Fast global punch: hypersound help
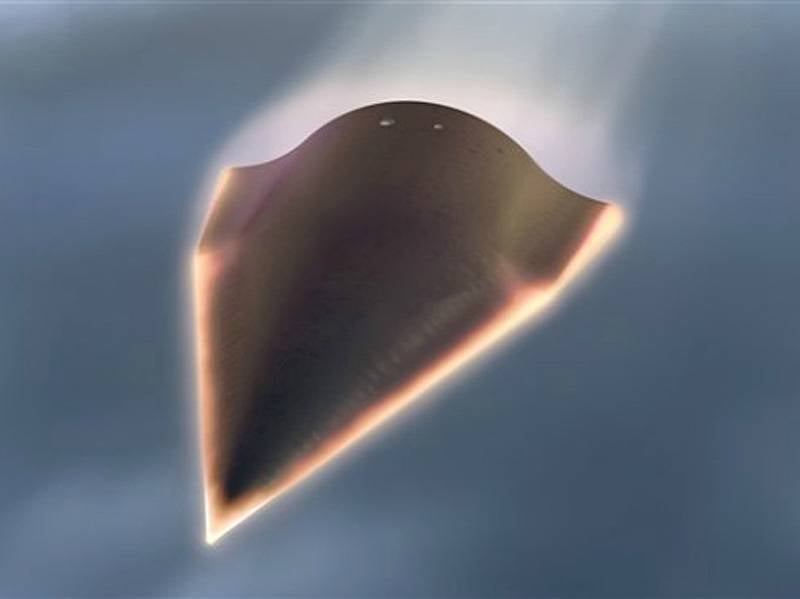
Picture of a detached planning block HSSW in flight. It is one of several hypersonic planning devices that have been developed as a means of quickly delivering ammunition to the target.
Progress in the field of hypersonic technology has led to the creation of high-speed weapons systems. They, in turn, were identified as a key area in which direction the military needs to move in order to keep up with the opponents in technological terms.
In the past few decades, large-scale developments have been carried out in this technological area, and the cyclical principle was widely used when one research campaign was used as the basis for the next one. This process has led to significant advances in hypersonic weapon technology. For two decades, developers have actively used hypersonic technology, mainly in ballistic and cruise missiles, as well as in planning blocks with a rocket booster.
Active work is carried out in such areas as modeling, testing in a wind tunnel, the design of the nose fairing, smart materials, the dynamics of the aircraft at entry into the atmosphere and special software. As a result, hypersonic land launch systems currently have a high level of readiness and high accuracy, allowing the military to attack a wide range of targets. In addition, these systems can significantly weaken the existing missile defense of the enemy.
American programs
The US Department of Defense and other government agencies are increasingly paying attention to the development of hypersonic weapons, which, according to experts, will reach the required level of development in the 2020-s. This is evidenced by the increase in investment and resources allocated by the Pentagon to hypersonic research.
The US Army Space Administration and the Sandia National Laboratory are working together on the Advanced Hypersonic Weapon (AHW), which is currently known as the Alternate Re-Entry System. This system uses the hypersonic glide vehicle HGV (hypersonic glide vehicle) hypersonic planning unit, similar to the Hyperonic Technology Vehicle-2 (HTV-2) concept developed by the DARPA and US Air Forces to deliver a conventional warhead. However, this unit can be installed on a smaller range launch vehicle than in the case of the HTV-2, which in turn may indicate the priority of the advanced deployment, for example, on land or at sea. The HGV unit, which is structurally different from the HTV-2 (conical, not wedge-shaped), is equipped with a high-precision guidance system in the final part of the trajectory.
The first flight of the AHW rocket in November 2011 of the year allowed us to demonstrate the level of sophistication of hypersonic rocket accelerator technology, thermal protection technology, as well as test the parameters of the test site. The planning unit, launched from a missile test site in Hawaii and flying the order of 3800 km, successfully hit its target.
The AHW complex was developed as part of the CPGS program to destroy priority targets anywhere in the world within an hour. Starting in 2006, the Pentagon has steadily increased funding for the AHW program of the US Army.
