NGSW Advanced Small Arms Program: Causes, Current and Expected Results
The origins of the problem
Currently in service with the largest armies in the world, assault rifles and automatic rifles, such as a Kalashnikov assault rifle or M-4 / M-16 rifle family, either have their pedigree since the mid-20th century, or, although they are based on new materials and design solutions, practically do not differ from them in their characteristics.
The main problem is that over time, the main ammunition used in machine guns is still intermediate cartridges of the caliber 5,56x45 mm, 5,45x39 mm and 7,62x39 mm. Periodically, disputes arise between adherents of the calibers 5,45x39 mm and 7,62x39 mm, but in fact this is the notorious replacement of sewed soap. Each cartridge has its own advantages and disadvantages, which are manifested in certain regions and scenarios of warfare.
A complicating factor is the rapid improvement of personal protective equipment (NIB). In particular, the use of ceramic armored elements, for example, of boron carbide, can significantly reduce the effectiveness of small arms of calibers 5,56x45 mm, 5,45x39 mm and 7,62x39 mm.
For example, the Russian military equipment of the Ratnik soldier includes the 6B45 body armor that can withstand ten hits from the SVD with an armor-piercing incendiary cartridge.
Given this, it can be assumed that the cartridges 5,56x45 mm, 5,45x39 mm and 7,62x39 mm have almost exhausted their modernization potential, and the scales in the opposition of the "sword and shield" began to lean towards the "shield".
The lack of effectiveness of the cartridges 5,56x45 mm, 5,45X39 mm and 7,62x39 mm led to the appearance in certain units of the US armed forces of rifles of the caliber 7,62x51 mm, designed to engage the enemy at a longer range than that of weapons of caliber 5,56x45 mm. For example, the US Special Operations Forces (MTR), as part of the purchase of Belgian FN SCAR rifles, refused to purchase the SCAR-L modification of the 5,56x45 mm caliber, focusing on the purchase of the SCAR-H modification of the 7,62x51 mm caliber.
In response to the demands of the armed forces for an increase in firepower, the German company Heckler & Koch also introduced the HK417 7,62x51 mm rifle, in addition to the 416x5,56 mm HK45 rifle.
However, all of these solutions can only increase the range of target destruction, but do not solve the issue of target destruction, protected by modern and promising NIB. Negative factors are also the reduction in wearable ammunition due to the increased mass of cartridges 7,62x51 mm compared to cartridges 5,56x45 mm, and higher recoil of the weapon.
Thus, having fully felt the flaws of the 5,56x45 mm caliber in Afghanistan, as well as being impressed by the progress in creating LEDs in Russia and China, the USA decided to significantly increase the firepower of the fighters due to the creation of a completely new weapon-cartridge complex, and began Next Generation Squad Weapons (NGSW) program - (new generation squad small arms).
