State of the air defense system of the countries - parties to the Treaty on Collective Security (part of 2)
The Republic of Kazakhstan is one of the most important CSTO allies for our country. Kazakhstan is of particular importance due to its geographical location and occupied area, as well as the presence in the republic of a number of unique defense facilities. During Soviet times, the territory of the Kazakh SSR was used to house various test sites and test centers. Here were conducted tests of nuclear weapons, tested air defense and missile defense systems.
Given the special role of Kazakhstan in ensuring the country's defense capability, very serious air defense forces were concentrated on its territory. In the form of a Soviet legacy, the republic got equipment and weapons from the 33rd Air Defense Division from the 37th Air Defense Corps, which in turn was part of the 12th separate air defense army. The 33rd Air Defense Forces included the 87th Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade, the 145th Guards Orsha Red Banner, the Order of Suvorov Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade, the 132nd Anti-Aircraft Missile Brigade, the 60th and 133rd Radio Engineering Brigades, the 41st radio regiment. Parts of the 56th corps from the 14th Air Defense Army, stationed in Kazakhstan, were represented by four anti-aircraft missile regiments: the 374th air defense regiment, the 420th air defense regiment, the 769th air defense regiment and the 770th air defense regiment. Until 1991, two air defense fighter regiments were also deployed in Kazakhstan on the MiG-31 and MiG-23MLD interceptors (the 356th IAP in Semipalatinsk and the 905th fighter aviation regiment - on the MiG-23MLD in Taldy-Kurgan). At the same time as front-line fighters of the air defense of the independent republic, front-line fighters of the 73rd Air Army departed: the 27th Guards Vyborg Red Banner Fighter Aviation Regiment - on the MiG-21bis and MiG-23MLD in Ucharal and the 715th Uap in Lugovoy on the MiG-23MLD and Mi -29. A certain number of MiG-25PDS and MiG-31 interceptors were available at the aerodromes of test centers and training grounds. In particular, Kazakhstan got several MiG-31Ds adapted for use as part of an anti-satellite aircraft-based system designed to destroy low-orbit satellites. But in Kazakhstan, fighters equipped with anti-satellite missiles were not in demand. In the early 90s, the MiG-31D was “deposited” in one of the hangars at the airfield of the Saryshagan training ground near the city of Priozersk. In total, the Air Force of Kazakhstan in 1991 included about 200 fighters capable of performing air defense tasks.
1 June 1998 in Kazakhstan formed the Air Defense Forces (SVO), in which the Air Force and air defense forces were combined under one command. At the end of 90-x in connection with the decommissioning of the MiG-21 bis, MiG-23MLD and MiG-25PDS and part of the MiG-29, the question arose about the replenishment of the fighter fleet. Of greatest interest to the Air Defense Forces of Kazakhstan were heavy fighters Su-27С. The first four aircraft of this type were transferred from the Russian Air Force in 1996 year. A number of media outlets indicate that the 4 generation fighters were delivered to Kazakhstan in exchange for the Tu-1992MS strategic missile-carriers launched in 95, which were based at the Chagan air base, not far from the Semipalatinsk nuclear test site. In total, from 1996 to 2001 year, the Air Defense Forces received about three dozen Su-27C and Su-27UB. There is information that second-hand Su-27S and “Sparky” Su-27UBs were received at a reduced price, due to the rent paid for the Baikonur cosmodrome.
In 2007, 10 Su-27С and Su-27UB were sent for reconditioning and modernization to Belarus at the 558-th aircraft repair plant in Baranovichi. In the course of modernization, the Kazakhstani “dryers” equipped a satellite navigation system, EW equipment and communications manufactured in Belarus. Thanks to the adaptation of the Lightning-3 target designation system for Kazakhstan, produced by the Israeli company Rafael, the range of high-precision weapons. After upgrading, fighters were given the designation Su-27BM2 and Su -27UBM2. According to open sources, the main location of the Kazakh Su-27 is 604-I air base in Taldykorgan. Su-27 fighters are also located at the 605 air base in Aktau.
According to Kazakh sources, the 25 is currently armed with heavy MiG-31 interceptor fighters. Interceptors MiG-31B, MiG-31БС, MiG-31ДЗ are based at 610-th air base in Karaganda.
In the flying state is about two dozen cars. It is reported that in the future, Kazakhstan's MiG-31 should be upgraded and overhauled in Russia at the 514 aircraft repair plant in Rzhev.
The main task of the 610 air base, where the MiG-31 is located, is to protect the capital of Kazakhstan. In Karaganda, combat duty constantly carries at least two interceptors with full ammunition. When entering the team, the MiG-31 should take to the air in 7 minutes. After 20 minutes after takeoff, they can already patrol over Astana.
In addition to the Su-27 and MiG-31, the Air Defense Forces include 12 single MiG-29 and two “Sparky” MiG-29UB. MiGs are permanently deployed at the 602 air base in Shymkent, and these aircraft, along with MiG-27 fighter-bomber and Su-25 attack aircraft, are based in Taldykorgan.
How many Kazakh MiG-29 are in flight condition is unknown, but with a high degree of confidence it can be argued that light fighters built in the USSR are in the final stages of their life cycle. More than 20 flying out their MiG-29 resource is now stored at the Zhetygen airbase in 50 km northeast of Almaty. It is also quite obvious that despite the modernization of the part of the Su-27 and MiG-31, the fleet of these machines will be greatly reduced in the next few years due to the development of the resource. To compensate for the “natural loss” of Soviet-made fighter jets, an agreement was signed at the KADEX-2014 exhibition in Astana to order a batch of Su-2014M multifunctional fighters at the KADEX-30 exhibition in Astana.
