How do satellites shoot down?
From the point of view of destruction methods and technologies, a spacecraft (SV) in orbit is not an easy target. Most of the satellites move on a predictable trajectory, which to a certain extent facilitates the guidance of the weapon. At the same time, the orbits are located at altitudes of at least several hundred kilometers, and this places special demands on the design and characteristics of anti-satellite weapons. As a result, interception and destruction of a spacecraft turns out to be a very difficult task, which can be solved in different ways.
"Earth-space"
The obvious way to deal with satellites is to use special anti-aircraft weapons with enhanced characteristics that can even reach targets in orbits. Such an idea appeared one of the first, and soon real results were obtained. However, complexes of this kind in the past did not receive special distribution because of their complexity and high cost.
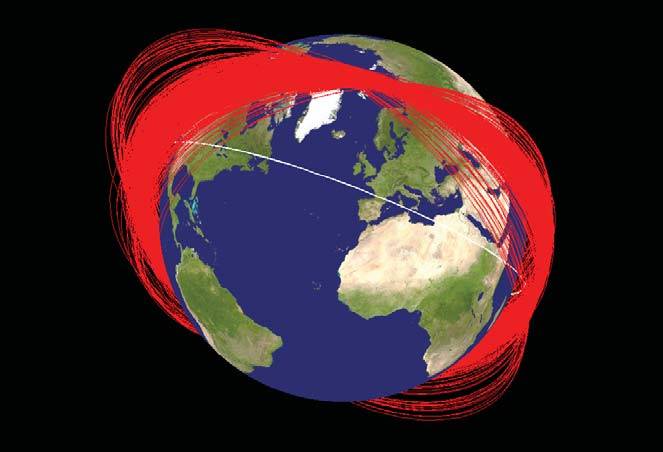
Distribution of fragments of the FY-1C satellite shot down by a Chinese rocket. NASA drawing
However, by now the situation has changed, and new land or sea missile systems have arrived for service, capable of attacking satellites in orbits. So, in January, 2007, the Chinese military conducted the first successful tests of its anti-satellite complex. The interceptor missile successfully rose to an altitude of about 865 km and struck an emergency weather satellite FY-1C on a head-on course. News about these tests, as well as a large number of satellite wrecks in orbit, have become a cause for serious concern of the foreign military.
In February, the United States conducted similar tests on 2008, but this time it was about the missile of the ship complex. The USS Lake Erie missile cruiser (CG-70), while in the Pacific, launched the SM-3 interceptor missile. The target for the rocket was designated emergency reconnaissance satellite USA-193. The meeting of the interceptor missile and the target took place at an altitude of 245 km. The satellite was broken, and its fragments soon burned down in dense layers of the atmosphere. These tests confirmed the possibility of deploying anti-satellite missiles not only on land but also on ships. In addition, they testified to the high potential of the SM-3 rocket, originally intended for work on aerodynamic and ballistic targets.
According to different sources, ground-based anti-satellite missiles are being created in our country. There is an assumption that the altitude of the latest C-400 missiles is not limited to official 30 km, and due to this, the complex can hit spacecraft in orbit. It is also assumed that specialized anti-satellite missiles will be part of the promising C-500 complex.
