Troops Smoke and Flame. Part of 1. Flame of the German Bloc
As we noted earlier, the pioneer units of the German Empire entered the war, having flamethrowing subunits in their composition — platoons of flamethrowers. The fact of using flamethrowers was allegedly established during the burning of the Belgian town of Louvain in August 1914.
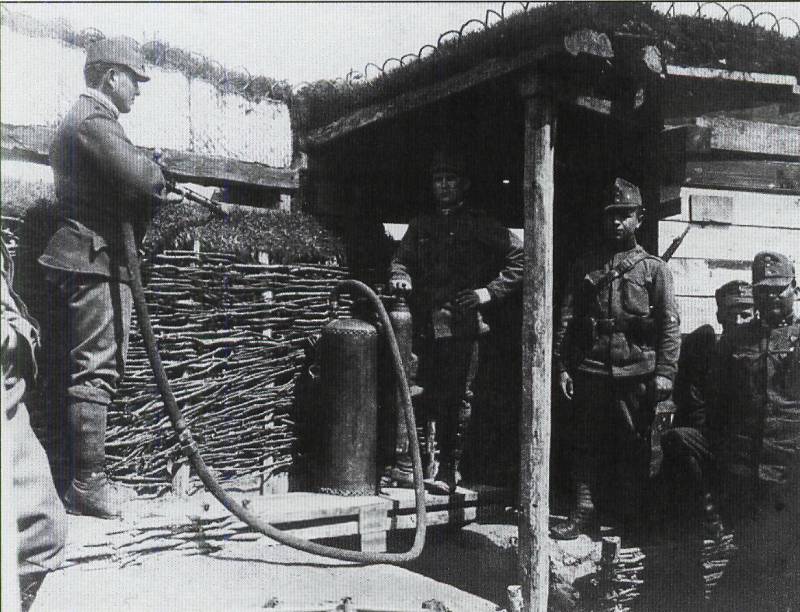
1. Non-commissioned officer of the German pioneer units, August 1914. Armed with a Kleif flamethrower arr. 1912 g. Austrian flamethrowers armed with “Gluefs” were equipped with similar masks to protect the face. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops of World War I., 2010
2. "Grof" arr. 1912 g. - a trophy of British troops. Photos in the same place
At the beginning of October, the use of flamethrowers took place in Argonnach - the 4 squadron of the 29 pioneer battalion supported the 27 division. Immediately after this battle, the commander of the 2 th company of this battalion, Captain B. Reddeman, left for Berlin to seek the creation of special flame-throwing units.
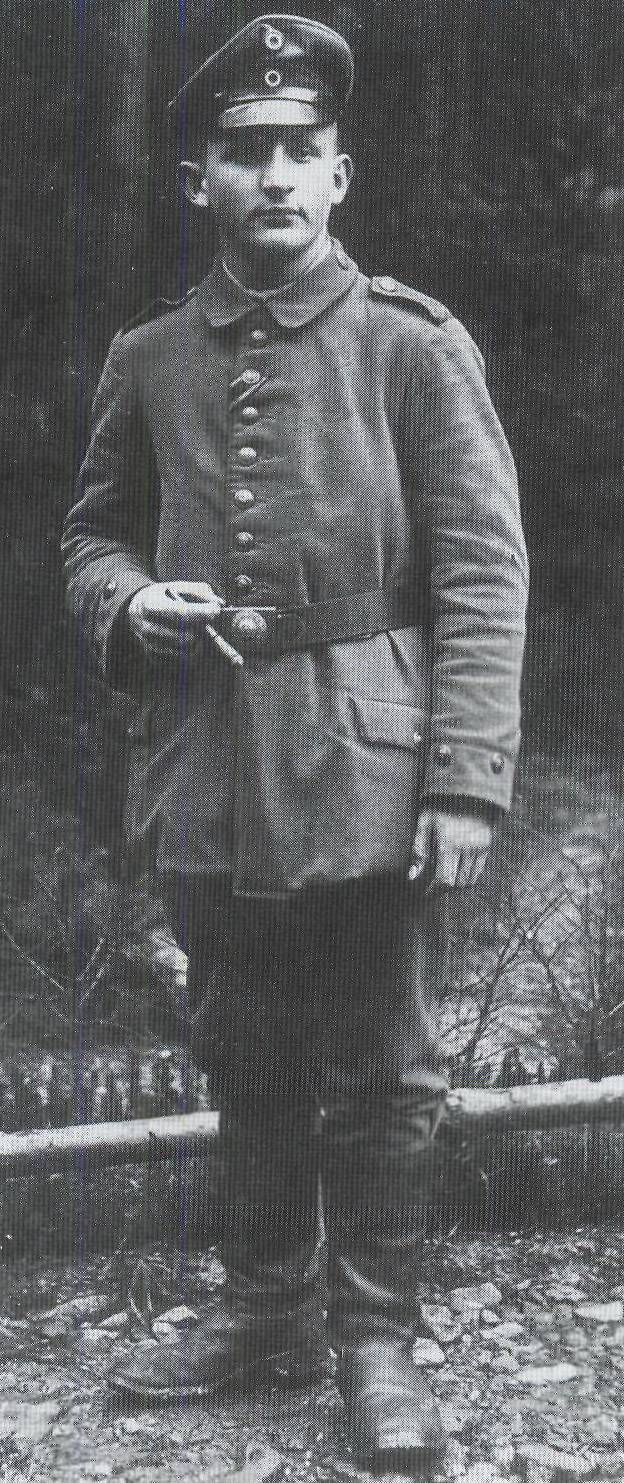

3. The corporal of the 4 Company of the 29 Pioneer Battalion, the unit that used flamethrowers for the first time in combat. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
At the end of 1914, flamethrowers are seized from pioneer units (although some have been retained using them in the campaign of the next year). It was decided to create special flamethrower parts. The Guards Pioneer Volunteer Battalion (then the 3 Guards Pioneer Battalion and the Guards Reserve Pioneer Regiment) became the first and most distinguished of them.
