Wheel armored vehicles of the Second World War. Part of 14. Armored vehicles Humber (UK)
Humber is a fairly old British car brand. The company was founded by Thomas Humber, who gave it his name, back in 1868, and initially specialized in the production of bicycles. In 1898, she began producing cars, and in 1931, she was bought up by the Rootes Rootes group of companies. During the Second World War, the company specialized in the production of armored cars and vehicles for the transport of troops and cargo.
Humber Light Reconnaissance Car
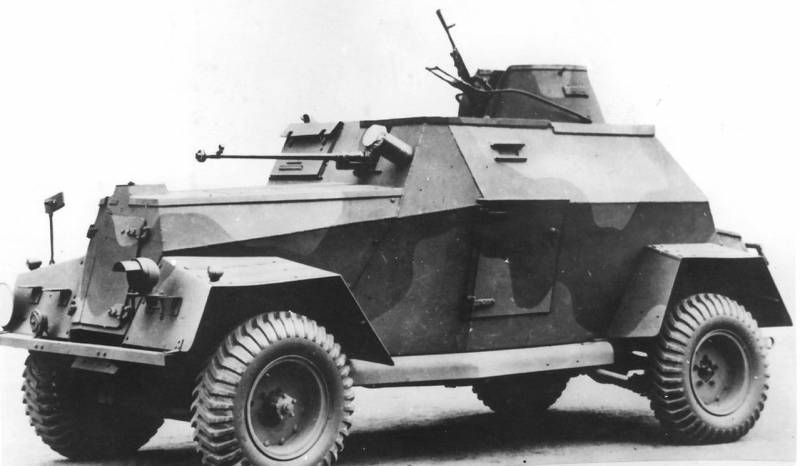
During the war years in the model range of armored vehicles under the brand Humber there was a place for two reconnaissance armored vehicles. In 1940, the company's engineers implemented a project to redesign the Humber Super Snipe production car into an armored car with the installation of the appropriate weapons and armor. The created combat vehicle received a rather tech-friendly and easy-to-manufacture body, the sheets of which were located at small angles of inclination. The booking thickness did not exceed 12 mm, however, small corners still increased the security of the car and its resistance to the effects of small caliber bullets. Initially, the armored car did not even have a roof; for this reason, the weapons, represented by the Bren machine gun and the Boys anti-tank rifle, were located right in the front hull plate. In addition, a smoke launcher was installed on the machine. According to the British classification, an armored car was called the Humber Light Reconnaissance Car.
The first serial modification of the armored car, which received the designation Humber Light Reconnaissance Car Mk.I, was slightly different from the prototype, but on the Mk.II version that was released soon, the roof had already appeared. In addition, directly above the fighting compartment there was a small turret, into which the 7,7-mm machine gun was transferred. In this case, the thickness of the reservation was reduced to 10 mm, since the total combat weight of the vehicle was already almost three tons.
Already in 1941, the armored car was again upgraded. In order to withstand the weight that has grown after the previous modifications and at the same time to increase the driving performance as a combat vehicle, the chassis of the armored car was significantly improved, becoming all-wheel drive (4x4 wheel formula). The rest of the armored car, designated the Humber Light Reconnaissance Car Mk.III, corresponded to the previous model of the combat vehicle.
The fourth modification of the combat vehicle, which received the designation Humber Light Reconnaissance Car Mk.IIIA, appeared only in 1943 year. It differed in a somewhat modified form of the body, the presence of a second radio station and additional viewing slots located in the frontal part of the body. A little later, the latest version of the Humber Light Reconnaissance Car Mk.IV armored car was released, differing from the previous version only in “cosmetic” improvements that were not reflected in the characteristics.