NGSW Program: Ammunition
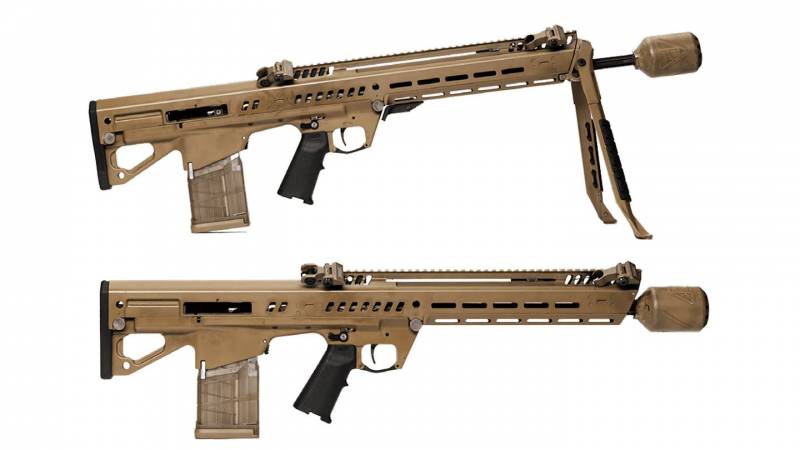
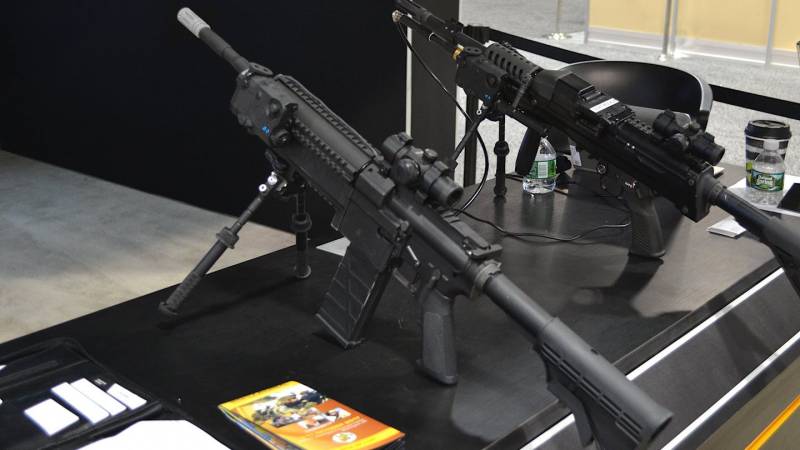
The NGSW program includes the creation of the Next Generation Squad Weapon Rifle (New Generation Squad Weapon Rifle), designed to replace the M-4 rifle, and the Next Generation Squad Weapon Automatic Rifle (New Generation Squad Weapon Automatic Rifle), designed to replace M249 machine gun. Companies including VK Integrated Systems, Bachstein Consulting and MARS Inc. took part in the competition. and Cobalt Kinetics, AAI Corporation Textron Systems, General Dynamics-OTS Inc. and Sig Sauer Inc.
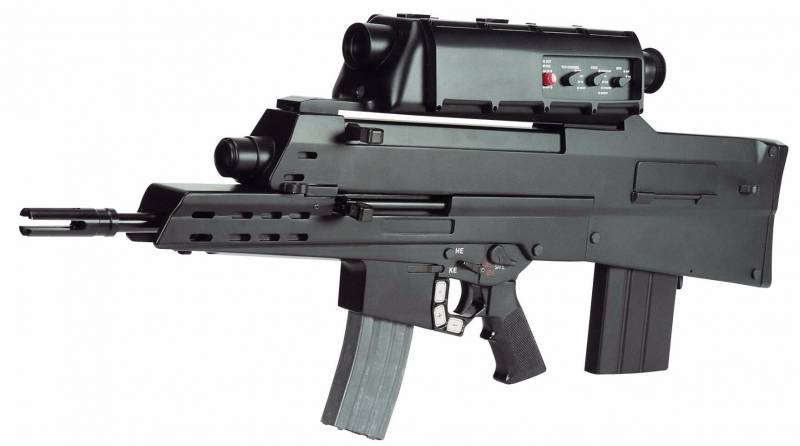
In principle, such programs have been carried out by the U.S. forces more than once, of the latter we can recall the Objective Individual Combat Weapon (OICW) program, in which an attempt was made to develop a small-grenade launcher system including an 5,56x45 mm caliber assault rifle and an 20-mm automatic grenade launcher.