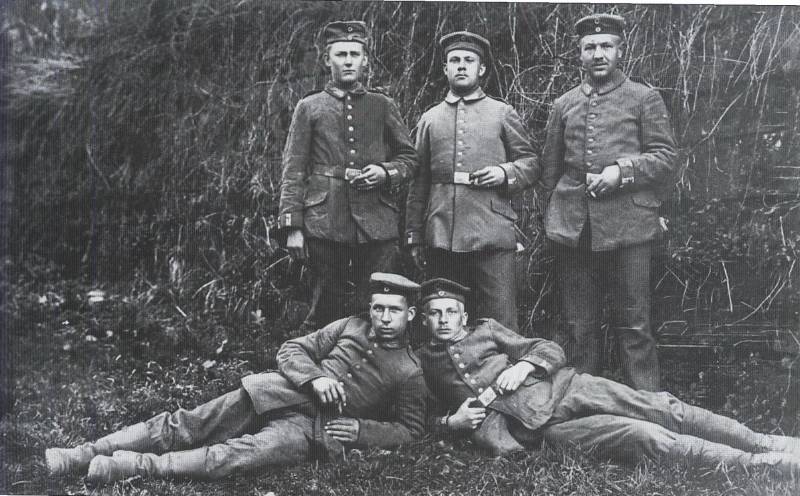
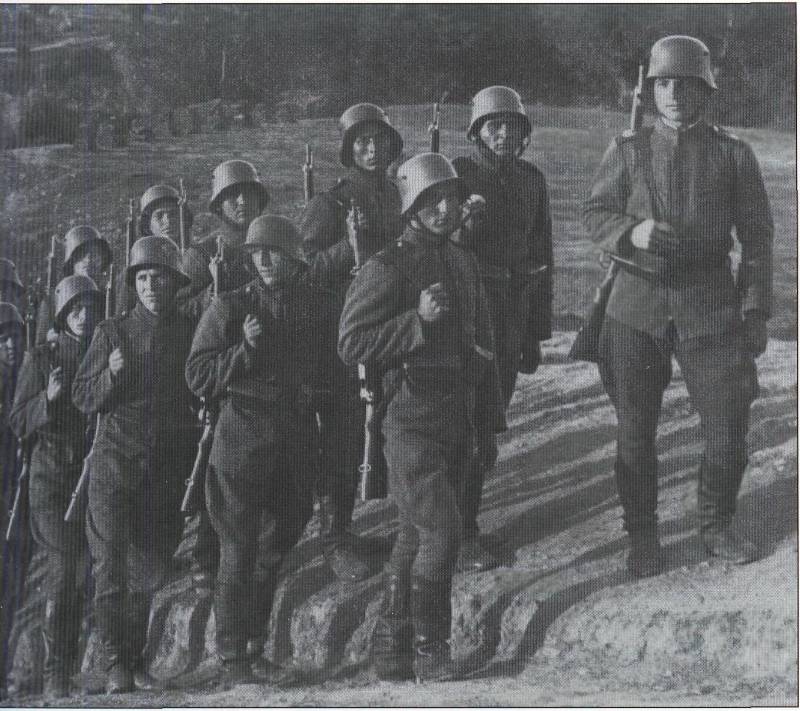
4. Volunteers of the Guards Pioneer Volunteer Battalion (“Reddeman Flamethrower Unit”), October 1914. In the first part of the unit there were many former firefighters (48 people). Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
The official date of birth of the unit is 18, January 1915 (although the formation took place in the fall of 1914). The battalion was attached to the 5 Army and distinguished itself in February during the battle of Malankour, near Verdun. In March, the Guards Pioneer Volunteer Battalion becomes the 3-m Guards - in its composition there were 800 people.
5. Fighters 3-th Guards Pioneer Battalion. March 1915. Photo from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
When German divisions began to form assault units in 1915 in May, flamethrower units appear in their composition.
May 22 fighters B. Reddeman had a chance to distinguish themselves near Neville. But the pioneers suffered serious losses.
July 30 held the first attack of flamethrowers on the British sector of the French front: 9-I company of the 3-th Guards Pioneer Battalion successfully applied the 9 "Grofov" and 11 "Cleife. The British were knocked out of their positions.
And 9 September 9-I and 10-I companies successfully attacked the French.
In total, during the 1915 campaign, the 3 th Guards Pioneer Battalion conducted 32 flamethrower attacks: in Pristerwald, in the Vosges, near Metz, in the Argonnes, in Flanders and Champagne.
At the beginning of 1916, in preparation for the Verdun operation, the battalion was tasked to provide each of the 6 shock divisions with a flamethrower company. The composition of the battalion was strengthened.