During the conclusion of the contract, a substantial discount was made to Kazakhstan, according to unconfirmed data, the cost of the Su-30CM is the same as for the RF ASC. In total, the Kazakh Air Defense Forces should receive an 24 aircraft. The first four brand new Su-30CMs came from the Irkutsk Aviation Production Association in April 2015. At the moment there is a X-NUMX Su-8CM in the republic, all of them are located at the 30-th air base in Taldykorgan.
Assessing the state of the fighter component of the SVO of the Republic of Kazakhstan, it can be noted that for the ninth largest state in the world, whose territory is 2 724 902 km², six dozen fighters, most of which have an age of about 30 years, is not enough just to protect strategic facilities, but also for effective airspace control. However, the combat readiness of the fighter fleet and pilot training are at a fairly high level. During joint exercises, Kazakhstan pilots invariably demonstrate a very high level of training and are among the best among the CIS countries. The average flight time per fighter pilot in Kazakhstan exceeds 120 hours.
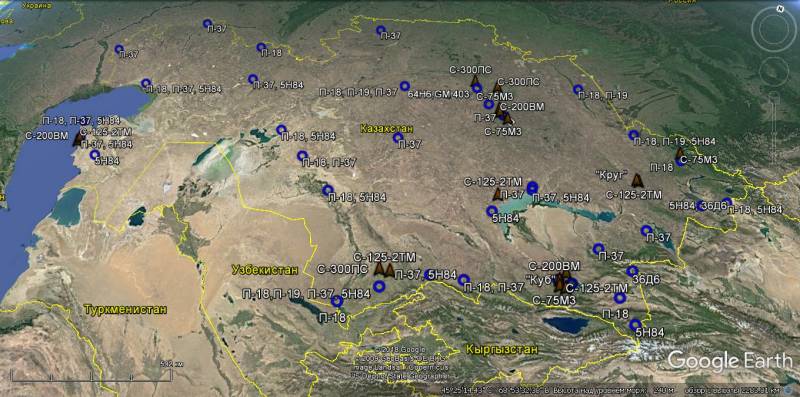
In 1991, on the territory of Kazakhstan, the X-NUMX C-80, C-75, C-125 and C-200П SAM systems were deployed around Kazakhstan. Another number of anti-aircraft complexes was available in warehouses. In addition, the republic got huge reserves of anti-aircraft missiles, spare parts, liquid rocket fuel and an oxidizer. In Soviet times, the airspace of the USSR from the south covered the belt of positions of anti-aircraft missile systems that stretched across the western and central parts of Turkmenistan, the center of Uzbekistan, and southern and eastern regions of Kazakhstan. The main part of the complexes deployed at these positions was C-300М75 / М2. The almost 3 3 km air belt was supposed to prevent a possible breakthrough by US strategic bombers from the south.
Kazakhstan also got at least one brigade set of military complexes on the Krug and Kub tracked chassis. There were more than two hundred Osa-AK / AKM, Strela-1, Strela-10 and Shilka ZSU-23-4 air defense systems, as well as several hundred anti-aircraft guns: 100- mm KS-19, 57-mm C-60, paired 23-mm ZU-23 and more 300 MANPADS.
The stockpiles of weapons inherited by Kazakhstan far exceeded the needs of the newly independent republic. After the collapse of the USSR, the content on the positions of numerous anti-aircraft complexes no longer made sense. Taking into account the relatively low population density in the south and east of the country, the leadership of Kazakhstan decided to cover up the most significant industrial-political and defense centers of the republic. At present, the air defense of Kazakhstan has a pronounced focal character. Military duty, according to official data, are 20 anti-aircraft missile battalions.
It can be noted that due to the large reserves of missiles and spare parts in the SVO, not only the C-300PS anti-aircraft missile systems built in the mid-to-end 80-s have been preserved, but also the first-generation C-75М3, С-125М / М1 and С-200ВМ complexes, built 35-40 years ago.
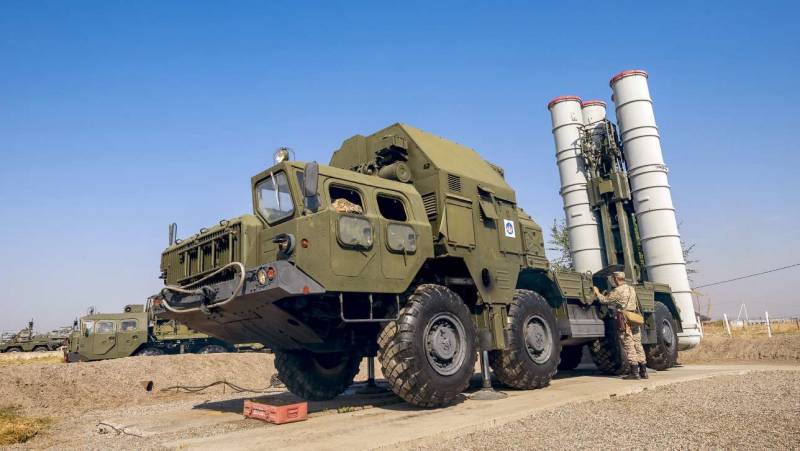
The “long arm” of the air defense of Kazakhstan is the S-200BM air defense missile system with a range of 240 km. Until now, apart from Russia, not a single republic of the former USSR has been armed with complexes and anti-aircraft systems that exceed the “two hundred” in range and height of target destruction. At present, C-200ВМ positions are located north-west of Karaganda and in the west of the republic in Munayli district, on the coast of the Caspian Sea, south of Aktau and north of Alma-Ata - a total of four target channels. The satellite images show that the combat duty is reduced. Of the six "guns" rockets loaded only three. That, however, is not surprising, long-range C-200 air defense systems of all modifications have always been very complex and expensive to operate.
