US light tanks in the interwar period

By the end of the war, the US Army had two tank corps, but in 1920, they were disbanded and no major tank units existed in the army until World War II. The attitude of the military to the creation of tanks was appropriate, and in the United States joint production of light tanks FT-17 and heavy Mk.VIII was organized. In total, 100 units of the first and 950 second units were released and in the 20-s they formed the basis of the armored forces of the American army.
In accordance with the program of equipping the army with armored vehicles adopted in 1920, its development was supposed to create tanks of direct support for infantry and cavalry of two types: lightweight, on the order of 5 tons with machine guns and the possibility of delivery to the front on trucks and average weights of the order of 15 tons, corresponding to the carrying capacity of modern then bridges, with cannon and machine gun weapons.
FT17 was chosen as a prototype for a light tank and its modifications, the middle class tank was to be developed and work in this direction with the manufacture of prototypes was carried out, but before the beginning of World War II, none of these tanks reached mass production. Two attempts were made to create a heavy tank that ended in failure.
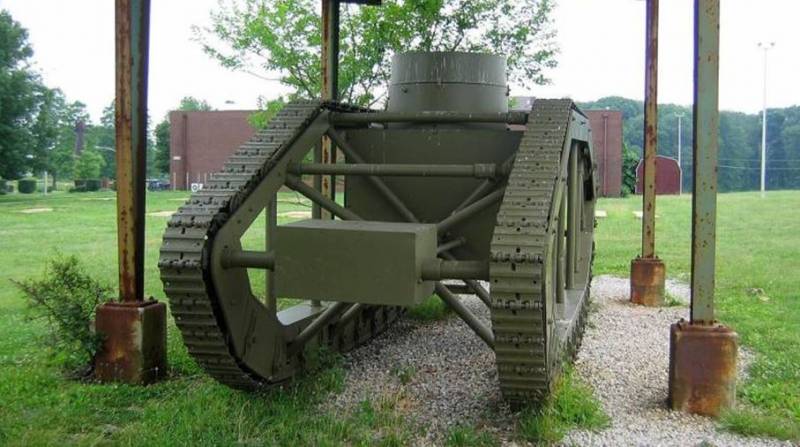
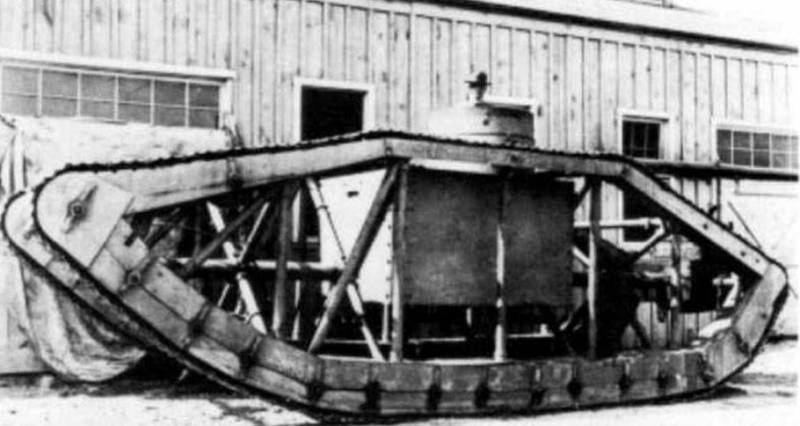
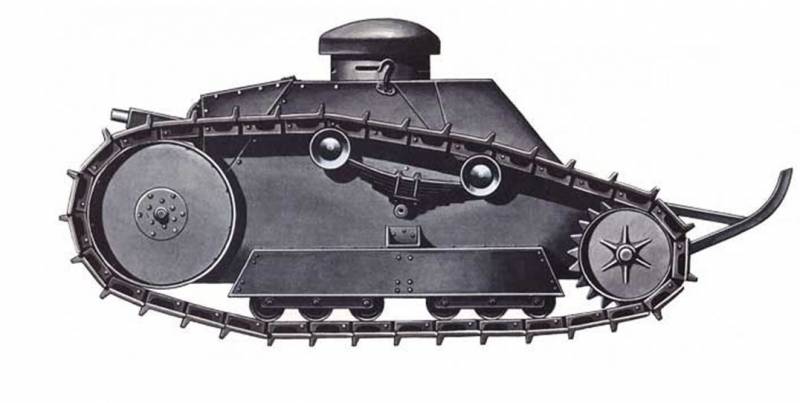
Skeleton Tank
The American designers had no experience in creating tanks, and they began their development by copying English and French tanks. Having received light tanks from France and heavy diamond-shaped ones from England, the American designers saw the advantages and disadvantages of those and other tanks. Heavy tanks had good maneuverability on rough terrain, but due to the heavy weight of the armored hull of the tank, low mobility. Light tanks had high mobility, but were inferior to heavy tanks in all terrain when overcoming obstacles.
