Guns "Hotchkiss" in World War II

For an automatic weapon, cartridges with a reduced charge of gunpowder and D bullets (mass 12,53 g), heavy N (lead core, mass 12,9 g), armor-piercing (steel core), incendiary P tracer T were used.
In the infantry battalion of the French army there was a platoon of a machine-gun and mortar company armed with 4 machine gun Mle1914 / 25 "Hotchks." As of 1940, each infantry regiment had thousands of 3 machine guns and 48 light machine guns on 112, which was a good indicator of saturation for that time.
In addition to the French army, Hotchkiss machine guns were in service in the Polish army under the designation Wz.1914, in the version chambered for the Mauser 7,92 mm cartridge - Wz.1925, mainly used on armored vehicles and tanks... With a heavy barrel "Hotchkiss" had a rate of fire of 380-400 rounds per minute. The machine gun was powered by a belt with a capacity of 252 rounds. Spain also had Hotchkiss Mle1914.
Trophy easel "Hotchkiss" Wehrmacht limited use under the designation MG.257 (f). There are references to the use of MG.257 (f) in the battles of Leningrad.
After the end of the Second World War, the Hotchkis machine-gun machine-gun did not return to service in the French army, but continued to be used in the former French colonies.
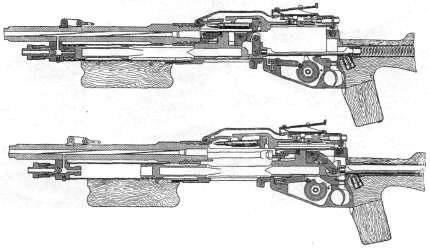
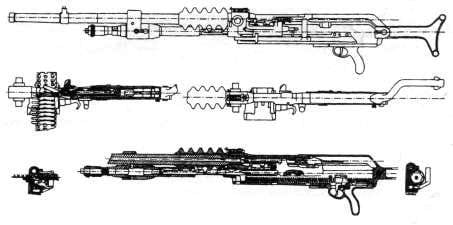
Manual machine gun M1922 / 26 "Hotchkiss"
Firm Hotchkiss (Hotchkiss) has developed a system for commercial purposes. It was launched on the market in 1922 year. In the machine gun "Hotchkiss" used familiar to the firm automation based on the removal of powder gas and locking swing arm (wedge). The machine gun system worked quite smoothly, but the large length of the locking assembly can be attributed to the shortcomings. The gas chamber was equipped with a screwable regulator with which its volume was varied. The barrel and receiver were threaded. A return spring was placed in the butt channel. The shot was made from the rear whisper. USM allowed only continuous fire. The fuse box on the right had two positions: the “fire” state corresponded to the front position (“A”), the “fuse” - back (“S”). When you install the fuse in position "S" blocked the trigger. Mechanical retarder rate of fire of the original design was mounted in the trigger box. The mechanism included a mechanism of gears, a drum with a lever, a balance bar and a moderator lever. The slowdown was determined by the selection of the balancer and gears.
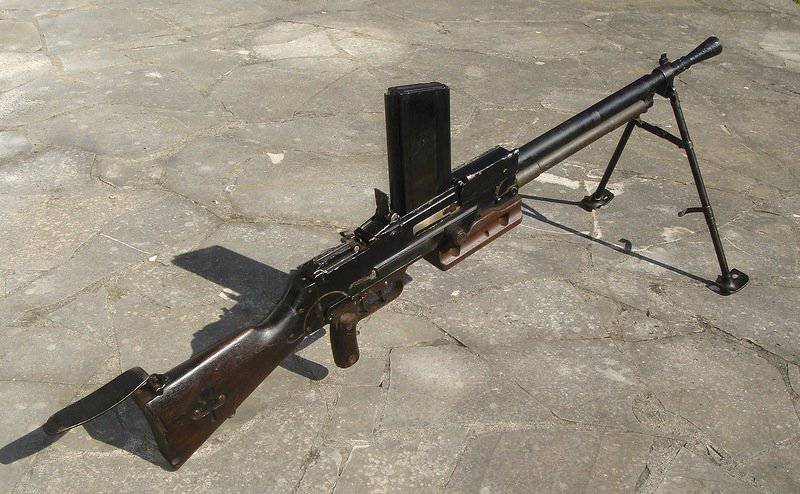

Modifications of this machine gun differed in the power supply system, which could be carried out from: a box-like sector store fastened on top, a rigid tape “Hotchkis” traditionally supplied from the side or a flexible metal tape having rigid links with three cartridges developed for the Mle1914 machine gun. The latter version of the modification could be equipped with a heavy barrel for firing long bursts. This machine gun could be mounted on a tripod machine, but it would be wrong to attribute it to the “one”.