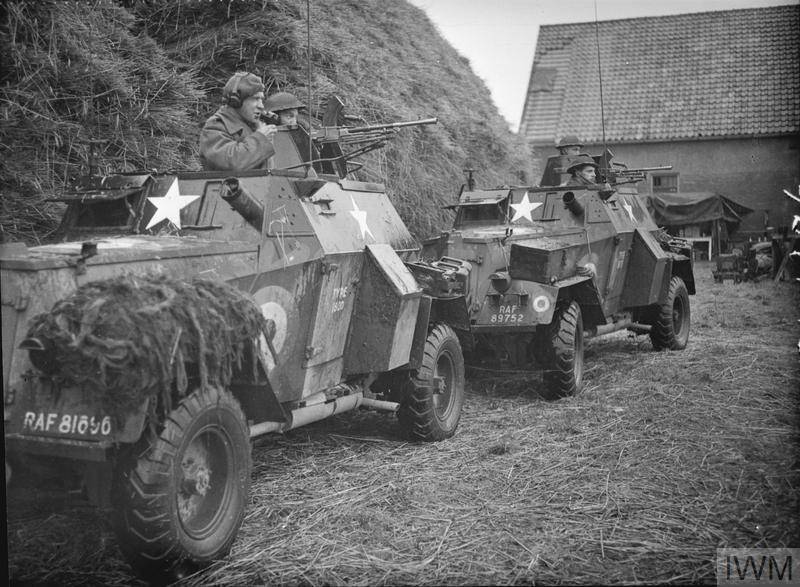

A fairly simple armored car, built on the basis of a commercial model and equipped with a standard gasoline engine, was produced in the UK for four years from 1940 to 1943 a year. In all this time, the country has assembled about 3600 Humber Light Reconnaissance Car of all modifications. These armored vehicles were widely used in battles in North Africa, where they, in particular, were used as part of the 56 th reconnaissance regiment of the 78 th infantry division. Since September, 1943, they can be found in the composition of the British troops who landed in Italy, and in the summer of next year, these wheeled armored vehicles took part in the battles in France. In addition to the army units, these combat vehicles were widely used in parts of the ground reconnaissance of the Royal Air Force (RAF).
After the end of the Second World War, Humber Light Reconnaissance Car light armored vehicles remained in service with only British units in India and the Far East, where in those years the liberation movement against the colonialists developed. The exact date of their full decommissioning is unknown, but, apparently, it happened at the beginning of the 50-s of the XX century.
Performance characteristics of the Humber Light Reconnaissance Car:
Overall dimensions: length - 4370 mm, width - 1880 mm, height - 2160 mm, clearance - 230 mm.
Combat weight - about 3-x (Mk III).
Reservations - up to 12 mm (forehead housing).
The power plant is a 6-cylinder Humber carburetor engine with horsepower 87.
Maximum speed - up to 100 km / h (on the highway).
Power reserve - 180 km (on the highway).
Armament - Bren 7,7-mm machine gun, Boys 13,97-mm anti-tank gun and 50,8-mm smoke grenade launcher.
Wheel formula - 4x4.
Crew - 3 person.
Humber scout car
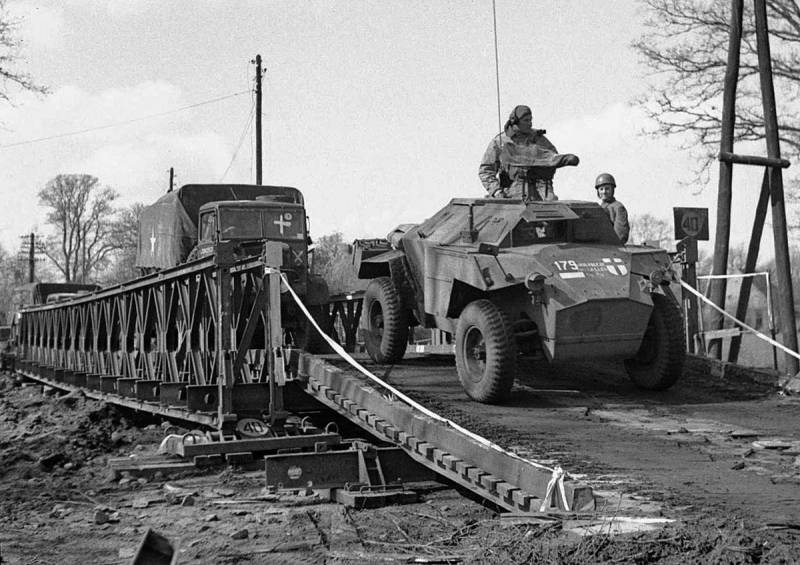
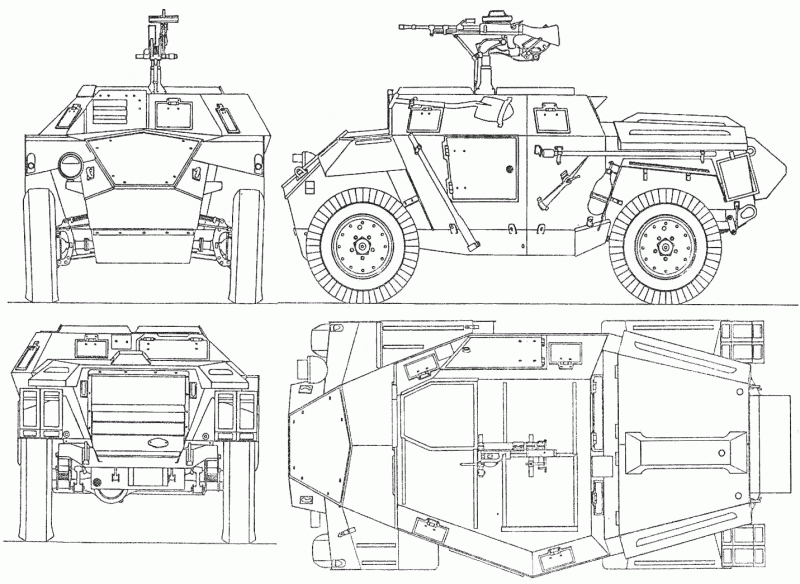