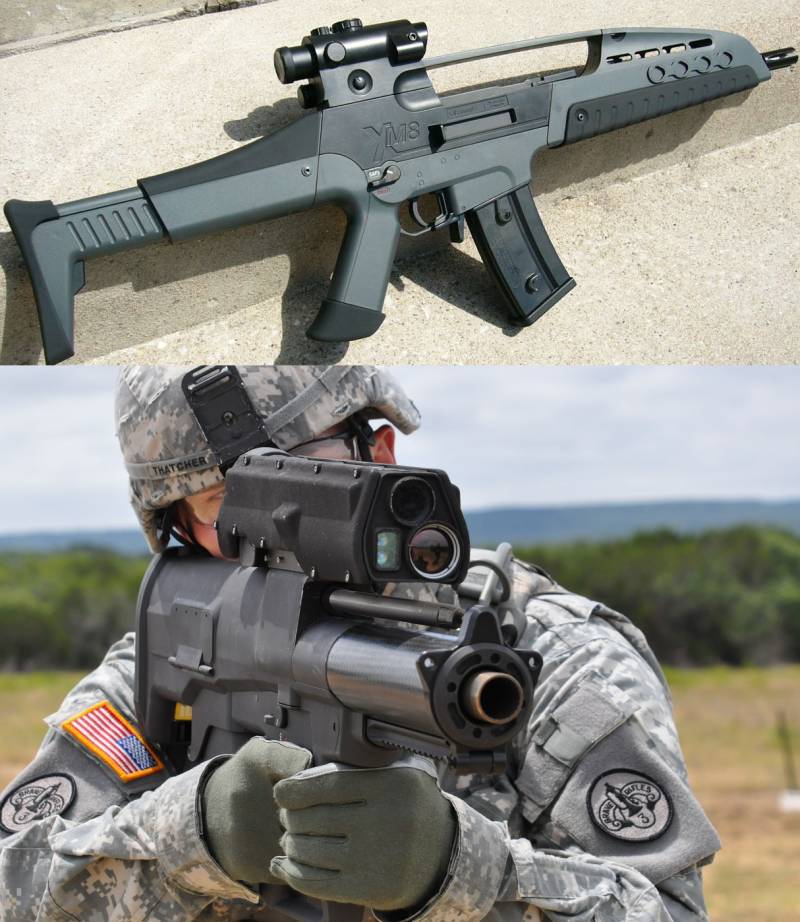
The complexity, high cost and unsatisfactory characteristics of the grenade launcher complex led to the separation of the OICW program for the creation of a separate XM8 modular machine gun of the 5,56x45 mm caliber and the XM25 self-loading grenade launcher of the 25 mm caliber. Ultimately, all of the above programs were closed despite the fact that the XM25 grenade launcher managed to be noted in Afghanistan, and received quite positive reviews from the military.
The key difference between the NGSW program is that it is planned to adopt not only new weapons, but also a fundamentally new 6,8 mm cartridge. And speaking of the NGSW program, you need to start with the new cartridge.
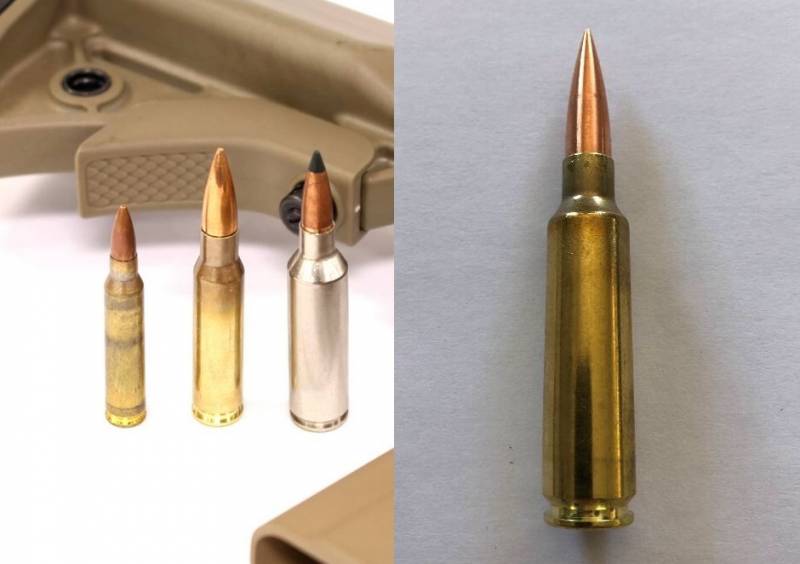
MARS and Cobalt have developed an 6,8 mm caliber cartridge with a bullet weight of 9,07 grams, which provides an initial bullet speed of 976 m / s. Based on these parameters, you can see that the initial energy of the bullet of this ammunition will be more than 4300 J, which exceeds the initial energy of bullets in most cartridges of calibers 7,62x51 mm and 7,62x54R. The case of the sleeve is supposedly made of stainless steel to provide the ability to withstand increased pressure and to provide a reduction in the weight of the ammunition.
