Laser weapons: navy. Part of 4
In 1976, the terms of reference (TOR) for the conversion of the project 770 SDK-20 landing craft into the Foros experimental vessel (project 10030) with the Aquilon laser complex were approved. In 1984, the ship under the designation OS-90 "Foros" joined the Black Sea fleet USSR and at the Feodosia training ground, for the first time in stories Soviet Navy were conducted test shooting from the laser gun "Aquilon". The shooting was successful, the low-flying missile was promptly detected and destroyed by a laser beam.
Subsequently, the Aquilon complex was installed on a small artillery ship built according to the modified 12081 project. The capacity of the complex was reduced, its purpose was to disable optical-electronic means and damage organs of sight to the personnel of the enemy antiamphibious defense.
At the same time, the Aydar project on the creation of the most powerful shipborne laser system in the USSR was being worked out. In 1978, the Vostok-3 timber carrying vessel was converted into a carrier of laser weapons - the Dikson ship (project 05961). Three jet engines from the Tu-154 aircraft were installed on the ship as an energy source for the Aydar laser facility.
During the tests in 1980, a laser volley was given at a target located at a distance of 4 kilometers. The target was hit the first time, but no one was present at the same time as the beam and the visible destruction of the target. The hit was recorded by a heat sensor mounted on the target, the beam efficiency was 5%, and a presumably significant part of the beam energy was absorbed by evaporation of moisture from the sea surface.
In the United States, research aimed at creating combat laser weapons has also been carried out since the 70s of the last century, when the implementation of the ASMD program (Anti-Ship Missile Defense - protection against anti-ship missiles) began. Initially, work was carried out on gas-dynamic lasers, but then the focus shifted to chemical lasers.
At 1973, TRW began work on an experimental demonstration sample of a continuous-action fluoride-deuterium laser NACL (Navy ARPA Chemical Laser) with a power of about 100 kW. Research and development (R & D) on the NACL complex was conducted until the 1976 year.
In 1977, the US Department of Defense launched the Sea Light program, aimed at developing a high-energy laser machine, with a capacity of up to 2 MW. As a result, a MIRACL (Mid-IniaRed Advanced Chemical Laser) fluoride-deuterium chemical laser range facility was created, operating in a continuous mode of radiation generation, with a maximum output power of 2,2 MW at a wavelength of 3,8 μm, its first tests were carried out in September 1980 of the year.
In 1989, the White Sands test center conducted experiments using the MIRACL laser complex to intercept radio-controlled targets of the BQM-34 type, simulating the flight of anti-ship missiles (ASR) at subsonic speeds. Subsequently, supersonic (M = 2) Vandal missiles that mimic the anti-ship missile attack at low altitudes were intercepted. In tests conducted from 1991 to 1993 years, the developers clarified the criteria for the destruction of missiles of various classes, and also carried out a practical interception of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), imitating the use of anti-ship missiles by the enemy.

At the end of the 1990s, the use of a chemical laser as a ship weapon was abandoned due to the need to store and use toxic components. (most likely, also because of the total amount of work and maintenance of weapons of this type).
In the future, the US Navy and other NATO countries focused on lasers powered by electrical energy.
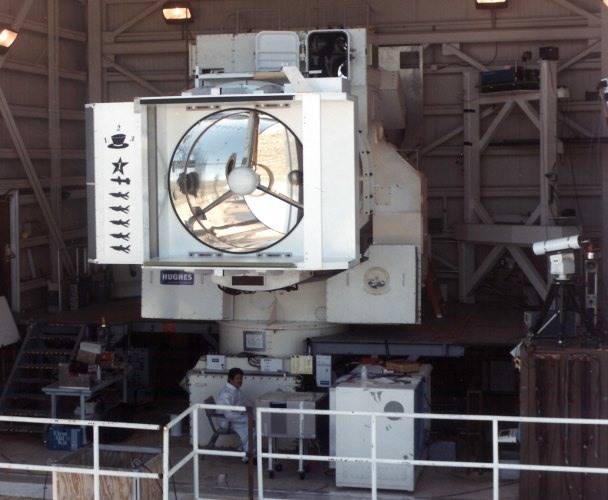
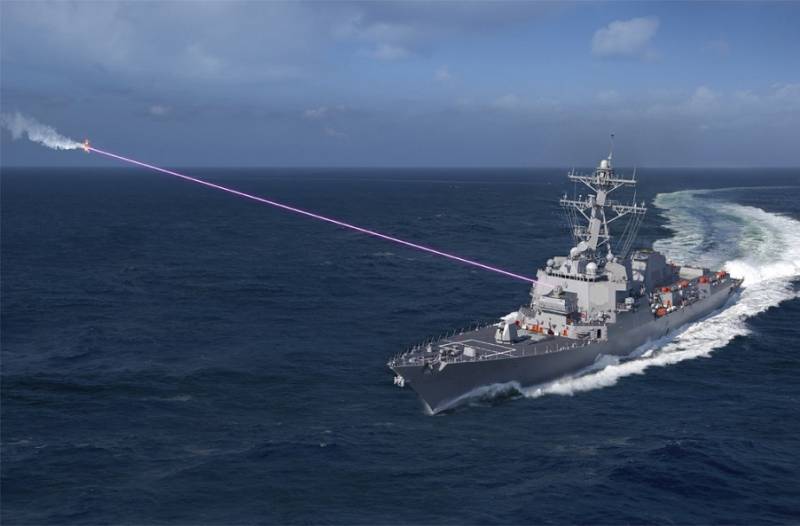
As part of the SSL-TM program, Raytheon created the LaWS (Laser Weapon System) demo laser system with a power of 33 kW. On tests in 2012, the LaWS complex, from the side of a destroyer (EM) "Dewey" (such as "Arleigh Burke"), was hit 12 targets BQM-I74A.
