Medium and heavy tanks of the USSR in the interwar period
At the end of 20, the military commanders considered it expedient to start developing medium tanks, two directions were chosen: the creation of their own tank and an attempt to copy foreign samples.
In 1927, the military issued requirements for the development of a medium "maneuverable tank" with machine-gun and cannon armament. The development of the tank was started by the Main Design Bureau of the Gun-Arsenal Trust, then this Robot was transferred to the Kharkov Locomotive Plant No. 183.
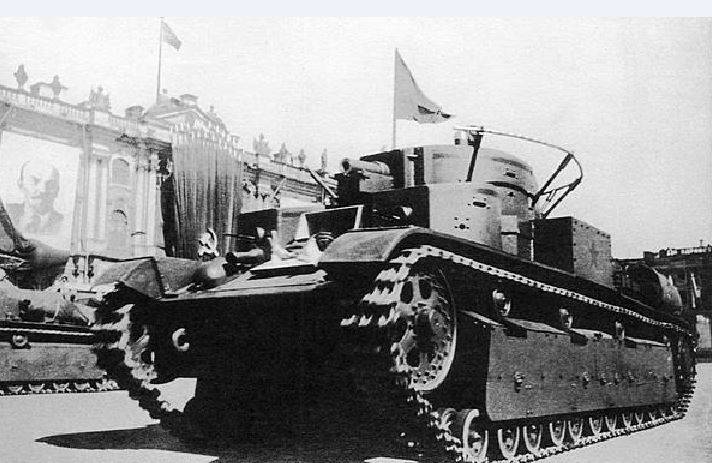
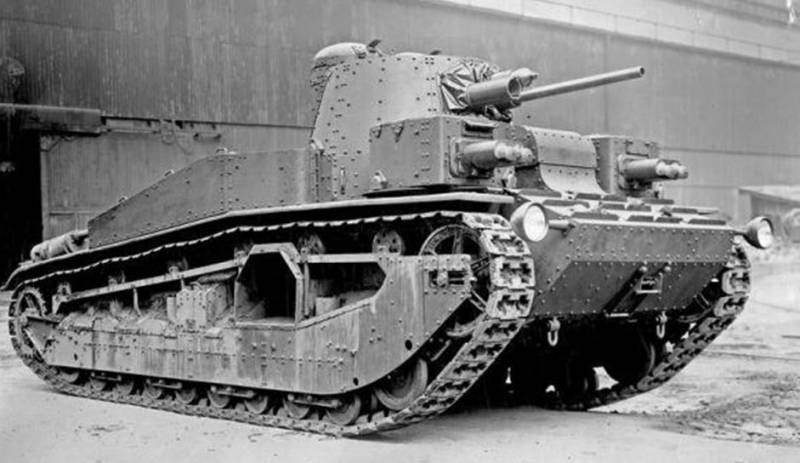
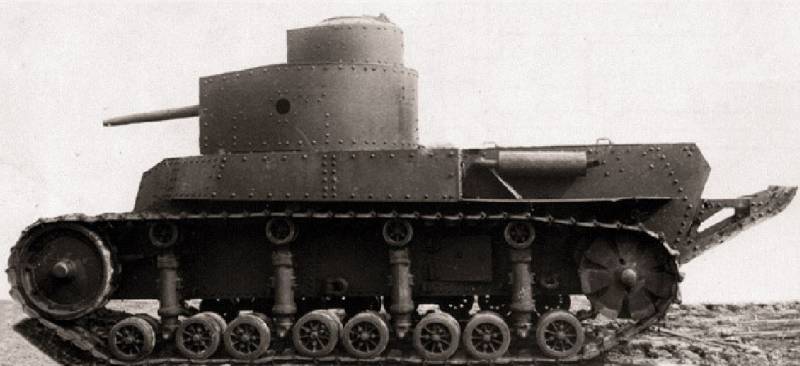
Medium Tank T-24
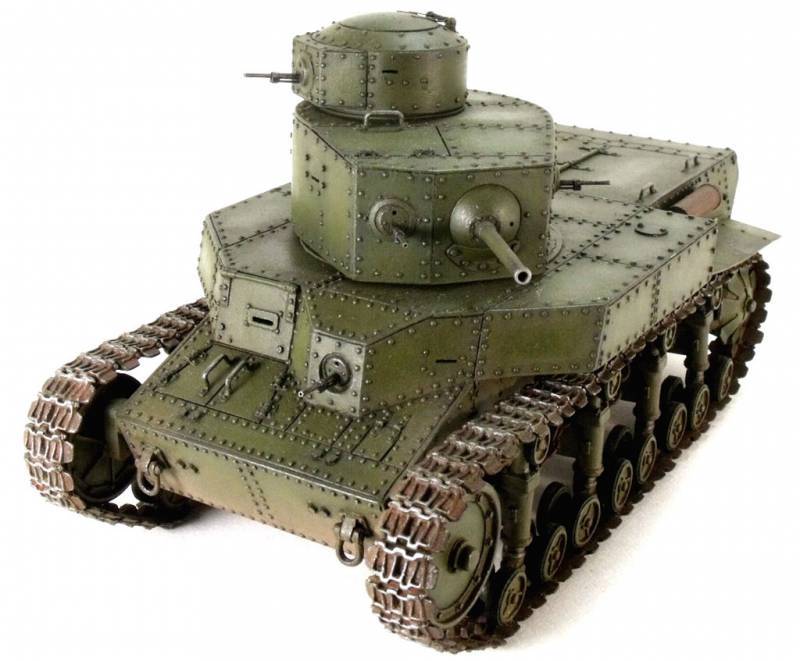
Development of design documentation for the tank was completed at KhPZ and at the beginning of 1930, a prototype tank was manufactured, which received an T-12 index. According to the test results, it was recommended to modify it, increase the power reserve, change the turret design, instead of the twin 6,5mm machine guns of Fedorov, install the 7,62 mm DT machine guns.