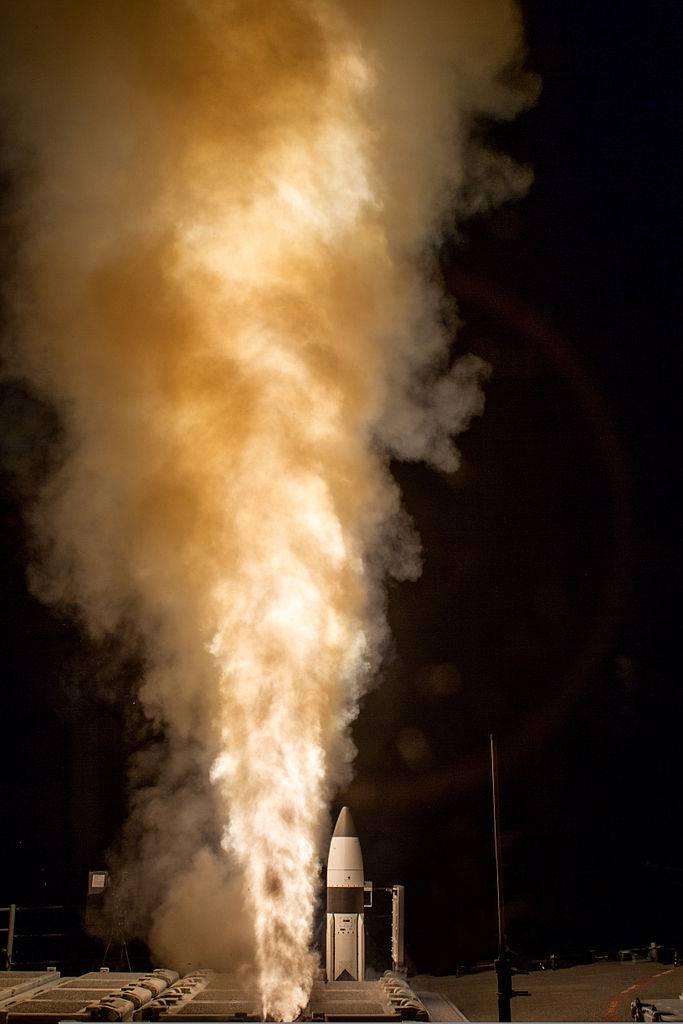

SM-3 rocket launch from USS Lake Erie cruiser launcher (CG-70), 2013 g. US Navy Photo
Currently, the Russian industry is engaged in the modernization of the anti-missile defense system А-235. As part of a larger program, a promising interceptor missile with the Nudol code is being developed. In the foreign press, the version according to which the Nudol missile system is precisely a means of dealing with satellites enjoys certain popularity. At the same time, the characteristics and capabilities of the complex remain unknown, and Russian officials do not comment on foreign versions.
"Air-space"
Ground-based anti-satellite missiles face a serious problem in the form of a significant altitude of finding a target. They need powerful engines, which complicates their design. At the end of the fifties, almost immediately after the first launch of an artificial satellite of the Earth, an idea emerged of placing interceptor missiles on a carrier plane. The latter was supposed to raise the rocket to a certain height and ensure its initial acceleration, which reduced the requirements for the power plant of the weapon itself.
The first experiments of this kind were conducted by the United States in the late fifties. At that time, the development of aeroballistic missiles of strategic purpose; Some samples of this kind, as it turned out, could be used not only against ground targets, but also to combat the spacecraft. As part of the flight tests of the Martin WS-199B Bold Orion and Lockheed WS-199C High Virgo missiles, test launches were conducted on targets in orbit. However, these projects did not produce the desired results, and were closed.
In the future, the United States tried several times to create new air-based anti-satellite missiles, but did not succeed in this. All new products had some or other disadvantages that did not allow to put them on board. At the moment, as far as we know, the American army does not have such weapons, and the industry is not developing new projects.

Destruction of the USA-193 satellite with the SM-3 rocket. Photo by US Navy
The most successful American development in the field of anti-satellite missiles for aircraft was the Vought ASM-135 ASAT product, the carrier of which was the modified F-15. In September, 1985, the only combat training launch of this rocket on an orbital target took place, confirming its capabilities. The fighter carrier, making a vertical climb, dropped the rocket at an altitude of about 24,4 km. The product was successfully guided to the designated target with the help of the GOS and struck her. The meeting of the rocket and the target occurred at an altitude of 555 km. Despite the obvious success and great potential, in 1988, the project was closed.
