Light tanks of the USSR in the prewar period
By that time, the Soviet government purchased documentation and samples of the British Vickers six-ton light-turbo tank in 1930, and the development of the T-26 light tank began on this basis. According to its characteristics, the T-19 was the same or inferior to the T-26 tank, and the cost was much higher. In this regard, in the 1931, work on the T-19 tank was discontinued, and T-26 was launched into mass production at the Bolshevik plant in Leningrad.
Light tank T-26
The T-26 tank was a copy of the Vickers Six-ton English Light Tank and became the most massive tank of the Red Army before the Great Patriotic War; in total, 11218 of these tanks was released.
Depending on the modification, the T-26 tank was weighing 8,2 — 10,2 tons and had an arrangement with the placement of the transmission compartment in the frontal part of the hull, the combined control compartment with the combat compartment in the middle part of the tank and the engine compartment. The 1931-1932 samples had a two-turret layout, and a single-turret from the 1933 of the year. The crew consisted of three people. On double-turbo tanks - the driver, the left turret and the tank commander, who also served as the right turret, and the single turret - the driver, gunner, and the commander, who also served as a loader.
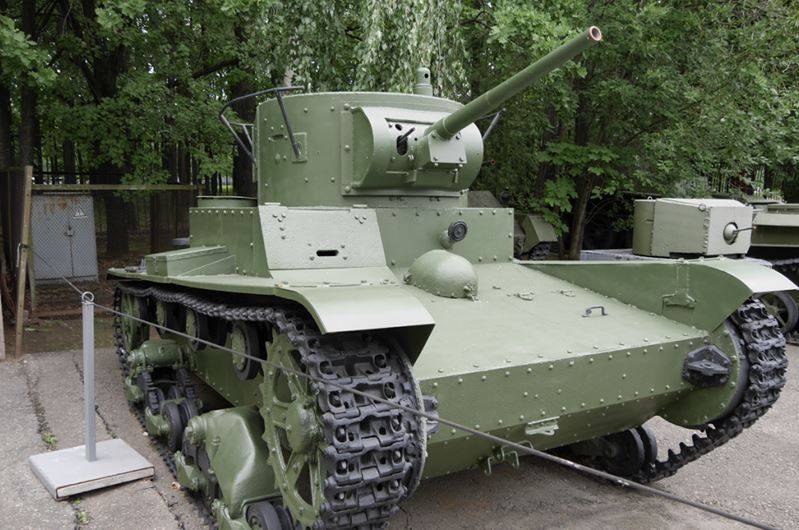

The hull and turret design was riveted from armor rolled sheets, the booking of the tank protected against small weapons. The thickness of the tower armor, forehead and sides of the hull 15 mm, roof 10 mm, bottom 6 mm.
The armament of two-machine-gun machine-tanks consisted of two 7,62-mm machine guns DT-29, placed in spherical installations in the frontal part of the turrets. On double-turbo tanks with cannon-machine-gun armament, in the right turret, instead of a machine gun, a 37mm threaded gun or a B-3 gun was mounted. Pointing weapons in the vertical plane was carried out using the shoulder rest, in the horizontal plane by turning the tower.
The armament of single-turreted tanks consisted of an 45-mm rifled semi-automatic 20-K L / 46 cannon and a paired 7,62-mm DT-29 machine gun. For the guidance of weapons used panoramic periscope sight PT-1 and telescopic sight TOP, which had 2,5-fold increase.
As the power plant used engine "GAZ T-26", which was a copy of the English "Armstrong-Sidley Puma", power 91 l. s., providing speed on the highway 30 km / h and power reserve 120 km. In 1938, a forced version of an 95 l engine was installed on the tank. with.
The undercarriage of the T-26 on each side consisted of eight dual rubber-supported road wheels, four dual rubber-supporting wheels, a sloth, and a front-wheel drive. The suspension of the road wheels was balanced on the springs, interlocked in carts of four rollers.
Until the end of the 30-ies, the T-26 tanks formed the basis of the tank fleet of the Red Army and by the beginning of the Great Patriotic War there were about ten thousand in the army. Due to poor booking and insufficient mobility, they began to become obsolete and yield to foreign models in terms of their main characteristics. The military leadership decided to develop new, more mobile and protected types of tanks and the modernization of completely outdated T-26 tanks was practically not carried out.