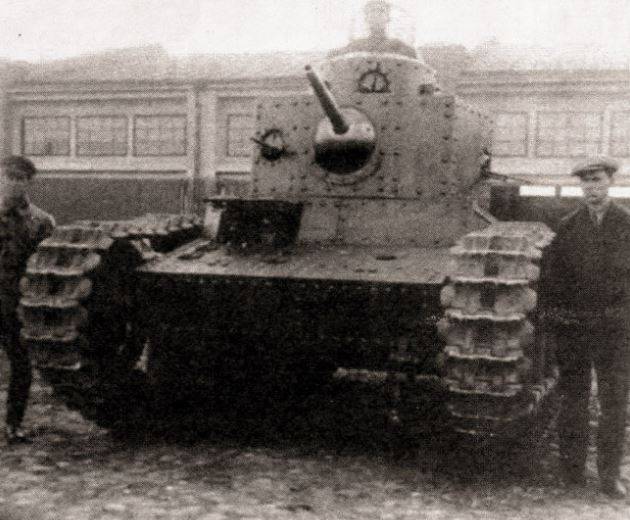

The tank was finalized, and under the symbol T-24 began its mass production. 26 tank sets were made, but only 9 tanks were assembled and production was stopped due to the launch of the production of the BT-2 tanks, an analogue of the American light-duty Christy tank, at this plant.
The layout of the tank T-24 was based on a three-tier arrangement of weapons. A machine gun was installed in the body, in the main turret a gun and two machine guns, in a small turret placed on the roof of the main turret on the right, another machine gun. The tank's weight was 18,5 tons, the crew consisted of a 5 man, a commander, a gunner, a driver and two machine gunners.
The department of management was ahead, behind it there was a fighting department, the engine-transmission was behind. The driver was in front of the right. The commander, gunner and machine gunner in the main nine-sided turret and another machine gunner in the small turret. For landing the driver was a hatch in the front hull sheet, for landing the rest of the crew had one hatch in the main and small towers.
An 45-mm cannon was mounted in the front sheet of the turret, one 7,62-mm machine gun on each side of it. One 7,62-mm machine gun was installed in the housing and a small turret.
The hull and turret were riveted of armor plates, the thickness of the turret armor, forehead and hull sides of the 20 mm hull, the bottom and the roof of the 8,5 mm. The armor plates of the hull forehead were located at rational inclination angles.
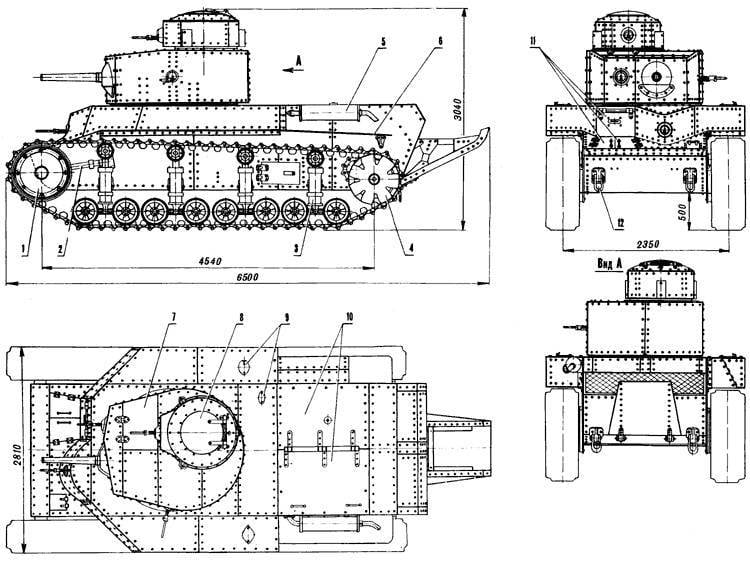
As a power plant was used aviation M-6 engine with a capacity of 250 hp, providing a speed of 25,4 km per hour and a power reserve of 140 km.
The chassis of the tank was unified with the Komintern tractor chassis and on each side consisted of 8 dual rubber coated small diameter track rollers with protected armor casings with vertical spring springs interlocked into four trucks of two, four supporting rollers, front guide and rear sprocket wheels.
The production of the tank at the plant was not prepared, there was no required equipment and specialists. Tanks were going almost by hand. Their reliability was very low, they often broke down and failed, and it was not possible to establish a high-quality production of tanks.

At this time, the procurement commission of Soviet specialists in the West was considering the issue of purchasing licenses for the production of Western-style tanks. As a result, it was decided not to develop their tanks and use the documentation for the tanks of England and the USA. The British Vickers Six-ton light tank was taken as a prototype of the light tank T-26 at the Bolshevik plant in Leningrad, and the American tank Christie M2 became the prototype of the BT-1931 high-speed cruiser tank, which was manufactured at the KhPZ.
Attempts by the KhPZ management and designers to continue the production and improvement of the T-24 medium tank failed and the work on it was discontinued. The military leadership considered it expedient to purchase and manufacture Western tanks under license and thereby get rid of the mistakes that their designers had already passed.
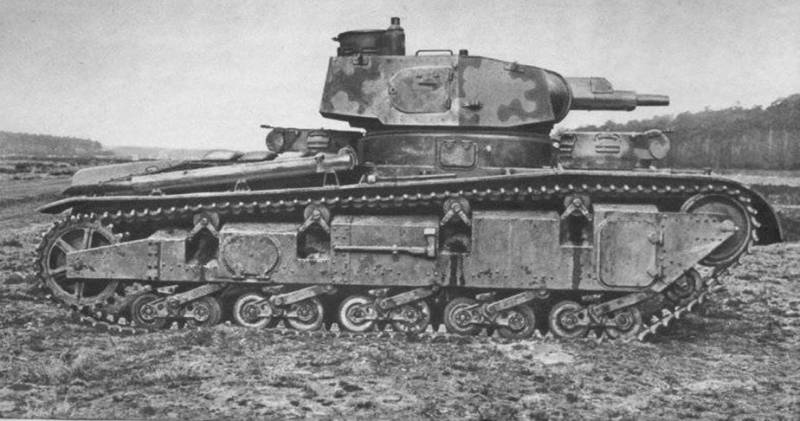
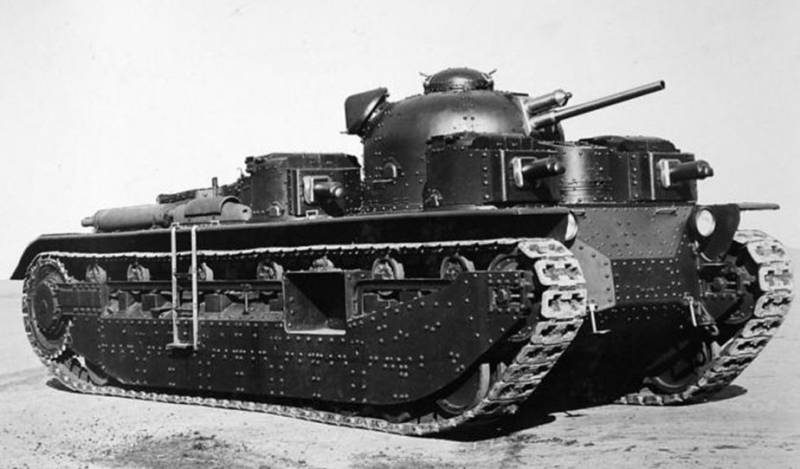
Medium Tank T-28
The medium tank T-28 was developed in Leningrad in 1930-1932, and from 1933 to 1940 the year was mass-produced at the Kirov plant. In total 503 tank T-28 was released. The prototype of the T-28 was the English medium three-tower Vickers 16-ton tank.
