Truck YAG-6. Last of its kind
The appearance of the project YAG-6 was preceded by curious events. In the mid-thirties, YAAZ and the Research Institute of Automobile and Tractor Institute (NATI) jointly conducted a large-scale research project to study their own and foreign experience in the field of truck construction, and then developed a whole line of vehicles for various purposes. In addition, a project was proposed for the modernization of production at the YAZ. However, due to objective difficulties, the plant was not updated, and therefore could not build new trucks developed by NATI. For this reason, KB YAZ was forced to use the old approach, providing for the next modernization of the existing project.
Deep upgrade
It should be recalled that the development of Yaroslavl trucks at that time was carried out through the gradual refinement of existing structures. Each new car was a modified version of the previous one, and the main innovations concerned the power plant and transmission. In the next project, KB YAAZ decided to use this approach again. However, this time it was necessary to apply a large amount of new solutions.

Truck YAG-6. Photo "M-Hobby"
The deeply modernized version of the YAG-3 / YAG-4 machine was designated as YAG-6. The presence of the new name indicated the most serious differences of trucks. About 270 made significant changes to the original project. The frame, the power unit, the chassis, etc. were subjected to refinement. At the same time, the hood, cabin and cargo platform remained the same. Thus, outwardly YAG-6 was minimally different from its predecessors. In fact, it could only be distinguished by the shape of the front wings and the new plate with the emblem of the manufacturer.
Curious reasons for the preservation of the old cab and body, not distinguished by high perfection of design and did not provide special comfort for the driver and passengers. The fact is that from a certain time the platforms and cabs were assembled by a related enterprise - the “Paris Commune” timber mill (Yaroslavl). Despite all the complaints, the accessory companies were in no hurry to improve the quality of production or to master the release of new products. It was not necessary to count on getting a new cabin, and therefore YAG-6 had to be done under the old one.
270 changes
The YAG-6 project envisaged the use of a used car architecture. At the same time, its individual features and various machine units were modified using available products and technologies. At the base of the truck was still a riveted metal frame in the form of a pair of spars and several crossbars. A power unit, a cabin and a cargo platform were installed on top of it, and undercarriage elements were suspended from below.
Under the hood of the truck left the power unit of the type ZIS-5, borrowed from the same machine of the Moscow development. The straight six-cylinder engine ZIS-5 developed the power of the HP 73. The motor was equipped with a carburetor type MAAZ-5 and was connected to a liquid cooling system based on a cellular radiator. Through the clutch with the engine mated transmission ZIS-5 with four forward speeds and one rear.
From the gearbox departed driveline drive drive rear axle. It was installed with a slope inside the conical part, transferring the load from the bridge to the frame. The main transmission of the car has retained the same design, but has been improved from a technological point of view. The gear ratio remained the same - 10,9, which was enough to get the desired performance. For the first time in the practice of the YAZ, a central disc brake type appeared in the transmission. It provided braking by locking the shafts.