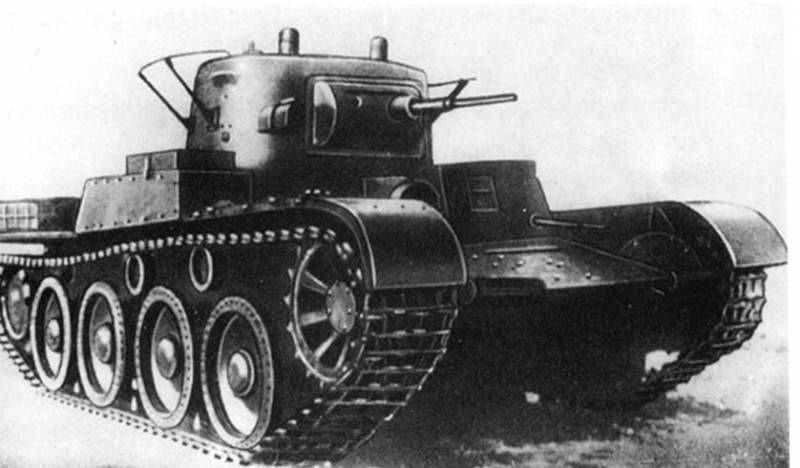
Light tank T-46
An experienced light-wheeled-tracked tank T-46 was developed in 1935 year at the Leningrad plant No. 174, four tank models were made, which were tested in 1937. The tank was developed to replace the T-26 light infantry escort tank, including to increase its mobility by transferring the tank to a wheel-track. It was also assumed the installation of a diesel engine and the strengthening of weapons and security. In the design of the T-46 tank, the T-26 units were widely used.
According to the layout of the tank, the transmission was located in the front of the hull, there was also a control compartment with the driver’s location in the protruding armored wheelhouse on the left side of the hull. The fighting compartment with the tower was in the middle of the hull and the engine in the stern. The weight of the tank was 17,5 tons.
The crew consisted of three men, the driver was in the hull, and the commander and gunner were located in the combat compartment in the turret. The landing crew was made through the double hatch of the driver and two hatches in the roof of the tower.
The design of the hull and turret was riveted and assembled from armor plates, the turret was enlarged and intended to mount a cannon and two machine guns. Reservations were differentiated, the thickness of the armor of the tower 16 mm, the forehead of the case 15-22 mm, the sides of the case 15 mm, the roof and the bottom 8 mm.
The armament of the tank consisted of 45-mm 20K L / 46 guns and two 7,6-2mm DT-29 machine guns, one paired with a cannon, the second in the stern niche in the ball mount. Planned to install 76,2-mm gun PS-3, but it was not mastered by industry.
As a power plant, an 330 hp engine was used, providing speed along the highway on 58 km / h tracks and on 80 km / h wheels. The diesel engine was not installed because it did not have time to master the production.
The chassis had the strongest differences, the “Christie chassis” was used in the tank. Instead of trolleys, four dual large-diameter roller wheels with rubber tires and a blocked spring suspension, two support rollers and a front-wheel drive wheel were installed on each side. When driving on wheels, there were only two rear pairs of wheels leading, and the turn was carried out with the help of a conventional differential with transmission to the front pair of wheels.
The tests of the T-46 were quite successful, the tank had a much higher speed and mobility than the T-26, and the tank’s handling was also simplified by using a new transmission.
The tank as a whole received a positive assessment, while there was a lack of reliability of the power plant and the unacceptably high cost of the vehicle. This led to the fact that in 1937, it was decided to cease further work on the T-46 and the main work on wheeled-tracked tanks focused on improving the wheeled-tracked tanks of the BT series.
In 1938, an attempt was made to create a T-46-46 medium tank based on T-5 with a counter-armor reservation, which did not lead to a positive result.