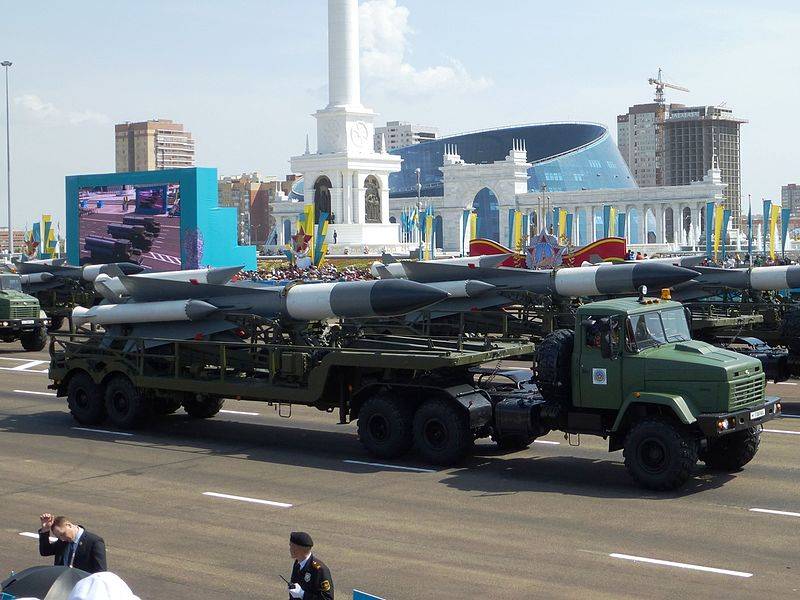

Nevertheless, there is no talk about the refusal of the Kazakhstani military from the modernized "Vega". In addition to the record range and height of destruction, anti-aircraft missiles 5B28 look very impressive during military parades.
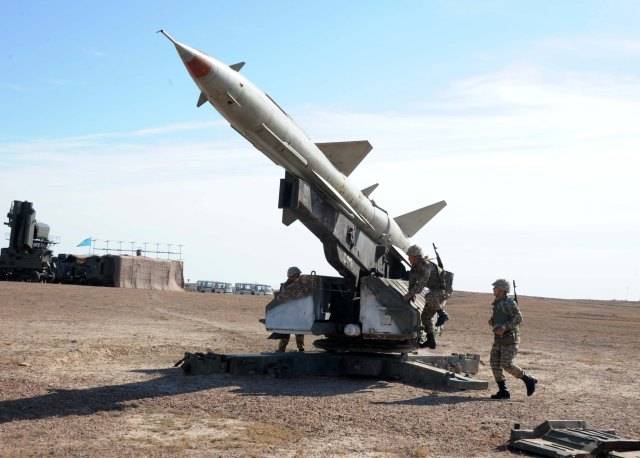
Oddly enough, in the NWO of the republic, the C-75М3 air defense systems still remain. After the removal of the main part of the complexes from combat duty, the most recent "seventy-dozen" were sent to the storage bases and subsequently became "donors" of spare parts for air defense systems that carry service. However, at the moment C-75М3 are used by the Kazakh air defense forces to a limited extent.
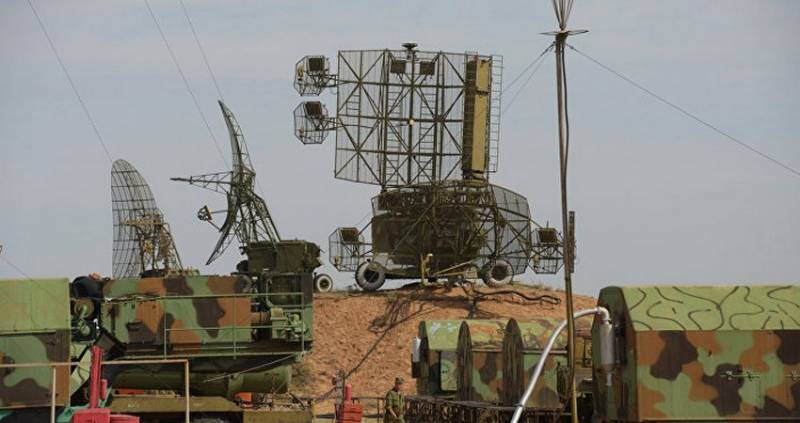
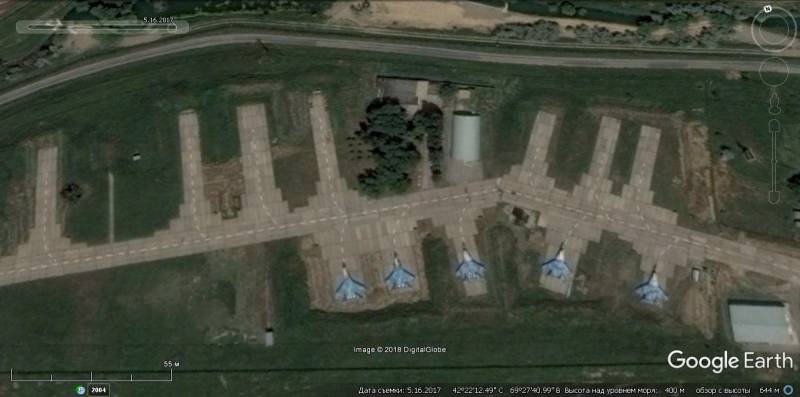
S-75М3 - СНР-75 guidance station during exercises at the Saryshagan training ground in August 2017
It is reliably known that combat duty is carried by a maximum of three anti-aircraft divisions, and several more SAMs are in storage. At present, the C-75 family of complexes no longer meet modern requirements in terms of immunity and the possibility of hitting actively maneuvering targets. In addition, they are not able to fight with low-altitude cruise missiles.