We have written earlier about the structure of the flamethrowing units of the Kaiser army. We add that for the Verdun battles, shock assault groups were formed that included infantrymen 16-20 (shooters and grenade throwers), a unit for the destruction of enemy barriers and a detachment of flamethrowers. A total of 372 "Kleif" was involved.
In February, the 1916 was created by the 4-th Guards Pioneer Battalion (initially - a two-year composition).
Between February 21 and 27, 10 flamethrower companies armed with 400 flamethrowers launched 57 attacks - of which 33 were successful.
February 25 was formed 2-th Guards Reserve Pioneer Battalion. On March 11, its flamethrowing units joined the assault battalion of Rohr, and then replenished the 3 and 4 th Guards pioneer battalions.
20 April The 3 and 4 th Guards pioneer battalions were merged into the Guards reserve pioneer regiment (initially there were 11-company squadrons; each field company consisted of three platoons; a company of 200 men).
2 - 5 June during the storming of the fort In the Germans widely used flamethrowers. So, 4 June 8-I company of the Guards reserve pioneer regiment destroyed the centers of resistance of the French in concrete tunnels. Four flamethrowers were destroyed by French artillery on the approach to the fort.
The Kleif 3 stormed the barricade in the western tunnel of the fort, while the shock troops from the 27 pioneer battalion and the 39 infantry regiment, supported by the 3 Cleves, attacked the French through the eastern tunnel. Flamethrowers climbed the concrete stairs - and landed under the downpour of French hand grenades. The French reported the destruction of flamethrowers and the capture of flamethrowers.
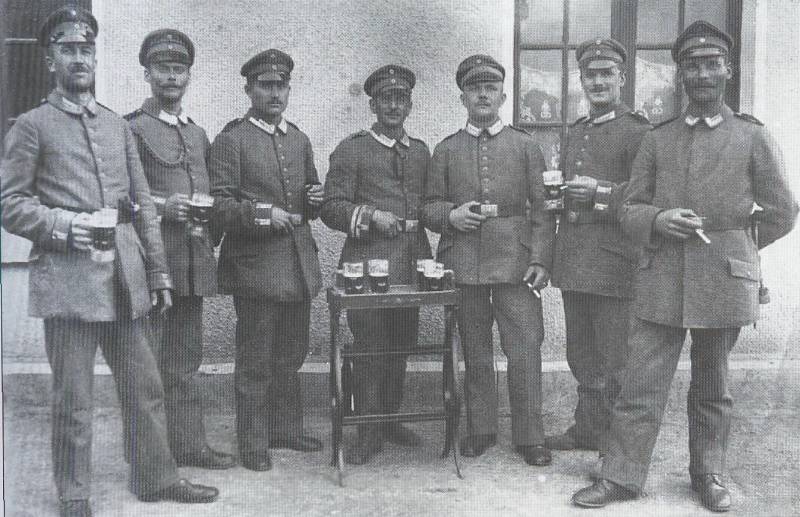
6. The ranks of the 6 Company of the Guards Reserve Pioneer Regiment. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
In July, 1916, during the battle of the Somme, the Germans used flamethrowers during defensive battles. In total, during the 1916 campaign, (on 19 February, 1917), the 8 Company of the Guards Reserve Pioneer Regiment conducted an 44 battle.
The flamethrowers of their flamethrower platoons were actively used by the Eger battalion No. 3 (Brandenburg Eger or Eger assault battalion No. 3) and the assault battalion No. 5 (Rohr).
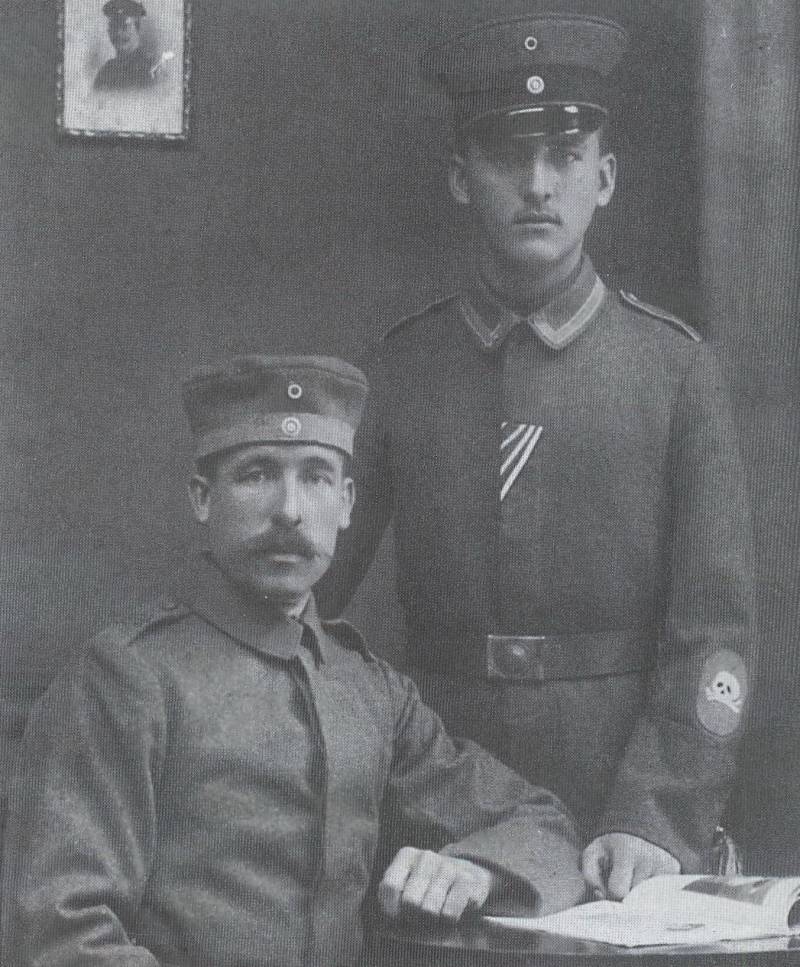
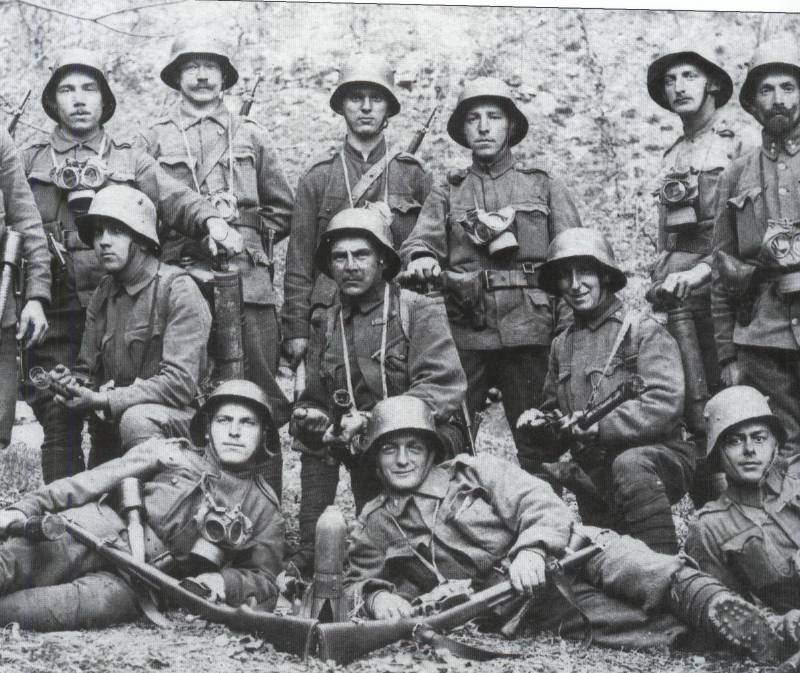
7. Fighters of the flamethrower platoon of the assault battalion No. 5 (Rohr). On the left sleeve of the standing non-commissioned officer - emblem flamethrower. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