The designers decided to combine these tanks and create a machine that ensures maneuverability in overcoming the trenches and the enemy’s defenses, typical of heavy tanks, and good mobility of light tanks.
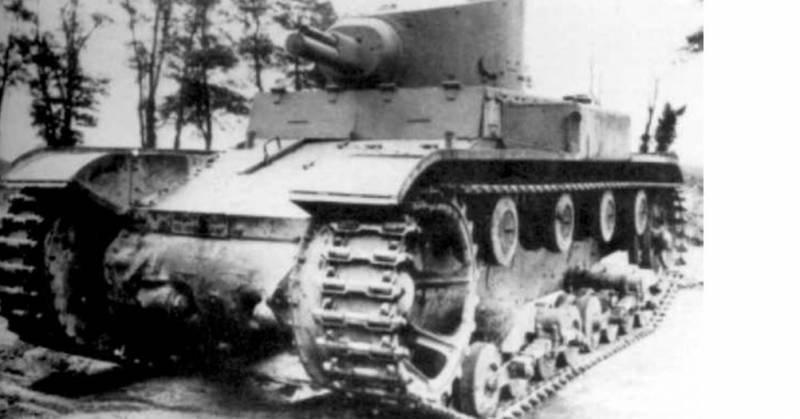
It was decided to abandon the overall and heavy hull of the tank. The running gear was based on the diamond-shaped undercarriage of the English tank Mk.VIII and placed it not on the hull, but on two tubular frames connected by a tubular frame.
In the center of the frame was installed armored box-shaped capsule of small size to accommodate the crew, power plant and weapons. The capsule was assembled from 12,7-mm armor steel with bolts and rivets.
The crew was two people - the driver and the commander-gunner, as a weapon 7,62-mm machine gun, the power plant based on two engines Beaver 50 hp power. each. In the stern of the hull housed the transmission in the box-housing. Torque from the engine was transmitted using special gearboxes and drive shafts.
With the weight of the tank 9,15 t its length was 7,62 m, width 2,56 m and height 2,89 m. "Skeleton tank" was much lighter than its prototype Mk. VIII (39 tons), but outnumbered light tanks.
In 1918, one tank was made and tested. The tank showed good mobility and maneuverability, developed a speed of at least 8-10 km / h and had a power reserve of 55 km, but had insufficient firepower, weak security, inconvenient to accommodate the crew and structurally difficult for mass production. The tank skeleton did not receive further development.
