Searchlight tanks based on M4 Sherman (USA and UK)
The original goal of the Canal Defense Light project was to build an armored vehicle with a powerful searchlight. It was assumed that a large group of such equipment would be able to highlight the positions of the enemy, ensuring the offensive of the troops at night. In addition, it was planned to use some original ideas aimed at further worsening the position of the enemy and increasing the survivability of searchlight tanks. The first carrier of the special CDL tower was the British infantry tank Mk II Matilda II. Subsequently, such a unit was installed on the American medium tanks M3.
Already at the beginning of 1943, the American and British military understood that the Li / Grant tanks were rapidly becoming obsolete and therefore had very limited capabilities even in the context of the construction of special and auxiliary vehicles, not to mention the use for its intended purpose. It was obvious that all new designs should be based on different chassis of the latest models. One of the most successful carriers of a variety of weapons or special equipment could be a medium tank M4 Sherman American development.
By June, 1943, the American experts have completed the development of the searchlight tank T10 Shop Tractor, which was actually a slightly modified version of the British CDL Grant. Immediately after that, work began on the creation of the next sample of this technique, using a newer chassis with enhanced performance. In addition, in the course of this modernization it was proposed to create an updated version of the projector installation with more features. First of all, it was necessary to increase the power of the existing lamp or lamps. Also, the updated car needed more sophisticated means of observation.
Further studies have shown that a promising searchlight tank can hardly do with just one high-power lamp and needs to use two such products. This allowed to significantly improve the basic characteristics, although it forced to develop a completely new tower. Such a price of deep modernization was considered acceptable, with the result that the final appearance of the future special machine appeared.
The next project of the CDL family was to be created using the approaches already known and proven in practice. It was proposed to take a ready-made medium tank, remove from it no longer needed units, install some new systems, as well as mount the turret with the required equipment. This allowed to save on mass construction and operation due to the maximum possible unification of searchlight tanks with linear ones.
As a basis for a new car, Sherman tanks of all existing modifications, differing from each other in various features, could be used. So, it is known that at least one of the prototypes built according to the American project was based on the M4A1 chassis. Such a tank had a molded hull with frontal armor 51 mm thick and 38-mm side elements. The project allowed to maintain the existing layout with a front-mounted transmission and control compartment, a central fighting compartment and aft engine compartment. Alteration of the chassis was carried out only by removing some large units and installing others.
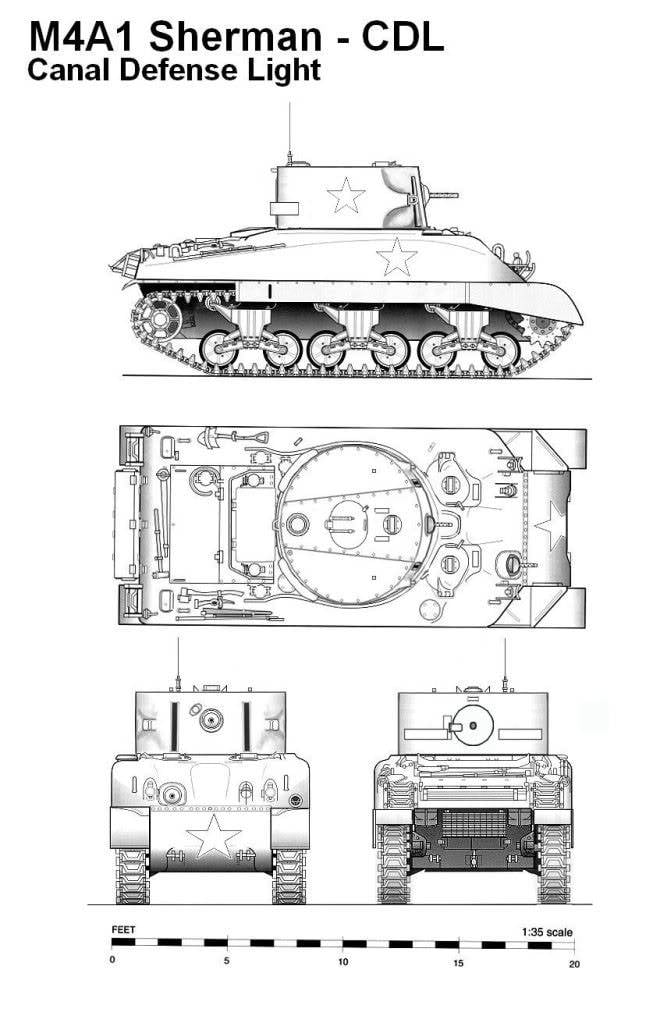
Projections of M4 Leaflet. Figure Network54.com
The M4A1 modification tanks were equipped with Continental R975 C1 radial petrol engines with 350 hp power. With the help of a cardan shaft, passing through a habitable compartment, the engine was connected with the transmission of the front location. The chassis had six road wheels on each side, interlocked in pairs on spring-loaded cushion carts. During the construction of searchlight tanks on the basis of the Shermans of other modifications, the composition of the power plant and the design of the undercarriage could be changed.