When the 23 of October was followed by an order from the High Command to form an assault battalion in each army, the Guards Reserve Pioneer Regiment allocated for each of them a flamethrower platoon.
November 9 (October 27 old style) Germans used 4 flamethrower companies (24 Grof and 216 Cleves), supported by 6 infantry battalions, during the attack at Skrobov (see Lights at Skrobova).
Trophy of Russian troops. Niva. 1916. No. 40.
In total, during the 1916 campaign, the Germans conducted 158 flamethrower attacks (of which 34 were successful).
3 April 1917. The 3 company of the Guards Reserve Pioneer Regiment participated in a successful operation for the Germans to liquidate the Rudk-Chervishchensky bridgehead (from Toboly village), and on June 29 of the same year, the flame-throwing squad of the 5 st assault battalion distinguished itself in the battle of the XMN battalion. Verdun. In July, units of the Guards Reserve Pioneer Regiment supported the Marines. And in August, flamethrowers waited for a fiasco during the battle with Canadians at the height of 304 - the latter managed to capture several Vexes as trophies.
8. Flamethrowers 5-th Assault Battalion. Armed with "Glue" arr. 1917. Photo from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
2 flamethrower platoon of the Germans fought in the fall on the Italian front.
From 1 January to 20 in March 1918, the Germans conducted 49 flamethrower attacks - mainly of an intelligence nature. But especially they had to distinguish themselves after the start of the Big Offensive.
9. Flamethrower platoon of the Bavarian Assault Battalion No. 1. April 1918 d. Armed with 2 "Vex" and 1 "Gluef". Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
During Operation Michael, the 42 shock division supported the 21 flamethrower platoon. Moreover, flamethrowers supported not only infantry, but also tankers - March 21 during the battle of Saint-Quentin.
In September, the Germans decide to return flamethrowers to all pioneer units again. But the war was over.
Only the Guards Reserve Pioneer Regiment made 653 attacks during the war (including 535 successful), losing about 900 people dead or dead. Flamethrower platoon assault battalion number 5 lost dead 14 people.
Austrian sapper units used both German-style flamethrowers and Fidler system flamethrowers (5 models) produced in accordance with the 1910 patent. Thus, at the beginning of 1915, the 50 Flammenwerfer was adopted. Flamethrowers (15 people; 12 large, 2 medium, or 4 small flamethrowers) were gradually assigned to a number of infantry and Tyrolean rifle regiments, chasseurs battalions and landwehr units.
The first use of weapons - June 23 - July 7 during the first battle on the river. Isonzo.