A second test run was conducted from the Kodiak launch site in Alaska in April 2014. However, after 4 seconds after launch, the controllers gave the command to destroy the rocket, when external thermal protection touched the control unit of the launch vehicle. The next test launch of the reduced version was carried out from the Pacific Missile Test Site in October 2017. This smaller version was sized to fit a standard ballistic missile launched from a submarine.
For scheduled test launches under the AHW program, the Department of Defense requested 86 millions of dollars for the 2016 fiscal year, 174 millions for the 2017 fiscal year, 197 millions for the 2018 year and 263 millions for the 2019 year. The latest request, along with plans to continue the AHW test program, indicates that the ministry is determined to develop and deploy the system using the AHW platform.
In 2019, the program will focus on the production and testing of the launch vehicle and the hypersonic planning unit, which will be used in flight experiments; on the continuation of the study of promising systems in order to verify the cost, mortality, aerodynamic and thermal characteristics; and to conduct additional research to evaluate alternatives, feasibility, and integrated solution concepts.
DARPA, together with the US Air Force, are simultaneously implementing the HSSW (High Speed Strike Weapon) demonstration program, which consists of two main projects: the TBG program (Tactical Boost-Glide) developed by Lockheed Martin and Raytheon, and the HAWC program (Hypersonic Air-breathing Weapon Concept) ), led by Boeing. Initially, it is planned to deploy the system in the air force (air launch) and then transition to offshore operation (vertical launch).
Although the main goal of the Ministry of Defense in the field of hypersonic development is arming the air launch, DARPA launched a new program for the development and demonstration of a hypersonic ground launch system that includes technology from the TBG program in 2017 during the Operational Fires project.
In the budget request for 2019, the Pentagon requested 50 millions of dollars to develop and demonstrate a ground launch system that allows the hypersonic planning winged unit to overcome enemy air defenses and quickly and accurately hit top targets. The goal of the project is: the development of an advanced carrier capable of delivering various combat units at different distances; development of compatible ground launch platforms, allowing integration into existing ground infrastructure; and the achievement of specific characteristics necessary for rapid deployment and redeployment of the system.
In its budget request for 2019, the DARPA Administration requested 179,5 million to fund the TBG program. The goal of the TBG (like HAWC) is to achieve the 5 speed of a Mac and more when it is planning to reach the target on a final trajectory. The heat resistance of such a unit must be very high, it must be highly maneuverable, fly at altitudes of almost 61 km and carry a warhead weighing about 115 kg (approximately the size of a small-diameter bomb, Small Diameter Bomb). Under the TBG and HAWC programs, the combat unit and guidance system are also being developed.
Earlier, the United States Air Force and DARPA launched a joint program FALCON (Force Application and Launch from CONtinental United States) as part of the CPGS project (Conventional Prompt Global Strike - the usual quick global strike). Its goal is to develop a system consisting of a launch vehicle like a ballistic missile and a hypersonic air entry device known as the CAV (common aero vehicle), which could deliver a warhead to anywhere in the world within one to two hours. A highly maneuverable planning unit CAV with a deltoid wing-fuselage that does not have a propeller can fly in the atmosphere at hypersonic speeds.
Lockheed Martin worked with DARPA on the early concept of the HTV-2 hypersonic device from 2003 to 2011 years. Minotaur IV light rockets, which became the vehicle for delivering HTV-2 units, were launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. During the first flight of the HTV-2 in 2010, data was obtained that demonstrated progress in improving aerodynamic quality, high-temperature materials, thermal protection systems, autonomous flight safety systems, as well as guidance, navigation and control systems for continuous hypersonic flight. However, this program was closed and now all efforts are focused on the AHW project.
The Pentagon hopes that these research programs will pave the way for various hypersonic weapons, and also plan to consolidate their efforts to develop hypersonic weapons as part of a roadmap being developed to further fund projects in this area.