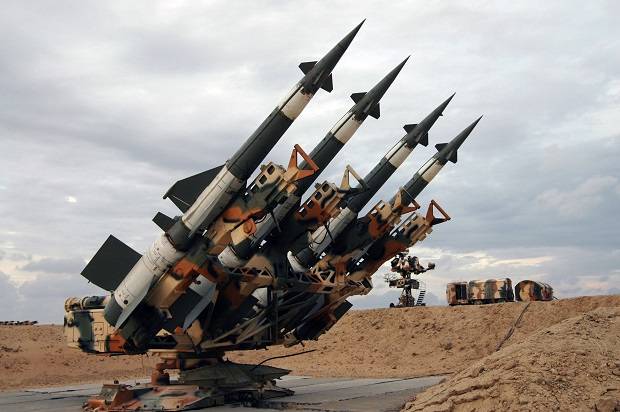
As part of the C-75, the missiles are fueled by liquid fuel and caustic inflammable inflammable substances. During combat duty, at a certain time interval, the missile defense system is removed from launchers and sent for maintenance with a drain of fuel and oxidizer. And the launchers charge ready-to-use rockets, prepared in the technical division. Due to all these circumstances, the combat value of the C-75 in modern conditions is not great.
Due to the costly and time-consuming process of preparing missiles, the main part of the states where C-75 existed in the past has already been abandoned. However, Kazakhstan is an exception, and satellite images clearly show that all launchers in divisions that are in combat duty are charged. Even taking into account the huge stock of spare parts, we should expect that the Kazakh military in the next few years will completely abandon the "seventy-fivefold". An indirect confirmation of this is the transfer of the existing C-75М3 air defense systems to Kyrgyzstan, despite the fact that Kazakhstan itself receives second-hand C-300PS airplanes from Russia.
In addition to medium-range and long-range systems with liquid missiles, the air defense forces of Kazakhstan have 18 upgraded in Belarus the C-125-2ТMS Pechora-2ТМ. Simultaneously with the restoration, the enterprise NPO Tetrahedr was able to significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of low-altitude complexes. After modernization, it became possible to fight with modern and promising means of air attack in a complex jamming environment. In exceptional cases, the air defense system can be used to destroy the observed ground and surface targets.

Troop mobile complexes "Circle" and "Cube" were also involved in combat duty. So, the Krug air defense system covered the Ayaguz military airfield in the East Kazakhstan region until 2014. The “Kub” air defense system was deployed in the vicinity of the Zhetygen military airfield in the Ili district of the Almaty region of Kazakhstan until the middle of 2016.
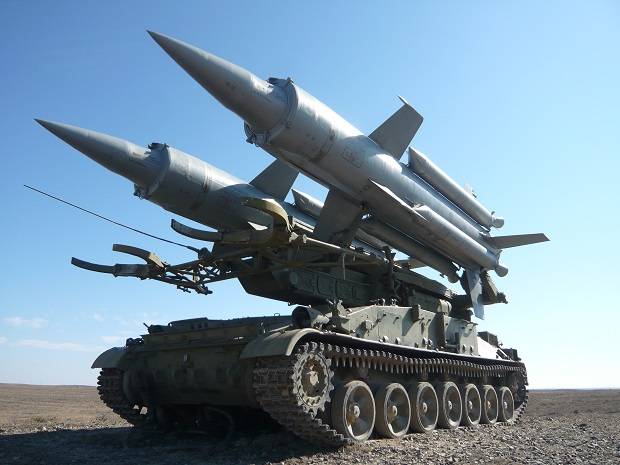

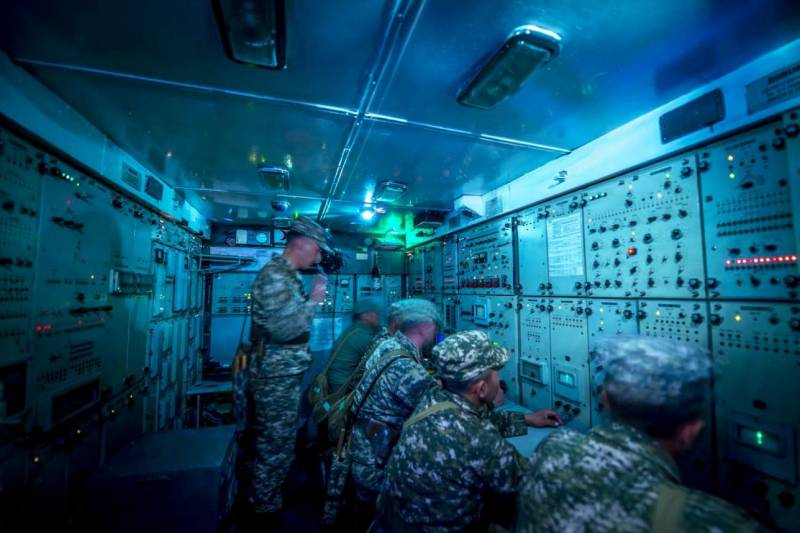
At present, due to the limiting wear of the hardware and the lack of standard anti-aircraft missiles, Kazakhstan’s Kub and Krug air defense missile systems are not brought into combat duty. However, according to information published on the “First Law Enforcement Website of the Republic of Kazakhstan”, the Krug air defense system participated in the second stage of the military combat drills held at the Saryshagan training ground in August 2017.
Although the Air Defense Forces of the Republic of Kazakhstan have a significant number of first-generation air defense systems, the C-300PS multi-channel long-range air defense systems are of the greatest combat value. According to open sources, with the division of Soviet military property, Kazakhstan received only one fully equipped C-300PS division. However, elements of the C-300P anti-aircraft systems were also present at the test sites where test and control-training shots were conducted.
