Remove from the geostationary. Is the famous NPO Mashinostroyenia developing space weapons for high orbits?
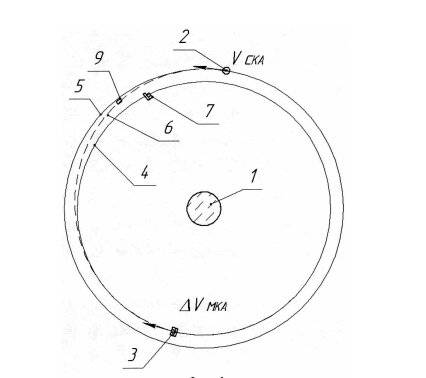
Legend:
1 - Earth;
2 - "Targetable", that is, the attacked spacecraft (the direction of the linear flight speed VСКА is shown by the arrow);
3 - MCA (direction of linear flight speed (shown by an arrow) at the moment of detachment of one autonomous maneuvering module and imparting an impulse ΔVMKA to the autonomous maneuvering module);
4 - MCA standby orbit;
5 - GSO;
6 - transfer orbit of autonomous maneuvering module flight;
7 - small spacecraft after separation of the autonomous maneuvering module;
8 - MCA, base unit;
9 - autonomous maneuvering module.
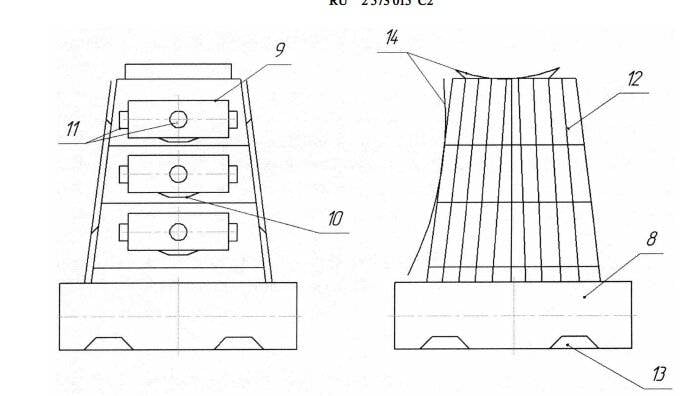
Legend:
10 - homing head of the autonomous maneuvering module;
11 - propulsion systems of the autonomous maneuvering module;
12 - MCA power plant;
13 - propulsion system MKA;
14 - onboard means of observation of the small spacecraft for the target.
Who is Herbert Alexandrovich Efremov, now very many know. Hero of Labor, Hero of Socialist Labor, Knight of the Order of Lenin, the Order of St. Andrew the First-Called with swords, and many other Soviet and Russian awards and state awards, 87-year-old professor, honorary general director and general designer of JSC MIC "NPO Mashinostroyenia" - and that's all about him, about Efremov. Recently, he communicated with the President and Supreme Commander-in-Chief of the RF Armed Forces V.V. Putin via video link (for obvious reasons), where he informed him that he had been awarded the highest award of Russia. In the conversation, Putin compared the creation of the Avangard system (a planning winged unit, PKB, 15Yu71 for the 15A35-71 ICBM) with the conquest of space. At one time, the author of this article also compared the creation of such systems weapons with the same, therefore it is pleasant to agree with the head of state himself.
Herbert Efremov's merits, of course, will be enough for ten: the creation of KR and anti-ship missiles P-5, P-6, P-35, 3M44 "Progress", 3M25 "Meteorite", P-500 "Basalt", P-1000 "Vulkan" , P-700 "Granit", P-800 "Onyx", 3M22 "Zircon", ICBMs of the "hundred" series - UR-100, UR-100K, UR-100U, UR-100N, and UR-100NUTTH (15A35, which now turns into "Vanguard"). He was also engaged in space technology - "Almazy", satellites "Condor". But it turns out that Herbert Alexandrovich was engaged and certainly has a relationship now to work, also related to space. But, how to say it, with an approach from the other side.
De-orbit
In 2014, in April, when the well-known events took place with the return of Crimea to its native harbor and the beginning of the uprising in Donbass, a patent application 2014114880/11 was filed by Efremov and a number of his colleagues (Leonova A.G., Palkina M.V. and others), the patent holder for it was JSC "MIC" NPO Mashinostroyenia ". The invention was called "a multi-module spacecraft for cleaning the geostationary orbit (GSO) and a method for cleaning the geostationary orbit." A seemingly peaceful and useful invention. Indeed, the GSO, unlike the other orbits, is very densely populated, because it is, in fact, one. "Clark's Belt" (as it is often called in the West, since the future great science fiction writer Arthur Clark predicted this orbit back in 1945) is packed with satellites, the number of points allocated to each state is also limited. Satellites with expired SAS - the period of active existence, on the geostationary it is supposed to withdraw from these points to the so-called. a disposal orbit several hundred kilometers above the GSO. But this does not always work out - the satellite may break down, communication with it cannot be established, etc. Such a satellite cannot go out of orbit on its own, under the influence of the remnants of the atmosphere, it is not 400 km, but 36000 km. So the issue of cleaning this particular orbit is quite relevant and the relevance will only increase.