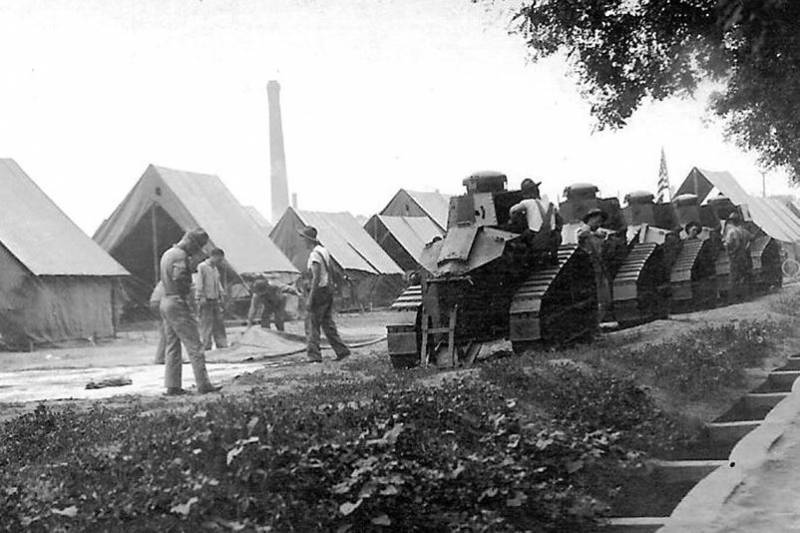
Light tank M1917 (Ford six-ton)
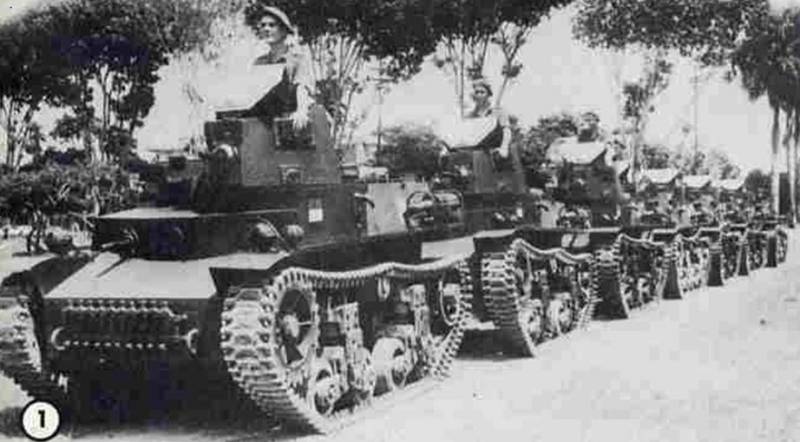
Given that there was no experience in the development of tanks in the United States, on the basis of the transmitted documentation of the French lightweight FT17 in 1917, it was decided to organize in the United States a joint production of this tank, which received the M1917 index. The development of the tank took the company "Ford", which produced cars. The design of the tank did not have significant differences from the prototype, it was allocated only for individual units that were already manufactured in the USA.
The classic layout of the tank was preserved, the driver was located in the front of the hull, the fighting compartment with a rotating turret was in the middle, and the engine and transmission compartment. The crew of the tank remained two people, weight 6,6 tons.
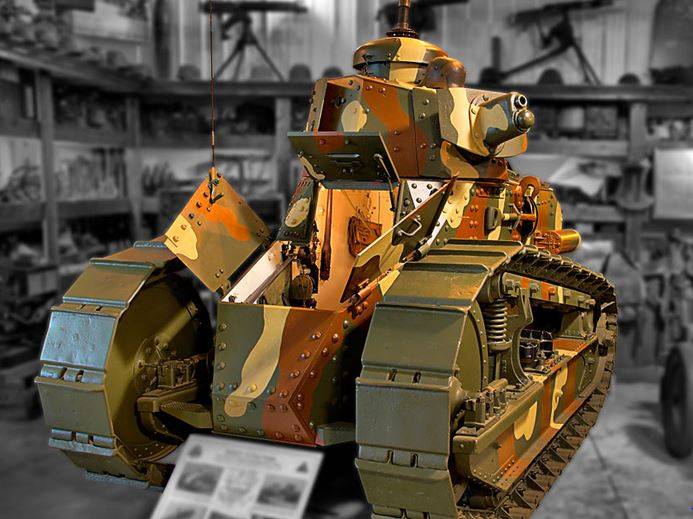
The tank was notable for a new riveted octagonal turret, in which two versions of weapons with a Hotchkiss 37-mm cannon with a telescopic sight or a Colt-Marlin 7,62-mm machine gun were supposed.
Reservations for the hull and turret consisted of 15-mm armor plates, and the bottom and roof of the hull and turret 8 mm.
The Buda HU engine with 42 horsepower, providing speed on solid ground up to 8,9 km / h, was used as a power plant. The chassis was completely similar to the FT17.