In the course of reworking in accordance with new ideas, the existing medium tank lost a turret with cannon and machine gun weapons. In addition, all racks and stowings were removed from the fighting compartment to accommodate standard ammunition. Part of the released volumes was used to install new electrical systems. The largest new component was the 20-kilowatt electric generator, directly connected to the main engine. Such a powerful generator was required to power the improved floodlight installation.
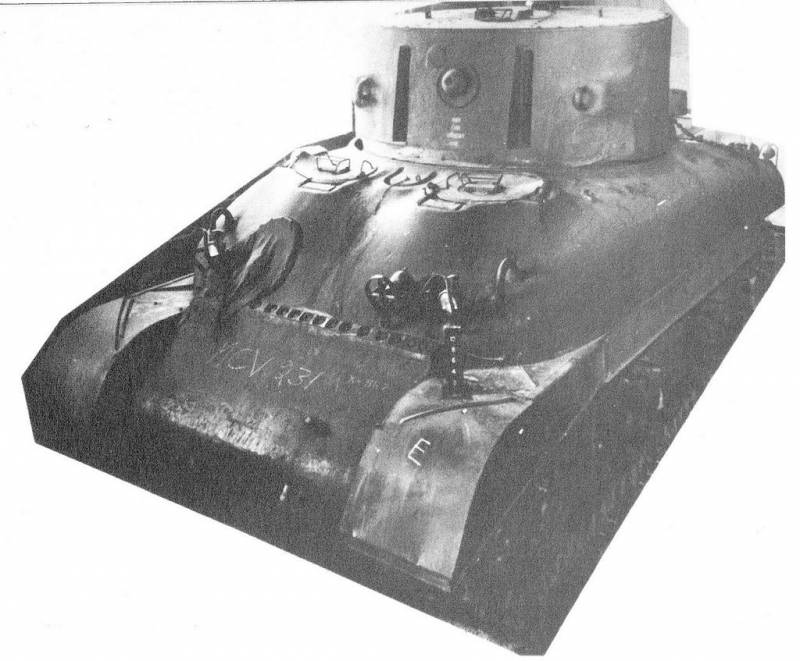
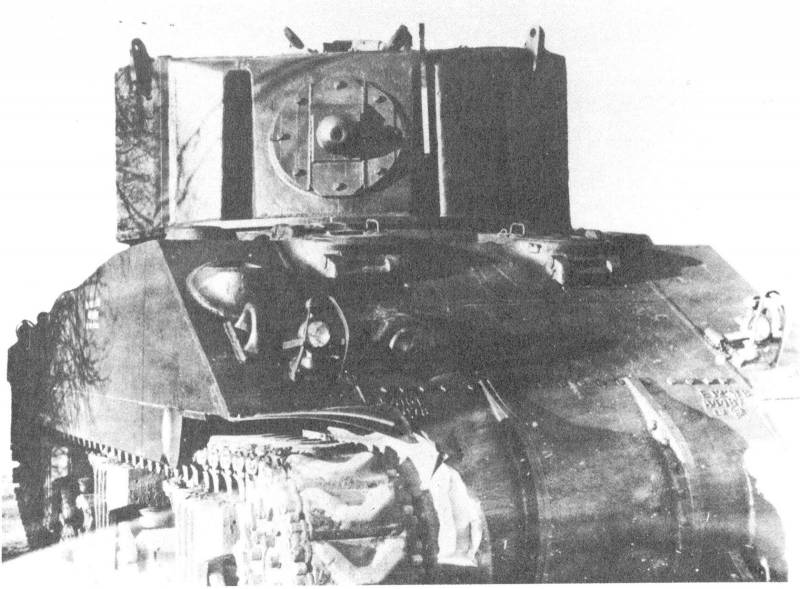
In accordance with the updated requirements, a new tower was created, containing two spotlight installations at once. At the same time, in its design the existing developments from previous projects were widely used. On the standard hull pursuit, a cast cap of a form that was close to cylindrical was to be installed. The front part of this unit had a slight tilt back. On the side, small overhangs-protrusions were required for the installation of some equipment. The center of the frontal part of the tower had an embrasure for a machine gun. On either side of it were narrow vertical windows for searchlights.