The Soviet purchasing commission in 1930 got acquainted with an English tank, but it was not possible to buy a license for its production. It was decided to create a similar tank of their own, taking into account the experience gained in studying the English tank.
At the beginning of 1931, the design bureau of the Artillery Gunnery (Leningrad) began to design the T-28 tank, in 1932, tank prototypes were manufactured and tested. According to the results of tests in the tank 1932 was adopted.
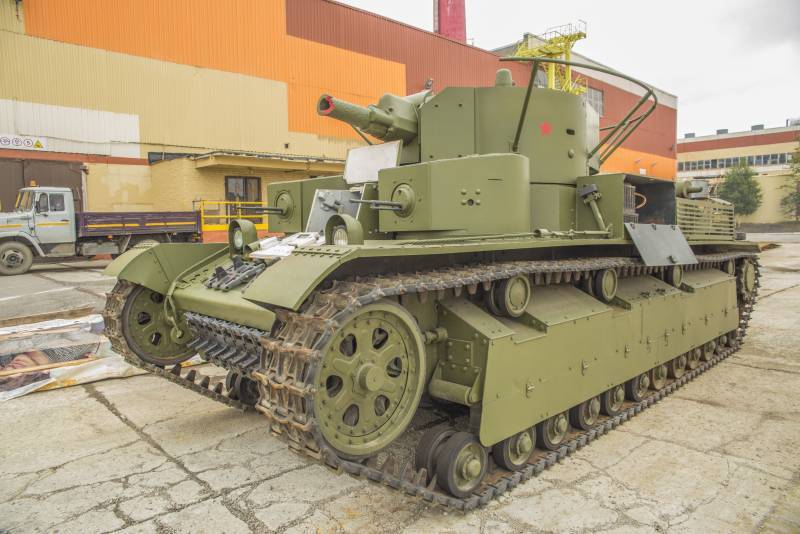

Tank T-28 was a medium tank of three-turreted layout with a two-tier arrangement of cannon-machine gun weapons, intended for fire support of infantry. The control compartment was in front, behind it was the combat compartment, in the aft engine-transmission, fenced off by a partition from the combat compartment.
The tank turrets were located in two tiers, on the first in front were two small machine-gun towers, on the second - the main tower. Between the machine-gun turrets there was a driver’s cabin with a folding armored door and a flap with a triplex opening upwards. Above the cabin was closed by another hatch, facilitating the landing of the driver.
The main tower had an elliptical shape with a well-developed aft niche and was identical in design to the main tower of a heavy T-35 tank. Outside the tower on the sides of the brackets mounted handrail antenna. Small machine gun towers were also identical in design to the T-35 machine-gun turrets. Each tower could be rotated from the stop into the cabin of the driver’s cabin to the stop into the wall of the tank hull, the horizontal angle of the machine gun fire was 165 degrees.
The crew consisted of six people: a driver, a radio operator, a machine gun, a commander and gunner in the main turret, and two machine gun turrets.
The tank hull was a box-shaped riveted-welded or welded structure, the tank turrets were of the same design. The tank reservation was anti-bullet, the thickness of the armor of the 30 mm hull forehead, the 20 mm forehead and sides of the turret, the 20 mm hull sides of the mm, the 15-18 mm bottom of the hull, and the 10 mm roof. An additional reservation was installed on the modification of the T-28E tank, armor plates with a thickness of 20-30 mm were attached to the hull and the turret. The shielding made it possible to bring the armor thickness of the frontal hull parts of the tank to 50 — 60 mm, and the towers and the upper part of the sides to 40 mm.
The main armament of the tank was the 76,2-mm gun KT-28 L / 16,5 and was designed to fight the enemy firing points and non-armored targets. As an armor-piercing weapons it wasn’t good, and with 1938, tanks armed with a new 76,2-mm L-10 L / 26 cannon with an initial speed of 555 m / s armor-piercing projectile, which allowed penetration of armor up to 50 mm at a distance of 1000 m.

Auxiliary armament of the tank consisted of four 7,62-mm machine guns DT, located in ball units. One of them was located in the frontal part of the main turret in an autonomous installation, to the right of the gun, the other in the turret's aft niche and two in the machine-gun turrets. On the tanks of the latest series, an anti-aircraft turret was also installed on the gunner's hatch with a DT machine gun.
The aircraft engine used was an M-17T aircraft engine with a power of 450 l. with., an attempt to install a diesel engine on the tank was not successful. The tank developed a speed of 42 km / h and provided a power reserve of 180 km.
The chassis of the tank on each side consisted of 12 paired rubberized small-diameter track rollers, interlocked with 6 balancers, with spring-cushioned carriages, which, in turn, were interlocked into two carts suspended from the body at two points, as well as rubberized 4 supporting roller.
The medium tank T-28 can be compared with foreign medium tanks of the same period with similar characteristics, these are the English Vickers 16-ton tank, the French Char B1bis and the German Nb.Fz.
The English "Vickers 16-ton" was essentially the "ancestor" of the T-28, with a weight of 16 tons it was three-turreted, armed with 47mm cannon with L / 32 and three machine guns, armor-proof at (12-25) mm and ensured speed 32 km / h.
German Nb.Fz. there was also a three-turreted, the L / 75 and 24mm L / 37 cannon was mounted on the main turret, as well as three 45-mm machine guns spaced along the turrets, the level of protection was 7,92-15 mm, and with the weight of 20 tons it developed speed 23,4 km / h.