To maintain anti-aircraft systems in working condition, the C-300PS division kit at the beginning of the 21 century underwent a refurbishment in Ukraine. However, due to the lack of standard anti-aircraft missiles 5В55Р combat duty was carried out in an abbreviated form, and 2-4 launchers were often in positions.
At the end of the 90-x repair and small modernization "three hundred" established at the Kazakhstan enterprise SKTB "Granit". The industrial and technical enterprise Granit was established in Almaty by a decree of the Council of Ministers of the USSR back in 1976. Until 1992, the enterprise granite "Granit" was the leading organization providing installation, configuration, docking, state testing and maintenance of experimental and ground test samples of electronic missile defense systems and missile attack warning systems at the Saryshagan test site. And also participated in the testing of long-range missiles C-300PT / PS / PM.
In 2015, the 5 anti-aircraft divisions C-300PS were deployed in positions in Kazakhstan. There was also a certain amount of equipment that needed to be repaired and modernized and located in warehouses. In the first place, this applied to radar facilities and equipment for controlling the battalion. We must pay tribute to the Kazakh leadership, which was not idle, and initiated the development of repair and small modernization in their own enterprises.
Satellite image of Earth Earth: elements of a C-300PS air defense system at the Granit production site in the village of Burunday
Approximately 6 years ago, in the vicinity of Almaty, the construction of workshops began, where the restoration of anti-aircraft systems built in the USSR should be carried out. 28 December 2017, a service center for the repair of anti-aircraft missile systems С-300П was solemnly opened in the suburban Almaty village of Burundai. Although the manufacturer is usually engaged in technical support of air defense systems, in relation to C-300PS, this is the Russian defense concern Almaz-Antey, the Kazakh side managed to obtain such powers. The service center of the air defense systems was created on the basis of a special design and technology bureau “Granit”. At the same time, the Russian side provided Kazakhstan with a technical documentation package for C-300PS, without the right to transfer it to third countries.
In 2015, it became known that the five C-300PS divisions, the command complexes of the 170 system, the 5В55РМ system, which had previously been at the storage bases of the Russian Federation Aviation Administration, were donated to Kazakhstan. As of the beginning of 2018 of the year, two divisional sets and one KPS were restored in the service center of SKTB “Granit”, and they were already on combat duty. Three more C-300PS SAMs are waiting for their turn. Armenia expressed interest in repairing its C-300PT / PS at SKTB Granit enterprise. The Kazakhstani side expressed readiness to accept Russian anti-aircraft missile systems for repair in the future.
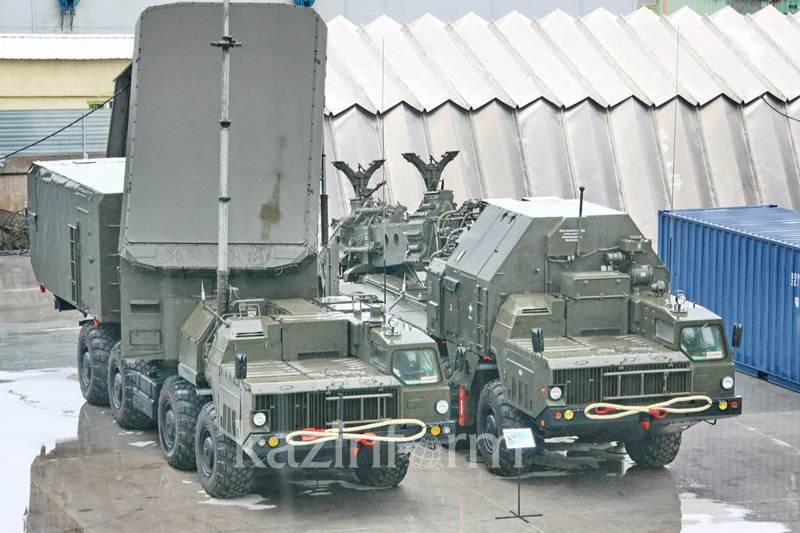

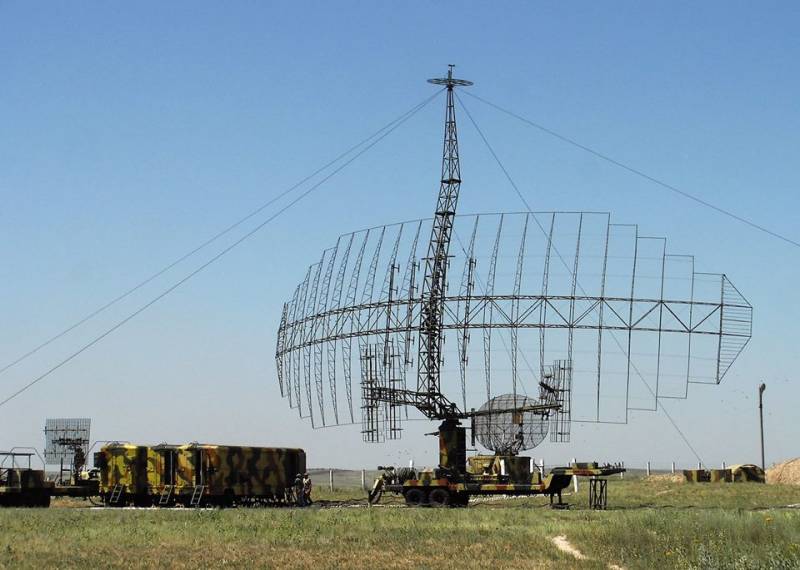
Due to the fact that tests of various air defense systems and systems were conducted at the sites of the Kazakh SSR, after the collapse of the USSR, many newer samples of radar technology remained in the republic, including the radar: Periscope-V, 5D75 (CT-35UM) and 6Ж68М Desna-M. However, having remained without technical support, the newest stations soon for the most part were out of order and now the monitoring of the republic’s airspace is carried out by quite old radars P-22, P-6, 18Н19, P-5, 84Н37. The failure to meet modern requirements for reliability and immunity criteria, lack of spare parts and physical wear and tear forced Kazakhstan to begin work on upgrading Soviet radar standby 5H59 (Defense-5) and П-84М (Terek) to 14Н18М and П-5М. Specialists SKTB "Granit" created a modernized version of the radar with the transfer of hardware to the modern element base. As of December, 84 was upgraded to more 18 radars.