So what is offered and developed at NPO Mashinostroyenia? After all, such applications for patents in our defense industry are most often written when the idea is already in active work and the result is not far from practical implementation. Let's turn to the patent.
A bit of history
But at the same time, interestingly, Efremov and his comrades do not refer to peaceful experience, but to the work of "maneuvering satellites", as they were modestly called in those years, that is, interceptor satellites. There were many of them: Polet, IS, IS-M, IS-MU. In principle, of course, the task of rapprochement is the task of rapprochement, for whatever purpose it may be carried out, but, of course, this is not the only issue. First of all, what is being developed at NPOM is a combat anti-satellite system for geostationary, geosynchronous orbits, orbits of satellites of global navigation systems (20 thousand km). At one time, the USSR bypassed all the circles by two in the anti-satellite race, an anti-satellite system based on interceptor satellites was created and improved and stood on alert, which reached the modification of the IS-MU, and the IS-MD was prepared specifically for the geostationary ... then the Union collapsed ... In low orbits, spacecraft interceptors have lost their relevance, and the new anti-space defense systems being tested by Russia are usually built on different principles.
The fact is that there are a lot of satellites in orbit and there are more and more satellites, and the interception system based on space rockets and the killer satellites they launch, not even disposable exploding like ISs, but equipped with some kind of reusable weapon, simply cannot organize a large-scale attack quickly and with the desired scope. We need other systems with greater efficiency and scale of application. These are either anti-missiles with an additional anti-satellite function (from the A-235 missile defense system, the Nudol long-range intercept missile, 77N6 from the S-500), or complexes for blinding and disabling equipment on the spacecraft of the enemy reconnaissance group (Peresvet, which is already covering many missile divisions of the Strategic Missile Forces with PGRK, and air-based Sokol-Echelon-2). There is also an airborne anti-satellite missile called the Burevestnik (not to be confused with the well-known nuclear-powered missile launcher, presumably having the 9M730 index), which "shone" under the MiG-31BM.
In the West, researchers write that the "inspector satellites" known to many, now actively tested by Russia, are in fact reusable interceptors, and they should be withdrawn normally by the "Petrel", at least some of the "inspectors" being tested. Well, perhaps it is. Perhaps the Petrel is using a disposable interceptor, say kinetic or explosive.
But in any case, such systems are capable, if desired, of organizing an attack on dozens and perhaps hundreds of satellites in low orbits at once. But there is also a geostationary. There are fewer satellites, but they are in the outset of a large-scale war (and no one will attack the enemy under any other spacecraft, the attack on the orbital grouping itself is already a "casus belli") are no less important. Efremov and his colleagues obviously offer their own solution.
Work principles
Let's turn to the patent. It says that there are different ways of bringing two automatic spacecraft closer together in order to de-orbit one of them and devices for this purpose. The first method was used for spacecraft of the IS series, it consists in placing the IS spacecraft into an orbit close in its parameters (inclination, longitude of the ascending angle, perigee argument, altitude, eccentricity) to the target spacecraft orbit in the period immediately preceding its use. ... In flight, the IS, making maneuvers on commands from ground control points, moves to an area close to the location of the target, detects it using an airborne radar seeker, and autonomously carries out final guidance. The disadvantages of this method are the high costs of the characteristic speed for maneuvering to reach the target area (up to 1/3 of the onboard fuel supply) and, in this regard, the impossibility of repeated maneuvers to another target. In addition, the satellite will simply self-destruct, but now we are not talking about the method of defeat.
But there are also less energy-intensive devices and methods for de-orbiting several spacecraft by interacting with them, including on a collision course. For example, by shooting (launching) unguided rockets from a space-based carrier (as planned in the Brilliant Pebbles missile defense system, and the remaining stillborn). The disadvantages of the system are that the missiles have no GOS and control on the trajectory, which leads to their increased consumption, the need to find the carrier in close proximity to the target, the impossibility of changing target designation after launching the shells. For ground-based or sea-based anti-satellite missiles and anti-satellite missiles, a method is possible in which the carrier rocket accelerates a maneuvering combat stage with a seeker and engines, which is aimed at the target, hitting it either kinetically or by exploding the warhead. The rocket brings the combat stage, maneuvering the spacecraft, to the calculated point of capture by the homing head of the target satellite, including on collision courses, after which the maneuvering spacecraft maneuvers to approach and de-orbit the target (disable the target).