The French Char B1bis as a weapon had a cannon in the 75 case, and in the tower a long-barreled 47 mm cannon with the 27,6 and two machine guns, armor protection at the level of (46-60) mm and with a weight of 31,5 tons developed 28 km / hour speed.
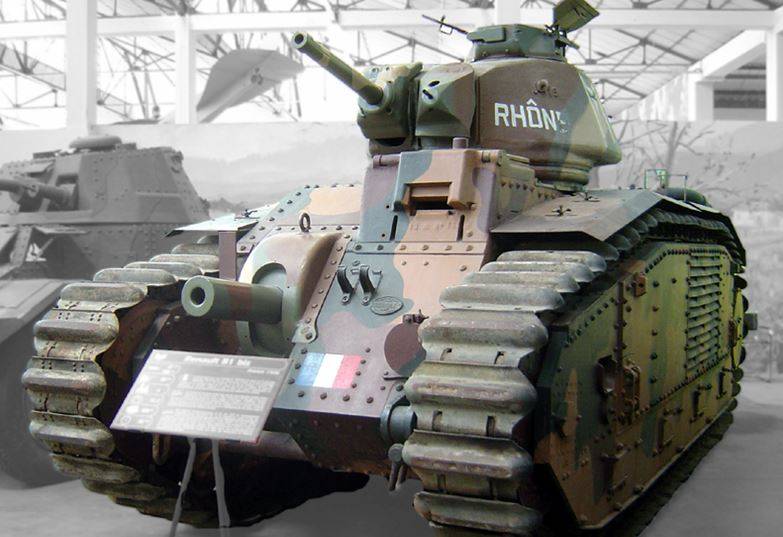

T-28 compared with the "Vickers 16-ton" surpassed him in terms of armament, security and mobility. Compared with the Nb.Fz, the T-28 was inferior in terms of armament, but superior in security and mobility. Compared with Char, B1bis was inferior in armament and security, but surpassed in mobility. In general, the combination of the main characteristics of the T-28 was at the level of foreign medium tanks at the same stage of development.
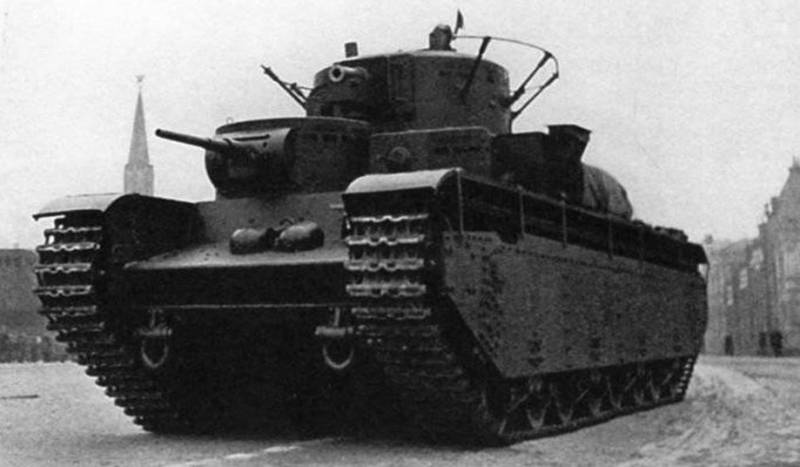
Heavy tank T-35
At the end of the 20-s in the Soviet Union began attempts to create a heavy tank breakthrough. After several failures in 1932, the design team specially designed to develop a heavy tank proposed a design for the T-35 tank and in the autumn of the year 1932 a prototype was made. After its testing and refinement, a second tank model was made, which showed satisfactory results and was even shown in the 1933 year at the parade in Leningrad. In 1933, the serial production of the T-35 tank was entrusted to the Kharkov Locomotive Works, where it was produced before the 1940 year, in total 59 T-35 tanks were produced.
The T-35 tank was a five-tower heavy tank with a two-tier arrangement of cannon-machine-gun weapons and anti-armor, designed to support and strengthen the infantry in the breakthrough of the fortified positions of the enemy.
According to the layout of the tank, the control compartment was located in the hull, in the frontal part of the hull a driver was located on the left. He had an access hatch with a triplex, which was thrown up on the march. Above the driver in the hull roof was a hatch for landing in a tank.
On the roof of the hull were five towers. The main tower of a cylindrical shape with a developed aft niche, identical in design to the main tower of the T-28 tank, was centrally located on the under-box in the shape of an irregular hexagon.
In the frontal part of the turret, an 76-mm cannon was mounted on trunnions, to the right of which a machine gun was placed in an independent ball mount. In the stern of the tower was installed another machine gun.
The two middle cylindrical towers with two hatches in the roof for the crew access were identical in design to that of the BT-5 light tank, but without a stern niche. The towers were located diagonally on the right-front and left-back relative to the main tower. In front of each turret, an 45-mm cannon and a machine gun paired with it were installed.
Two small cylindrical machine gun turrets were identical in design to the machine gun turrets of the medium T-28 tank and were located diagonally from the left-front and right-behind. In front of each tower was set machine gun.
The main tower was fenced off from the rest of the combat compartment by a partition, the rear and front towers communicated with each other in pairs.
The crew of the tank, depending on the release series, was a 9-11 man. The commander-gunner, machine-gunner and radio operator-loader were placed in the main tower. There were two people in each middle turret - the gunner and the machine gunner, and one machine gunner in the machine gun turrets.
The hull and turret of the tank were welded and partially riveted from armor plates. The armor protection of the tank provided protection against bullets and shell fragments, as well as a frontal projection of the tank against the shells of small-caliber anti-tank artillery. The thickness of the forehead armor 20-30 mm, towers and hull sides 20 mm, bottom 10-20 mm and roof 10 mm. During the production of tanks, the booking increased and the weight of the tank with 50 tons reached 55 tons.
The main armament of the tank was the 76,2-mm tank gun KT-28 L / 16,5. Guidance on the horizon was carried out by turning the tower with manual or electric actuators. The power of the armor-piercing projectile due to its low initial speed was very low.