Based on the experience of previous projects, the tower was divided into three sections. The central part was given under the deployment of the operator and weapons for self-defense. The front of this compartment was completed with a machine-gun installation and controls for electrical systems. In addition, the workplace was equipped with tools to control the targeting of spotlights in two planes. Next to them was the operator. Access to the camera bay was provided by hatches in the roof and stern of the tower. Over the operator in the roof were installed three periscope viewing devices.
To highlight enemy positions in the new project, it was proposed to use two spotlights at once, based on existing ideas. The side compartments of the tower were completed with units of similar design. Each of them used its own high-power coal arc lamp equipped with a system of mirrors. With the help of a curved mirror placed in front of the tower, the light flux was redirected to the stern. There was a direct mirror, with which the rays were transferred in the direction of the frontal vertical embrasure. As in the case of the British searchlight installations, such a system illuminated the sector with a width and height of several degrees. The presence of two searchlights was supposed to appropriately improve the "combat" characteristics of the machine. The tower received funds for the maintenance of coal arc lamps: the operator could bring the electrodes together as they burned out.
According to some information, the new American project proposed to preserve the additional equipment of the searchlight, previously proposed by British designers. The searchlight recess should be equipped with a movable shutter-shutter and light filters. The first allowed to stop and renew the backlight without turning off the lamp. The filters should have made it difficult to determine the real location of the carrier of searchlights, but at the same time they did not interfere with their own troops to observe the highlighted area.
During the modernization of the tank M4 Sherman lost the original turret with gun and machine gun weapons. Nevertheless, the new project of the armored searchlight still implied the use of weapons for self defense. To fight with manpower and unprotected enemy equipment, tank crews could use two machine guns of the M1919 rifle caliber. One of them was placed in the standard course installation frontal sheet, at the right side. The second was offered to mount in the embrasure of the forehead of a new tower. The use of anti-aircraft machine gun was not provided.
The lack of gun armament and the reduction of manned volumes led to a decrease in crew. Only three people were to control the searchlight tank. The driver and the gunner were placed in their regular places in front of the hull. The commander, who also served as the operator of searchlight installations and the arrow, was in the tower. All crew jobs were equipped with their own hatches and viewing devices.
