H&K G36

For half a century stories in the Bundeswehr, its soldiers have already received the fourth "soldier's bride". Before that, the "girlfriends" of the German recruits were the G98, FAL and G3 rifles. In 1995, the Heckler & KochG36 assault rifle was adopted by the Bundeswehr.
ПThe search for a replacement for the G3 began in 1970, when the tactical and technical requirements for a new assault rifle were formulated. The contract for its development was received by Heckler & Koch, who in 18 years created the G11 rifle for a caseless cartridge. However, the G11 did not enter service and in 1992 the Bundeswehr returned to the issue of replacing the G3. There were three reasons for this.
First, by the 90 years, the armies of all the leading countries switched to assault rifles for a low-pulse cartridge. Only Germany maintained its commitment to the patron 7,62x51, which by this time was already an anachronism. This was contrary to the NATO standardization program, where the cartridge 7,62x51 was recommended for single machine guns and sniper rifles.
The second reason is the change in the tasks of the Bundeswehr. After the fall of the Iron Curtain, the military doctrine of the Federal Republic of Germany radically changed. The primary objectives of the Bundeswehr became peacekeeping and counter-terrorism operations, the fight against drug trafficking, smuggling and pirates. This required high reliability. weapons in any climate - in the mountains and deserts, with strong dust, with prolonged lack of proper maintenance and lubrication. The heavy and bulky G3 rifle was not very suitable for these purposes, and the effectiveness of firing bursts with such a powerful cartridge left much to be desired.
The third reason lay in the technical plane. In addition to obsolescence, infantry weapon systems (P1, MP2, G3, MG3) have developed their resource physically and required replacement. It would be unwise to resume the production of outdated weapons systems to replace worn-out samples.
The financial situation of the Bundeswehr in the early 90s differed significantly from the situation in the 70s and 80s, and therefore it was decided not to finance the development of new models of small arms, but to purchase samples already available on the market. This provided for the new tactical and technical requirements for the assault rifle and light machine gun developed on September 1, 1993. The selection of rifle models for participation in the competition was carried out by a special working group, which included representatives of the army, air force and navy. The group selected 10 models of assault rifles and 7 models of light machine guns. After the preliminary stage, two systems remained - the Austrian Steyr AUG and the German Heckler & Koch HK50. If a decision was made in favor of the Austrians, it was envisaged to deploy the production of AUG rifles in Germany. However, this did not happen: after comparative tests at the WTD91 training ground in Mepn and military tests of weapons in infantry schools, the military opted for the HK50 rifle and the MG50 light machine gun based on it. Another argument that tipped the scales in the direction of the Oberndorf firm was that Heckler & Koch was already the official supplier of the Bundeswehr.
On May 8, 1995, an official decision was made to adopt the HK50 assault rifle and the MG50 light machine gun with the assignment of the army designations G36 and MG36. In September 1996, new rifles began to enter the armed forces, special forces and military units operating in crisis regions. They continued military trials of the G36. Then the remaining parts of the Bundeswehr and infantry schools were equipped with new rifles. The adoption of the G36 rifle was of great importance for the German army. This is evidenced by a special official ceremony of the transfer of new weapons to the army, aviation и the fleetHeld on December 3, 1997 at the Hammelsburg Infantry School. After that, equipping the troops with new rifles was to take on a massive scale. In July 1998, the 50th G36 was released, and over the next five years it was planned to completely complete the replacement of the G3 with the G36. Despite this, even to this day, the Bundeswehr has not been equipped with new assault rifles. A certain number of G3 rifles were kept in service, where they are used mainly for training purposes, for training in shooting recruits and training reservists.
Most of the parts of the rifle (receiver, butt, handguard, handle, magazine) are made of high-strength polymer. These parts have a rough outer surface that allows you to securely hold the rifle, and in severe frost they do not create problems when you touch the weapon with your bare hands. Thanks to plastic, the cost of the G36 rifle is small and amounts to 600 euros.