The LaWS complex is modular, the power is gained by summing the beams of lower-power solid-state infrared lasers. Lasers are located in a single massive case. Since 2014, the LaWS laser complex has been installed on the USS Ponce (LPD-15) USS to assess the effect of actual operating conditions on the performance and effectiveness of the gun. By 2017, the capacity of the complex should have been increased to 100 kW.
LaWS laser demonstration
Currently, several US companies, including Northrop Grumman, Boeing and Locheed Martin, are developing laser self-defense systems for ships based on solid-state and fiber lasers. To reduce the risks of the US Navy in parallel, it implements several programs aimed at obtaining laser weapons. Due to the change of names in the framework of the transfer of projects from one company to another, or the merging of projects, there may be intersections by names.
Northrop Grumman Corporation is working on a modular combat laser, designated MLD (Maritime Laser Demonstration). The initial power of the 15 laser kW, modular design allows you to get a total power up to 105 kW. In the future, the output power of the plant can be increased to 300-600 kW.
Boeing received a contract worth 29,5 million for the development of a laser beam control system that could provide precise guidance of the laser weapons of US Navy ships.
In 2019, the SNLWS program for installing a solid-state laser with a power of 60 kW and higher allocated 190 million dollars from the budget to destroyers of Arleigh Burke class URO. The equipment of three destroyers is envisaged, the Navy awaits the first destroyer equipped with a laser weapon at the end of the 2020 of the year.
Corporation Locheed Martin received a contract worth $ 150 million (with the possibility of increasing to $ 942,8 million) for the supply of the US Navy high-energy laser weapons HELIOS. Plans include testing aboard the Arly Burke destroyers in 2019-2020 (possibly as part of the SNLWS program).
There is also information about the 150 kilowatt laser weapon setup program at UDC of the San Antonio type and the RHEL (Ruggedized High Energy Laser) laser weapon program with a power from 150 kW.
According to US media reports, the US Navy FFG (X) advanced frigate project includes a requirement for installing a combat laser with a power of 150 kW (or reserving a place to install), under the control of the combat system COMBATSS-21.
In addition to the United States, the former "mistress of the seas", the United Kingdom, is most interested in sea-based lasers. The absence of the laser industry does not allow to implement the project on its own, and in this connection, in 2016, the UK Ministry of Defense announced a tender for the development of the technology demonstrator LDEW (Laser Directed Energy Weapon), in which the German company MBDA Deutschland won. In 2017, the consortium introduced a full-size prototype of the LDEW laser.
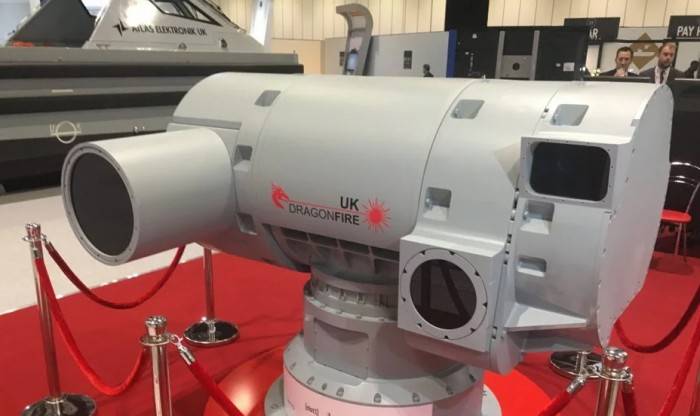

Earlier in 2016, MBDA Deutschland introduced the Laser effector laser complex, which can be installed on land and sea carriers and is designed to destroy UAVs, missiles and mortar shells. The complex provides defense in the 360 degrees sector, has a minimal reaction time and is able to repel shots coming from different directions. The company reports that its laser has great potential for development.