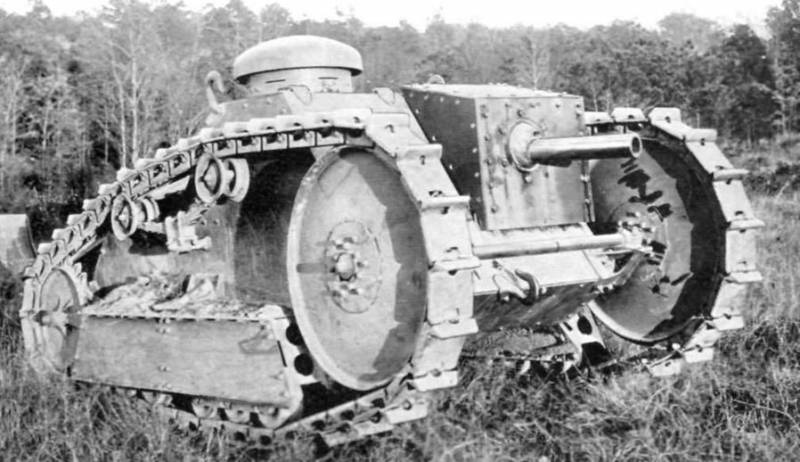
Light tank M1918 (Ford three-ton)
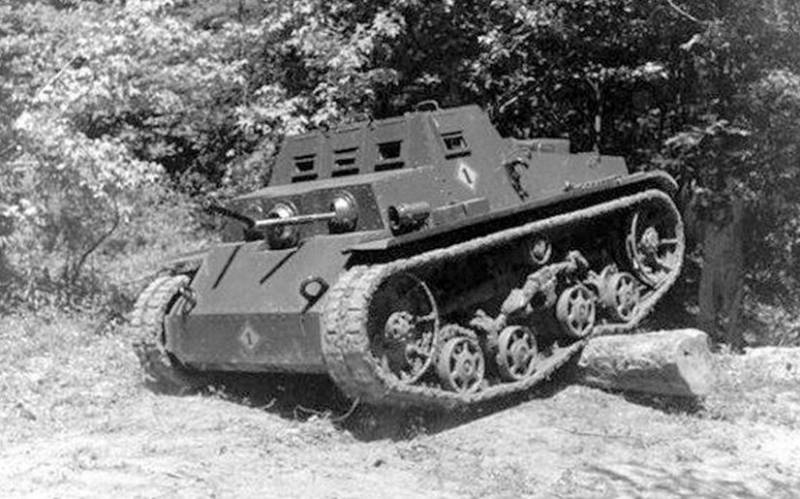
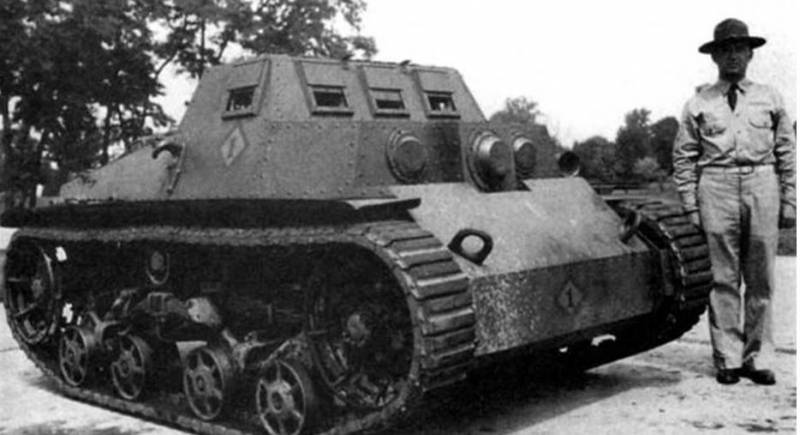
A further development of American light tanks was the creation by Ford of 1918 of its own version of the M1918 light tank with the maximum use of car units. Only an experimental batch of machines in the amount of 15 units was released.
The layout of the tank changed, the command and control compartments were in front, the turret was missing, the engine-transmission rear. The crew of the tank two people. As weapons 7,62-mm machine gun Colt-Browning, installed in the front hull plate. Observation of the terrain was carried out from a small mushroom-shaped turret.