More than half of the restored and upgraded stations are the P-18 radar of the meter range, upgraded to the P-18М level. After transferring from an electrovacuum elemental base to a solid state, the information update rate increased by 10%, the detection range increased, the time between failures increased, ease of operation was provided with diagnostic automation, and the operational life was extended by 12 years.
Simultaneously with the repair and restoration of Soviet-made radars in Kazakhstan, efforts were being made to gain access to a new generation of radar equipment. At the beginning of the 21 century, Kazakhstani representatives at the arms and military equipment exhibitions showed great interest in the latest foreign-made mobile radars and were actively searching for possible partners who could share technology. Negotiations on the possibility of co-production of the radar were conducted with Israel, Spain, France, Russia and the United States. Initially, Kazakhstani specialists tended to acquire Spanish locators from Indra Sistemas. But since there were difficulties in linking the Spanish radar with the equipment for determining nationality created at SKTB Granit, this option was not considered further. In 2013, the contract was concluded with the French company Thales Group. The agreement provided for the establishment of a joint production of the Ground Master 400 (GM400) radar, which has a phased antenna array and is able to work effectively in radio electronic conditions.
In May, a memorandum of understanding was signed with representatives of Thales Raytheon Systems at the exhibition of defense products KADEX-2014 in Astana, the capital of Kazakhstan, Astana, which provided for the supply of 2014 radars. For the assembly of French radars in Kazakhstan, a joint venture Granit - Thales Electronics was established with the participation of Thales and Granit Design and Technology Library. In 20, the first station assembled in Kazakhstan was transferred to the radio engineering unit near Astana. The radar is capable of measuring the height, range and azimuth of an air target. One such system replaces the standby radar and the radio altimeter, which are individually capable of determining the range and azimuth or altitude and azimuth.
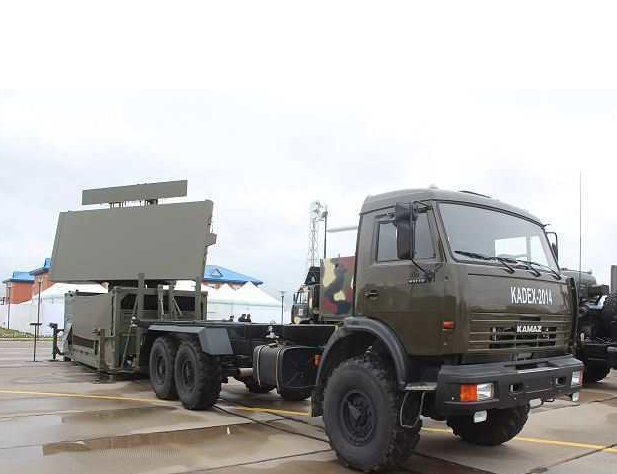

In 2015, after trial operation, the Kazakh radio engineering units of the three-centimeter “NUR” (GM 403) three-coordinate radar station were officially put into service, which was designed on a modern element base. At present, there are two stations in the North-West Military District of Kazakhstan - near Karaganda in Sarani and near Astana in Malinovka. In 2018, the Kazakh military should receive three more stations.
According to the information sounded by the general director of SKTB Granit LLP, the GM 403 radar, installed on the KAMAZ chassis, has a detection range of large high-altitude targets to km 450. The radar is able to work autonomously, without human intervention, and to track airborne targets in the coverage zone around the clock. After processing the information, the finished packet is transmitted to the central command post of the air defense. Currently, the level of localization in the assembly of the radar "NUR" in Kazakhstan reaches 28%. The radar system of the NATO standard is integrated by a ground interrogator developed by specialists from the Special Design and Technological Complex Granit. At the same time, it was allegedly possible to coordinate the codes received from the French with the system for determining the nationality of the Password. At present, the need for an SVO of Kazakhstan is estimated at 40 Nur radar. Also, the Republic of Belarus and Azerbaijan showed interest in radars of this type.
Among the CSTO countries, the Republic of Kazakhstan ranks second after Russia in terms of the number of fighter aviation fleets, the number of deployed anti-aircraft missile divisions and radar posts. The air situation is monitored by more than 40 radar stations, which are mainly equipped with Soviet-made modernized radars. This makes it possible for radio engineering units to form a radar field over the entire territory of the republic, which, of course, is possible only if the radars, which have a service life of about 30 years, have been working for some time. At the same time, experts in the field of radiolocation rightly point out that Soviet-made stations: P-18, P-37 and 5H84, which are mainly equipped with RTV Air Defense Forces of Kazakhstan, are unable to reliably detect air targets flying at a height of less than 200 m , and low-altitude P-19 radars in Kazakhstan are few and they are close to the full development of the operational resource.
At the moment, according to Kazakh sources, the NWO has 20 srdn, of which only half are armed with relatively modern C-300PS. The others are С-200ВМ, С-125-2ТМ and С-75М3. Taking into account the size of the territory of Kazakhstan, the republic’s air defense system has a pronounced focal character, and it is absolutely unrealistic to fight off the available forces from a full-scale aggression from a technologically strong enemy, which has numerous and modern means of air attack. In addition, not all Kazakhstani anti-aircraft missile divisions are combat-capable, approximately 4-5 equipment requires repair and modernization, and therefore does not carry a permanent combat duty.