Another reconnaissance armored vehicle of the British army was the Humber Scout Car. Despite the fact that Daimler’s Dingo armored car was adopted as the main reconnaissance vehicle back in 1939, the need for new armored vehicles was so great that in the fall of the same year the British military issued a new order to create a similar combat vehicle . But due to the beginning of the Second World War, the main efforts of British industry were concentrated on mass production and already mastered products, especially since the British army suffered a major defeat in France, losing almost all military equipment. As a result, the company Rootes Group Humber from Coventry took up the creation of a new armored reconnaissance vehicle only in the 1942 year. When creating a prototype, the company's engineers took into account the combat experience of using Dingo armored cars, which proved themselves quite well in 1940-42 battles, and they also took into account the experience of building heavier Humber Armored Car armored vehicles.
In terms of its dimensions, the new Humber armored car to the already produced Daimler, however, differed in layout with the front engine. The hull of the new armored vehicle, which received the designation Humber Scout Car, was assembled from armored plates of thickness from 9 to 14 mm. A small thickness of armor was partly compensated by the rational angles of the armor plates in the front part and along the sides of the hull. This gave the armored car some similarity with the German armored car Sd.Kfz.222.
When creating an armored vehicle, the designers used the chassis from the all-wheel drive car Humber 4x4, used tires of dimension 9,25 x16 inches. The front wheels had a transverse suspension, the rear - suspension on semi-elliptical leaf springs. The transmission of the armored car consisted of a two-speed transfer case, a front axle to be disconnected, a single-plate clutch, a four-speed gearbox and hydraulic brakes.
The heart of the Humber Scout Car was a standard 6-cylinder liquid-cooled carburetor engine with a volume of 4088 cubic centimeters, it developed a maximum power - 87 hp. at 3300 rpm. The same engine was installed on the Humber Light Reconnaissance Car armored car. Engine power was enough to accelerate an armored vehicle weighing just over two tons to 100 km / h speed when driving on paved roads, which was a very good indicator for those years.