The design of the tank was riveted from armor rolled sheets. With a weight of 3,26, the thickness of the armor of the forehead and hull sides was 13 mm, the bottom and roof of the 6mm. Armament tank consisted of 7,62-mm machine gun "Marlin". As the power plant used two engine power 17 hp each providing 13 km / h speed and 55 km cruising range.
Tank М1918 possessed low security, weak armament and power plant, did not have a rotating tower, turned out to be ineffective and did not receive further development.
Light tank "Ford Mk.I"
In order to eliminate the shortcomings of the M1918 tank, the Ford company in 1918 developed a more sophisticated Ford Mk.I model. The tank’s firepower was reinforced; it received a rotating turret with an 37-mm cannon and a Colt-Browning 7,62-mm machine gun. The crew of the tank remained two people.
With the weight of the tank 7,5 t he had a weak reservation, the forehead of the hull 12,5 mm, sides of the 9mm and feed 6,35 mm. The Hudson engine with a power of 60 hp, providing 12,5 km / h speed and cruising range along the 65 km highway, was used as a power plant.
The chassis of the Mk.I was similar to the M1918 tank, a typical “tail” for the time was installed at the rear to overcome the ditches and trenches.
The tank had no clear advantages over the M1917, only one instance of the tank was manufactured and tested and work on it was discontinued.
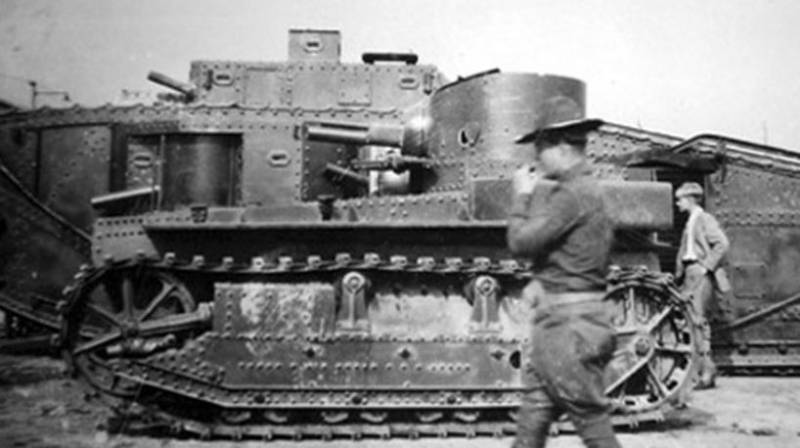
Light tank T1
At the next stage, Cunningham took up the development of an American infantry support light tank to replace the M1917 tank. In 1926, the T1 light tank was developed, and testing and fine tuning continued until the end of the 20. Several modifications of the T1-1-T1-3 tanks were produced and tested.
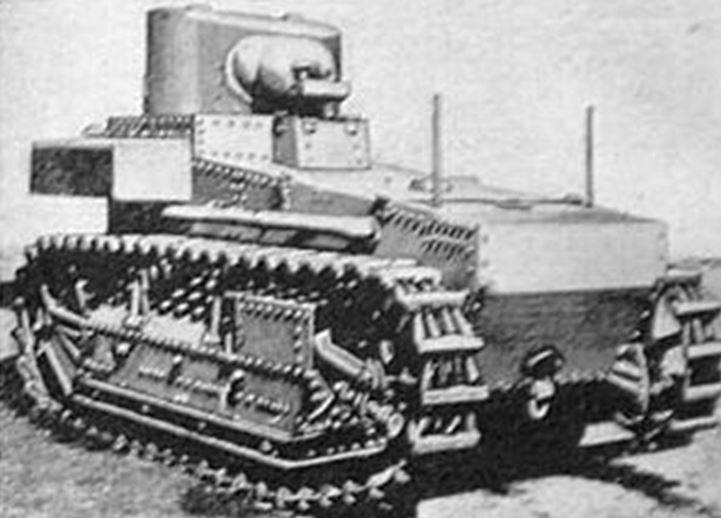
The layout of the tank compared to the M1917 fundamentally changed, the power plant was placed in front, the driver and the commander in the back in a rotating turret. The hull structure was riveted-welded, with the thickness of the armor of the forehead and sides of the hull and turret 10mm, the bottom and the roof 6mm. The weight of the tank was 7,1 tons.