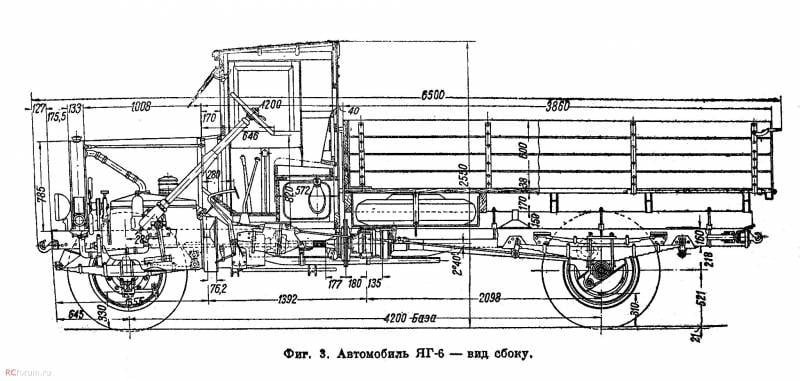
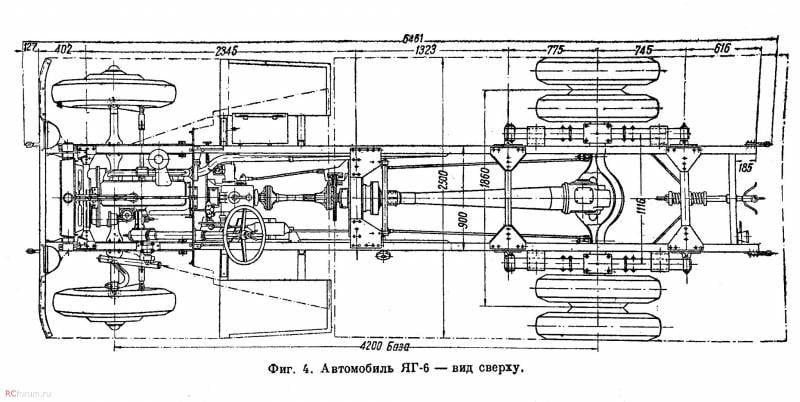
The most serious changes were made to the design of the chassis. The main element of the wheel is now a bulging stamped disc. The use of such parts has led to the need to increase the length of the axles. In addition, due to the convex discs, it was possible to increase the distance between the tires of the rear dual wheels and sharply reduce their wear due to friction of the side surfaces. New discs and related changes have led to an increase in the gauge of both axles. Front track increased by 30 mm, rear - by 72 mm.
Especially for the YaG-6, an updated and improved foot brake was developed. First of all, they changed the brake drum, increasing its thickness. Copper wire appeared in the friction linings of brake pads, which improved thermal conductivity. To adjust the brake, a special worm gear was now used.
The hood for the new truck was almost unchanged from the base YG-3 / YAG-4. The functions of its front wall served as a large radiator, and on top and side of the power unit was covered with metal shields. The bonnet had a pair of longitudinal hatches. The blinds cut through the lifting sides. On the sides of the hood secured new wings of a modified form. Now they were a whole with the steps of the cabin.
The design of the cabin remained the same and included metal and wooden parts. The windshield with the lifting mechanism was kept. In the sides there were doors with their own windows. All the necessary controls and control devices were placed at the driver’s workplace. Together with the driver in the cabin could be two passengers. Under the common seat was placed fuel tank capacity 177 l.
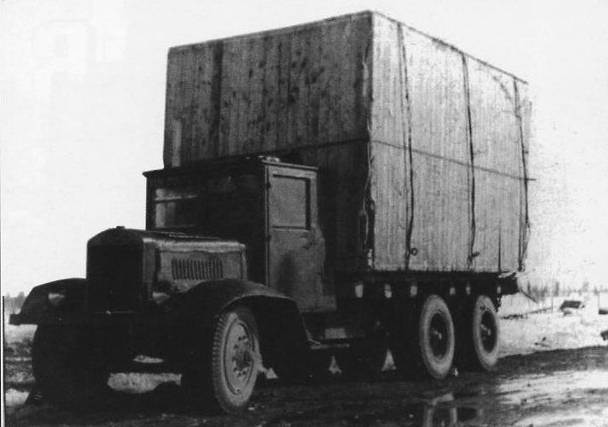
The cargo platform for the YG-6 was similar to the existing ones, but was slightly different from them. A change in the rear wheel track made it possible to increase the width of the body by 130 mm. Its design remained the same: the hinged sides were attached to a wooden horizontal platform.
On the basis of the onboard truck YAG-6, a new version of the dump truck was immediately developed. This machine is called Yas-3. From the point of view of architecture, this dump truck most closely resembled the existing YAS-1 serial. In addition, the similarity of the base cars and the unification of the special equipment led to the absence of serious external differences. As in the case of YAG-6, YAS-3 could only be identified by individual elements.
The dump truck was equipped with a hydraulic pump that ensures the operation of a pair of cylinders. The back of the frame has been reinforced and equipped with a hinge for a swinging body. The latter was a cargo platform of the old type with fixed sides (with the exception of the movable rear), inside it was upholstered with metal. The main characteristics of the dump truck remained at the same level. The new equipment increased the weight of the YAS-3 machine by 900 kg compared to the base YaG-6, which resulted in a reduction in the load capacity to 4 tons. The time of raising and lowering the body is in 25 seconds.