The disadvantage of this method is the critical dependence of the result of the maneuvering spacecraft on the accuracy of the missile reaching the target location area, the impossibility of changing target designation after the launch of the carrier rocket from the Earth, the impossibility of using such an apparatus for several targets.
The aim of the present invention is to create a spacecraft device for cleaning the geostationary orbit from anthropogenic objects due to the kinetic energy of collision and the cleaning method, characterized by the possibility of flexible changes in the flight program (selection of a new target), information from orbit of several spacecraft, reduced costs of the characteristic speed for maneuvers.
This goal is achieved by the fact that the spacecraft (SC) for cleaning the GSO from anthropogenic objects, containing a propulsion system with fuel reserves, a power plant and a control system with a complex of means for observing and determining the parameters of the motion of a spacecraft being de-orbited (SCA), is designed as its board houses at least one autonomous maneuvering module with a propulsion system, a control system, a homing head, a payload, with the ability to separate the module at a given time.
I will translate it from patent language into human language: the interceptor satellite is equipped with space-to-space homing missiles or is itself a block of such missiles. By the way, at one time in the USSR they tested not only a 23-mm cannon of a special modification for destroying enemy spacecraft, but also developed a similar "space-to-space" rocket based on the smallest in the world (in those days, and now, too, if you do not take SAM MANPADS used in this capacity) UR "air-to-air" type R-60 / 60M. But the topic was then abandoned for some reason.
The scheme of operation of a satellite interceptor on the GSO will look like this. We launch the interceptor spacecraft into a standby orbit close to the GSO, say, under the guise of a peaceful spacecraft. The orbit should be opposite to the attacked grouping of the enemy spacecraft. Why are we launching an attacking "multi-module stage" (the MCA in the patent is a multi-module spacecraft). From the control point we transfer data on the coordinates of targets, movement elements and the time of the predicted physical contact to the spacecraft. When a small spacecraft passes through a standby orbit for more than one orbit, using the spacecraft equipment, they autonomously find the assigned targets and refine the parameters of their orbit, calculate the parameters of the maneuver for physical contact with the target or targets, separate one (several) "autonomous maneuvering modules" (rockets) to perform the maneuver , physical contact (attack, hitting the target) with the target spacecraft and "removing it from orbit" (elimination). The attack can be carried out both sequentially against several targets, and, in the case of the proximity of the physical location of targets and elements of their movement, simultaneously.
The movement in the orbit of the interceptor vehicle (MCA) on duty until the time of the maneuver (attack signal) received by the commands from the Earth is carried out in the mode of reduced power consumption or temporary deactivation of at least one technical system (the so-called MCA sleep mode) ... In principle, the device can generally pass itself off as broken.
Moving along the turns of the duty orbit, the small spacecraft autonomously determines and maintains a given inclination and altitude relative to the geostationary orbit (orbits of the target or targets). While the small spacecraft is in the standby orbit, the ground control stations determine the coordinates of the spacecraft intended for "information" and transmit them to the spacecraft; the parameters of the time (time interval) of the target "information" maneuver with the GSO are also transmitted. Upon receiving the aforementioned information from the Earth, the spacecraft automatically calculates the time to recover from the "sleep mode", selects the module that will attack the target. After exiting the "sleep mode" with the use of onboard surveillance equipment, the spacecraft autonomously identifies the target in the GSO, specifies the parameters of its movement, calculates the time, direction and magnitude of the thrust impulse for maneuvering the corresponding module on the GSO and physical contact with the target.
In the event of receiving information from the ground control points about the change in the choice of the spacecraft being brought down from the GSO, the MCA recalculates the maneuver parameters of the autonomous maneuvering module. After separation from the multi-module spacecraft, if necessary, repeated rendezvous for the purpose of rendezvous or rendezvous with another target (set by commands from the base unit of the small spacecraft), the autonomous maneuvering module (rocket) independently calculates and maneuvers temporarily out of the geostationary orbit and maneuvers back to the area where the spacecraft is located.
After separation and departure of all modules for rendezvous with the spacecraft to be brought down, the small spacecraft (base unit) can remain in the standby orbit, make rendezvous and contact with the selected target on the GSO; to perform a maneuver to transfer to a burial orbit or a maneuver from Earth orbit.
Of course, the implementation of this technology will make it possible to reach the enemy's spacecraft in high orbits, which until now was a practically unrealizable task, but in itself was in demand, since we are engaged in large-scale anti-satellite systems of both destructive and non-destructive action. So let’s wait for "signals" to say that something like this is already being tested.
Information