The 37-mm short-barreled gun and the twin machine gun 7,62-mm were used as a weapon of the tank. Subsequently, the gun was replaced by a long-barreled semi-automatic Browning 37-mm gun.
Engine power 110 HP provided speed on the highway 29 km / h and power reserve 120 km. The basis of the chassis used tractor with a large number of small road wheels. Suspension was absent.
According to the test results, the tank did not show the required characteristics and at the beginning of the 30's it was completely redone. New versions of the T1-4 - T1-6 little resembled previous models. Practically it was a new tank.
The new development was created under the influence of the English light tank Vickers 6 tonn (Vickers E) and was also intended to support infantry on the battlefield. The layout of the tank has changed. In front of the hull housed the driver, in the middle part of the fighting compartment with a rotating turret, power plant behind.
The tank body remained riveted-welded. Reservations increased, hull forehead and turret were 16 mm thick, 10 mm bead, roof and bottom 6,4 mm. The tank turret was cylindrical with a partially sloped roof armor sheet. Tank weight increased to 8 tons.
The armament of the tank consisted of the 37-mm semi-automatic gun M1924 and the 7,62-mm machine gun Browning M1919A4.
The engine used was an 140 horsepower engine, which increased the speed of the tank to 37 km per hour and the cruising range on the highway to 160 km.
The T1EX4 undercarriage in many respects resembled the English Vickers E. On each board it consisted of eight small-diameter support rollers interlocked in pairs in four trucks with elliptical leaf springs, four support rollers, a front driving wheel with a tensioning mechanism and a rear guide wheel. The crew consisted of three people.
In 1931, the first model of the T1EX4 tank was presented, the tests of the prototype did not satisfy the military. The modification of the T1EX6 tank with a more powerful engine that was presented later was not accepted either.
By that time, the military had paid more attention to the medium tank T2, in connection with which the work on the light tank T1 was stopped.
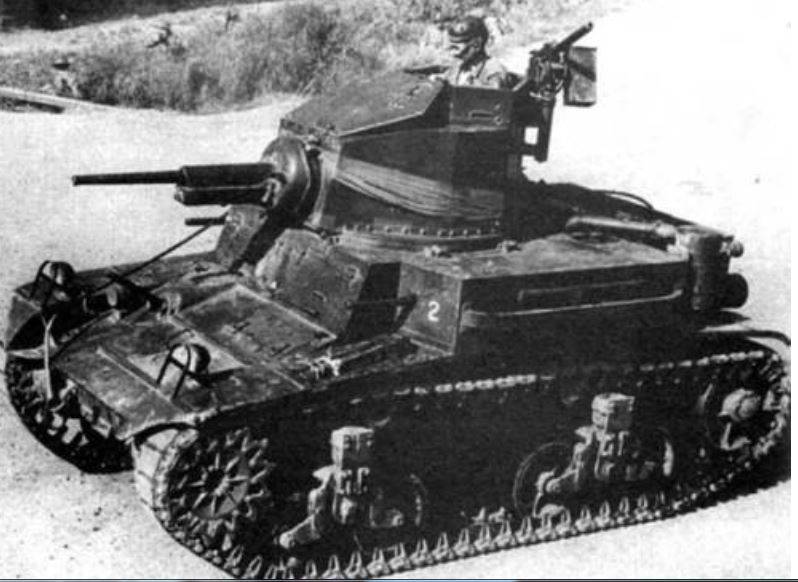
CTL Tannels by Marmon-Herrington Company
The company Marmon-Herrington Company, previously engaged in the production of trucks, tractors and armored vehicles, joined the development of light tanks in the middle of 30's. She began developing the CTL family of light tank shoes for export, then the tank shoes were used by the US Marines and Army.