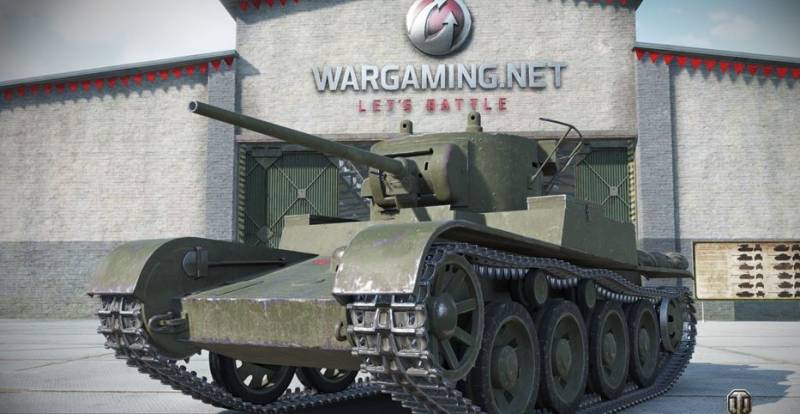
Cruising tank BT-2
At the end of the 20-s, the military doctrine of using cruising high-speed tanks to make deep breaks in the enemy’s defense and operating in the operational rear at a great distance found widespread use. Under this doctrine, cruising tanks began to be developed in the West, in the USSR there was no such experience, and in the USA in 1930 a license was acquired for the production of the cruiser wheeled / tracked tank Christie M1931.
The wheeled-tracked high-speed tank BT-2 was a copy of the American M1931 tank. With the license, the design documentation was transferred to the tank and two tanks without towers were supplied. Development of documentation for the BT-2 and its production was entrusted to the Kharkov Locomotive Plant, where a tank design bureau and production facilities for the production of tanks were created. In 1932, the KhPZ began mass production of BT-2 tanks. So in the Soviet Union there were two tank design schools, in Kharkov and formed earlier in Leningrad, which for many decades determined the direction of development of Soviet tank construction.
The BT-2 tank was a light-wheeled-tracked tank with a classic layout, a front control compartment, a fighting compartment with a turret in the middle, and a power transmission in the stern.
The design of the hull and the cylindrical tower were riveted of rolled armor, the angles of inclination were only at the front of the hull, which had the appearance of a truncated pyramid to ensure the rotation of the front drive wheels. The number of crew of the tank was two people, weight 11,05 tons. In the upper front plate there was a hatch for landing the driver, and in the roof of the tower there was a hatch for the commander.
The tank armament included the X-NUMX-mm B-37 (3K) L / 5 cannon and the 45-mm DT machine gun in the ball mount to the right of the gun. In part of the tanks, due to the lack of guns, a twin machine-gun installation with two 7,62-mm DT machine guns was installed instead of a gun.
Body armor was only from small arms and shell fragments. The thickness of the tower armor, forehead and sides of the hull 13 mm, roof 10 mm, bottom 6 mm.
As a power plant was used aviation engine "Liberty" M-5-400 with a capacity of 400 liters. sec., providing a speed of 51,6 km / h on the tracks, 72 km / h on wheels and a power reserve of 160 km. It should be noted that the average technical speed of the tank was significantly lower than the maximum.
The tank had an individual spring “candle” suspension, commonly known as “Christie suspension”. Three vertical springs with respect to each side of the hull were located between the outer armor plate and the inner wall of the hull side, and one was placed horizontally inside the hull in the fighting compartment. The vertical springs were connected through the balancers to the rear and middle support rollers, and the horizontal springs were connected to the front controlled rollers.
The tank had a combined wheeled-tracked propulsion unit consisting of a rear sprocket wheel, a front guide wheel and large diameter 4 road wheels with rubber tires. During the transition to the wheel track, the track chains were removed, disassembled into 4 parts and placed on the nadgusenichesky regiments. The drive in this case was carried out on the rear pair of road wheels, the tank was driven by turning the front rollers.
The BT-2 tank was a landmark for the Soviet tank industry, serial production of complex tank assemblies was organized, technical and technological production support was organized, a powerful engine was launched and a tank suspension was used, which was successfully applied later on the T-34.
In 1932 — 1933, 620's BT-2 tanks were manufactured at KhPZ, of which 350 had no guns due to their lack. On 1 June 1941, the troops had 580 BT-2 tanks.