The additional artillery armament consisted of two 45mm semi-automatic 20K L / 46 cannons with an initial speed of an 760 armor-piercing projectile, m / s. Guidance on the horizon was carried out by turning the tower with a screw-turning mechanism
Auxiliary armament of the tank consisted of six 7,62mm DT machine guns, which were installed inside the towers of the tank. On the tanks of the latest series, an anti-aircraft turret was also installed on the gunner's hatch with a DT machine gun.
The aircraft used was an M-17 aircraft engine with an 500 horsepower, providing speed on the 28,9 highway km / h and power reserve 80 km.
The chassis of the tank on each side consisted of eight rubber-coated small diameter diameter rollers, six supporting rollers with rubber tires, and a guide for the front and rear wheels. The suspension was blocked, two rollers in a trolley with suspension in two spiral springs. The undercarriage was closed with a solid 10mm armored screen.
The five-tower T-35 tank, like the German Nb.Fz., was regularly used for propaganda purposes. He participated in maneuvers and parades, many newspapers wrote about him and published his photos, and he symbolized the power of the armored forces of the Soviet Union.
The concept of multi-turreted heavy tanks in the interwar period was also attempted to be implemented in France and England, but it turned out to be a dead end and did not receive further development in world tank design.
The ancestor of the "tank monsters" can be considered the French heavy double-topped tank Char 2C, of enormous size, weighing 69 tons, with anti-bullet armor (30-45) mm thick, armed with a 75mm gun and four machine guns and having low maneuverability and reliability. A total of 10 tanks were manufactured and the work was stopped.
More successful was the project of the English heavy five-turreted tank A1E1 "Independent" weighing tons of 32,5, with armor protection 13-28 mm thick, armed with an 47-mm cannon and four machine guns. Thanks to a more rational layout of the tank, he avoided a number of shortcomings of the French Char 2C, one sample was made, but because of the depravity of the concept of multi-turret tanks, it also did not go into mass production.
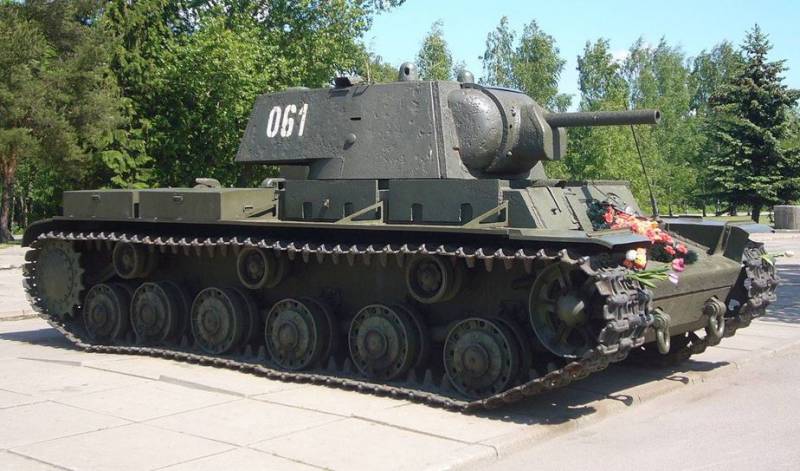
Heavy tank KV-1
The KV-1 heavy tank was developed in 1939 at the Kirov plant in Leningrad as part of the concept of heavy tanks needed to crack the front of the enemy and organize a breakthrough or overcome the fortified areas.
Due to the fact that the concept of a heavy multi-turret T-35 tank was a dead end and attempts to create more sophisticated multi-turret tanks, such as SMK and T-100, were also unsuccessful, it was decided to develop a heavy tank of the classic layout with powerful anti-roll-over armor and armed a gun capable of striking fortifications and armored vehicles of the enemy.
The first model of the tank was made in August 1939 of the year and immediately sent to the Soviet-Finnish front to participate in the breakthrough of the Mannerheim line, where he successfully passed the tests in a real combat situation. The tank could not hit any enemy anti-tank gun, and in December 1939, he was put into service. Before the start of World War II tanks were made only at the Kirov factory, the 432 tank KV-1 was produced in total. With the beginning of the war, the production of the tank was organized at the Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant.
The KV-1 tank was a classic 43 ton-ton design with anti-spar armor, a powerful cannon, a diesel engine and an individual torsion bar suspension. The control unit was located in the frontal part of the corps, the fighting compartment with a tower in the middle part and a power transmission unit in the stern.
The crew of the tank was a 5 man, the driver was centrally located in front of the hull, the radio operator to his left, three crew members located in the turret, gunner and loader on the left, and commander on the right. The crew landed through the hatch in the tower above the commander’s workplace and the hull on the hull’s roof above the gunner’s position.
The tank hull was welded from rolled armored plates. The armor plates of the frontal part of the vehicle were installed at rational inclination angles (bottom / middle / top - 25 / 70 / 30 degrees). The thickness of the armor of the forehead, sides and tower 75mm, the bottom and roof 30-40 mm. The tank's armor was not affected by the 37-mm and Wehrmacht's 50-mm cannons, only with a caliber of 88 mm and above, the tank could be hit.
The tank turret was produced in three versions: cast, welded with a rectangular niche and welded with a rounded niche. The armor cannon was a cylindrical bent rolled rolled armor plate of thickness 90mm, in which the gun, coaxial machine gun and sight were installed.
The tank’s armament consisted of an X-NUMX-mm L-76,2 cannon, soon replaced by an X-NUMXmm F-11 cannon with similar ballistics, and in the fall of 76, the long-barreled ZIS-32 L / 1941 cannon was installed. Auxiliary armament consisted of three machine guns DT-5: paired with a gun, course in the body and stern in the turret.
A diesel engine В-2К with power 500 l was used as a power plant. s., providing speed on the highway 34 km / h and power reserve 150 km.
The chassis on each board contained 6 stamped gable small-diameter road wheels. Opposite each support roller, armors of the suspension balancers were welded to the armored hull. The suspension was an individual torsion bar with internal depreciation. The upper branch of the caterpillar was supported by three small rubberized supporting rollers.
Tank KV-1 was a major breakthrough in the development of heavy tanks, the optimal combination of firepower, security and mobility allowed him to occupy a decent niche in the class of heavy tanks of the time, he became the basis for the creation of heavy Soviet tanks IS series.