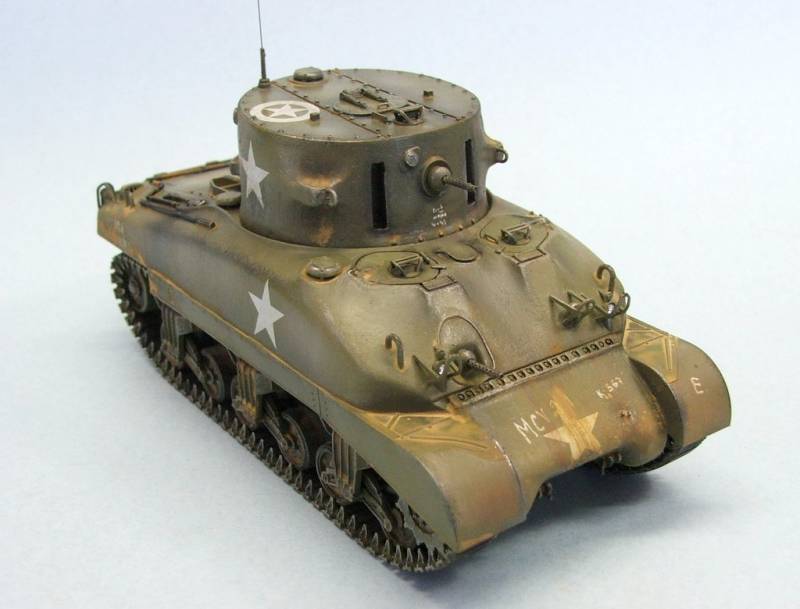
The development of the new project was completed in the spring of 1944, after which one of the American arsenals, with the assistance of the defense industry, rebuilt the M4A1 serial tank. The prototype machine received the official designations M4 Leaflet (after the name of the American program of searchlight tanks) and "E". Also, some sources use the name T10E1, indicating the continuity of projects. Tests of the prototype were to be held at the site of the military base of Fort Knox. In May of the same year, the prototype was submitted for testing.
Like many other samples of wartime, searchlight tank "E" passed all the necessary checks in just a few weeks. The tests fully confirmed the calculated advantages of the new model over the existing T10. The use of the chassis of a newer medium-sized Sherman tank offered obvious advantages. M4 Leaflet was distinguished by improved mobility, increased level of protection and greater ease of operation. In addition, by this time, M4 of various modifications had become the most massive tanks in the American army, which was also an important plus. At the same time, the new searchlight tank was in some respects inferior to the previous CDL Grant / T10. The fact is that the replacement of the existing M4 turret led to the removal of the main gun. In the case of the M3 Lee / Grant vehicle, replacing the turret did not affect the main 75-mm gun in the sponson of the hull.
Thus, having significant advantages in the mass of characteristics, the searchlight tank based on the M4 Sherman lost to the previous type of machine in firepower. The absence of artillery and the use of only machine-gun armament became the decisive factor. The US military, comparing the two original samples of special equipment, came to the conclusion that a well-armored, but poorly-equipped searchlight tank was not of interest to the army. Moreover, the potential customer considered that the construction of such equipment would be a uniform waste of good and modern tank chassis.
The tests of the first and only prototype of the “E” / M4 Leaflet / T10E1 type were completed in June of the 1944 year, shortly after the outbreak of hostilities in Normandy. The negative response of representatives of the military department in an appropriate way affected the further fate of the project. All work on the current modernization of "Sherman" were discontinued due to non-compliance with the wishes of the customer. The revision of the existing project with the use of a gun of acceptable power was not possible. As a result, the development of the existing tank “E” was stopped.
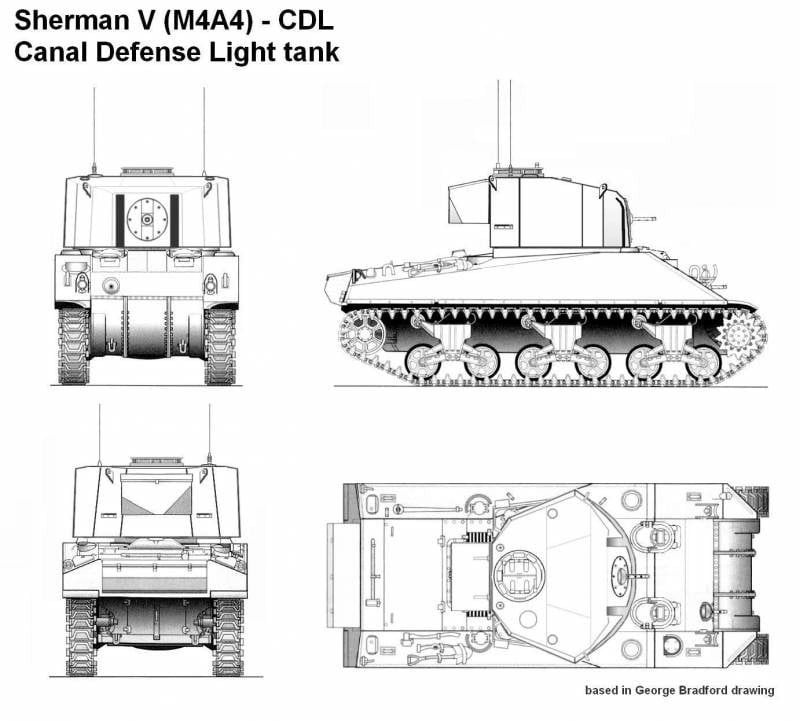
It is known that the creation of a searchlight tank based on the M4 combat vehicle was also engaged on the other side of the Atlantic Ocean. Simultaneously with the United States, the UK studied this problem, which created the first projects of such equipment. There is reason to believe that the British project was a direct development of the American one, or at least it was created taking into account the developments on it. As a result, the main features of the architecture of different armored vehicles coincided, but there were certain differences.