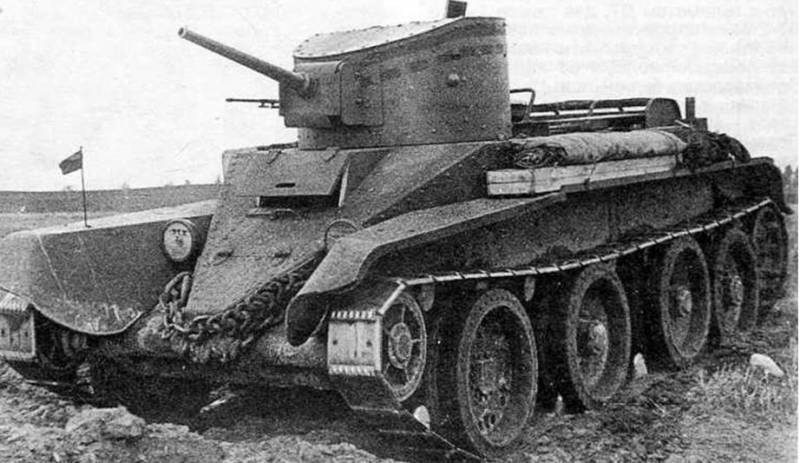
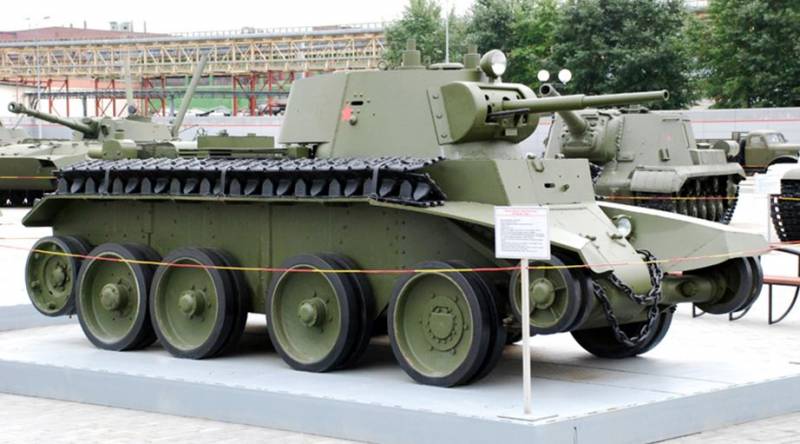
Cruising tank BT-5
The wheeled-tracked tank BT-5 was a modification of the BT-2 tank and outwardly did not differ from its prototype. The difference was in the new elliptical turret, 45K L / 20 gun 46 and a number of design improvements aimed at improving the reliability and simplifying the serial production of the tank.
The weight of the tank increased to 11,6 tons, and the crew of up to three people, the commander and the gunner were placed in the tower.
The tank was not difficult to master, it was distinguished by unpretentious maintenance and high mobility, thanks to which it was popular with tankers. BT-5 was one of the main tanks of the pre-war period, it was produced in 1933-1934, the 1884 tank was produced in total.
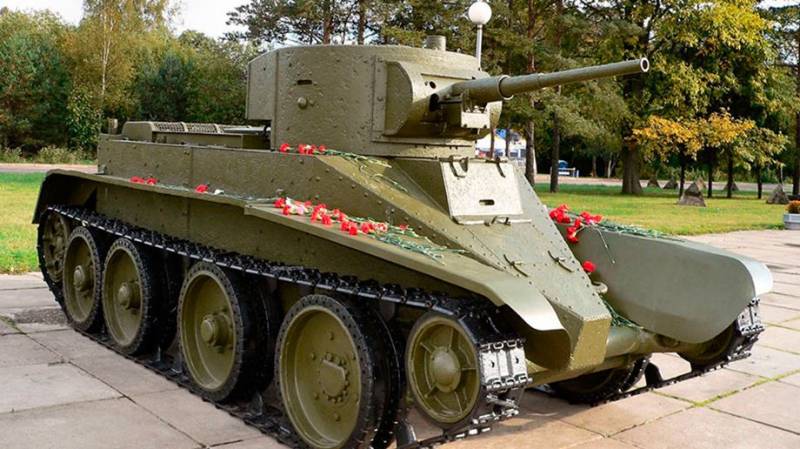
Cruising tank BT-7
The wheeled-tracked tank BT-7 was a continuation of the line of tanks BT-2 and BT-5. It was distinguished by a welded modified case of increased armor protection and a new engine, the tank’s armament was similar to the BT-5.