Since January, 2013, between Russia and Kazakhstan, in the framework of the Agreement on the creation of a Unified Regional Air Defense System, has been a fairly close and mutually beneficial cooperation. Kazakhstan is an active member of the CSTO, it has one of the longest external borders in Eurasia and extensive airspace, which is actively used in different strategic directions. There is a close exchange of information about the air situation in the Central Asian region between our countries and the Central Command Point of the North-Eastern Military District of Kazakhstan has a multi-channel connection with the Central Command Point of the air defense of the Aerospace Forces of Russia. But, as in the case of the Republic of Belarus, the overall control of its own air defense forces is subordinate to the national command, and the decision on the use of fire weapons is made by the military-political leadership of Kazakhstan.
The two other Central Asian republics - Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, also formally part of the United Air Defense System of the CIS, do not possess any significant forces capable of posing a threat to the means of air attack of a potential aggressor. During the stay of the Soviet Union, the 145-th Guards anti-aircraft missile brigade, which was part of the 33-th air defense division, ensured air defense of the objects on the territory of Kyrgyzstan. In total, 8 C-75М2 / М3 and С-125М divisions were deployed along the border with Kazakhstan and in the vicinity of Frunze. In addition, military air defense systems Osa-AKM, Strela-10 and ZSU-23-4 were in the 8-th Guards Motorized Rifle Division and the 30-th separate motorized rifle regiment. Formed in May, the 1992 of the Kyrgyz armed forces also inherited several dozen MANPADS and anti-aircraft guns of the 23 caliber and 57-mm. Subsequently, 23-mm anti-aircraft installations ZU-23 and 57-mm anti-aircraft guns C-60 were used against the militants of the Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan who invaded the country. During the fighting in the highlands, the 57-mm anti-aircraft guns mounted on the tracked tractor showed themselves very well. A large elevation angle and a high initial velocity, combined with a fairly powerful fragmentation action of the projectile, made it possible to conduct effective fire on targets located on mountain slopes at a distance of several thousand meters.
After independence, all MiG-21 322 training regiment departed Kyrgyzstan, where, in addition to training cadets at the Frunze Military Aviation School, military pilots from USSR-friendly developing countries were trained. In total, the republic got about 70 single combat and double training fighter jets.

Part of the aircraft in 90-e was sold abroad, the rest because of the lack of proper care quickly decayed and became unsuitable for flight. In independent Kyrgyzstan, there were no financial resources to maintain even very easy-to-operate MiG-21 in flight condition. The remaining three dozen of the MiG-21 until 2014 were “stored” at the Kant airbase. At present, almost all Kyrgyz MiGs have been “utilized”, several aircraft have been preserved as monuments.
However, the air defense system of Kyrgyzstan was not completely degraded. Thanks to the Russian and Kazakhstani support in the republic, there is a relatively combat-ready state: one C-75М3 and two C-125М1. The transfer of the C-75М3, anti-aircraft missiles and spare parts from the armed forces of the Republic of Kazakhstan took place relatively recently.
As of 2017, two C-125М1 divisions and one C-75М3 divisions were deployed in the vicinity of Bishkek. There are six radar stations on the territory of Kyrgyzstan where the P-18 and P-37 radar are operated. The most modern radar 36Д6 and 22Ж6 are operated by the Russian military at Kant airbase.
Kant Air Base is located in 20 km east of Bishkek. The agreement on the creation of the Russian 999 air base in Kyrgyzstan was concluded in September 2003. Currently, a dozen and a half Russian attack aircraft Su-25 and combat training L-39 are based on the airbase. As well as military transport An-26, IL-76 and Mi-8 helicopters. The reconstruction of the air base is scheduled for the near future, after which fighter-interceptors can be deployed here, if necessary.
Historically, when the division of the Soviet military legacy, the armed forces of Tajikistan practically did not get the equipment and weapons of the air defense forces. The civil war that began in the republic at the beginning of 90, led to the collapse of the airspace control and air traffic control system. To create a radar field over the territory of Tajikistan in the second half of 90, Russia donated several P-18, P-37, 5Н84А and 36Д6 radars, which are still used to monitor the air situation and control the movement of aircraft. Also, within the framework of military assistance, one C-75М3 and two C-125М1 were delivered. Three anti-missile battalions became part of the 536-g anti-missile regiment of the armed forces of Tajikistan. However, the Tajik military was unable to maintain the C-75М3 SAM systems with liquid-propelled missiles in working condition, and this complex was written off at the beginning of the 21 century. At present, two C-125М1 and Pechora-2М divisions are deployed in the vicinity of Dushanbe. The transfer of the modernized Pechora-2М complex to the armed forces of Tajikistan took place in the 2009 year.
All radar posts in the republic are located near the Tajik capital. Thus, the southern districts of the republic are very poorly controlled due to the mountainous nature of the terrain. Currently in Tajikistan there are no combat aircraft of their own capable of intercepting air targets and patrolling air borders. In addition to the C-125, the Tajik army has a number of ZU-23 anti-aircraft guns and MANPADS. Of course, the combat value of the Kyrgyz and Tajik air defense systems is not great. The radars operating in Central Asia are much more important, provided they are included in the unified data exchange system of the CIS air defense system. Of considerable value on the territory of the Central Asian republics are the remaining runways, to which, if necessary, Russian combat aircraft can be deployed.
In 2004, in Tajikistan, on the basis of the 201 th motorized rifle Gatchina twice Red Banner division, the 201 th Russian military base was formed (the official name is the 201 th Gatchina Order of Zhukov twice Red Banner military base). Russian troops stationed in the cities of Dushanbe and Kurgan-Tyube. Air defense groups of the Russian troops in Tajikistan are provided by short-range military mobile complexes: 12 Osa-AKM, 6 Strela-10 and 6 ZSU ZSU-23-4 Shilka. Also at the disposal of the Russian military are towed anti-aircraft installations ZU-23 and MANPADS "Igla".