In April, 2018, the Deputy Minister of Defense announced that he was ordered to carry out the “80% plan”, and this was the conduct of evaluation tests before 2023, the goal of which is to achieve hypersonic capabilities over the next decade. One of the priority tasks of the Pentagon is also to achieve synergies in hypersonic projects, since very often components with similar functionality are developed in different programs. “Although the processes of launching a rocket from a sea, air or ground platform differ significantly. it is necessary to strive for maximum unification of its components. ”
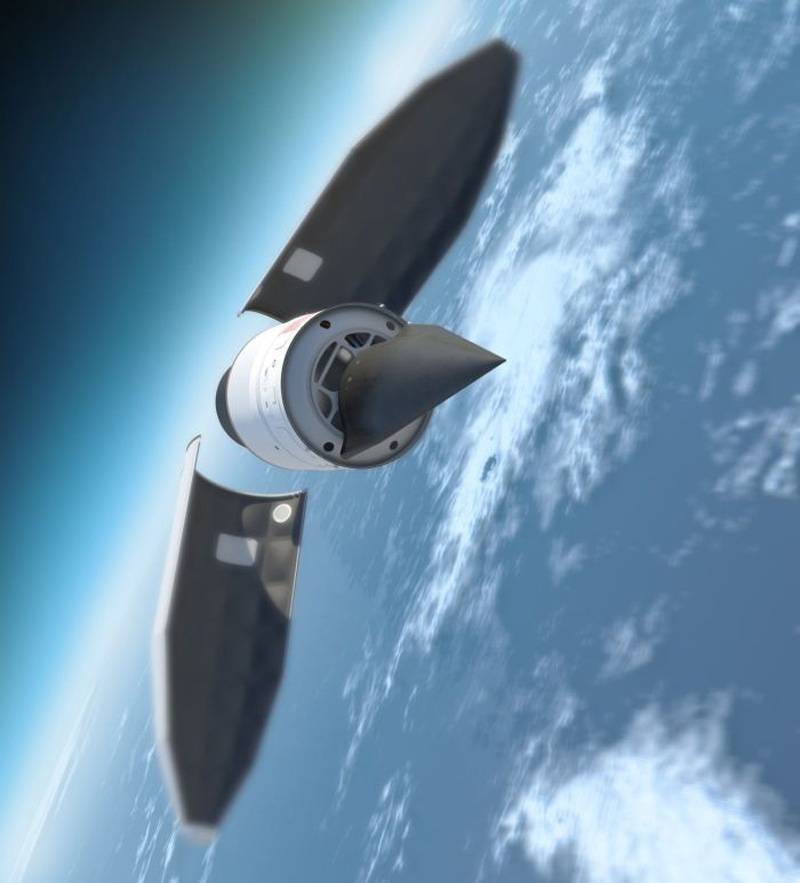

The moment of separation of the carrier and the planning block HSSW. In April, the United States Air Force 2018 issued a Lockheed Martin contract worth 928 million dollars to develop and demonstrate a hypersonic weapon system for non-nuclear strikes.
Russian successes
The Russian program for developing a hypersonic rocket is ambitious, which is largely supported by the state’s full support. This confirms the annual message of the President to the Federal Assembly, with which he spoke on March 1 of 2018. During the message, President Putin introduced several new weapons systems, including the promising strategic missile system Avangard.
Putin presented these weapons systems, including Avant-garde, as a response to the deployment of a global US missile defense system. He said that “the United States, despite the deep concern of the Russian Federation, continues to systematically implement its plans for the missile defense system,” and that Russia's response is to increase the strike capabilities of its strategic forces to defeat the defensive systems of potential adversaries (although the current US missile defense system is barely It will even be able to intercept some of the 1550 nuclear warheads that Russia has).
The avant-garde appears to be a further development of the 4202 project, which was transformed into the U-71 project of developing a hypersonic guided combat unit. According to Putin, he can maintain the speed of 20 Mach numbers on the march section or the planning section of his trajectory and “when moving towards the target, perform deep maneuvering, as a side movement (and several thousand kilometers). All this makes it absolutely invulnerable to any means of air and missile defense ".
The flight of the Avant-garde takes place practically under plasma formation conditions, that is, it moves towards the target like a meteorite or a fireball (plasma is an ionized gas formed due to the heating of air particles, determined by the high velocity of the block). The temperature on the surface of the block can reach "2000 degrees Celsius".