The tower had the shape of a truncated elliptical cone. Reservations for the hull and turret have been enhanced. The thickness of the armor tower 15 mm, the forehead of the case 15-20 mm, the sides of the case 15 mm, the roof 10 mm, the bottom 6 mm. The weight of the tank increased to 13,7 tons.
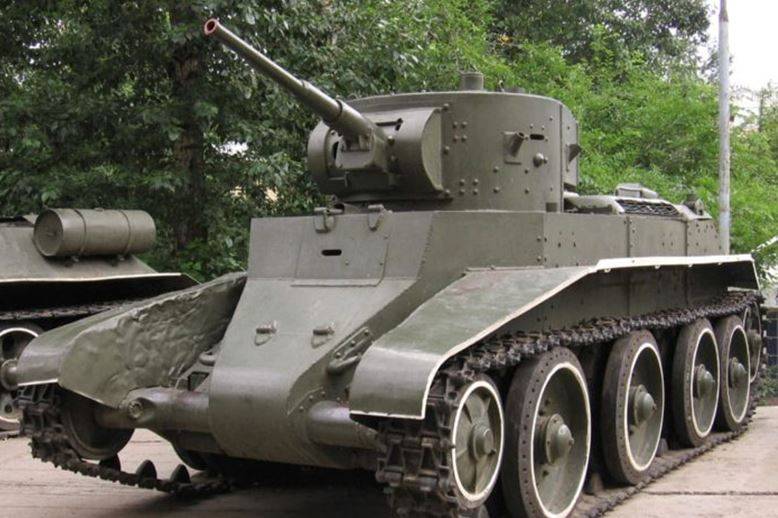

A new M-17T aircraft engine with an 400 hp power was installed, providing speed up to 50 km / h on tracks and up to 72 km / h on wheels and a cruising range of 375 km.
The main problems on the tank caused the engine. It is often ignited due to its unreliability and the use of high-octane aviation fuel.
The tank was produced in 1935-1940's, in total 5328 tanks BT-7 were produced.
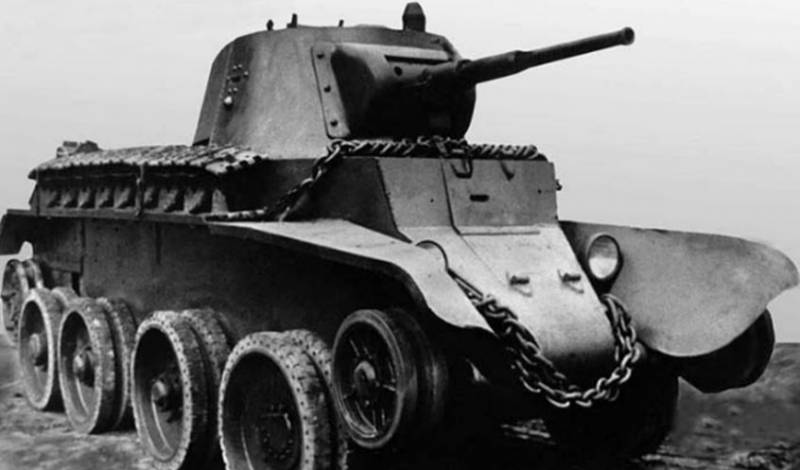
Cruising tank BT-7M
The BT-7М tank was a modification of the BT-7 tank, the main difference was the installation on the tank instead of the M-17T aircraft engine of the B-2 diesel engine with 500l power. The rigidity of the tank body increased due to the installation of braces, structural changes were made in connection with the installation of the diesel engine, the weight of the tank increased to 14,56 tons. The speed of the tank increased to 62 km / h on tracks and to 86 km / h on wheels and cruising range to 600 km.
Installing a diesel engine has reduced the recoverable amount of fuel and to abandon the additional tanks on the fenders. However, the main fundamental advantage of a diesel engine over a gasoline engine was low flammability, and tanks with this engine were much safer than their gasoline counterparts.
The BT-7M tank was developed in the 1938 year, was mass-produced in 1939-1940, the 788 tanks of the BT-7M were produced in total.
