"Warning, birds are in the air!" Aviation against birds
Get out of here!
In the first part of the story we met history military and civil aviation ornithology. In the end, we will pay attention to techniques for preventing collisions of aircraft with birds, which, unfortunately, are still far from perfect.
Probably the most frugal way to protect aircraft from innocent birds is regular maintenance of the airfield. The goal is to create an appearance that does not attract birds. Therefore, there is no landfill nearby, and all household waste needs to be stored only in opaque bags so as not to attract too much attention from the keen bird's eyes. In addition, all shallow water bodies should also be eliminated - they can become the habitat of the most dangerous, heavy and slow-moving waterfowl. The grass near the runway, of course, is regularly mowed (so that all kinds of quail nests do not twist) or replaced with a low clover with alfalfa. The absence of tall grass also helps to avoid the resettlement of small rodents hunted by predatory birds. It is also preferable to cut down all trees and shrubs at a distance of 150-200 meters from taxiways and runways.
This is one of the instructions of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), which coordinates compliance with the safety of air travel. More complicated. In self-respecting companies, experts examine the flora on the subject of honey plants, which attract insects, which, in turn, are the food supply for birds. Often, all the above techniques do not give a tangible effect - flocks of birds continue to fly shoals across the runway. We have to carefully examine the territory at a distance of several kilometers from the airports. Thus, in Tomsk, it was possible to stop the deadly flights of pigeon flocks across the runway of the local airport. It turned out that pigeons flew hundreds to feed from the nearest village to the farm. I had to isolate all available feed from birds, which was the solution to the problem. By the way, it is impossible to take airports to the backwoods from the whole settlements - birds consider the villages as an excellent forage base and are not distracted once again by the aircraft base.