- says the head of the company for sales and business development, Peter Heilmeyer.
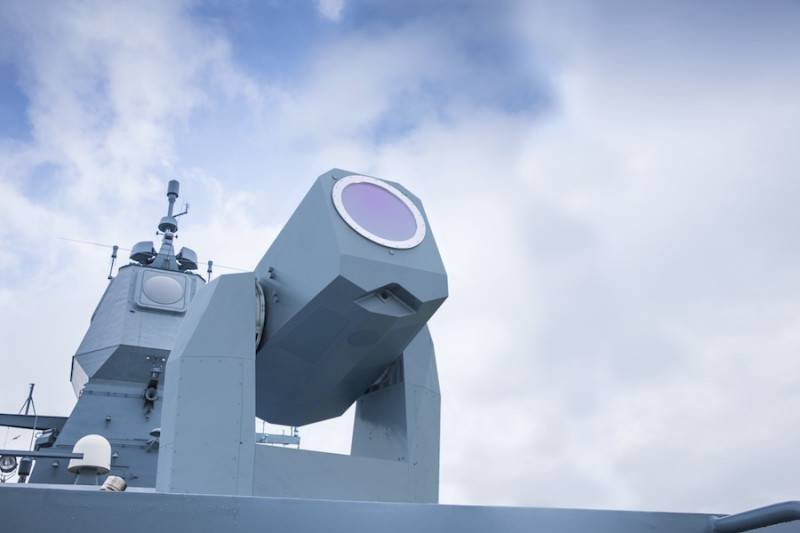

German companies are on the same level, and, perhaps, overtake the US companies in the laser arms race, and are quite capable of being the first to introduce not only laser complexes terrestrialbut also sea-based.
In France, the DCNS perspective Advansea project is being considered using full electric propulsion technology. The project “Advansea” is planned to be equipped with an 20 megawatt electricity generator capable of meeting the needs of advanced laser weapons.
In Russia, according to media reports, laser weapons can be placed on the advanced Leader nuclear destroyer. On the one hand, the nuclear power plant suggests that there is enough power to supply laser weapons with power, on the other hand, this project is at the stage of preliminary design, and it is clearly premature to talk about something concrete.
Separately, it is necessary to single out the American project of a free electron laser - Free Electron Laser (FEL), developed in the interests of the US Navy. Laser weapons of this type have significant differences compared with other types of lasers.
Radiation in a free electron laser is generated by a monoenergetic electron beam moving in a periodic system of deflecting electric or magnetic fields. By changing the energy of the electron beam, as well as the strength of the magnetic field and the distance between the magnets, it is possible to change the frequency of the laser radiation over a wide range, receiving at the output radiation in the range from X-ray to microwave.
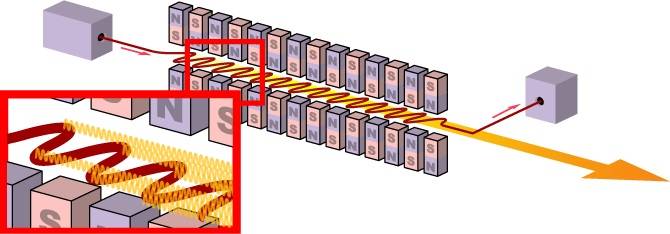
Free electron lasers are characterized by large dimensions, which makes them difficult to place on compact carriers. In this sense, large surface ships are the optimal carriers of lasers of this type.
Development of the FEL laser for the US Navy is the company Boeing. A prototype of the FEL laser with a power of 14 kW was demonstrated in the 2011 year. At the moment, the state of work on this laser is unknown, it was planned to gradually increase the radiation power up to 1 MW. The main difficulty is to create an electron injector of the required power.
Despite the fact that the dimensions of the FEL laser will exceed the dimensions of lasers of comparable power based on other technologies (solid-state, fiber), its ability to change the radiation frequency over a wide range will allow to choose the wavelength in accordance with weather conditions and the type of target affected. The appearance of FEL lasers of sufficient power is difficult to expect in the near future, rather it will happen after the 2030 year.
Compared to other types of armed forces, the deployment of laser weapons on warships has both its advantages and its disadvantages.