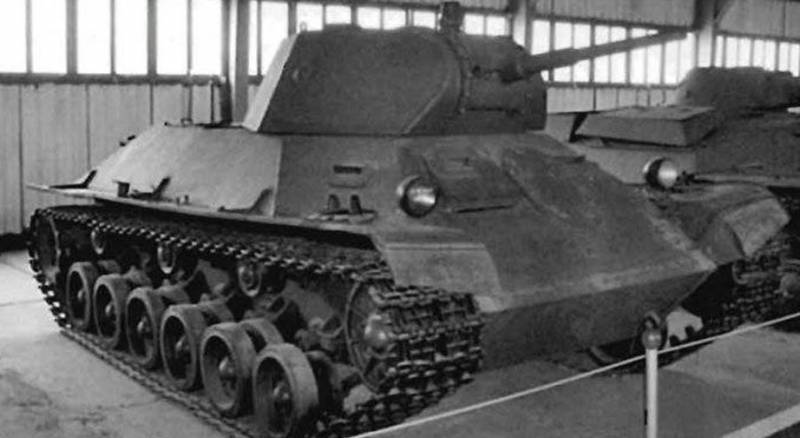
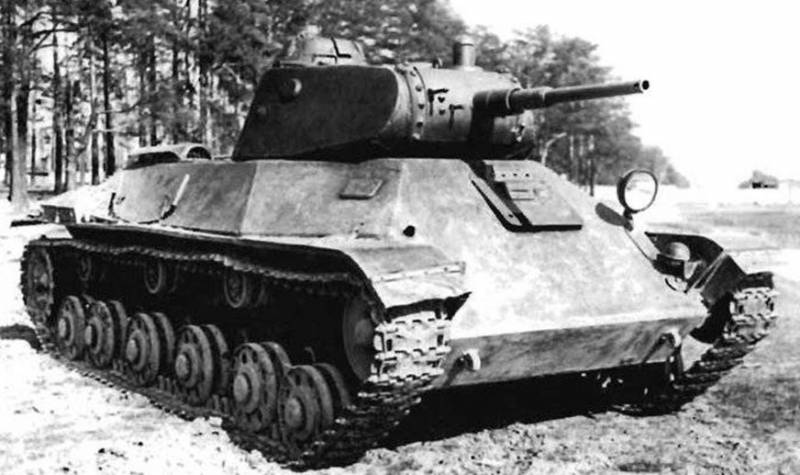
Light tank T-50
The reason for the development of the T-50 tank was the lag in the second half of the Soviet light tank 30 in firepower, security and mobility from foreign samples. The main Soviet light tank T-26 is hopelessly outdated and it needed replacement.
According to the results of the Soviet-Finnish war 1939-1940, the need for a significant increase in the reservation of Soviet tanks was revealed, and in 1939, the development of a light tank in armor protection up to 40mm, a B-3 diesel engine and a torsion suspension began. The tank was supposed to be weighing up to 14 tons.
The development of the T-50 tank was also influenced by the results of tests of a sample of the medium tank PzKpfw III Ausf F purchased in Germany. According to its characteristics, it was recognized in the USSR as the best foreign tank in its class. The new Soviet tank should be massive and replace the T-26 infantry support tank and the BT high-speed tanks. The T-34 tank for this role of a mass tank was not yet suitable because of the high cost of its production at that stage.
Light tank T-50 was developed in 1939 year in Leningrad at the plant number 174. At the beginning of the 1941 of the year, prototypes of the tank were manufactured and successfully tested; it was put into service, but before the start of the Great Patriotic War, they did not have time to deploy serial production.
The layout of the T-50 was classic, the control compartment in front, the fighting compartment with a turret in the middle of the tank, the engine compartment in the stern. The hull and turret of the tank had significant angles of inclination, so its appearance T-50 was similar to the average tank T-34.
The crew consisted of four people. In the control department, with a shift from the center to the left side, the driver was housed, the rest of the crew (gunner, loader and commander) were in the triple tower. The gunner's workplace was located to the left of the gun loading the right, the commander in the rear of the tower to the right.
A fixed commander's turret with eight triplex viewing devices and a hinged flap for flag signaling were installed in the roof of the tower. Landing commander, gunner and loader was made through two hatches on the roof of the tower in front of the commander's turret. The rear stern of the turret also housed a hatch for loading ammunition and discharge of spent cartridges through which the commander could leave the tank in an emergency. Manhole for landing the driver was located on the frontal armor plate. Because of the stringent requirements for weight, the layout of the tank was very tight, which led to problems with the convenience of the crew.