Putin’s message on video showed the concept of Avant-garde in the form of a simplified hypersonic missile capable of maneuvering and overcoming air defense and missile defense systems. The president said that the winged unit shown in the video is not a “real” presentation of the final system. However, according to experts, the winged unit on the video may well be a fully implemented system project with the tactical and technical characteristics of the Avant-garde. Also, given the famous history test project Yu-71, we can say that Russia is confidently moving towards the creation of mass production of hypersonic planning winged blocks.
Most likely, the configuration of the device shown in the video is constructively represented by a wedge-shaped body of the wing-fuselage type, which has received the general definition of a “waveguide”. It was shown his separation from the launch vehicle and the subsequent maneuvering to the target. The video showed four steering surfaces, two at the top of the fuselage and two fuselage deceleration plates, all in the back of the vehicle.
It is likely that Avant-garde is designed to launch with a new heavy multi-stage intercontinental ballistic missile "Sarmat". However, in his address, Putin said that "it is compatible with existing systems," which indicates that in the near future, the upgraded UR-100Н UTTH complex will most likely be the carrier of the Avant-garde winged block. The estimated range of the Sarmat 11000 km combined with the 9900 km range of the U-71 controlled combat unit allows you to get the maximum range of damage over 20000 km.
Modern developments of Russia in the field of hypersonic systems began in the 2001 year, when they passed tests of ICBM UR-100Н (according to the NATO classification SS-19 Stiletto) with a planning unit. The first launch of the 4202 Project missile with the Yu-71 combat unit was conducted on 28 on September 2011. Based on the Yu-71 / 4202 project, Russian engineers developed another hypersonic device, including a second prototype of the Yu-74, which for the first time in 2016 was launched from a test site in the Orenburg region, hitting a target at the Kura test site in Kamchatka. 26 December 2018 of the year carried out the last (in time) successful launch of the Avangard complex, which reached a speed of about 27 Mach.
Chinese project DF-ZF
According to fairly scarce information from open sources, China is developing a DF-ZF hypersonic device. The DF-ZF program remained top-secret until the start of the January 2014 trial. American sources tracked the test and called the unit Wu-14, since the tests were conducted at the Wuzhai test site in Shanxi Province. Although Beijing does not disclose the details of this project, the US and Russian military suggest that there have been seven successful trials to date. According to US sources, until June 2015, the project was experiencing some difficulties. Only starting with the fifth series of test launches can we talk about the successful implementation of the tasks.
According to the Chinese press, in order to increase the range in the DF-ZF, the capabilities of non-ballistic missiles and planning units are combined. A typical DF-ZF hypersonic drone, moving after launching along a ballistic trajectory, accelerates to the suborbital velocity 5 Mach, and then, entering the upper layers of the atmosphere, flies almost parallel to the surface of the Earth. This makes the overall path to the target shorter than that of a conventional ballistic missile. As a result, despite the reduction in speed due to air resistance, a hypersonic device can reach the target faster than a conventional ICBM warhead.
After the seventh control test in April 2016 of the year, during the following tests in November 2017, the apparatus with the nuclear missile DF-17 on board reached a speed of 11265 km / h.
From local press reports, it is clear that the Chinese hypersonic DF-ZF was tested with a carrier — a medium-range ballistic missile DF-17. This rocket will soon be replaced by a DF-31 rocket in order to increase the range to 2000 km. In this case, the warhead may be equipped with a nuclear charge. Russian sources suggest that the DF-ZF unit may enter the production phase and be adopted by the Chinese army in 2020. However, judging by the development of events, China is still around 10 from adopting its hypersonic systems.
According to US intelligence, China can use hypersonic missile systems for strategic weapons. China may also develop technologies for a hypersonic ramjet engine to enable it to deliver a quick strike. A rocket with such an engine, launched from the South China Sea, can fly 2000 km in near space at hypersonic speeds, which will allow China to dominate the region and be able to break through even the most advanced missile defense systems.
Model promising hypersonic rocket BrahMos II
Indian development
The Indian Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) has been working on hypersonic land-launch systems for more than 10 years 10. The Shourya rocket project (or Shaurya) is progressing most successfully. Two other programs, BrahMos II (K) and Hypersonic Technology Demonstrating Vehicle (HSTDV), have some difficulties.
