimental Dove satellites were launched in 2013.
Following the acquisition of the German company BlackBridge AG, the Planet Labs satellite constellation has been expanded with RapidEye satellites. And after the acquisition of TerraBella from Google by the SkySat constellation.
In July 2015, Planet Labs placed 87 Dove satellites and 5 RapidEye satellites into orbit. In 2017, Planet launched 88 more Dove satellites. By September 2018, the company had launched about 300 more satellites, 150 of which are active. In 2020, Planet Labs launched six additional high-resolution SkySats and 35 Dove satellites.
Dove satellites weigh 4 kilograms. Their dimensions are 10x10x30 centimeters, the orbit height is 400 kilometers.
The satellites provide images with a resolution of 3-5 meters.
RapidEye satellites weighing less than one cubic meter and weighing 150 kilograms, located at an altitude of 630 kilometers, provide an image with a resolution of 5 meters using a multispectral sensor in blue (440-510 nm), green (520-590 nm), near red (630 –690 nm), far red (690–730 nm) and near infrared (760–880 nm) wavelength ranges.
SkySat satellites provide sub-meter resolution video images. Their design is based on the use of inexpensive, commercially available electronic components.
SkySats are about 80 centimeters long and weigh about 100 kilograms.
SkySat satellites are in orbit at an altitude of 450 kilometers and are equipped with multispectral and panchromatic sensors. Spatial resolution in the panchromatic range of 400-900 nm is 0,9 meters.
The multispectral sensor collects data in the blue (450-515 nm), green (515-595 nm), red (605-695 nm) and near infrared (740-900 nm) ranges with a resolution of 2 meters.
Do we have something similar?
Russian private cosmonautics
The successes of Russian private astronautics are much more modest.
First of all, one can recall the SPUTNIX company founded in 2011, which in 2014 launched into low-earth orbit the first Russian private microsatellite-technological demonstrator Tablettsat-Aurora weighing 26 kilograms.
As the main payload, the vehicle is equipped with a panchromatic camera for photographing the earth's surface in the spectral band 430-950 nm with a resolution of 15 meters and a swath width of 47 kilometers.
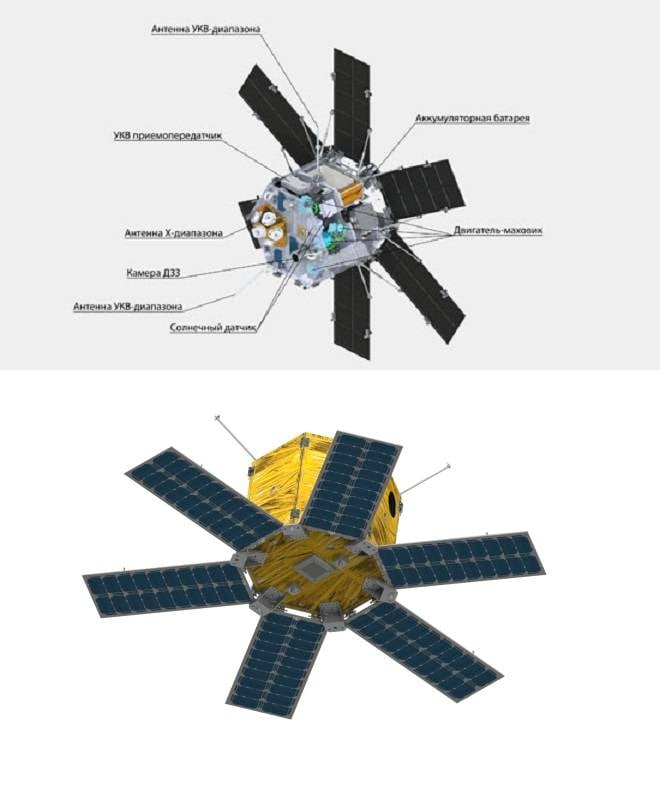
Microsatellite Tablettsat-Aurora
Also, several scientific and educational nanosatellites developed by students and schoolchildren were launched.
Among the devices under development, the ultra-compact satellite for remote sensing of the Earth RBIKRAFT-ZORKIY can be noted.