The first sample of the CTL-1 from this family was developed in 1935 year. Weight tanketki 4,0 tons, crew of two people, thickness of armor 6,35 mm, armament one 7,62-mm Browning machine gun in a spherical installation, body riveted design, engine power 110 hp provided speed 48 km per hour. A batch of cars was sold to Iran.
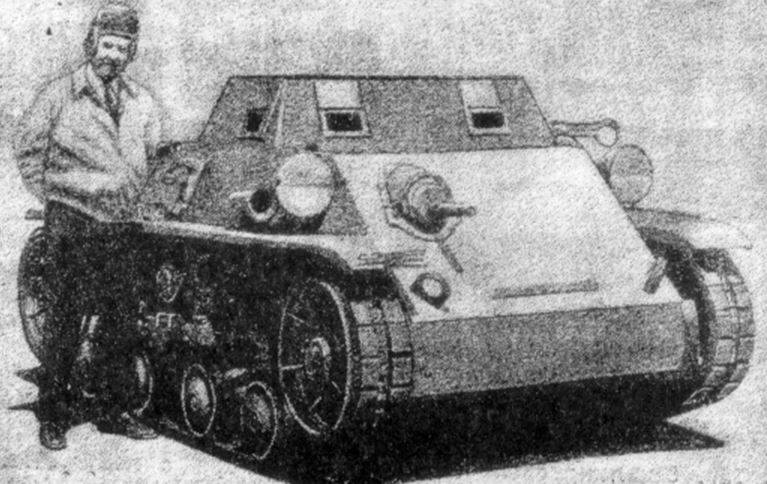
The sample CTL-3 was created according to the requirements of the US Marine Corps. Weight 4,3 tons, crew of two people, armor thickness 6,35 mm, armament one 12,7-mm machine gun and two 7,62-mm machine guns installed in the front plate, 110 engine power hp provided speed on the highway 48 km / h. Made a batch of 5 samples for the Marine Corps.
The sample CTL-3M was a modification of the CTL-3, a crew of two, reinforced suspension on vertical spiral springs, a wider track was used, the armament consisted of five Browning machine guns 7,62mm, 124 HP engine.
The sample CTL-6 was a further development of the CTL-3M, crew of two, weight 6,7 t, booking 11 mm, arming three 7,62-mm machine guns, hp 124 engine. provided speed 53 km / h and power reserve 200 km. In 1941, 20 samples were made.
The sample СLS-4 was created by the order of the Dutch East Indies, the crew is two people, the weight of the 7,2 is tons, equipped with a single tower, booking forehead 25,4 mm, board 12,7mm, HP 124 engine. provided speed 48 km / h, arming three 7,62-mm machine gun, one in the tower, two in the body.
The driver’s high cabin to the left of the tower restricted the shelling sector to 240 degrees. In connection with this, two modifications of the machine were created: the СLS-4TAС had a tower shifted to the starboard side, and СLS-4TAY- to the left one. A total of two modifications of the 452 model was released. Subsequently, the modification СТLS-4TAY received the index Т14, and СТLS-4TAС - Т16.
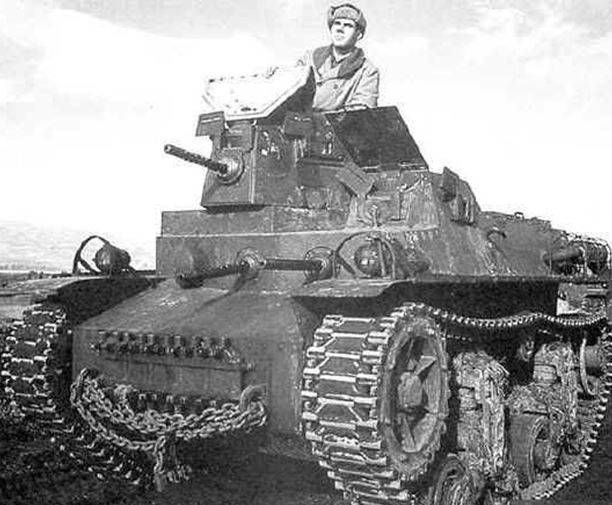

During the Second World War, these combat vehicles were used only in Pacific theaters. Tankers responded far from the flattering way and the family of these machines. The excessive number of machine guns for two crew members did not improve the effectiveness of the fire, and the attempt to mark the third crew member in the turret was not particularly successful.