The feeding of the tape on the right was carried out using a lever-type feeder, which was actuated by a bolt. Frequent delays due to sticking during filing were caused by the uncertainty of the position of the cartridge during unloading. More reliable was the food from the store. Reflection of the spent cartridges carried down.
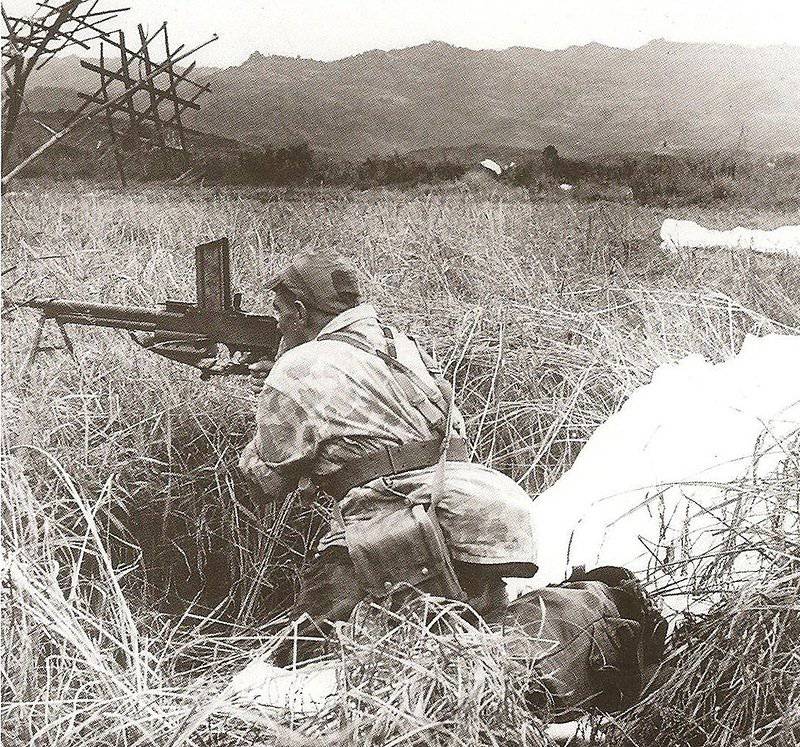

Sector sight was used. Marking included: on the right side of the receiver - the inscription "HOTCHKISS 1922 (1924 or 1926) Brevete", on top of the box - the serial number.
The French army handguns "Hotchkiss" used very limited. Separate deliveries to other countries allowed the company to continue production until 39. Thus, the model M1922 in calibers 6,5 - 8 millimeters was supplied to Greece, Norway, Yugoslavia, South Africa, Czechoslovakia. This model was powered by a box magazine with an 20-30 capacity of cartridges or a rigid metal tape with a volume of 15-30 cartridges. 7,92-mm modification was supplied to Czechoslovakia (party in 1000 units) and Yugoslavia. This machine gun had a significant impact on the Czech ZB-26. 7-mm modification M1925 chambered for "Mouser" was delivered to Spain, probably from this same party deliveries were made to Brazil and the Dominican Republic. “Hotchkiss” M1926 with 25 cartridge-powered tapes was also supplied to other countries, including Greece, which included about 5 ths. Of “Hotchkos” hand-held ones.
Little is known about the combat use of the Hotchkis machine gun during World War II. Is that they were in service with the Vichy French troops in Africa and the British troops insignificant batch purchased in 22-23 years for testing (modification caliber .303).
The order of unloading machine gun with store supply. Disconnect the magazine, pull the bolt handle back, inspect the chamber. Release the bolt handle, pull the trigger.
The order of unloading machine gun with tape feed. Pull back the latch of the receiver cover by moving the cover forward and upwards. Take out the tape with cartridges to the right. Lead the loading handle back and inspect the chamber. After releasing the charging handle, pull the trigger.
The order of incomplete disassembly of the Hotchkis М1926 machine gun:
1. Unload a machine gun.
2. In the case of tape power - open the lid, remove the receiver.
3. Remove the butt plate pin, pull back the butt plate and remove it.
4. Remove the moving system from the receiver, remove the connecting rod.
5. Push out the axis of the earring and separate the bolt, as well as the bolt carrier and the earring.
6. Separate drummer.
7. Pulling the handguard back and take it down.
8. Pulling the charging handle back and moving it to the right to remove it.
9. Unscrew the regulator from the front of the gas chamber.
10. Remove the bipod.
11. Remove the trigger box. Why turn down the box pin lever, take it to the left. Take the box down.
When assembling actions were performed in reverse order.