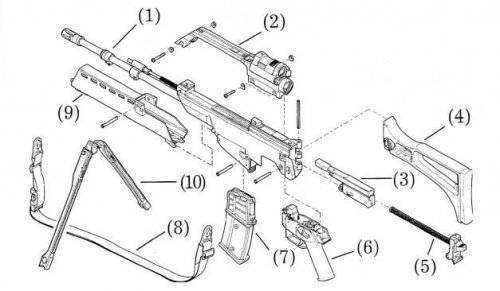
Explosion-scheme rifles G36: 1 -trunk withreceiver a box;
2 -lever for carrying с sights; 3 -gate;
4 -brachial emphasis; 5 -back plate withrefundable spring loaded; 6 -lever c USM в gathering; 7 -shop; 8 -belt for carrying; 9 -fore-end; 10 -bipod
The barrel of the G36 rifle has 6 right-hand grooves of a regular profile with a pitch of 109 '' (7 mm) typical for rifles chambered for SS178. The bore is chrome-plated. The barrel is screwed into the receiver liner with a special wrench and fixed in it with a threaded nut. The insert is poured into the receiver and has cutouts from the inside, into which, when locked, the bolt lugs enter.
A slit-type flame arrester is screwed onto the muzzle of the barrel. When firing blank cartridges, an MPG device (Manoverpatronengerat) is installed in its place to ensure the normal operation of the weapon’s automatics. This device also prevents the release of unburned powder particles from the barrel, so that the rifle can be used at relatively close distances in the exercises. If the weapon is accidentally charged with live ammunition, the MPG device is capable of holding the bullet without causing harm to either the shooter or the weapon. On the muzzle of the barrel can also be mounted laser simulator shooting AGDUS.
Considering the fact that in modern conditions the bayonet battle is unlikely, the first series G36 did not provide for the bayonet attachment. However, later the flame arrester of the rifle was modified to ensure the mounting of the bayonet from AK74, a large number of which was inherited from the army of the GDR. Given the solid price of a new bayonet, this idea saved a lot of money. The original G36 bayonet has export Spanish only.
The 185 mm from the muzzle is a gas chamber, fastened to the barrel with pins.
Powder gases discharged into it affect a spring-loaded rod with a gas piston (its stroke is 6 mm), which has no rigid connection with the gate. This ensures reliable operation of automation with different cartridges.
The bolt unit consists of two main parts: the butterfly valve with 6 lugs and the bolt carrier. Mounted at the top of the bolt spring-loaded ejector has a wide tooth. Inside the slide there are a hammer and a reflector of a spent cartridge case, and in the back there is a large round hole. A finger is inserted into it, interacting when locking and unlocking with a curved groove on the bolt carrier and causing the bolt to turn. The unusual device has a cocking handle. It is located in the upper front of the bolt carrier and in the non-working position is parallel to the trunk. To load it, you need to rotate it by 90 degrees, and this can be done both to the right and to the left. The reloading process itself can be done in two ways. Under normal reloading, the bolt handle is retracted and released - the bolt returns to its most forward position under the action of a spring. If it is necessary to perform the reloading process silently, then the shutter is retracted, but not released completely, but held by the handle.
Why did the developers of G36 abandon the roller shutter, which proved itself well in G3?
The fact is that unlocking in the semi-free shutter starts immediately after the shot, which is acceptable for a weapon chambered for 7,62x51 and causes problems with the 5,56xXNNXX cartridge with a less durable sleeve. The problem was complicated by the considerable variety of cartridges of this caliber, produced by different NATO countries, and differing in ballistics and case materials. The Germans also do not hide the fact that when creating the G45 they were largely guided by the conceptual scheme of the Kalashnikov assault rifle, which they considered to be the benchmark of reliability for small arms. The AK36 option for NATO's patron even was considered at the preliminary stage of the 74 contest of the year as one of the possible alternatives to replace the G1993 rifle.