VK Integrated Systems introduced the 6,8 Sherwood cartridge, developed on the basis of the .284 Winchester cartridge. The characteristics of the 6,8 Sherwood cartridge are unknown, but based on the characteristics of the .284 Winchester cartridge, which provides a bullet weighing 9,7 grams with an initial speed of 858 m / s at a muzzle energy of the order of 3600 J, it can be assumed that the characteristics of the 6,8 Sherwood cartridge will be comparable to those of the 6,8 mm cartridge MARS and Cobalt.
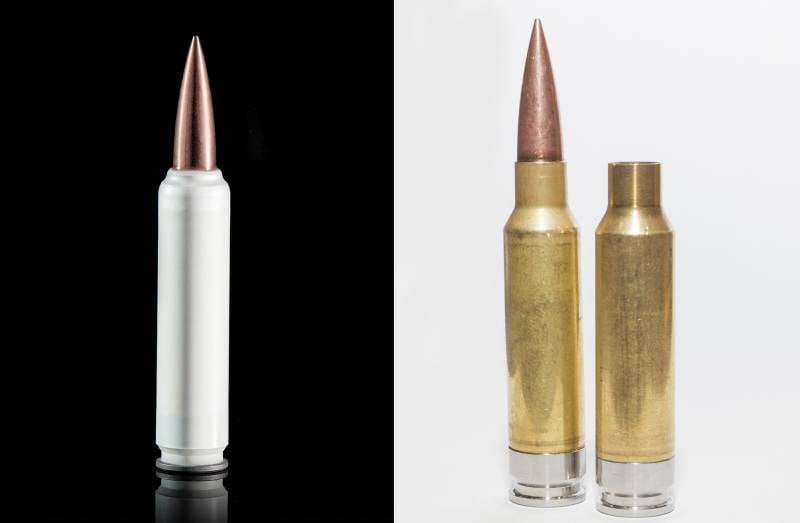
The most innovative ammunition can be considered a telescopic cartridge with a polymer sleeve from the company Textron Systems. Presumably, it will reduce to the maximum extent the weight of the ammunition load, taking into account the increase in ammunition power, but at the same time, the diameter of cartridges made in a telescopic form factor can exceed that of a cartridge of the same power made in a traditional layout. That which is uncritical for a light machine gun, with its voluminous box, may not be acceptable for an automatic rifle with a box magazine. However, it seems that an increase in the diameter of the cartridge case of all declared ammunition is expected, so this drawback can be considered uncritical.
A more significant argument is the lack of experience in the long-term operation of telescopic munitions with a polymer sleeve in real combat conditions, which could potentially lead to unsolvable problems during the operational phase, for example, cartridge deformation due to heating of weapons, mechanical or climatic influences.