Technical characteristics of the Hotchkiss M1926 machine gun:
Cartridge - various calibers;
Weight 6,5-mm modifications - 9,52 kg (without cartridges);
Weight 8-mm modifications - 12,0 kg (without cartridges);
The full length of the weapon is 1215 mm;
Barrel length - 577 mm;
Grooves - 4 right;
The initial velocity of the bullet - 700 m / s (when using the cartridge 8x50,5R);
Sighting range - 2000 m;
Effective range - 800 m;
Power system - hard cassette (tape) with a capacity of 15, 20, 25 cartridges;
Tape weight - 0,75 kg (for 15 cartridges);
The rate of fire - 450-500 shots per minute;
Combat rate - 150 shots per minute;
Machine weight - 10,0 kg.
Large-caliber machine gun "Hotchkiss" model 1930 g
The French were engaged in the development of large-caliber machine guns among the first, but the XnUMX-millimeter machine gun Mle11 “Ballun” (“Hotchkiss”) was not too successful, and the requirements for this type of weapon changed very quickly. By the end of the 1917-s, the Hochkiss based on the Hotchkis machine gun, the M20 developed the 1922-mm machine gun. In the design were used elements of the easel Mle13,2. This machine gun is also known as Ml1914 SA (Contre avions - anti-aircraft). This machine gun was not the only challenger, for example, the “Putoto” plant for the same purpose was offered at the same time 930-millimeter twenty-barrel gun.
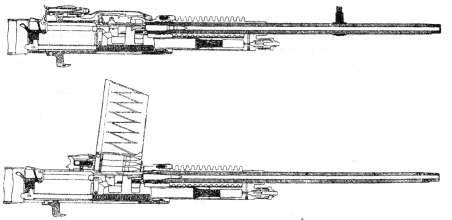
Automatic machine gun had a gas engine. To change the volume of the gas chamber there was a special gas regulator. The barrel and the receiver were connected with a thread, supplied with a radiator having transverse ribs, a conical flame arrester could be installed. To lock the barrel served as a wedge, which is connected with a hinged earring with bolt carrier. The shot was carried out from the rear whisper, which held the slide frame behind the combat platoon. The sear was the front of the swinging release lever, assembled in the back plate. Between the control knobs acted the head of the trigger lever. The loading handle was located on the right. The cartridge case was removed from the chamber by the bolt ejector and the removal from the weapon by a lever reflector in the receiver. The armor-piercing bullet used in the machine gun (mass of 52 g) pierced 30-millimeter steel armor at a distance of 200 meters, the armor-piercing tracer bullet (mass of 49,7 g) was mainly used for anti-aircraft fire.
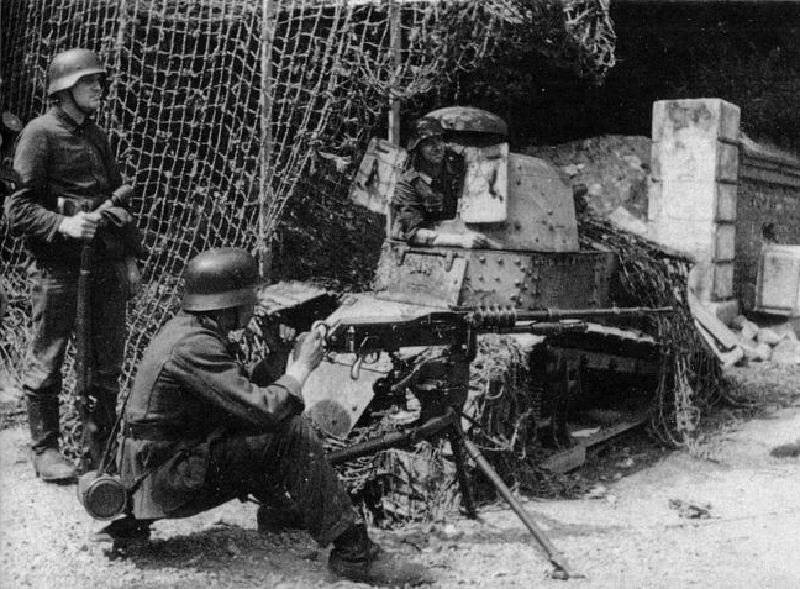

The power supply was carried out in two ways: from the rigid cage (tape) inserted into the right of the 15 capacity of cartridges or from the box magazine with the capacity of 30 cartridges and inserted from above. The weight of the tape with 15 cartridges was about 2 kilogram. To feed the rigid tape on the left served a lever mechanism, located in the hinged lid of the receiver. The mechanism was driven by a moving shutter. In the version of the machine gun with store supply used another receiver box. There was a special stop that kept the bolt carrier in the rear position after the ammunition was spent. After the installation of a new equipped magazine, the stop automatically released the bolt carrier. Sector sight had a notch in the range 200-3600 meters. The maximum horizontal range is 7000 meters, the slant range is 4500 meters, the height reach is 3000 meters.