On existing ships, the power of laser armament, which can be installed at the retrofit entrance, is limited by the capabilities of electric generators. The newest and most promising ships are being developed on the basis of electric propulsion technologies, which will provide enough laser power.
On ships, there is much more space than on land and air carriers, respectively, there are no problems with the placement of large equipment. Finally, there are opportunities to provide effective cooling for laser equipment.
On the other hand, the ships are in a hostile environment - sea water, salt fog. High humidity above the sea will significantly reduce the power of laser radiation, if targets are hit above the surface of the water, and therefore the minimum power of a laser weapon suitable for placement on ships can be estimated at 100 kW.
For ships, the need to defeat “cheap” targets, such as mines and unguided missiles, is not so critical; such weapons can pose a limited threat only in the basing sites. It is also not to be considered as a justification for the placement of laser weapons, the threat posed by small vessels, although in some cases they can cause serious damage.
Small-sized UAVs are a definite threat to ships, both as a means of reconnaissance and as a means of destroying vulnerable points of the ship, such as radar. The defeat of such UAVs with rocket-gun armament can be difficult, and in this case, the presence of laser defensive armament on board the ship will completely solve this problem.
Anti-ship missiles (anti-ship missiles), against which laser weapons can be used, can be divided into two subgroups:
- low-flying subsonic and supersonic anti-ship missiles;
- supersonic and hypersonic anti-ship missiles, attacking from above, including along the aeroballistic trajectory.
In the case of low-flying CRPs, the curvature of the earth’s surface, which limits the range of a direct shot, and the saturation of the lower atmosphere with water vapor, which reduces the power of the beam, will serve as an obstacle for laser weapons.
To increase the area of destruction, the options for placing the radiating elements of a laser weapon on a superstructure are considered. The power of a laser suitable for hitting modern low-flying anti-ship missiles is likely to be from 300 kW.
The affected area of anti-ship missiles attacking along the high-altitude trajectory will be limited only by the laser power and the capabilities of the guidance systems.
The most difficult goal will be hypersonic RCC, both because of the minimum time spent in the affected area, and because of the presence of regular thermal protection. However, the thermal protection is optimized for heating the RCC case during the flight, and the extra kilowatts will definitely not bring any benefit to the rocket.
The need for guaranteed destruction of hypersonic anti-ship missiles will require lasers with a power above 1 MW placed onboard the ship, the best solution would be a free electron laser. Also, laser weapons of such power can be used against low-orbit spacecraft.
From time to time, publications on military topics, including the Military Review, discuss information about the weak security of anti-ship missiles with a radar homing head (HLRG), against radio-electronic interference and masking curtains used from the ship. The solution to this problem is the use of a multispectral homing system, including television and thermal imaging channels. The presence on board a ship of a laser weapon, even a minimum power of the order of 100 kW, can offset the advantages of RCC with a multispectral homing system, due to the constant or temporary blinding of sensitive matrices.
In the United States, versions of acoustic laser guns are being developed that allow reproducing intense sound vibrations at a considerable distance from the radiation source. Perhaps based on these technologies, ship lasers can be used to create acoustic noise or decoys for sonars and enemy torpedoes.
Prototype Acoustic Laser Gun
Thus, it can be assumed that the appearance of laser weapons on warships will increase their stability in front of all types of attack weapons.
The main obstacle for placing laser weapons on ships is the lack of the necessary electrical power. In this regard, the emergence of truly effective laser weapons will most likely begin only with the commissioning of promising ships with full electric propulsion technology.
On the upgraded ships can be installed a limited number of lasers with a power of the order of 100-300 kW.
On submarines, the placement of laser weapons with a power of 300 kW or more with radiation output through the terminal device located on the periscope will allow the submarine to carry out defeat from the periscope depth aviation enemy anti-submarine weapons - anti-submarine defense aircraft and helicopters.
A further increase in the power of lasers, from 1 MW and higher, will make it possible to damage or completely destroy low-orbit spacecraft, according to external target designation. The advantages of placing such weapons on submarines: high secrecy and global reach of the carrier. The ability to travel in the World Ocean to an unlimited range will allow the submarine - the carrier of laser weapons to reach the point that is optimal for hitting a space satellite, taking into account its flight path. And the secrecy will make it more difficult for the enemy to make claims (well, the spacecraft went out of order, how to prove who shot it down if obviously armed forces were not present in this region).
In general, at the initial stage, the navy will feel less advantage from the introduction of laser weapons in comparison with other types of armed forces. However, in the future, with the continuous improvement of anti-ship missiles, laser complexes will become an integral part of the air defense / missile defense of surface ships, and, possibly, submarines.








Information