Heavy tank KV-2
The basis for the development of the KV-2 tank was the experience of the combat use of the KV-1 tank in the fall of 1939 in the Soviet-Finnish war in breaking the Mannerheim line. The KV-1 tank gun was not strong enough to fight well-supported enemy strongholds. It was decided to develop an assault tank based on the KV-1 with 152mm howitzer installed on it. In January 1940, the KV-2 tank was developed and adopted in February. Serially produced at the Kirov plant until July 1941, the 204 of the KV-2 tank was produced in total.
The base of the tank was taken hull KV-1 and it installed a new tower with 152 mm howitzer. The weight of the tank reached 52 tons. The crew consisted of a 6 man, an assistant was added to the loader in the turret in connection with the installation of a howitzer with separate loading of ammunition. The landing of the crew in the tower was carried out through the stern door of the tower and the hatch in the roof of the tower on the site of the commander.
The tank was allocated with a huge tower with a door in the rear of the tower, the height of the tank reached 3,25 m.
The KV-2 tower was produced in two versions: MT-1 and a later “reduced” tower of lesser weight. The MT-1 tower had inclined zygomatic armor plates, and the “lowered” one was vertical. Both versions of the towers were welded from rolled armored plates 75 mm thick.
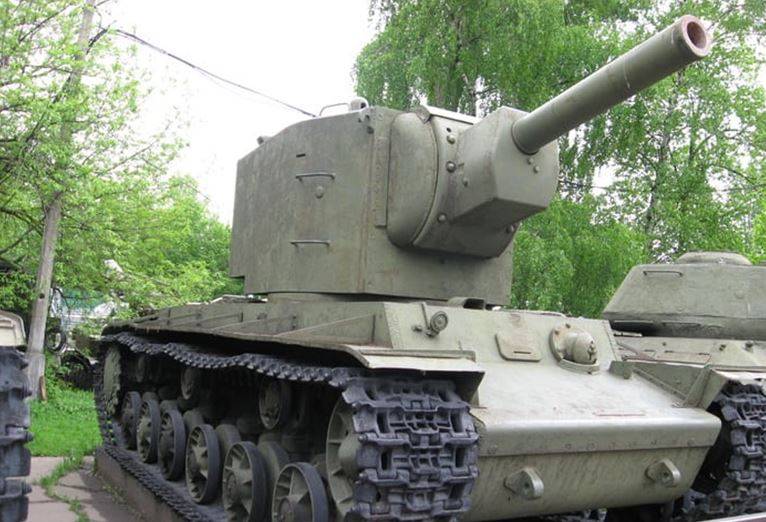

In the turret, an X-NUMX-mm M-152T tank howitzer was installed in the turret, similarly to the KV-10, in the KV-1, three DT-2 machine guns were installed.
Concrete-breaking and armor-piercing shells were used as ammunition for the howitzer; according to both types of shells there were two types of charges. The use of a charge that did not correspond to the type of ammunition, could lead to the failure of the gun, so the crews were strictly forbidden to load one machine with projectiles and charges of different types to them.
Shooting at full charge was strictly forbidden, because of the high recoil and recoil it could jam the tower, components and assemblies of the engine-transmission unit could suffer from shock. For this reason, shooting was allowed only from the spot, which further increased the tank's vulnerability in battle.
In the initial period of the war, the KV-2 easily destroyed any enemy tank, while it was invulnerable to the tank guns and anti-tank artillery of the enemy. KV-2 compared with KV-1 not found widespread use in the army and with the beginning of the war its production was discontinued
Medium tanks А20 А30 А32
The medium tank T-34 did not appear as a result of the requirements for the development of a medium tank, but grew out of an attempt to improve the family of high-speed tanks of the BT series and took the most successful components from them - the Christie suspension and the diesel engine.
At the end of 1937, the military issued to Kharkov Plant No. 183 tactical and technical requirements for the design of the BT-20 light wheeled / tracked tank, according to which it was necessary to develop a wheeled-tracked high-speed light tank weighing (13 – 14) tons with three pairs of driving wheels with a tracked vehicle and wheel drive, armored (10-25) mm and a diesel engine.
It should be noted that a difficult situation has developed in the design bureau of plant No. XXUMX at this time. Chief Designer Firsov was removed from his post and accused of sabotage due to defects in the BT-183 tanks, a number of leading experts were also removed, and soon they were shot. The design bureaus under the leadership of Firsov have already been developed into a fundamentally new tank, and work in this direction was headed by the newly appointed new chief designer Koshkin.
The design of the BT-20 tank was developed and in March 1938 was submitted to the ABTU RKKA for consideration. When considering the draft, the opinion of the military on the type of propulsion divided. Some insisted on a tracked version, others on a wheel-tracked. The design of the tank was approved, the tank’s characteristics were clarified, security requirements were increased, the crew was increased to 4 people and the permissible tank weight to 16,5 tons, therefore the tank moved from the lightweight class to the medium class. The purpose of the tank has also changed; now it was intended for independent actions in tank formations and for actions in tactical interaction with other branches of the military.
The plant was ordered to develop two versions of the tank, make two tracked tanks and one wheeled / tracked tank and present them for testing. In a short time, documentation was developed for two variants of the tank, their models were made and in February 1939 was presented to the Defense Committee for consideration. Based on the results of the review, it was decided to make both options in the metal, test them and then decide which tank to launch.
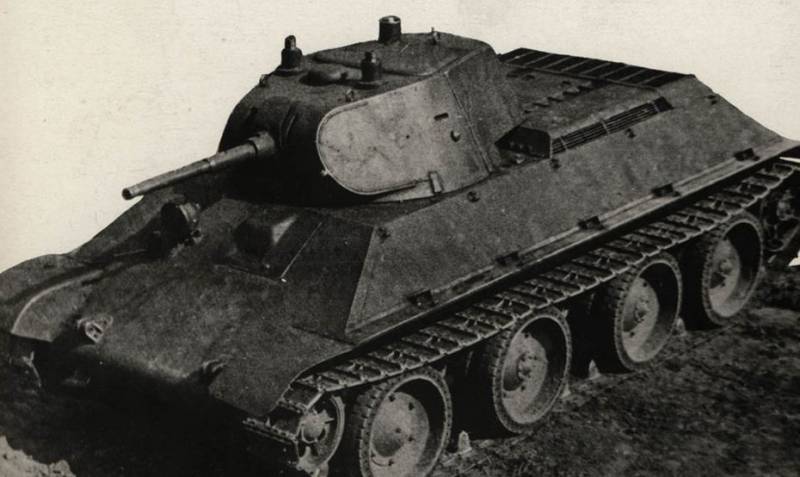
In May, the 1939 of the year, the A20 wheeled / tracked tank model was made with synchronized wheel and crawler tracks. The tank from each side of the three leading skating rink of large diameter and one in front of the guide, the nose of the hull of the tank was cut to rotate the guide roller. The armament of the tank consisted of 47-mm cannon and two machine guns, the weight of the tank increased to 18 tons.