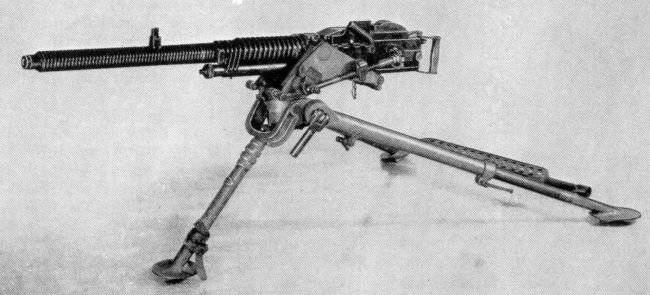
The machine gun, depending on the destination, was installed on a tripod light machine with a seat on the back leg (for making fire on ground targets), on a universal field tripod machine or a special stationary single or integrated anti-aircraft gun. The universal tripod machine allowed circular firing with vertical guidance angles from 0 to + 90 degrees. The seat for the machine gunner and the swivel (top machine) rotated together. The machine gun box and the machine tool formed a parallelogram, which allowed the shooter to not change the position of the head at different elevation angles. The machine was a little maneuverable and massive. There was also a field wheeled machine equipped with an anti-aircraft stand and sliding supports.
Of the anti-aircraft systems, the most successful were the paired R3b on a heavy folding tripod and the R4 on the stand installation (widely used), and the quad-line installations HLP4. In complex installations used machine guns with store supply. Paired installations were installed not only on the ground, but also mounted on railway platforms, cars, trailers, ships, supplied with mechanisms of vertical and horizontal guidance, and a counterbalancing spring mechanism. A seat for the shooter was installed on the upper machine, the steps were equipped with separate pedal descents for each machine gun. Before the head of the arrow on the bracket, the Le Priere collimator sight corrector was installed (automatically correcting for the flight time of the bullet to the pointing angles). Installing KZ on a tripod with machine guns and a sight had a mass of 375 kg. French paired ZPU used in some other countries.
The weight of the quad install HLP4 with machine guns was 1200 kg. It was used as a semi-stationary or stationary. Firing Rate HLP4 - 1800 shots per minute. The installation was mounted on a circular pursuit, the sides of the gunners were installed on their sides with their pedal descents and sights. Shooting was opened only in case of coincidence of pressing the pedals, that is, when the pickup coincides horizontally and vertically. Accuracy increased due to the low height of the line of fire. The loading of machine guns was carried out with one big handle at a time. The French ZPU were among the first to be equipped with pointing mechanisms with handwheels, which increased the speed of guidance and reduced errors. Other more advanced sights were also used.
The 13,2 mm Hotchkiss machine gun of the 1930 model was placed on light tanks. In addition, on the basis of this machine gun in 1934 was created aviation machine gun "Hotchkiss" having a rate of fire of 450 rounds per minute.
The 13,2 — Hotchkis 30 mm machine gun was exported to a number of countries, including Greece, Spain, Poland, Romania and Yugoslavia. In Japan, this machine gun was released under the designation Type 93 under license. In Finland, the French cartridge 13,2x99 developed the L-34 Lahti machine gun.
The order of incomplete disassembly of a machine gun having a band feed:
1. Unload a machine gun.
2. Pressing the latch of the receiver cover (located on top of the butt plate) to open it.
3. Drown the rear end of the return spring action guide rod (located at the bottom of the butt plate), remove the deadbolt, separate the butt plate and the returnable spring spring.
4. Remove the bolt carrier and the bolt, pushing the axis of the earrings to separate the bolt from the frame.
5. Remove the drummer from the slide.
Reassemble in the reverse order.
Technical characteristics of the Hotchkiss machine gun model 1930 year:
Cartridge - Hotchk 13,2-mm (13,2x99);
The mass of the "body" machine gun - 39,7 kg;
The length of the "body" of the machine gun - 1460 mm;
Barrel weight - 14,0 kg;
Barrel length - 992 mm;
The length of the threaded part of the trunk - 896 mm;
The grooves are left sided;
Initial bullet speed - 800 m / s;
The rate of fire - 450 shots per minute;
Fighting rate - 90-100 / 180-200 shots per minute.
Aim range - 3600 m (ground firing);
Weight curb tape on 15 cartridges - 2,0 kg;
Machine gun weight - 97 kg (on a tripod machine);
Calculation - 5-6 people.
Information