Its weight will be 10,5 kilograms. The launch is scheduled for 2021.
The device will carry a telescope camera with a resolution of 6,6 meters per pixel, produced by NPO Lepton. The camera is equipped with a thermal stabilization and focusing system, as well as a built-in memory device, which allows shooting on demand, without being bound to receiving stations.
The estimated orbital altitude of the RBIKRAFT-ZORKY satellite will be 550 kilometers with an inclination of 98 degrees.
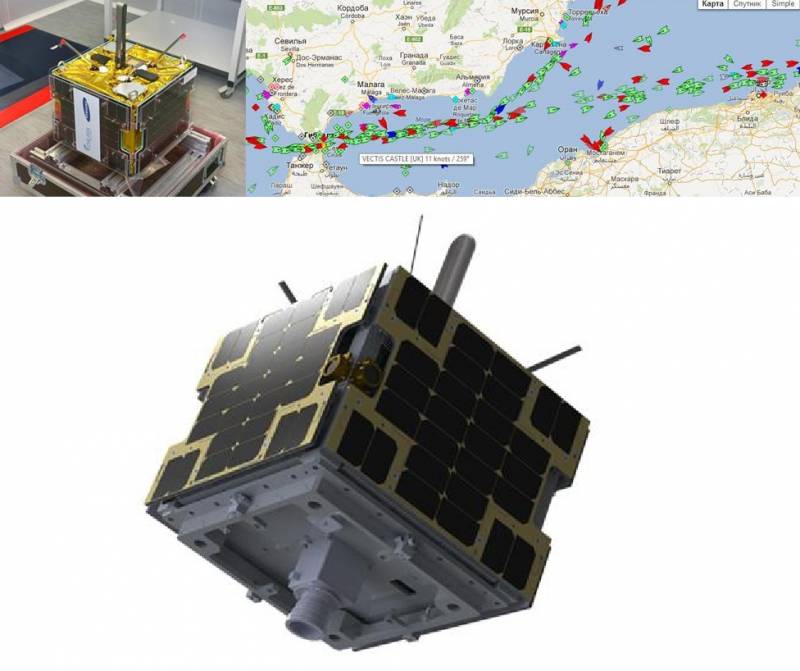
Another company is OOO NPP Dauria Aerospace, founded in 2011 and becoming one of the first Russian companies to create and launch commercial satellites.
On July 8, 2014, Dauria Aerospay launched the first satellite of the DX series equipped with a payload for receiving and transmitting signals from the Automatic Identification System, designed for navigation and identification of ships in the World Ocean and on river lines.
By the way, such satellites can be useful when working in conjunction with satellites for radio engineering, optical and active radar reconnaissance in terms of solving the problem of selecting civil and military ships.
Two more satellites, PERSEUS-M1 and PERSEUS-M2, were sold to the American Aquila Space at the end of 2015.
In the same 2015, Mikhail Kokorich, founder of NPP Dauria Aerospay LLC, sold his share in the company and emigrated to the United States.
As we can see, our lag in the field of commercial satellites from the leading countries of the world is about 10-15 years.
Formally, there are companies that manufacture components for satellites - ion engines, sensors, electronic components. But the creation of a production facility that produces final products - high-tech satellites - somehow does not grow together.
We have a similar situation with launch vehicles. In general, we have nothing comparable to Spaсe X or Capella Space yet.
Conclusions
Space commercialization is developing at the highest rates, both in terms of placing payloads into orbit and in creating artificial earth satellites for various purposes. It can be noted that the trend of commercialization of space was outlined at the beginning of the XNUMXs and has become explosive in the last decade. Taken together, this has allowed the emergence of equipment, technologies and services, not only recently available not only for commercial, but also for government customers.
In this light, the prospect of the deployment by the US armed forces of hundreds or even thousands of reconnaissance and communications satellites, and in the future also satellites of the anti-missile defense (ABM) system, no longer raises any doubts.
What does this mean for us in practical terms?
It can be argued that from a certain moment, as an increasing number of reconnaissance satellites of various classes and purposes are deployed, as well as their technical characteristics improve, it will become almost impossible to avoid the detection of many types of weapons from space.