In June, a sample of the tracked version of the tank was manufactured by 1939, it was assigned an A32 index. The tank was distinguished by the installation of the 75-mm gun, the elimination of a complex wheel drive for six rollers, reinforced tank shell armor, the installation of five rollers on each side rather than four rollers and a simpler, not narrowed nose design of the tank hull. Tank weight increased to 19 tons.
In the summer of 1939, the A20 and A32 tanks passed field tests and showed good results. According to the test results, it was concluded that the A32 tank has a weight reserve and it is advisable to protect it with more powerful armor. Plant number XXUMX was given the task to consider the possibility of increasing the reservation of the tank to 183 mm. This was due to the fact that there was a need to protect the tank from anti-tank artillery caliber 45 mm, which received serious development in the late 37-s. The design of the tank showed that it was possible to do this without degrading the mobility characteristics, while its weight increased to 30 tons.
The undercarriage was made of such a tank, which received the A34 index, which successfully passed the sea trials. Numerous changes were made to the design of the tank and it was decided to manufacture two A34 pilot tanks. In December, the 1939 was decided to use only the A20 tank with anti-bullet armor, which became the T-34 tank, the weight of which increased to 34 tons from two A34 and A26,5 tanks.
At the beginning of 1940, two T-34 tanks were manufactured. They successfully passed the tests and in March were sent to Moscow by their own moves to state leaders. The show was successful and the factory began mass production of T-34, in September, the tank began to arrive in the army.
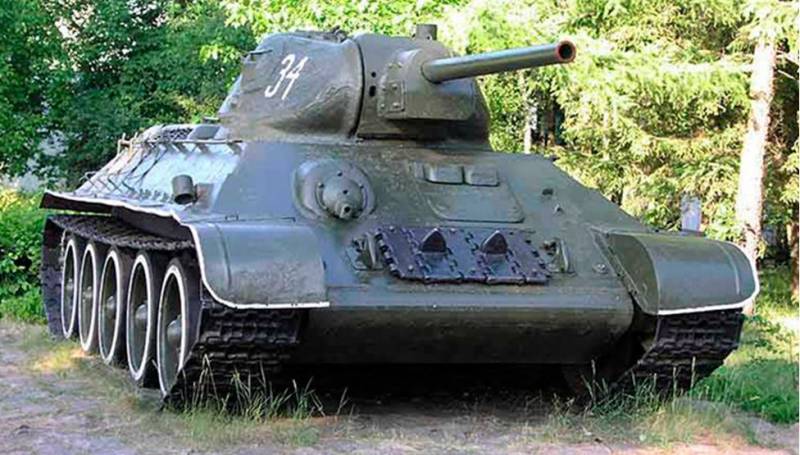
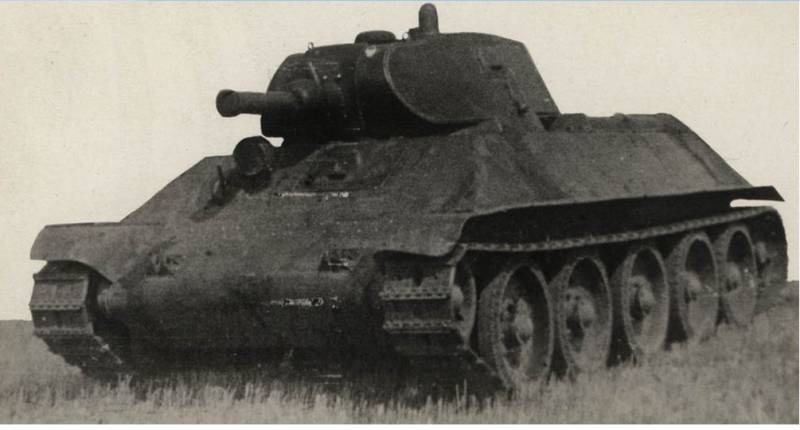
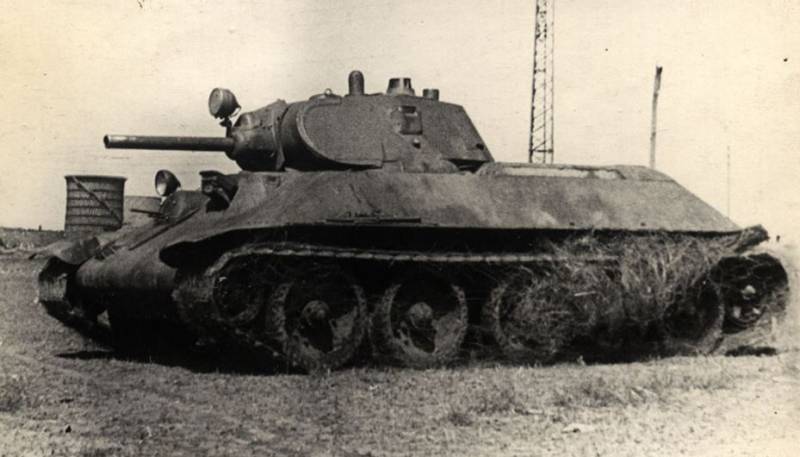
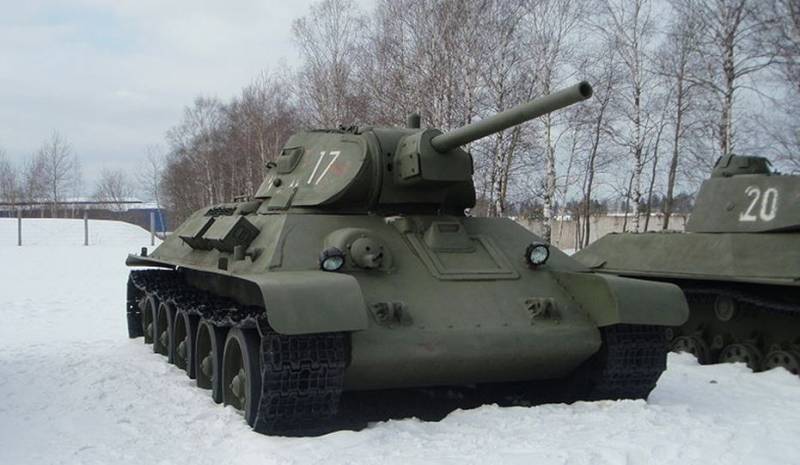
Medium Tank T-34
After the military operation of the T-34, reviews from the army were extremely controversial, some praised, others stressed the unreliability of components and systems of the tank, frequent breakdowns, poor visibility and imperfection of observation devices, tightness of the fighting compartment and the inconvenience of using an intercom.