Naturally, passive methods of protecting the airfield and airports are absolutely inadequate and should be used in conjunction with active deterrent techniques. It is important to remember that only in Russia every tenth bird species is listed in the Red Book. This forces us to develop special approaches to the active protection of air routes.
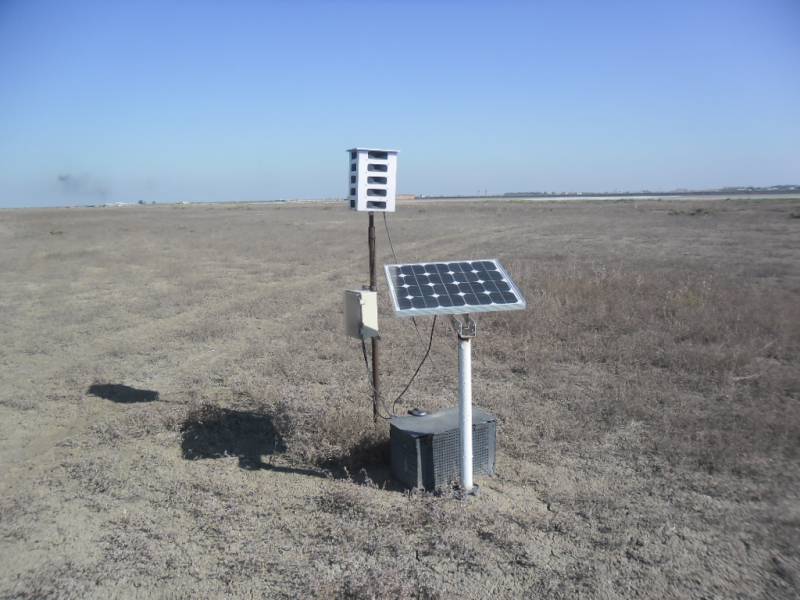
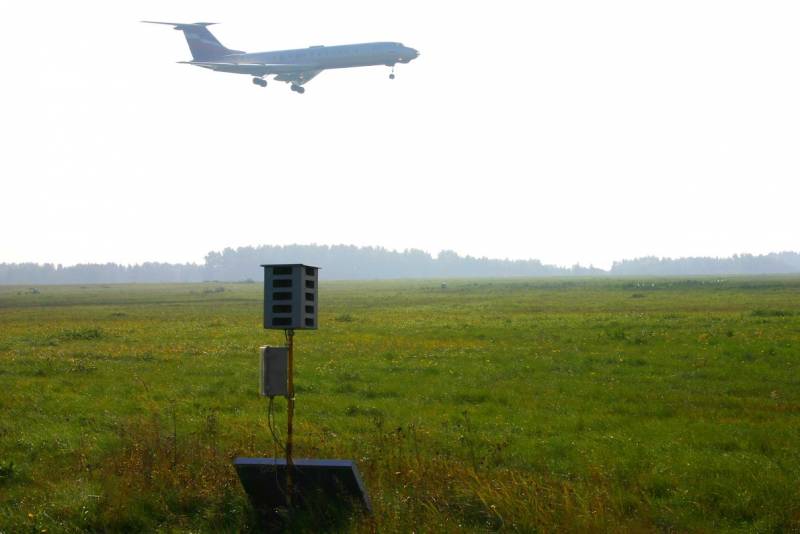
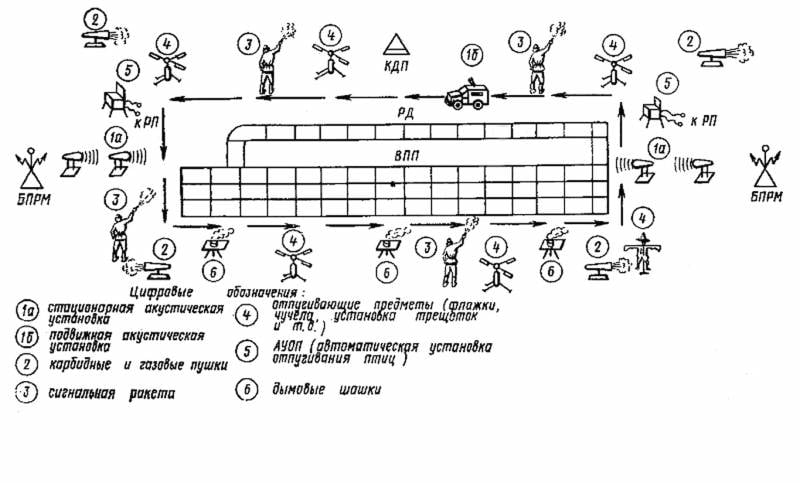
One of the earliest ways to scare away birds was bioacoustic devices that broadcast alarms to birds and birds of prey. The first in this business were the Americans, when in 1954 they dispersed unwanted flocks of starlings with recorded bird cries of disaster. A modern example is the foreign Bird Gard installation, which has a wide range of applications - from bird-toxic industries and agricultural land to large aviation transport hubs. From domestic counterparts, you can bring the installation "Biozvuk MS" and "Golden Eagle". The general requirements for using such a technique are remoteness from people's places of residence - the sounds emitted are very loud (over 120 dB) and can upset the mental balance of the inhabitants of a small village. At a distance of 100 meters, such a sound can cause a person to vomit. The Biozvuk MS system and a less powerful MM modification have been supplied to the Russian Ministry of Defense since 2017. Obviously, one of the most important objects for using bioacoustic repellers was the air base in Khmeimim. Firstly, in winter there the activity of birds, if it decreases, is insignificant, therefore, the danger of encountering birds is practically year-round. And, secondly, the Middle East is one of the main migratory routes of birds of different varieties and calibers. Producers of bioacoustic systems recall that only panic signals for birds are insufficient. At least noise propane guns are also required, sometimes imitating weapons shots. The real high-tech robot was the Airport Birdstrike Prevention System from South Korean engineers, which is able to autonomously patrol around the airport and military base. In case of detection of a feathered intruder by the on-board locator, the car scares him away with acoustic weapons (knows the “language” of 13 bird species) and irradiates with a laser.