The ability to obtain global, round-the-clock and all-weather intelligence data, in near real time, will allow high-precision strikes weapons and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to the entire depth of enemy territory, not only for stationary, but also for moving targets, re-targeting weapons in flight.
Under threat will be mobile ground-based missile systems (PGRK), which make up one of the elements of the Russian nuclear deterrent forces (SNF), and surface ships of the traditional layout will lose the slightest opportunity to get lost in the depths of the ocean, which means that long-range enemy aircraft will always have the initiative and will be able to provide the necessary concentration of forces for a strike by anti-ship missiles (ASM), sufficient to overcome the air defense (air defense) of aircraft carrier and naval strike groups (AUG and KUG).
If the United States officially legalized the sale of images from space with a resolution of 50 centimeters, then what resolution is available to the military - 25, 10 centimeters or less?
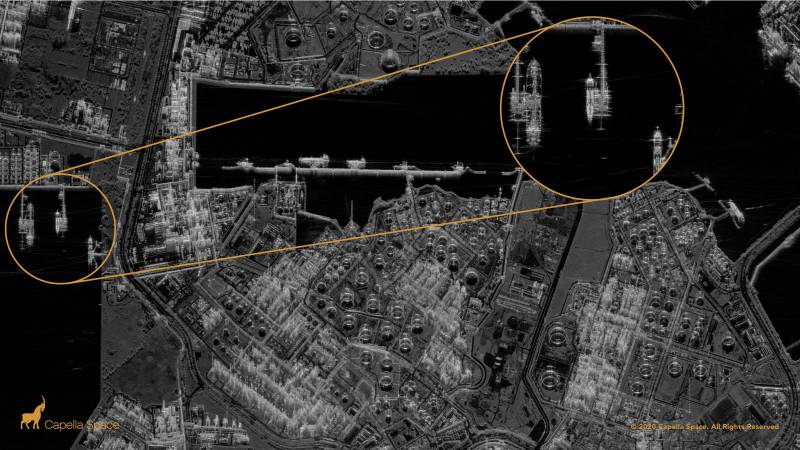
With this image quality, no corner reflectors will help. For example, when attacking ships, their initial detection can be carried out with a resolution of 3–5 meters, then identification with a resolution of 50 centimeters or less will be performed. And after that, after the launch of the anti-ship missile system, ships can be tracked and their coordinates transmitted in real time directly to the anti-ship missile system via a satellite communication channel (retargeting in flight).
Someone will say why not use electronic warfare?
They can solve some of the problems, but not all. Electronic warfare equipment itself is a "beacon" for the enemy; it is impossible to use them continuously. In addition, optical reconnaissance equipment remains.
It is practically unrealistic and economically ineffective to destroy a network of small-sized satellites from the surface - it is possible to replenish the group of small-sized satellites with less economic losses than to shoot them down with missile defense missiles. This requires specialized space interceptors capable of intensive maneuvering and being in orbit for a long time, ensuring the consistent destruction of many targets.
And do not rely on the common misconception about "a bucket of nuts in orbit." The entire economy of the planet will not be able to transport "nuts" into orbit in an amount sufficient to destroy satellites.
Improvement of technologies for creating small satellites and missile defense technologies, with a high probability will lead to the resumption of implementation at a new technical level projects of orbital missile defense interceptors of the "diamond pebble" type, which, taking into account the strengthening of intelligence and percussion capabilities of the US armed forces can largely neutralize the potential of Russian strategic nuclear forces.
At the end of the XNUMXth century, much was said about the fact that the XNUMXst century will be the century of virtual reality, nano- and biotechnology. Space, on the other hand, has become "everyday-applied", associating with something like satellite TV.
The emergence of private companies with ambitious goals and projects changed everything. And space again found itself at the forefront of technological progress.
Space is not only projects of scientific research and human expansion into new territories, but also a cornerstone in ensuring the security of the state. Even now, without gaining an advantage, or even parity in outer space, any ground, air and sea forces are doomed to defeat. In the future, this situation will only get worse.
This makes projects for the creation of promising launch vehicles and spacecraft for various purposes among the most high-priority tasks of our country.














Information