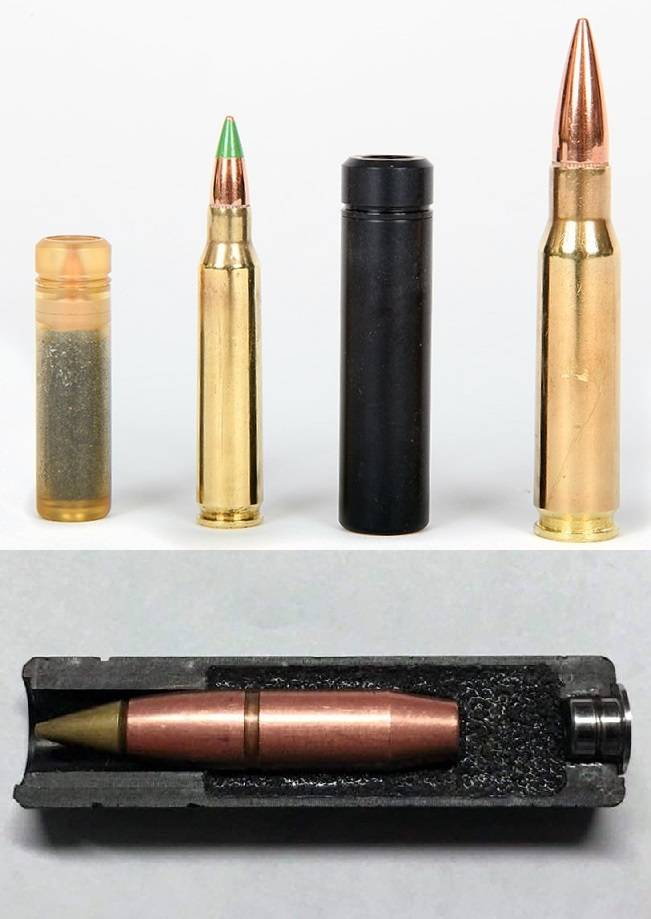

General Dynamics-OTS Inc. and Sig Sauer Inc. 6,8 True Velocity and 6,8 Hybrid round cartridges were submitted to the competition respectively. The sleeve of the 6,8 True Velocity cartridge is made of a polymer composite with a metal base. The 6,8 True Velocity cartridge sleeve is made of brass with a stainless steel base. Both companies claim a reduction in the mass of wearable ammunition. Sig Sauer explains its choice of a hybrid metal sleeve with the inability of existing polymer composites to provide resistance to high pressure.
Given some conservatism inherent in the military, it should be noted that the solution is from Sig Sauer Inc. may well get priority. Also to the benefits of ammunition design from Sig Sauer Inc. we can attribute the fact that at the initial stage the 6,8 Hybrid round cartridges can be used in a variant with a hybrid metal sleeve, and in the future the user (US Armed Forces) can switch to the use of fully or partially composite ammunition, for example, with a stainless steel bottom and a polymer shell body .
It can be assumed that the initial energy of the promising cartridge adopted by the NGSW program will lie within 4000-4500 J. This is necessary to solve the problem of breaking through existing and perspective NIBs, which are already able to withstand not only intermediate cartridges 5,56х45 mm, 5,45х39 mm and 7,62х39 mm and mm, but also for rifle cartridges of the caliber 7,62x51 mm and 7,62x54R. A distinctive feature of promising ammunition will be the pressure, approximately two times higher than the pressure developed in the barrel by the existing ammunition of army small arms.
NGSW Program: Weapons
The need to use ammunition separation in promising small arms, the initial energy of which will significantly exceed not only the initial energy of intermediate ammunition of the caliber 5,56x45 mm, 5,45x39 mm and 7,62x39 mm, but also rifle cartridges of the caliber 7,62x51 mm and the 7,62X gun design reduce the impact of recoil on the arrow.
It should be noted that the US armed forces already had experience using automatic weapons under powerful rifle cartridges. We are talking about an automatic rifle M14 under the then new cartridge caliber 7,62x51 mm. In pursuit of the US ammunition capacity, the appearance of the Soviet intermediate cartridge 7,62x39 mm “missed”, creating as a result, although powerful, but large-sized and slow-moving weapon.
The M14 rifle did not perform well during the US military operations in Vietnam, especially when compared to the Soviet AK-47 assault rifle available to the Vietnamese. Due to the large size and weight of the 7,62x51 mm cartridge, compared to the 7,62x39 mm cartridge, the magazine capacity (20 cartridges versus 30 to AK-47) and the wearable ammunition of an American soldier with M14 were 1,5 times inferior to those of a Vietnamese soldier with AK-XNUM. Shooting in bursts from an M47 rifle with a minimum acceptable accuracy is actually possible only with bipods or an emphasis, and at a range of about 14 meters. However, replacing the M100 with the M4 did not greatly improve the position of the American military due to the behavior of small-caliber 16 mm bullets in the dense jungle.