Processing the design of the base YG-3 led to some changes in the dimensions of the machine. The length remained the same, 6,5 m, while the width increased to 2,5 m, and the height remained at the level of 2,55 m. With the old wheelbase (4,2 m) the front axle track was 1,78 m, the rear axle was 1,86 m. The curb weight of the truck was 4750 kg, load capacity - 5 t. The 73-strong engine ZIS-5 in a known manner limited the characteristics of the equipment, and the maximum speed on the highway did not exceed 40-42 km / h. Fuel consumption - about 43 liters per 100 km.
YAG-6 in the series
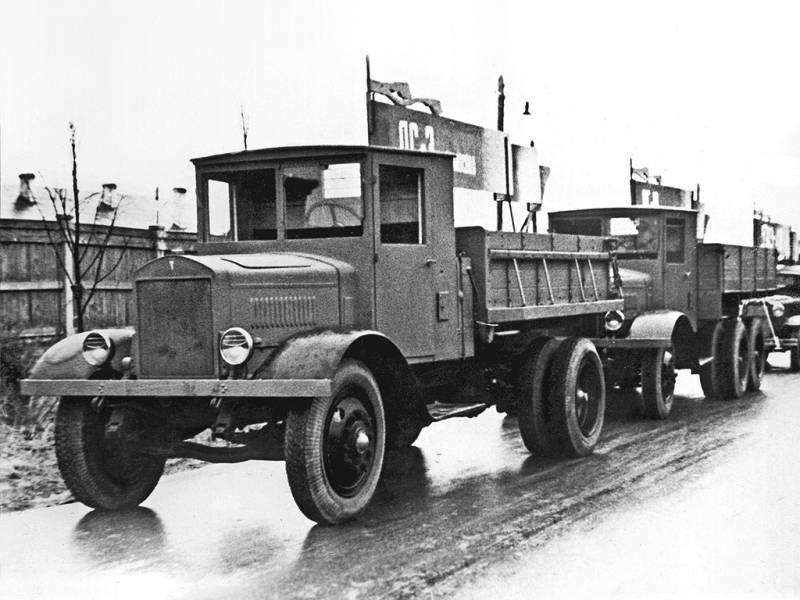
In 1936, the Yaroslavl Automobile Plant ceased production of cars of the previous family. YAG-3 and YAG-4 trucks and the YAS-1 dump truck were removed from the conveyor. Instead, the company now had to produce new samples - YAG-6 and YAS-3. The country still needed five-ton trucks, and Yaroslavl automakers did their best. Until the end of the first year of production, several hundreds of two types of machines were built, which soon went to their operators.
As before, high performance trucks were distributed among different organizations from different industries. First of all, five-ton cars were supplied by the Red Army. Also, this technique was of interest for construction and mining organizations. Until a certain time, they received only on-board trucks and dump trucks, but later, through various enterprises, production of specialized modifications was mastered.