According to a number of sources, in 130 kilometers southeast of Dushanbe is the Indian military air base, Parhar, located near the city of Farkhor. This is the first and only air base of the Indian Air Force outside its own territory. India has invested about $ 70 million in rebuilding aerodrome infrastructure. Currently, information relating to the functioning of the air base is classified, and the Tajik authorities in the past have generally denied the presence of an Indian facility on its territory. According to some reports, Mi-17 helicopters, Kiran training aircraft and MiG-29 fighter jets are located on the base. Radar stations must be available to support flights at an aerodrome, but it is unclear whether data is provided from the Tajik and Russian military.
Of the former Soviet republics in the Transcaucasus, only Armenia is a member of the CSTO. The defense capacity of Armenia, which has unresolved territorial disputes with Azerbaijan and difficult relations with Turkey, directly depends on military cooperation with Russia. Of all the post-Soviet states that are members of the United Air Defense System, Armenia is the most integrated with the armed forces of Russia. In the past, our country handed over to Armenia at least six C-300PT / PS systems, as well as a significant number of medium-range air defense systems: C-75, C-125, Krug, Cube and Buk-M2. The sky protection of the friendly republic is also conducted by the Russian C-300В missiles at the base in Gyumri and MiG-29 in Erebuni. I will not describe Russian-Armenian cooperation in the field of air defense in detail, since in mid-February there was already a publication on this topic. More information about the state of the air defense of Armenia can be found here: The current state of the air defense system of Armenia.
However, it can be noted that at the moment there is no own fighter aircraft in Armenia, and the republic cannot maintain the armament-based anti-aircraft systems and complexes in working condition, and in this respect is completely dependent on Russia. For our country, friendly relations with Armenia are of very important defense importance. It is no coincidence that quite modern radar stations have been deployed in this Transcaucasian republic: 22Ж6М, 36Д6, Heaven-SV and Periscope-VM, information from which is sent to the air defense command post of the air defense forces of Russia.
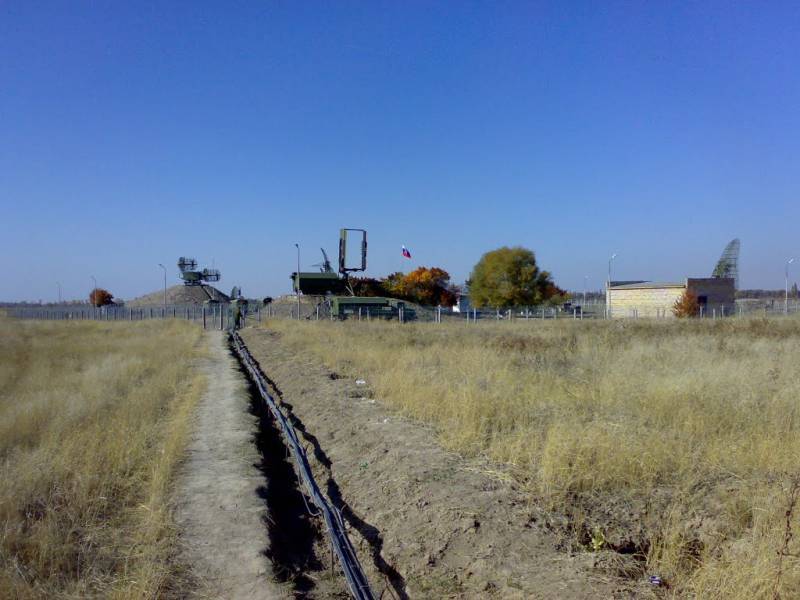

At present, the declared tasks of the unified air defense system are reduced to the protection of the air borders of the commonwealth, joint control over the use of air space, notification of the aerospace situation, warning of a rocket attack and coordinated repulse of this attack. According to open source data, the air defense system of the CIS includes 20 fighter regiments, 29 anti-aircraft missile regiments, 22 radio engineering units and 2 electronic warfare battalion. It is clear that approximately 90% of these forces are Russian aviation, anti-aircraft missile and radio parts. Although the capabilities of the air defense systems of most of the CSTO countries are relatively small, in the case of timely notification from radar stations located outside our country, the Russian Aerospace Forces receive a reserve of time to prepare for repelling the attack. In the case of aggressive actions against Russia, we can hope that our partners, included in the CIS air defense system, will provide all possible assistance, and the funds invested in maintaining the defense capability of friendly states will not be wasted.
Based on:
https://informburo.kz/stati/su-27-v-kazahstane-vzlyoty-i-padeniya.html
https://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/centralasia/kazak-airforce.htm
https://defence.ru/article/kazakhstanskie-mig-31-v-ozhidanii-modernizacii/
https://lenta.ru/news/2010/06/29/su27ubm2/
http://news.ivest.kz/60993447-iz-granita-v-kazahstane-smasterili-pervyy-otechestvennyy-radiolokator
https://informburo.kz/stati/vooruzhyonnye-sily-kazahstana-itogi-2017-goda.html
https://informburo.kz/stati/kak-v-kazahstane-remontiruyut-s-300.html
https://patrul.kz/novost/v-kazahstane-startoval-2-j-etap-uchenij-sil-pvo
https://www.facebook.com/sarbaz.kz/posts/584629631679522
http://www.lenta.inform.kz/ru/zavod-po-vypusku-voennoy-tehniki-otkryli-v-almatinskoy-oblasti_a3021849
http://www.ca-portal.ru/article:702





















Information