However, birds are far from always ready to adequately respond to sound stimuli. So, at the end of the 80's in the USSR, military and civilian aviators decided to conduct an experiment and determine how quickly the seagulls adapt to bioacoustic repellers. For the test site, we chose a landfill near Pulkovo Airport, which was like in a snow cover from feeding gulls. Included scare signals. It turned out that every time a smaller number of birds reacted to the stimulus. Surprisingly, even the hens that live on farms near helipads have become completely indifferent over time to rotorcraft flying directly above them. Therefore, all the tricks of bioacoustic can only be effective against non-intimidating specimens.
At one time, the Soviet Air Force with such protective airfield systems came to a standstill. Every year, the army lost from a collision with birds to 250 engines and several aircraft with pilots. Here is what Major General Viktor Litvinov, head of the Air Force Meteorological Service, said at the beginning of the 80's:
The result of such criticism was the decree of the government of the USSR, which explicitly spoke of the need to develop a set of measures to combat birds near aircraft objects. But it happened a few years before the collapse of the country ...
Firecrackers, chemistry and balls
To enhance the deterrent effect, pyrotechnic means such as the Khalzan rocket launcher with PDDOP-26 cartridge (bird repelling cartridge) are additionally used. The device creates a real show in the sky with pops up to 50 decibels, sparks and orange smoke. The predecessors of noisy gas guns were carbide plants in which acetylene exploded. Over time, they realized that it was much safer and more convenient to explode the finished gas than to synthesize it from carbide and water. But in any case, such systems are of little use for civilian airports because of their explosion and fire hazard. Since the end of the 80's, laser emitters capable of creating a situation of discomfort in birds at a distance of up to 2 km have entered the world practice. The pioneers in this business were also Americans who tested devices on the birds of the Mississippi Valley.
A cardinal way to fight birds was the banal poisoning of animals. This practice is not permitted in all countries. So, Italy, Austria, Portugal and several other EU countries do not apply chemical effects on birds. Avicides (bird poisons) are also prohibited in the United States. In Russia, such substances are not used in the aviation sector, but to protect agricultural fields. The main drug was avitrol. He and his derivatives in the most minimal concentrations cause involuntary convulsions in animals, accompanied by cries of avian horror. This very well scares the rest of the brothers in appearance. Alpha chloralosis is a sleeping pill for birds used at airfields. The sight of the brothers sleeping in arbitrary poses causes the rest of the birds to panic, suspicion of mass and fatal poisoning of the territory. As a result, winged airspace intruders retreat for a long time. By the way, the technique of hanging corpses of birds on public display is also an effective means of deterring. The disadvantage of using chemicals is a considerable percentage of mortality, as well as the weathering of poison from airfields.
The birds have very sharp eyes. Scientists decided to turn this property against them. A vivid image of the bird of prey's eye or simply contrasting circles on the balls became a new means of combating birds. But only for the first time. From the memoirs of Soviet military meteorologists:
More precisely, the effectiveness of visual means of struggle can not be said ...
Among many other ways to protect aircraft (nets, rattles, radio-controlled bird models, mirror balls, scarecrows and radars), manual predatory birds of the falcon and hawk detachments stand out in their effectiveness. At the genetic level, they instill fear in most birds. For the first time, falcons and hawks took up service in the main airports and military bases of the world in the 60's, but in the USSR they came only to the end of the 80's. The neighbors in the socialist camp from Czechoslovakia helped, who created a methodology for training Central Asian saker falcons. However, the Soviet Union did not manage to establish the practice of widespread use of winged predators in the interests of aviation. Perhaps the falcons worked effectively only in the Kremlin, driving away peaceful birds from well-groomed landscapes and flower beds. Now, most of Russia's major airborne harnesses the expensive services of the ornithological service, the main roles in which are falcons and hawks. This is also not a panacea: animals get sick, molt, get tired, require specific care and training. In addition, some birds are fearless (for example, gulls), and as soon as the predator sits on the hand of the "operator", they immediately return to their old place.
The confrontation between the plane and the birds is far from its final. With each new step of a person, birds find ways of adaptation and again return to their usual habitat. And the man, as was superfluous in the air, remained so to them.
- Evgeny Fedorov
- travelask.ru, otpugivateli.ru, "Military History Journal"
- Plane vs birds - fatal confrontation




Information