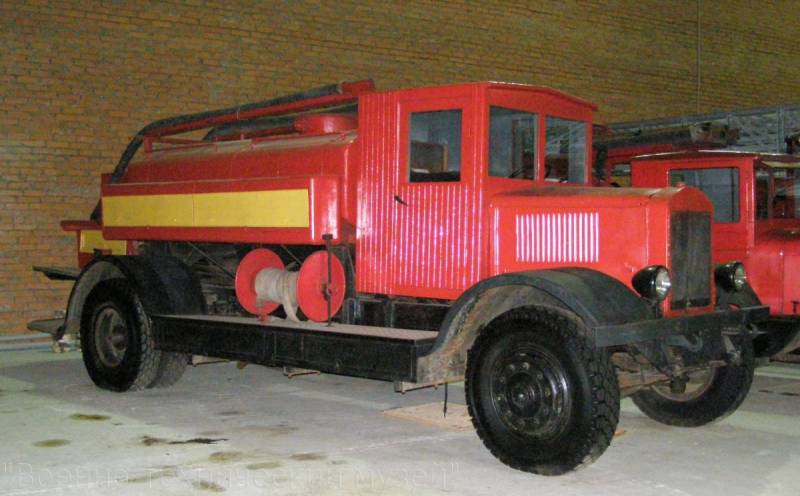
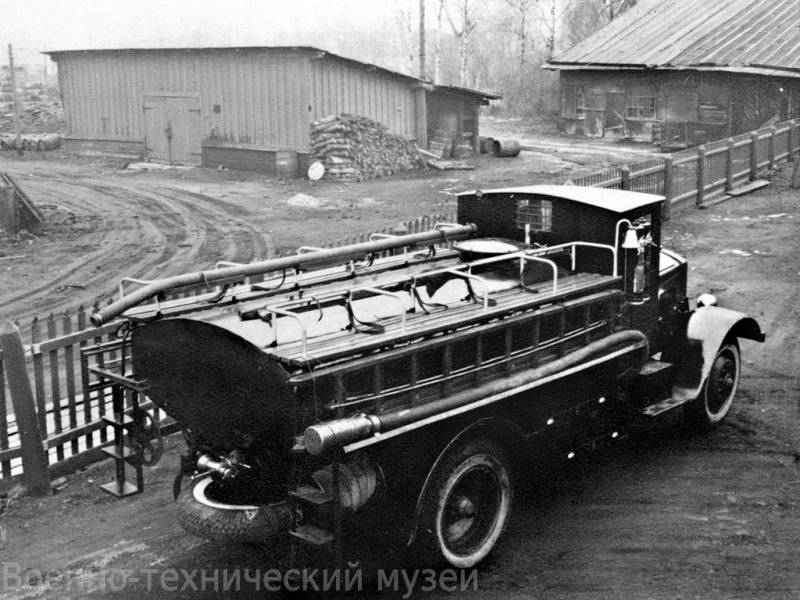
By removing the standard body and installing the new YAG-6 equipment, it turned into a fire-fighting tank truck, a truck-mounted concrete mixer, a fuel truck, a watering machine, and even a self-propelled ice picker on highways. There were also less serious but interesting improvements. Thus, two axles of the chassis could be supplemented by a crawler axle, which improved the performance of the car on difficult tracks.
It should be noted that the new versions of YAG-6 were created not only by third-party workshops, but also by the Yaroslavl Automobile Plant. As the serial production continued, the company developed new modifications of equipment of one kind or another.
For example, in 1938, the YAG-6M truck was created. The main difference of this technique was an improved cabin with improved conditions. In addition, cars with the letter "M" had a new power unit. Some of them were equipped with American Hercules-YXC-B engines, while others were equipped with domestic ZIS-16. According to some sources, YaG-6М were intended for the supply of one of the foreign countries. It was built no more than fifty of these machines.
In 1940, a long truck chassis version called the YG-6A appeared. It was distinguished by an elongated frame, due to which the base was increased to 5 m. Such chassis could be used as a basis for special equipment, buses, etc. However, the project encountered technical and organizational difficulties. Point in his stories marked the beginning of World War II. Before the German attack in Yaroslavl, they managed to build the entire 34 YG-6 machines.
Engine problem
The full-scale production of the YG-6 five-ton trucks continued until the 1942 year. In the next 1943, the Yaroslavl Automobile Plant managed to assemble only three dozen of these machines, after which their production stopped. The reason for this was the lack of the necessary engines. Moscow Plant them. Stalin was loaded with army orders, and he had no “surplus” to send to Yaroslavl. In the first months of 1943, YAZ exhausted the available supply of power units, and the production of five-tones stopped.
For all the production time, 8075 trucks of the basic modification were produced. The total output of other machines did not exceed hundreds of copies, and a significant number of them were exported. The production of YAS-3 dump trucks reached 4765 units.