In the first half of the eighties, our country launched its own project of an anti-satellite complex with an air-based interceptor missile. The 30P6 "Contact" complex included a number of products, and the main one was the 79М6 rocket. It was proposed to be used in conjunction with a MiG-31D type carrier aircraft. According to different sources, the Kontakt rocket could hit spacecraft in orbits at least 120-150 km high. As far as is known, in its original form the 30P6 complex was not brought to operation. Later, however, a project emerged that included the restructuring of the 79М6 interceptor missile into a launch vehicle for small payloads.
At the end of September, new photos of the MiG-31 with an unknown product on the external suspension appeared in free access. Dimensions and form of such a load were the reason for the emergence of a version about the development of a new anti-satellite air-launched missile. However, so far these are only assumptions and there is no data on an unknown object.
As far as is known, the subject of anti-satellite missiles for aircraft at one level or another has been studied in different countries. At the same time, it came to real products and launches only in our country and the United States. Other states did not build and did not test such weapons. Their anti-satellite programs are based on different concepts.
Satellite vs satellite
A variety of means can be used to destroy an object in orbit, including a special orbital spacecraft. Ideas of this kind were worked out in different countries, and in the Soviet Union they were even considered priorities, which led to the most interesting consequences. At the same time, the development of interceptor satellites, apparently, continues to this day.
The development of the Soviet project with the straightforward name "Fighter of satellites" or IP started in the early sixties. Its goal was to create a spacecraft capable of intercepting and destroying other objects in different orbits. The development of a complex that includes various means, including a special satellite with special capabilities, took a lot of time, but still led to the desired results. At the end of the seventies, a military IP satellite with all the additional means was entered into service. The operation of this complex continued until the 1993 year.
From the beginning of the sixties, pilot missions of the “Flight” series were launched using the P-7A launch vehicle in a two-stage configuration. The spacecraft had maneuvering engines and a shrapnel warhead. Over time, the appearance of the complex changed, but its main features remained the same. In the mid-seventies, test launches took place, according to the results of which the IP complex entered service.
Foreign countries also worked on the idea of an interceptor satellite, but it was considered in a different context. Thus, within the framework of the Strategic Defense Initiative program, the American industry developed the project of the small-sized satellite Briliant Pebbles. It provided for the placement in orbit of several thousand small satellites with their own guidance systems. When receiving an order to attack such a spacecraft, it should have come closer to the goal and collide with it. A satellite weighing 14-15 kg at a speed of approaching 10-15 km / s guaranteed to destroy various objects.
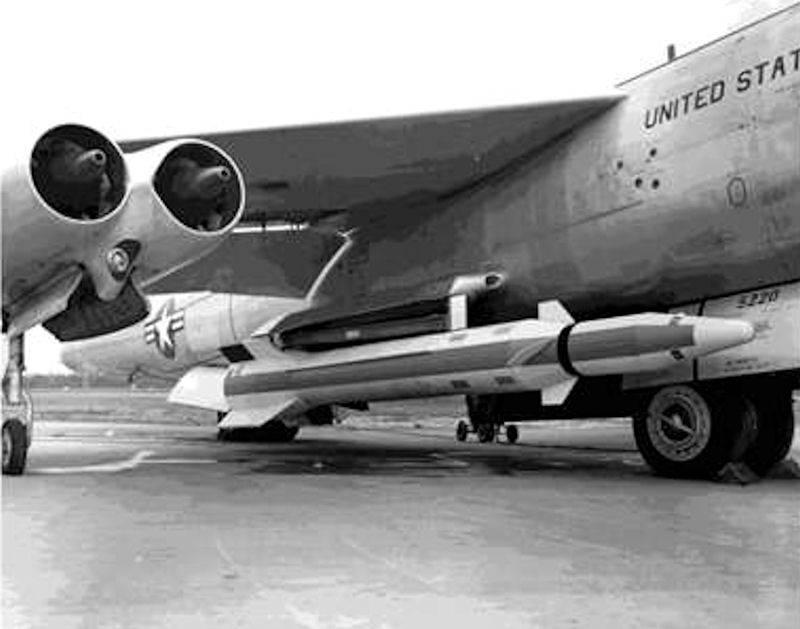

Aeroballistic rocket WS-199 Bold Orion and its carrier. Photo Globalsecurity.org
However, the aim of the Briliant Pebbles project was to create a promising anti-missile defense. With the help of such satellites, it was planned to destroy warheads or whole stages of ballistic missiles of a potential enemy. In the future, interceptor satellites could be adapted to intercept the spacecraft, but it never came to that. The project was closed along with the entire SDI program.