The development of a surface-to-surface tactical missile began in the 90s. A typical missile range is reported to be 700 km (although it can be extended) with a circular probable deviation of 20-30 meters. The Shourya rocket can be launched from the launch canister, which is installed on the 4x4 mobile launcher, or from a fixed platform from the ground or from a launch shaft.
In the embodiment of the launch container, a two-stage rocket is launched using a gas generator, which, due to the high rate of combustion of the propellant, creates a high pressure sufficient to launch the rocket out of the container at high speed. The first stage supports flight for 60-90 seconds before the second stage begins, after which it is fired off with a small pyrotechnic device, which also works as a pitch and yaw engine.
The gas generator and engines developed by the Laboratory of High-Energy Materials and the Laboratory of Advanced Systems accelerate the rocket to the speed of 7 Mach numbers. All engines and stages use specially developed solid fuels, allowing the device to achieve hypersonic speeds. A 6,5 ton rocket can carry a conventional high explosive warhead weighing almost a ton or a nuclear warhead equivalent to 17 kilotons.
The first ground tests of the Shourya missile at the Chandipur test site were conducted in 2004, and the next test launch in November was 2008. On these tests, the speed of the 5 Mach was achieved and the range of 300 km.
The Shourya rocket launcher tests in the final configuration were conducted in September 2011 of the year. According to reports, the prototype had an improved navigation and guidance system, which included a ring laser gyroscope and an accelerometer developed by the DRDO. The rocket relied mainly on a gyroscope, designed specifically to improve maneuverability and accuracy. The rocket reached speed 7,5 Makhov, flying 700 km at low altitude; at the same time the surface temperature of the case reached 700 ° С.
The Department of Defense conducted the latest test launch in August 2016 of the year from the Chandipur test site. The rocket, reaching an altitude of 40 km, flew 700 km and again at a speed of 7.5 Mach. Under the action of an expelling charge, the rocket flew along the ballistic trajectory of 50 meters, and then switched to a march in a hypersound flight, having completed the final maneuver before the meeting with the target.
At the exhibition DefExpo 2018 it was reported that the next model of the Shourya rocket will undergo some refinement in order to increase the flight range. Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) is expected to do batch production. However, the representative of the BDL said that they did not receive any instructions from the DRDO on the production, hinting that the rocket is still being finalized; the information on these improvements is classified by the DRDO Organization.
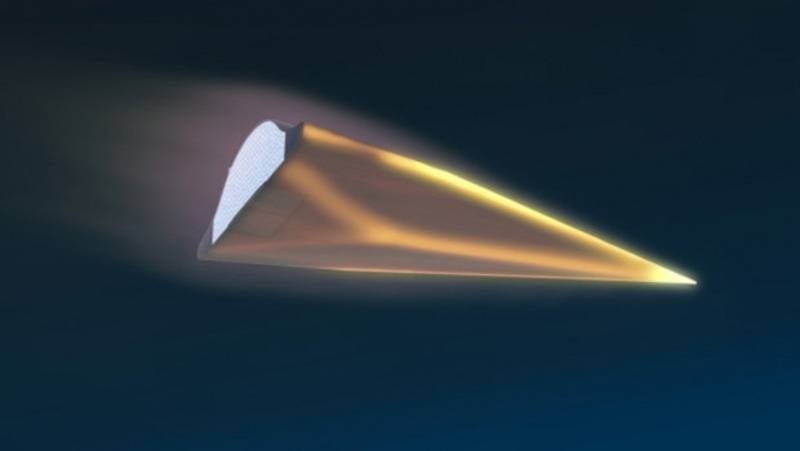
Department of Falcon combat unit in flight
India and Russia are jointly developing the BrahMos II (K) hypersonic cruise missile as part of the joint venture BrahMos Aerospace Private Limited. DRDO is developing a hypersonic ramjet engine, whose ground tests were successful.
India, with the help of Russia, is creating a special jet fuel that allows the rocket to reach hypersonic speeds. No more detailed information about the project is available, but company representatives reported that they are still at the preliminary design stage, so it will take at least ten years before BrahMos II becomes a workable system.