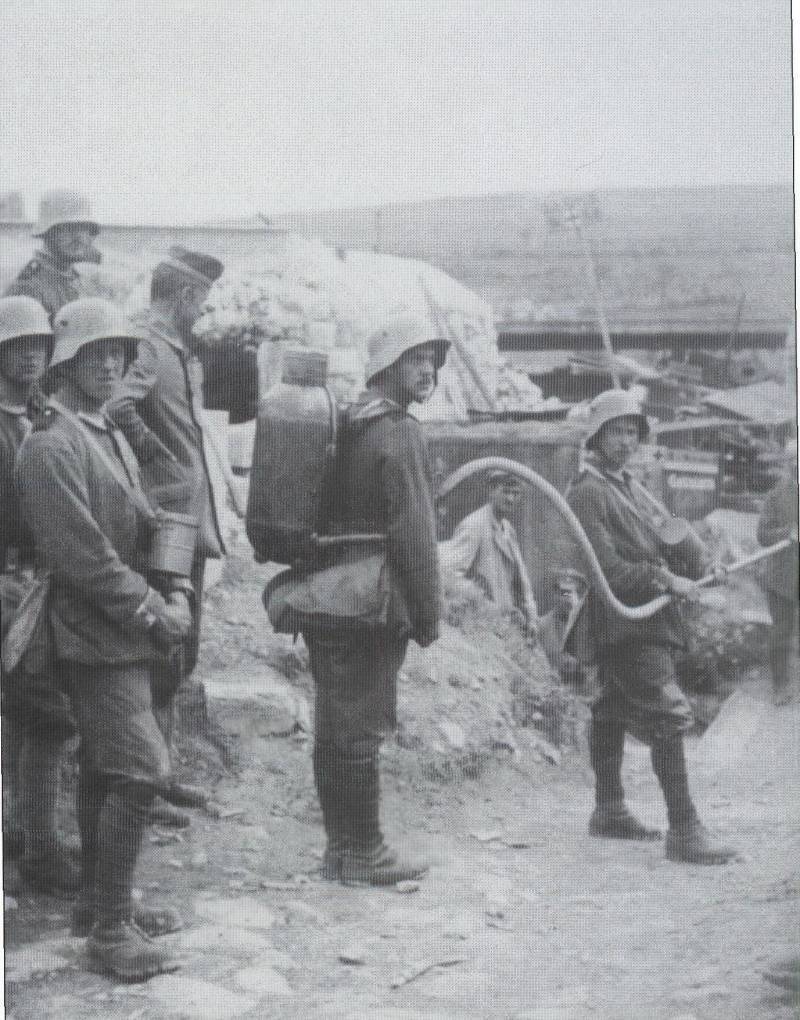
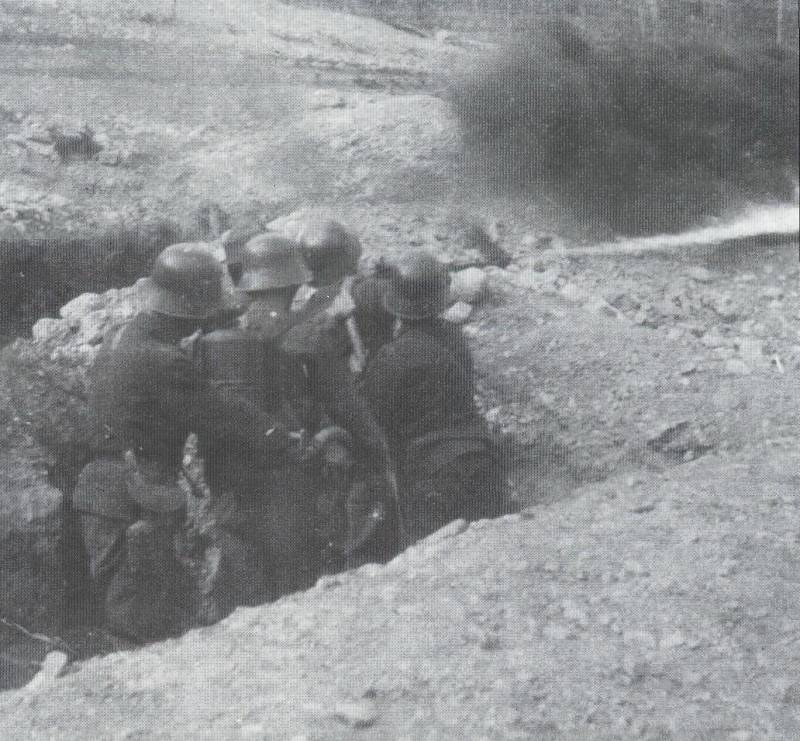
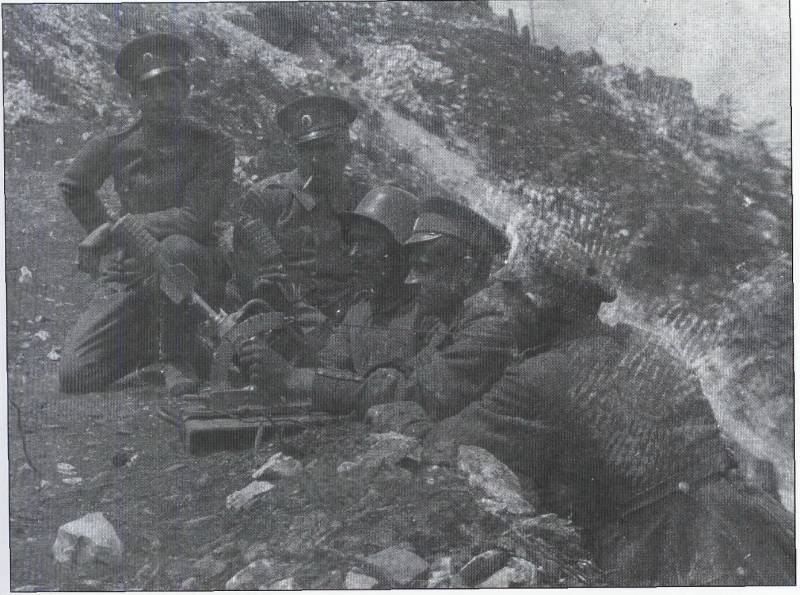
10. Calculation of a flamethrower 50L M. 15 Flammenwerfer. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
During this period, flamethrowers were used mainly as defensive weapons.