Back to the NGSW program. Of all the candidates announced above, General Dynamics-OTS Inc., AAI Corporation Textron Systems and Sig Sauer Inc. were allowed to create prototypes. Some sources also mention FN America LLC and PCP Tactical, LLC, but their status in the NGSW program is not clear.
As we recall, the recoil of the aforementioned M14 rifle of the caliber 7,62x51 mm did not allow us to ensure any acceptable accuracy and accuracy of fire bursts. In a new weapon under the NGSW program, this problem should be solved in spite of the fact that the initial energy of a new cartridge of caliber 6,8 mm should exceed the initial energy of a cartridge of 7,62x51 mm.
The proposed solutions include the use of standard silencers on promising rifles and machine guns, which reduce the return by a third.
An additional advantage that an integrated silencer will provide can be a reduction in the impact on the fighter's hearing organs, especially indoors. Of course, the soldier of the modern army should have hearing protection equipment - active headphones, but in reality a huge number of situations are possible when they either will not exist or they will fail. Also, the use of silencers on an ongoing basis will reduce the detection range of a soldier by a muzzle flash and the sound of a shot.
As other ways to reduce recoil, recoil impulse schemes, balanced automation, various designs of shock absorbers and other design solutions can be used, information about which may appear closer to the final of the NGSW program in 2022.
It can be assumed that the main mode of firing a weapon of caliber 6,8 mm will be the regime with a cut-off line for the 2 cartridge, which is declared as desirable in the developed weapons models.
Conclusions
What advantages will the American army give weapons under the NGSW program if it is successfully implemented?
Actually, for what this program was conceived for: increasing the range of hitting targets and confident hitting targets protected by modern and promising NIBs. Of the minuses, a possible decrease in the density of fire from small arms of the caliber 6,8 mm at short range is possible due to increased recoil and a high probability of reducing the stores of promising automatic rifles to twenty rounds.
In general, based on the prospects for the implementation of the American NGSW program, two questions can be asked:
1. How big a threat is the promising weapon created by the NGSW program for the Russian armed forces?
It can be assumed that in the event of a conflict between Russia and the United States, machines may not reach the point, so you can take your time responding to NGSW. But with a high probability the United States will want to test new weapons in the field, and in this context it is impossible to exclude its appearance, for example, in Ukraine, or among fighters of various private military companies (PMCs), for example, in Syria. And the likelihood of a clash between fighters of Russian and American special forces cannot be completely ruled out due to the specifics of their activities, combined with increased secrecy. In this case, the absence of a weapon adequate to the potential enemy’s available may lead to unacceptable losses of personnel of the Russian special forces.
Of course, you can hope that nothing "they" will not work out under the NGSW program, or that this is just another cut. But, in my opinion, this is somewhat risky.
2. Is there any need for a reaction from the Russian armed forces if the American NGSW program is successfully implemented?
The most interesting thing is that the reaction should be regardless of whether the US Armed Forces are successfully implementing the NGSW program or not. The need for a new weapon-cartridge complex has been brewing for a long time, and the NGSW program is a litmus test showing the need to develop a new generation of small arms. The starting point here is not the appearance of a new weapon in the U.S. Armed Forces, but the appearance of NIBs that can effectively withstand both intermediate ammunition of the caliber 5,56x45 mm, 5,45x39 mm and 7,62x39 mm, and rifle ammunition of the caliber 7,62x51 mm and 7,62XN.
In the following material, we will try to figure out what developments can be used by domestic gunsmiths to create promising small arms.
- Andrey Mitrofanov
- militaryarms.ru, army-news.ru, bronegilet.ru, tvzvezda.ru, thefirearmblog.com, soldiersystems.net, warhead.su












Information