As a result, a negative attitude towards the tank developed at ABTU and, at their suggestion, it was decided to discontinue the production of T-34 and resume production of BT-7М. Plant management appealed this decision and secured the resumption of T-34 production. Many changes were made to the design documentation and control over the manufacturing quality of tanks was strengthened; by the end of 1940, all 117 tanks were made.
Regarding the attitude of the military to the T-34, I suddenly had to face in our time. At the beginning of 80-s, in defending my dissertation, my opponent was a man from the “Stalinist Guard”, who during the war was head of the armaments department in the USSR State Planning Committee. We met, he seemed to be over seventy, the star of the Social Labor Hero glittered on his chest. Upon learning that I was from a tank design bureau, he began to be keenly interested not in his dissertation, but in what is now happening in the design bureau. During the conversation, he told me that before the war, the military was against three types of weapons: the T-34 tank, the Katyusha MLRS BM-13 and the Il-2 attack aircraft. At the first stage of the war, they were among the best in their class. Stalin did not forget anything, gave the command to find everyone and they were shot for sabotage. Fair or not, it's hard to say times were like that. This is such an interesting episode, I don’t know how real it is, but it was told by a man from that system.
Taking into account the comments received during the operation of the tank in the army in January 1941, the draft of the upgraded T-34M was presented. In fact, it was a new tank, with other hull and turret of increased volume, improved visibility from the tank, replaced observation and aiming devices, running gear with torsion suspension and support rollers with internal damping and a number of other measures.
In May 1941, it was decided to discontinue the release of the T-34 and begin production of the T-34M. In early June, the release of the T-34 was stopped and the pre-production for the new tank began. In total for the first half of 1941, 1110 T-34 tanks were launched. With the beginning of the war, the production of T-34 was immediately resumed and for the time being it was necessary to forget about T-34M.
The T-34 tank of the 1940 model of the year was a medium tank weighing 26,5 tons with the crew of a 4 man, with anti-spun armor, armed with a 76,2-mm cannon and two 7,62-mm machine guns. The layout of the tank was classic, the front control compartment, the fighting compartment with a turret in the middle of the tank and a motor-transmission in the rear of the hull.
The driver was located to the left in the building, to his right was the position of the gunner-radio operator. In the tower on the left was placed the commander and the right loader. The composition of the crew of the tank was made an unjustified decision to entrust the functions of the gunner to the commander and he almost could not perform their commanding functions. In addition to the close layout of the tower, he had an unsatisfactory set of sights and observation devices, which were extremely unfortunate in his workplace.
The hull tank was welded from rolled armor plates. The lower ones were set vertically, and the upper ones with rational tilt angles (forehead top / forehead bottom / top sides / stern - 60 / 53 / 40 / 45 degrees). The thickness of the armor of the forehead and sides of 45 mm, stern 40 mm, bottom 13-16 mm, roof 16-20 mm. The nose part of the hull at the junction of the upper and lower frontal armor plates was made rounded. The upper and lower front plates were fastened with tugs to a transverse steel beam. The driver's hatch was located on the upper front plate, viewing devices were installed in the hatch.
The tower was also welded from rolled armor plates, the side and rear walls are inclined to the vertical at an angle of 30 degrees. The thickness of the forehead armor tower 45-52 mm, sides and stern 45 mm. On the part of the tank model 1940, the cast tower was installed. On the roof of the tower was one large trapezoid-shaped hatch.
On commander vehicles installed radio 71-TK-3 with the antenna on the right side in front of the hull.
The armament of the tank consisted of an X-NUMX-mm long-barreled L-76,2 L / 11 cannon, replaced in the 30,5 year with a more advanced X-NUMX-mm F-1940 L / 76,2 cannon, and two 34-mm DT machine guns. One machine gun was paired with a gun, the other was stirred in the body on a ball bearing.
A diesel engine B-2-34 with a power of 500 hp, providing speed on the 54 km / h and power reserve 380 km, was used as the power plant.
The running tank was carried out according to the Christie scheme; on each side there were five large-diameter support rollers with an independent suspension of each roller on vertical helical springs inside the hull. The drive wheel was at the back, guiding the front. The tracks of the tracks were similar to tracks of the BT-7, but of greater width - 550 mm.
On the basis of the characteristics of firepower, security and mobility of the T-34 at the outbreak of war, it surpassed all foreign tanks of this class, but its use in the first battles was unsuccessful, most tanks were quickly lost.
The reasons for the low efficiency and high losses of the T-34 during this period were due to the weak development of new tanks by personnel, poor visibility from the tank and the extremely unsuccessful layout of the fighting compartment, tactically illiterate use of tanks, their low reliability, lack of repair and evacuation facilities on the battlefield, hasty the introduction of tanks into battle without coordination in other branches of the armed forces, the loss of command and control of troops and long marches over long distances. Over time, all this was eliminated, and T-34 was able to prove himself with dignity in the subsequent stages of the war.
The development and production of medium and heavy tanks that started in the Soviet Union at the beginning of 30 in the early stages relied on copying foreign designs and creating multi-tower medium and heavy tanks in accordance with the trends of that time. A long way was traveled in search of an acceptable concept for such tanks, as a result of which the medium tank T-30 and the classic tank KV-34 heavy tank were developed and launched at the end of the 1; tanks of these classes and in many respects determined the direction of development of Soviet and foreign tank building.
To be continued ...
- Yuri Apukhtin
- warspot.ru, imgprx.livejournal.net, fishki.net, warspot-asset.s3.amazonaws.com, topwar.ru











Information