When assault units appeared in the Austrian army in November 1916, they included small flamethrower units. Appearing in February 1917, the assault battalions were equipped with flamethrower platoons from 6 flamethrowers.
In May 1917, flame-throwing companies appear - each of the 4-x platoons (for 64 man).
11. Flamethrower division of the Austrian assault battalion. 15 LM Flamethrower 16 Flammenwerfer. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
During the 1917 campaign, Austrian flamethrowers showed themselves in the June battles on the Italian front. And in September, the Special Engineer Battalion No. 61 appears, incorporating the 4 flamethrower companies. A new battalion distinguished himself at the Isonzo in October - November. The downside of the use of flamethrowers in these battles was the distribution of flamethrower units to infantry commanders - and the latter often did not really represent the specifics of using a new weapon.
12. Calculation of the Austrian flamethrower. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops

13. The emblem of the 2 Company of the Special Engineer Battalion No. 61. Fig. ibid
At the beginning of 1918, the companies of the Special Engineer Battalion No. 61 were assigned to the assault battalions: 1-i - 55-i (1-i army corps), 2-i-27-i (26-i army corps), 3-i-X 6-th (3-th Army Corps) and 4-th - 18-mu (6-th Army Corps). To crush companies without the permission of the High Command was forbidden. They were under the control of the corps commander, who could transfer them to various assault battalions as part of his corps. But this order did not touch the flamethrower platoons attached to the divisional assault battalions.
Four flamethrowing companies took part in hostilities, conducted demonstrations, tested new equipment, trained flamethrower platoons, and repaired their weapons.
In spring, the Special Engineer Battalion No. 61 was reorganized - now it had 48 kleine 151M. 16 Flammenwerfer and 20 mittlere 50 LM. 15 Flammenwerfer.
18 May Italians ripped off a large-scale Austrian flamethrower attack.
In the middle of the 1918, the Special Snapper Battalion No. 61 was renamed Special Assault Battalion No. 61. The current army also had 75 flamethrowing platoons attached to the divisional assault battalions.
In the course of the Battle of Piav, assault units, supported by flamethrowers, acted efficiently.
But after the failure of the June offensive, flamethrower units were no longer actively used.
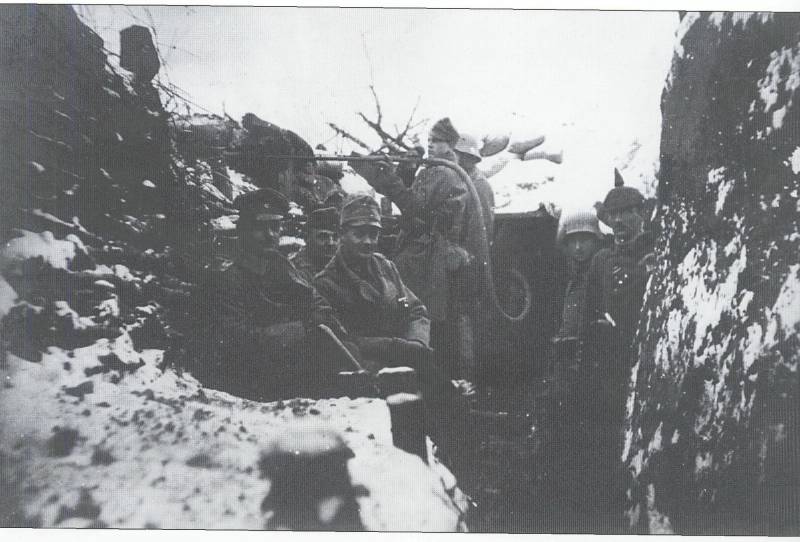
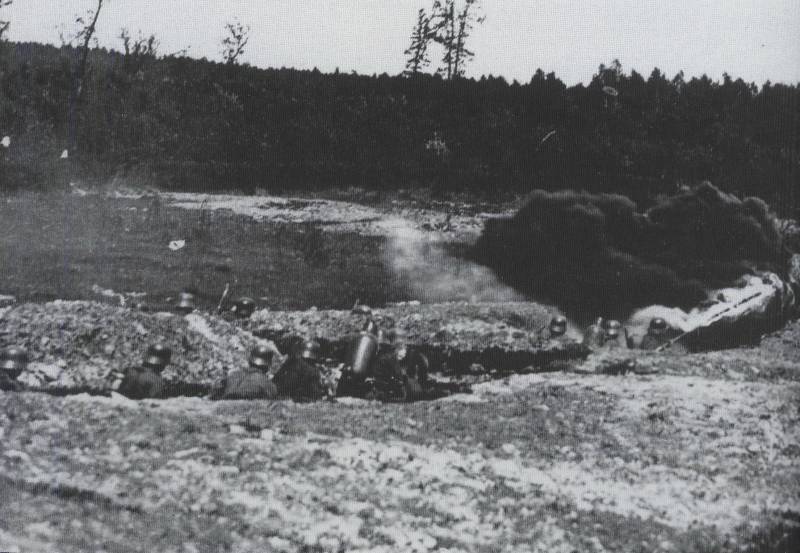
14. In the trenches. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
And what about flamethrowing weapons from the Balkan powers of the German bloc?