The armament of an armored car was exclusively machine-gun and consisted of one or two Bren 7,7-mm machine guns with disc magazines on 100 cartridges. One of them was installed on the roof of the fighting compartment on a special pin. The driver led the observation of the surrounding area through two hatches located in the front hull plate. In the hatches there were armored plates, in addition, they could hide behind armored covers. In the sides of the hull there were also small inspection hatches, which were covered with armored hulls. All cars had a radio station Wireless Set No. 19. The full crew of the Humber Scout Car armored reconnaissance vehicle consisted of two people, but if necessary it could be expanded to three people.
The first serial modification of the reconnaissance armored car under the designation Humber Scout Car Mk.I was put into service in the 1942 year, after which for nearly two years about 2600 copies of this combat vehicle were assembled. The second modification of the Humber Scout Car Mk.II had practically no external differences, the modifications concerned only the transmission and the engine, in this version more 1700 armored cars were produced. Since by the time these armored vehicles appeared, the fighting in North Africa was almost over, they were sent first to southern Italy and then to France and Belgium, where they took an active part in battles with the Germans. They were part of the 11 of the British Tank Division, and were also in service with the 2 Polish Corps, which fought in Italy, the Czechoslovak Tank Brigade and the Belgian armored squadron.
After the end of World War II, a significant number of Humber Scout Car armored vehicles continued to serve in the British army, with some of the vehicles being transferred to the armies of the Netherlands, Denmark, France, Czechoslovakia, Italy and Norway. They were actively replaced with 1949-1950 years, as a result, only armored vehicles assigned to the Belgian gendarmerie were in service until the 1958 year.
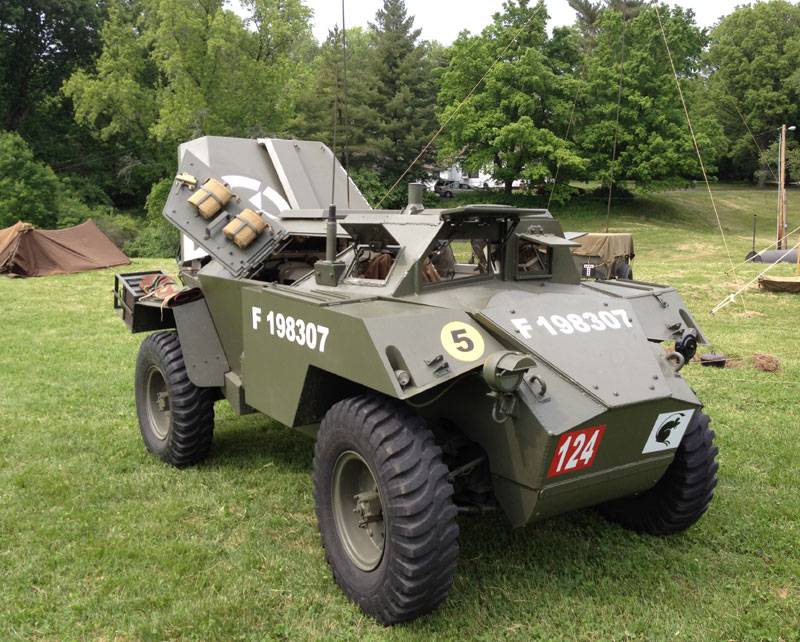

Tactical and technical characteristics of Humber Scout Car:
Overall dimensions: length - 3840 mm, width - 1890 mm, height - 2110 mm, clearance - 240 mm.
Combat weight - 2,3 t.
Reservations - up to 14 mm (forehead housing).
The power plant is a 6-cylinder Humber carburetor engine with horsepower 87.
Maximum speed - up to 100 km / h (on the highway).
Power reserve - 320 km (on the highway).
Armament - one or two 7,7-mm Bren machine guns.
Wheel formula - 4x4.
Crew - 2 person.