Combat Car M1 and Combat Car M2 light tanks
The development of the Combat Car M1 began in the 1931 year as a cavalry support tank as part of the combat vehicle concept. This tank was the first US serial light tank after the First World War. In 1933, a prototype was made and tested, in 1935-1937, 148 М1 tanks of various modifications were made.
According to the layout, the tank differed from the classic one; in front of it, in the hull, there was a transmission, connected by a cardan shaft to the power plant, located in the stern. Crew tank 4 man. The driver and machine gunner of the frontal machine gun was placed in front in the building, the commander and the turret gunner in the tower.
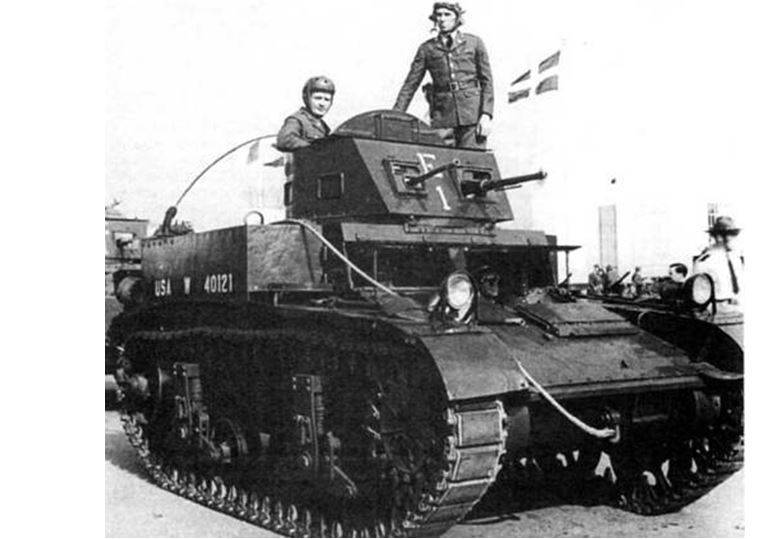

In the turret, one 12,7-mm and 7,62-mm machine guns were installed, another Browning 7,62-mm machine gun was located on the right-hand side of the hull front plate. The tower had a circular rotation using a manual drive.
With the weight of the tank 8,8 t body booking was 6 forehead - 16 mm, board - 13 mm, bottom and roof - 6,4 mm, tower 16-6,4 mm.
As the power plant was installed gasoline engine Continental W670-7,7 power 250 hp or a Guiberson T1020 diesel engine providing 72 km / h speed and 209 km cruising range.
The undercarriage on one side contained 4 rubberized track rollers interconnected in pairs in two trucks, two support rollers, a front drive and rear guide wheel, a caterpillar with a width of 295 mm.
Based on the M1 tank, several modifications of prototype tanks were created to test various design solutions. Based on the modification МХNUMXА1Е1 an infantry support tank was developed. The latest modification of the M1А2 tank weighing 4 tons was armed with an 11-mm cannon and four 37mm M7,62 machine guns, one of which was anti-aircraft. On the M1919 tank, the location of the transmission driveline, which previously divided the fighting compartment into two parts, was changed and the chassis was improved.
A total of 696 M2 tank samples were released. The M1 and M2 tanks were used only as training tanks and did not take part in the hostilities.
The state of US light tanks before the war
The US military leadership, making a bet on equipping the army mainly with light tanks, used for these purposes tanks developed during the First World War and their modifications. In the interwar period, several models of light tanks were developed and tested, but due to the imperfection of their characteristics, none of them went into mass production.
The Combat Car M1 and Combat Car M2 tanks, launched in the 30-ies in a series of several hundred units, did not meet the requirements of the coming war, were inferior in their characteristics to German tanks and were used only as training tanks. With the beginning of the war, it was necessary to develop and organize production, including the new generation of light tanks.









Information