British industry was built immediately two pilot tanks CDL Sherman. Both of them were based on a chassis with a welded armored body, but the main features of the modernization were borrowed from a foreign project. Thus, all units of the fighting compartment were completely removed from the corps, instead of which an electric generator was installed, etc. The tower of the first prototype in its design, in general, repeated the American design, but had a different dome. Taking into account the existing production technologies, the dome was divided into several cast and rolled parts assembled into a single unit by welding.
Like the M4 Leaflet, the first version of the British CDL Sherman had two spotlights placed on the side of the tower. Between their vertical windows, embrasures was a machine-gun, designed to use weapons that meet the standards of the army of Great Britain.
The second prototype of the CDL tank at the Sherman base was different for its turret design. Now a curved frontal sheet of wide width was used, to which the beams placed at an angle joined at the back. At the stern there was a rectangular niche. The increased volume of the tower made it possible to equip the commander’s workplace in the stern, due to which the tower became a double. The commander could use his own sunroof, equipped with a set of viewing devices. Apparently, the strengthening of the crew of the fourth tank was proposed to reduce the load on its individual members. The original American project and its version of the British development assumed that the commander would coordinate the work of the crew, control the searchlights and fire the machine gun. The separation of such duties between the commander and the shooter operator could significantly facilitate their work.
Tests of two searchlight tanks of British development were also held in 1944 year and confirmed the conclusions made by American experts. Once again, it was found that the M4 Sherman tank chassis provides improved mobility compared to the M3 Lee / Grant machine, and also differs from it in an increased level of protection. At the same time, the lack of artillery guns and the impossibility of installing them without serious redesign of the project were considered a disadvantage. As a result, CDL Sherman tanks were not recommended for use in mass production.
The fate of the three prototypes is unknown. Apparently, they were rebuilt according to initial projects and handed over to armies for use in hostilities. Thus, in the configuration of searchlight tanks, machine types “E” and CDL Sherman have not survived to this day.
After the unsuccessful completion of the project of a searchlight tank based on the M4 Sherman armored vehicle, the British army refused to further develop this area. The emergence of such a decision contributed not too great successes of recent developments, as well as the almost complete lack of practical results of the use of sufficient mass technology. For various reasons, the existing Canal Defense Light tanks based on the two types of chassis were only able to take part in battles a few times, fulfilling their basic functions. At other times, they had to solve completely different tasks of an auxiliary nature.
The United States Army, in turn, did not abandon the original ideas and the creation of new searchlight tanks. The command and designers took into account the shortcomings of the existing project M4 Leaflet / "E" / T10E1 and formed the updated look of a promising special-purpose armored vehicle. With the help of a number of original ideas and solutions, they managed to combine in one project both searchlight installations and artillery weapons. Initially, this version of the tank had the already known designation "E", but later it was given a new name T52. This combat vehicle can be considered one of the most interesting and successful samples of its class.
Based on:
http://tanks-encyclopedia.com/
http://shushpanzer-ru.livejournal.com/
http://network54.com/
http://panzerserra.blogspot.fr/
Hunnicutt RT Sherman. A History of the American Medium Tank, Navato, CA. Presidio Press, 1971.


Information