In the fall and winter of 1916, a group of German soldiers (from the Assault Battalion Rohr) trained Bulgarian colleagues. We studied the assault and technical issues - including skills in handling flamethrowing weapons.
The Bulgarian command wanted to have an assault battalion with each of its armies.
15. Pioneers of the assault battalion 1 Army. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
16. The emblem of the Bulgarian pioneer. Photos in the same place.
The assault battalion also included a flamethrower detachment armed with German-style flamethrowers ("Vex", "Kleif", "Grof" arr. 1917). The squad was commanded by a lieutenant under the command of a non-commissioned 4, non-combatant 34 and non-combatant 22. The department had 6 small ("Vex" or "Kleif") and 2 large ("Grof" lightweight sample) flamethrower.
The assault battalions were crushed, and did not participate in full combat.
18 May 1917 - the first use of flamethrowers in a battle with the French on the Thessaloniki front, at Baba Planina in Macedonia. The pioneers of the 1 st assault battalion excelled. The Bulgarians got the 261 prisoner in their hands - all that remained of the two regiments.
In December, the composition of the flamethrower units was changed and began to consist of 50 people.
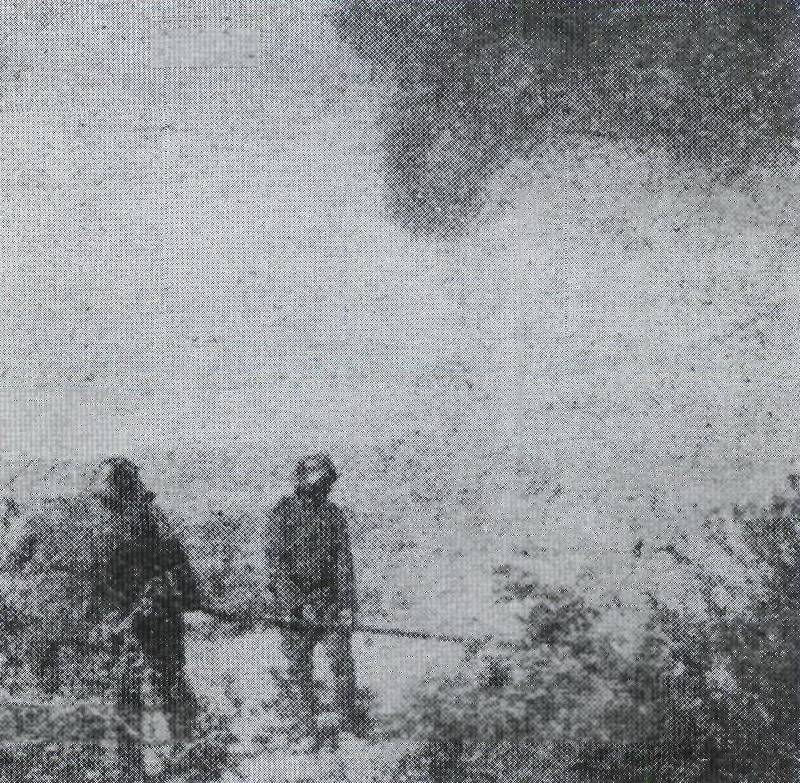

17. Bulgarian flamethrowers. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
In August, 1918 flamethrowers were reformed again. The flamethrower company of the assault battalion included 3 light and heavy flamethrowing units (120 people).
Flamethrowers also participated in the final battles on the Balkan front. So, on September 18, the British attacked a Bulgarian stronghold at the height of “Cerberus” - where the 3 Brigade flamethrower was located. When the flamethrower was preparing to open fire, the British units rushed to the attack and destroyed the flamethrower using hand grenades. The second flamethrower opposed the attack of the British - until a bullet hit his tank. In the September battles, the flamethrower company and the company of trench mortars of the assault battalion of the 1 Army lost 68 people.