The tower was a complex geometric shape, the sides of the tower were located at an angle of inclination 20 degrees. The frontal part of the turret was defended by a cylindrical armor with a thickness of 37 mm, in which there were embrasures for mounting a cannon, machine guns and a sight.
The hull and turret of the tank were welded from rolled armored plates. Frontal, upper side and stern armored plates had rational 40 — 50 ° angles, the lower part of the board was vertical. The tank weight reached 13.8 tons. The armor protection was counter-equipped and differentiated. The thickness of the armor of the upper frontal sheet 37mm, lower 45mm, tower 37mm, roof 15mm, bottom (12-15) mm, which significantly exceeded the protection of other light tanks.
The armament of the tank consisted of a 45mm semi-automatic 20-K L / 46 cannon and two 7,62mm DT machine guns, which were mounted on axles in the frontal part of the turret, paired with it.
The diesel engine B-3 with the power 300 hp, providing speed on the 60 km / h and power reserve 344 km, was used as the power plant.
The undercarriage of the tank was new for Soviet light tanks. The suspension of the car was an individual torsion bar, on each side there were 6 gable support rollers of small diameter. Opposite each track roller to the hull, the travel limiters of the suspension balancers were welded. The upper branch of the track was supported by three small supporting rollers.
Light tank T-50 was the best tank in the world at that time in its class and was fundamentally different from its “brothers” in class. The car was maneuverable and dynamic, with a reliable suspension and good armor, which protected anti-tank and tank guns from fire.
The main weakness of the tank was its weaponry, the 45mm gun 20-K no longer provided sufficient firepower. As a result, the medium tank T-34, which was with much more powerful weapons, turned out to be more promising in the Soviet tank building.
After the evacuation of the plant from Leningrad to Omsk, due to the lack of engines and organizational problems, the tank could not be put into mass production; in total, according to various sources, X-NUMX-65 T-75 tanks were launched.
Its mass production was not developed at the evacuated factories, since the production of the B-3 diesel engine was not organized and the factories were reoriented to the production of T-34 tanks.
In the 1942 year, tried to establish mass production of T-50, but this was prevented by objective factors. After a heavy defeat in the summer of 1942, it was urgently necessary to replenish the losses in the tanks, all forces were thrown at expanding the production of T-34 and its engines, and a number of enterprises also launched a wide production of a simple and cheap T-70 light tank, which characteristics seriously inferior to the T-50. Serial production of the tank was never organized, and later even T-34-76 was not suitable for its weapons, and tanks with much more powerful weapons were required.
The development of light tanks in the USSR, which had neither experience nor a production base for the creation of tanks, began with copying foreign samples. The Russian Renault, MS-1 and T-19 tanks were a replica of the French FT17 light tank, the T-27 wedge and T-37, T-38 and T-40 amphibious tanks and a copy of the light floating English Carket-Loyd Mk.I and T-26 tanks the Vickers-Carden-Loyd floating tank, the T-46 and T-1931 tanks were a replica of the Vickers Six-ton English Light Tank, the BT series of tanks of the American Series M30 Christie. None of these copied light tanks became a breakthrough in world tank building. Having studied the advantages and disadvantages of foreign prototypes and having gained experience in the development of tanks, Soviet tank builders were able to create in 50-ies such masterpieces of world tank building as the light tank T-34 and the medium tank T-34. If T-50 became famous all over the world, then T-XNUMX was awaited by a difficult fate and undeserved oblivion.
In the interwar period, 21658 light and amphibious tanks were launched in the USSR, but all of them were outdated designs and did not shine with their characteristics. Only the light tank T-50 seriously stood out from this series, but it was never possible to launch it into mass production.
- Yuri Apukhtin
- tanki-tut.ru, alternathistory.com, armedman.ru, topwar.ru
- The first light and floating tanks of the USSR in the interwar period
What contributed to the emergence of tanks in World War I
German tanks of the First World War
French tanks of the First World War
Tanks of England in the interwar period
Light tanks of France in the interwar period
Middle and heavy tanks of France in the interwar period
US light tanks in the interwar period
Inter-war period medium and heavy tanks
Germany's light tanks in the interwar period
Germany's medium tanks in the interwar period











Information