Humber armored car
At the end of 1939, Roots designed a new wheeled armored vehicle that could be attributed to middle-class armored vehicles; the vehicle received the official designation Humber Armored Car. Taking the artillery Karler KT4, which was quite successfully used in the colonial possessions of Great Britain (for example, India) and had excellent driving characteristics, it was possible to create a fairly good armored car. The chassis of the new combat vehicle was all-wheel drive and had the wheel formula 4х4, tires of the dimension 10,5х20 inches and suspension on semi-elliptical leaf springs. The armored car transmission consisted of a four-speed gearbox, a two-speed transfer case, a dry friction clutch and hydraulic brakes. The Rootes 6-cylinder carburetor engine with liquid cooling was used as a power plant; it developed the maximum power in the 90 hp. at 3200 rpm.
The body of the new armored vehicle with some modifications was involved from the model Guy Armored Car. Guy Armored Car was a British medium armored car of the Second World War period, according to the national classification it was designated as the “Light Tank (Wheeled) Mark I). This combat vehicle was created by engineers of Guy Motors back in 1938 year on the basis of the artillery tractor Guy Quad-Ant, becoming the first British all-wheel drive armored car. Given the numerous contractual obligations for the release of artillery towers and trucks to the UK government, Guy Motors was not able to produce armored cars (in sufficient quantities), so their production was transferred to the industrial corporation Rootes, which during the war years produced up to 60% of all British wheeled armored vehicles under its own brand Humber. At the same time, Guy Motors continued to produce welded hulls for armored vehicles.
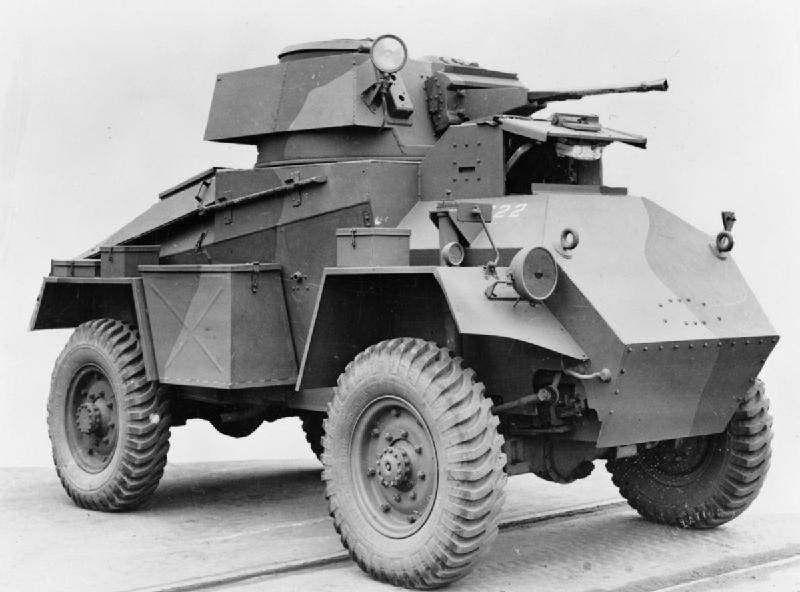

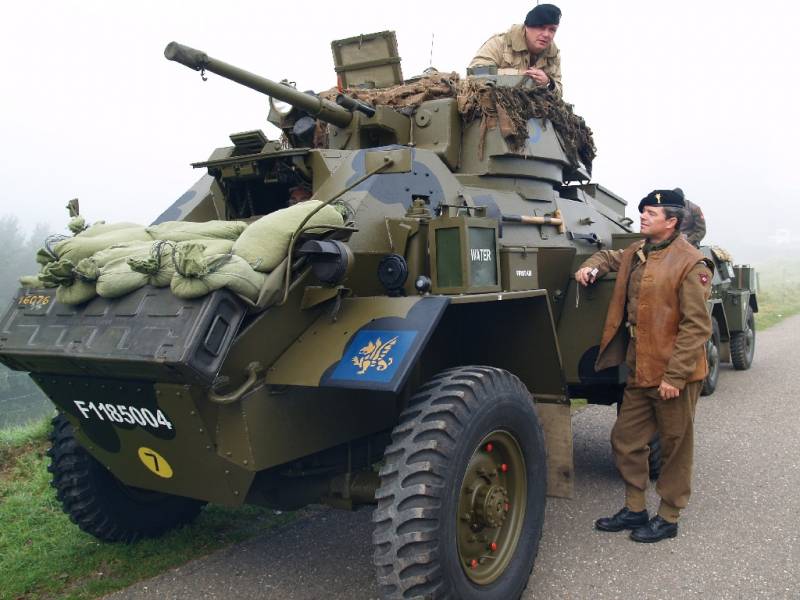
The body of the Humber Armored Car armored car had a riveted-welded structure and was assembled from armor plates with a thickness from 9 to 15 mm, while the upper armor plates were located at rational inclination angles, which increased the security of the car. A distinctive feature of the armored car was a relatively high body, which could be attributed to the shortcomings. The thickness of the frontal armor of the hull reached 15 mm, the thickness of the frontal armor of the turret reached 20 mm. In front of the body of the armored car there was a department of management with a driver's seat, in the middle part there was a combat compartment for two people, in the rear part there was a motor compartment.