Understanding that the release of the YG-6 is under threat, and the country still needs equipment with a high payload, the YAZ design bureau developed a new project. The truck under the designation YAG-9 was a revised version of the YAG-6, which had a number of characteristic differences. First of all, it was planned to abandon the domestic engine in favor of the imported one. It was proposed to use a power unit with a GMC-4-71 engine with an 110 horsepower, Long 32 clutch and a Spicer 5553 gearbox. The rear axle should be made by casting, and the regular braking system was replaced by a pneumatic one, borrowed from the JBT-4A bus.

YG-6 truck with sliding axle installed by operators. Photo "M-Hobby"
A machine with such a composition of aggregates was supposed to surpass the existing YaG-6 on a number of indicators and could be of greater interest to the army and the national economy. However, production could not be started. YAAZ turned to the State Committee for Defense with a proposal to purchase a batch of engines for a new truck. For a number of objective reasons, the proposal was not approved. The plant managed to build only one experienced GM-9 engine with a GMC engine, and after that the project was closed for lack of real prospects.
Around the same time, the Yaroslavl engineers decided to give a second life to the old project, closed a few years ago. In the mid-thirties, a pair of I-5 trucks with a promising domestic-made Kouju diesel engine passed full-scale tests. KB YAAZ considered the possibility of installing such a motor on the YaG-6 and came to optimistic conclusions. However, the work on the Koju diesel engine family by then had virtually stopped, and their continuation did not make sense. The engines needed further fine-tuning and serialization. In the conditions of war, all this was considered impossible.
Thus, the production of five-ton trucks YAG-6 remained without engines, and therefore it had to be stopped. Moreover, the entire issue of automobiles in Yaroslavl and the prospects of the plant were in doubt. Fortunately, quickly found a way out of this situation. Yaz reoriented to release tracked artillery tractors. In 1943, the plant received documentation from NATI on a new machine of this kind, and soon built prototypes. Production continued from 1943 to 1946 years. During this time, several thousand types of machines I-11, I-12 and I-13 were manufactured.
Contribution to victory
Much of the serial YG-6 trucks were immediately sent to serve in the Red Army. After the start of the Great Patriotic War, hundreds of cars of enterprises of the national economy were mobilized and also went to the front. Most often, the five-ton trucks were used as artillery towers capable of towing guns in caliber up to 122 mm, as well as carrying ammunition and crew. However, in this capacity, they did not show themselves in the best way - an insufficient engine power had an effect.

YG-6 tank truck in the exposition of the Military Technical Museum, c. Ivanovo. Photo "Military Technical Museum" / gvtm.ru
Also, the five-ton truck was a convenient vehicle that perfectly complemented the lorry and three-tonne existing models. In addition, during the war, other modifications of the YaG-6 were used. Four-ton dump trucks took part in the construction of the fortifications, and fuel trucks ensured that fuel was delivered in units. It is worth noting watering machines based on the YAG-6. It was these machines that symbolically washed the streets of Moscow after the march of German prisoners of war in July 1944.
However, Yaroslavl heavy-duty trucks could not compete with other vehicles in terms of strength. Since the beginning of the 1930s, the Yaroslavl Automobile Plant built a total of about 20-22 thousand five-ton machines of various models and modifications. Other domestic trucks were built in much larger quantities. As a result, high-traffic vehicles, having special significance for the army and the economy, had limited potential.
The YG-6 trucks were produced only before the start of the 1943 year, after which their production was stopped, and the Yaroslavl Automobile Plant was transferred to the construction of tracked tractors. The company again returned to the subject of the truck industry only after the war. In 1947, the first truck of the fundamentally new YAZ-200 series came off the assembly line. In the history of Soviet trucks began a new chapter.
Based on:
http://denisovets.ru/
http://gruzovikpress.ru/
http://russianarms.ru/
http://gvtm.ru/
http://autohis.ru/
Shugurov L.M., Shirshov V.P. Cars Country of the Soviets. - M .: DOSAAF, 1983.
Dashko D. Soviet trucks 1919-1945. - M .: Automobile archival fund, 2014.
Polikarpov N. YAG-6 // M-Hobby, 1999. No.1.


Information