Although the traditional BrahMos supersonic rocket has successfully recommended itself, within the BrahMos II project, the Indian Institute of Technology, the Indian Institute of Science and BrahMos Aerospace itself carry out a large amount of research on materials, since the materials must withstand high pressure and high aerodynamic and thermal loads associated with hypersonic speeds.
Chief Executive Officer of BrahMos Aerospace Sudhir Mishra said that the Russian rocket Zircon and BrahMos II have a common engine and propulsion technology, while the guidance and navigation system, software, housing and control systems are developed by India.
It is planned that the range and speed of the rocket will be 450 km and 7 Mach respectively. The range of the missile was originally defined in 290 km, since Russia signed the document "Missile Technology Control Regime", but at present India, which also signed this document, is trying to increase the range of its missile. As expected, the rocket can be launched from an air, ground, surface or underwater platform. The DRDO organization plans to invest 250 millions of dollars in testing a rocket capable of developing the hypersonic speed 5,56 Machs above sea level.
Meanwhile, the Indian project HSTDV, in which a ramjet engine is used to demonstrate self-sustained flight, faces constructive difficulties. Nevertheless, the Laboratory for Defense Research and Development continues to work on improving the technology of a ramjet engine. Judging by the declared characteristics, with the help of a launching solid-propellant rocket engine, the HSTDV unit at 30 km altitude will be able to develop the 6 Max speed for 20 seconds. The basic design with housing and engine mount was designed in 2005 year. Most of the aerodynamic tests were carried out by the National Aerospace Laboratory NAL.
Video of the avant-garde hypersonic planning winged block demonstrates its flight in a plasma cloud and maneuvering in order to avoid missile defense systems.
The reduced HSTDV model has been tested in NAL for air intake and exhaust flow. In order to obtain a hypersonic model of the behavior of the apparatus in a wind tunnel, several tests were also carried out at higher supersonic speeds (due to a combination of compression and rarefaction waves).
In the Laboratory of Defense Research and Development, work was carried out related to the study of materials, the integration of electrical and mechanical components and a ramjet engine. The first base model was presented to the public in 2010, at a specialized conference, and in 2011, at Aerolndia. According to the schedule, the production of a full-fledged prototype was scheduled for 2016 year. However, due to the lack of necessary technologies, insufficient funding in the field of hypersonic research and the lack of readiness of the production site, the project was far behind schedule.
Nevertheless, the aerodynamic qualities, propulsion system and characteristics of a ramjet engine were carefully analyzed and calculated, in connection with which it is expected that a full-sized jet engine will be able to create 6 kN thrust, which will allow launching satellites nuclear warheads and other ballistic / non-ballistic missiles on large range. The one-ton octagonal hull is equipped with flight stabilizers and rear steering wheels.
The most important technologies, for example, the engine combustion chamber, are being tested at another Terminal Ballistics Laboratory, also part of DRDO. DRDO hopes to build hypersonic wind tunnels for testing the HSTDV system, but it all comes down to a lack of funds.
In connection with the advent of modern integrated air defense systems, the armed forces of militarily powerful countries are counting on hypersonic weapons in order to counter the strategy to ban access / block the zone and deliver regional or global strikes. At the end of the 2000-x in defense programs, special attention was paid to hypersonic weapons as the optimal means of delivering a global strike. In connection with this, and also with the fact that geopolitical rivalry every year becomes more and more fierce, the military is trying to maximize the amount of funds and resources allocated to these technologies.
In the case of ground launch hypersonic armament, in particular, systems used outside the active enemy air defense systems, the optimal and low-risk launch options are standard launch complexes and mobile launchers for armament of ground-to-ground and ground-to-air classes, and underground mines for strikes at medium or intercontinental distances.
On the materials of the sites:
www.nationaldefensemagazine.org
www.sandia.gov
www.darpa.mil
kremlin.ru
mass-destruction-weapon.blogspot.com
www.drdo.gov.in
www.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
www.youtube.com
pinterest.com
www.army-technology.com


Information