In recent years, the issue of interceptor satellites has become relevant again. For several years, the Russian military sent into orbit a number of satellites of unknown destination. Watching them, foreign experts noted unexpected maneuvers and changes of orbits. For example, in June last year, the launch of the Cosmos-2519 spacecraft took place. Exactly two months after launch, a smaller apparatus separated itself from this satellite, which carried out a series of maneuvers. It was alleged that it was a so-called. satellite inspector, able to study the state of other equipment in orbit.
Similar events in the near-Earth space caused a curious reaction of foreign experts and the media. In numerous publications it was noted that the possibility of free maneuvering and changing the orbit can be used not only to study the state of the spacecraft. A satellite with such functions can also become an interceptor and destroy designated objects in one way or another. For obvious reasons, Russian officials did not comment on such versions.
In 2013, China sent three unidentified satellites into space at once. According to the available data, one of them carried a mechanical manipulator. During the flight, this device changed the trajectory, deviating from the original by almost 150 km. At the same time he got close to another satellite. After the publication of information about such maneuvers, there were concerns about the possible use of a satellite with a manipulator as an interceptor.
Defeat without contact
In the recent past, it became known about the existence of a promising anti-satellite weapon project capable of neutralizing a target without direct contact with it. We are talking about a specialized complex of electronic warfare, designed to suppress radio communication channels and, possibly, damage to the onboard electronics of the target apparatus.

Fighter MiG-31 and 79М6 rocket. Photo Militaryrussia.ru
According to available data, the development of a new Russian EW complex with the cipher "Tirada-2" started back in 2001 year. Last year, state tests of the Tirada-2C system were reported. In August of this year, a contract was signed at the Army-2018 forum for the supply of Tirade-2.3 serial products. At the same time, accurate data on the composition, architecture, tasks and other features of the complex have not yet been announced.
Earlier it was claimed that the Tirada line of various modifications are designed to suppress radio communication channels used by spacecraft. The inability to exchange data or transmit signals of various kinds does not allow the satellite to perform its functions. Thus, the spacecraft remains in orbit and remains operational, but loses the ability to solve the set tasks. As a result, the enemy cannot use navigation, communications and other systems built using satellites.
Future systems
Modern armies of developed countries are actively using space groups with devices for various purposes. Satellites are used for reconnaissance, communications, navigation, etc. In the foreseeable future, spacecraft will remain an essential element of defense, and there is reason to believe that their importance for armies will grow. As a result, the armed forces also need the means to combat the enemy’s spacecraft. The development of such systems has been going on since the middle of the last century, and has managed to give some results in a number of areas. However, due to the particular complexity, anti-satellite systems have not yet become widespread.
Yet the need for anti-satellite weapons is obvious. Despite the complexity of such systems, leading countries continue to develop them, and the most successful models even come into service. Modern anti-satellite weapons, in general, cope with the tasks, although it has limited potential in height and accuracy. But its further development should lead to the emergence of new designs with special characteristics and capabilities. What options antisatellite weapons will develop in the near future and reach operation - time will tell.
On the materials of the sites:
http://tass.ru/
http://rg.ru/
http://vpk-news.ru/
http://freebeacon.com/
https://globalsecurity.org/
http://russianspaceweb.com/
http://astronautix.com/
http://militaryrussia.ru/blog/topic-699.html
https://bmpd.livejournal.com/

Information