The armament of the armored car was located in a welded turret, which was also partially borrowed from the Guy armored car. It included a twin installation with 15-mm and 7,92-mm Besa machine guns. A double-barreled smoke grenade launcher was also located on the hull front plate. As an auxiliary weapon on the armored car, it was possible to install another Bren 7,7-mm machine gun as anti-aircraft. In this case, the most massive modification of the armored car Humber Armored Car Mk.IV had more powerful weapons, on it the 15-mm machine gun was replaced by the 37-mm American gun M6.
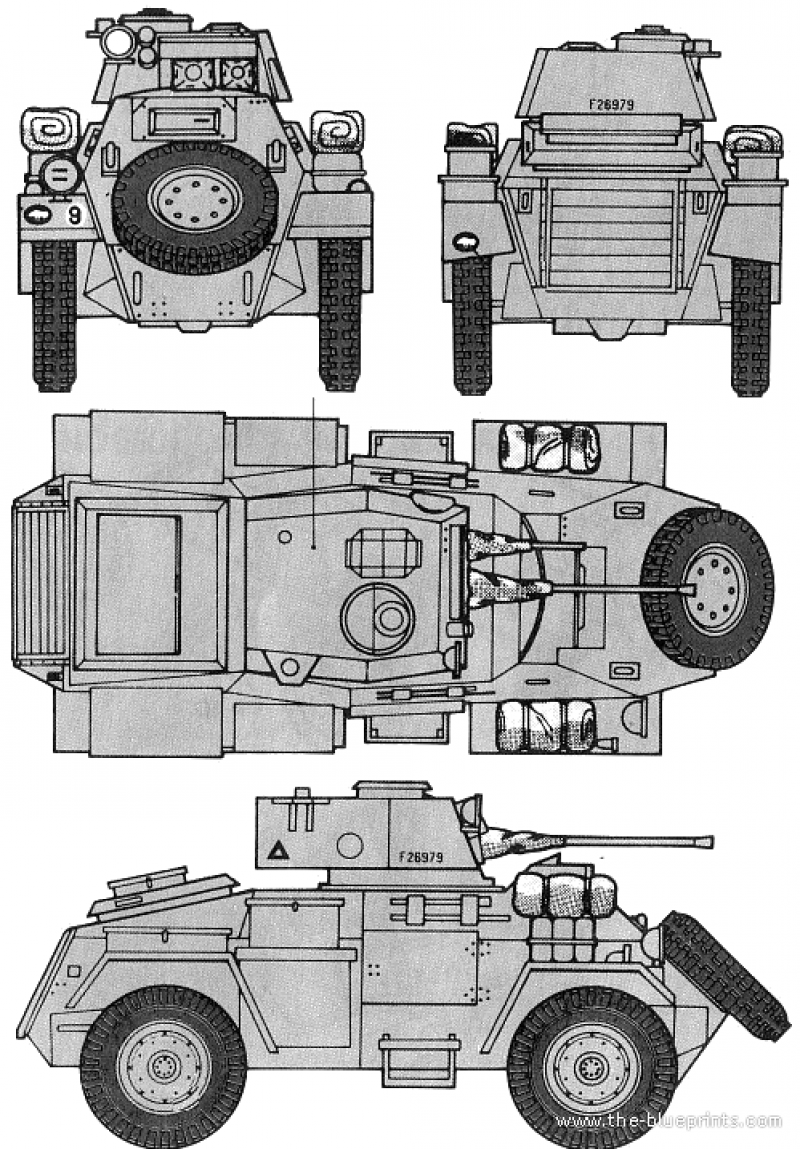
In general, it should be recognized that the British wheeled armored vehicles of the period of the Second World War were quite successful and were technically superior to the vehicles of many countries. Humber Armored Car was no exception. Rather well-armed and well-armored, this medium-sized armored car had excellent cross-country maneuverability, and on hard-surface roads it could travel at speeds up to 80 km / h. All later modifications of the Humber retained the 90-strong gasoline engine and chassis, the corps, turret, and weapons composition were mainly affected. The combat vehicle was presented with the following modifications:
Humber Armored Car Mk.I - welded turret and hull, similar in shape to the hull and turret of an armored car Guy Mk.IA. The driver was located in the front of the hull in an armored wheelhouse with inspection slits. Produced order 300 armored vehicles.