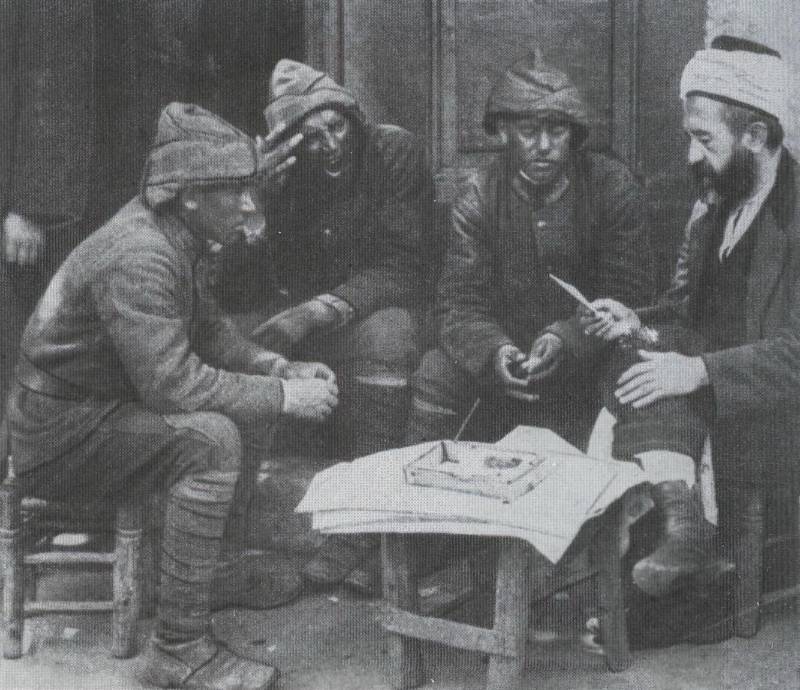
18. Bulgarian pioneers in Thessaloniki front. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
The German military mission that arrived in Turkey brought along with it several Kleif flame throwers arr. 1912
In 1915, German specialists prepared for the Turkish army a company of 200 men (6-8 flamethrowers) armed with the above flamethrowers. Turkish sappers trained in a special camp near Istanbul. The company then ended up in Iraq, but did not participate in the hostilities and was disbanded.
In 1916, the Turkish sappers from the 3-th and 20-th engineering battalions, the 15-th and 25-th engineering companies, in Bulgaria studied the basics of flamethrowing under the guidance of their German and Austrian colleagues.
19. Turkish flamethrowers. The end of spring is the summer of 1917. Training detachment near Rogatin. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
In January, 1917. The 15 Army Corps formed two divisional assault companies. The 7 th assault company of the 19 Infantry Division included the sappers of the 3 th company of the 3 th sapper battalion, armed with Kleif flamethrowers.
In June-July, the corps fought near Brzezani in Galicia.
In 1917, the Turkish Engineering Corps received an 4 flamethrower from the Germans.
In the spring of 1918, the 48-I Infantry Division tested flamethrowers at sites on the r. Jordan on the Palestinian front. But flamethrowers were not used in combat.
20. Sappers of the assault unit of the 48 Division. Photos from the book. Thomas Wictor Flamethrower Troops
In total, during the war, the Germans handed over to the Turks 30 flamethrowers - "Cleves" arr. 1912 and 1917
To be continued
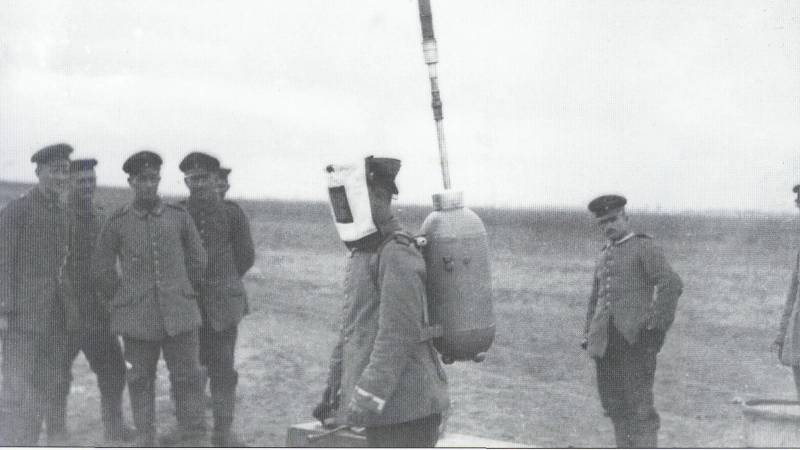
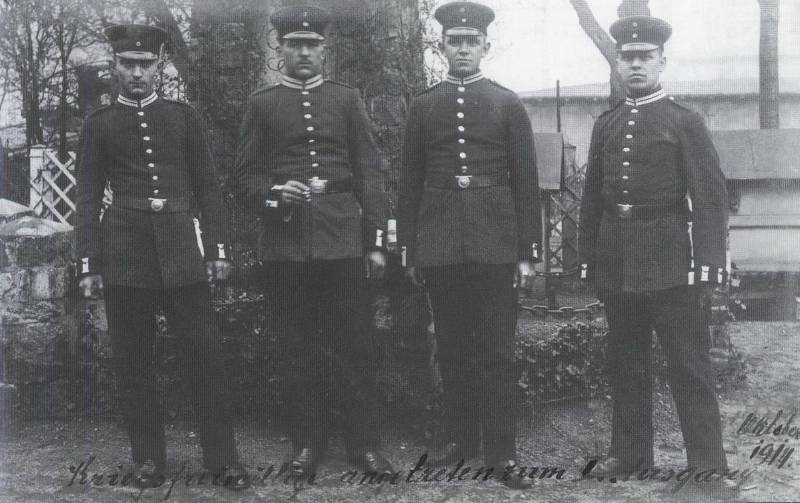

















Information