The Humber Armored Car Mk.I AA is an anti-aircraft version of a medium armored car with a turret installed from an experienced self-propelled anti-aircraft gun based on the Mk VIB tank, the armament of this vehicle consisted of Besa 4x7,92 mm machine guns.
Humber Armored Car Mk.II - Modification received the body of an improved form and 7,7-mm anti-aircraft gun Vge. Combat weight increased to 7,1 t. Total produced 440 armored vehicles.
Humber Armored Car Mk.II OP (Observation Post) - armored car artillery observers. Armed with two Besa machine guns caliber 7,92 mm.
The Humber Armored Car Mk.III is a modified Mk.II armored vehicle with a new triple turret. Crew increased from three to four people.
The Humber Armored Car Mk.IV is a modified Mk.III armored car that received the American M37 6-mm cannon, paired with the 7,92-mm Besa machine gun. Combat weight increased to 7,25 t. A total of about 2000 armored vehicles of this type were produced.
Humber Armored Car armored cars did not have time to fight in France in the spring-summer of 1940, so their combat debut came in the second half of the 1941 of the year when they were first used by the British in battles in North Africa. The first combat unit to receive these medium-sized armored cars was the 11 th hussar regiment stationed in Egypt. These armored vehicles were actively used by the British, from the 1941 year to the end of the war, being used in all theaters of war. With a favorable set of circumstances (for example, when firing from ambushes), they could effectively deal with enemy armored vehicles. True, when meeting with German tanks in the open field, the chances of surviving them were extremely small.
After the end of the Second World War, the Humber armored cars were soon removed from the weapons of the British army as outdated combat vehicles. However, their service continued in the armies of other states. The United Kingdom delivered armored vehicle data to Burma, Portugal, Mexico, Ceylon and Cyprus. In the armies of some of these countries they were actively used until the beginning of the 1960-s.
Performance characteristics of the Humber Armored Car:
Overall dimensions: length - 4575 mm, width - 2190 mm, height - 2390 mm, clearance - 310 mm.
Combat weight - 6,85 t.
Reservations - up to 15 mm (forehead housing)
The power plant - 6-cylinder carburetor engine liquid cooling Rootes horsepower 90 power.
Maximum speed - 80 km / h (on the highway).
Power reserve - 320 km (on the highway).
Armament - 15-mm and 7,92-mm Besa machine gun (modifications Mk I-III), on the modification of the Mk IV - 37-mm gun M6 and 7,92-mm machine gun Besa.
Ammunition (for Mk IV) - 71 projectile and 2475 cartridges for machine guns.
Wheel formula - 4x4.
Crew - 3-4 person.
Information sources:
http://www.aviarmor.net
http://arsenal-info.ru/b/book/3074485325/4
http://pro-tank.ru/bronetehnika-england/broneavtomobili/194-hamber-4
Open source materials



Information