The receiver connects all the most important parts of the weapon and is made of plastic, reinforced with several steel liners. Two of them play the role of guides for the shutter, and the rest perform a protective function in the attachment points of the magazine, butt pad and pistol grip. On the right side of the receiver has a window for ejection of spent cartridges. Behind the window there is a rigidly fixed sleeve reflector with a height of 14 mm. With it, the spent cartridges leave the weapon at an angle of 90-100 degrees, without interfering with the shooter when firing from both the right and left shoulder. Another purpose of this detail is that it also serves as a fixer for the folded butt.
The receiver of the store is a separate part, attached to the receiver with the help of two axles and an axis. Latch shop "Kalashnikov" type, located in front of the trigger guard.
Another part that is separate from the receiver is the carrying handle, on which the rifle sights are mounted. It is attached to the receiver with three screws and is located near the center of mass of the weapon, which makes the rifle more convenient to carry.
Carbine G36K с shortened the trunk
Performance characteristics of the rifle G36
|
Brand name |
HK50 |
|
Manufacturer |
Heckler & Koch, Oberndorf / Neckar |
|
Caliber |
5,56x45 mm (.223 Rem) |
|
The principle of operation of automation |
removal of powder gases from the barrel |
|
Locking |
shutter rotation |
|
Length (with folded butt) |
999 (758) mm |
|
Height with store |
320 mm |
|
Height without store |
263 mm |
|
Width (with folded butt) |
64 (98) mm |
|
Barrel length |
488 mm |
|
Bore |
chromium-plated |
|
Rifling |
6 right rifling |
|
Pitch rifling |
178 mm |
|
Initial bullet speed |
about 920 m / s |
|
Muzzle Bullet Energy |
1725 J |
|
Effective Shooting Range |
500 m |
|
Target range |
800 m |
|
Maximum firing range |
2860 m |
|
Weight without store and bipod |
3,63 kg |
|
Bipod weight |
0,21 kg |
|
Empty magazine weight on 30 cartridges |
0,127 kg |
|
Shop weight with 30 cartridges |
0,483 kg |
|
Kind of fire |
single / automatic |
|
Rate of fire |
750 shots / min |
|
Pull force |
30 ... 55 H |
|
Store capacity |
30 cartridges |
|
Bullet weight |
4 g |
|
Sights |
1: 1 collimator sight, 3x optical sight ZF 3 x 40 |
|
Application |
Albania, Australia, Brazil, UK, Germany, Georgia, Indonesia, Jordan, Ireland, Spain, Italy, Canada, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Malaysia, Mexico, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Singapore, Slovakia, Slovenia, USA, Thailand, Uruguay, Philippines, Finland, France, Croatia, Chile, Sweden, Estonia |
The butt plate of the receiver is connected to it by means of an axis that also secures the pistol grip. A return spring with a tubular guide is inseparably connected to it, as well as an elastomer shock absorber with a length of 14 mm and a diameter of 12 mm, which softens the impact of the bolt in the rearmost position. The pistol grip of the G36 rifle is practically borrowed from the G3, but with a number of important improvements. It is attached to the receiver with two axles and contains a trigger and safety mechanisms, as well as a slide delay. Compared to the G3, the trigger is simpler and easier to clean. The holes for fixing the lever of the translator-safety catch from the outer surface of the handle are transferred to its inner surface. It is believed that in this case there is less risk of dirt getting into these holes and interfering with the change of fire modes. There are three positions of the safety-translator - "protection" (white letter "S"), "single fire" (red "E") and "automatic fire" (red "F"). The safety-translator lever is reversible and can be easily operated with your thumb. In addition, the length of the lever is selected in such a way that in the positions "F", "S" it slightly touches the index finger, so that the arrow can determine its state by touch. The gate lag of the G36 is very peculiar. With the help of a small latch at the front of the trigger guard, it can be turned on and off, depending on the wishes of the shooter. Disabling the slide delay is recommended in bad weather to reduce the likelihood of dirt getting into the receiver. The dimensions of the trigger guard provide the ability to shoot both thick winter army gloves and neoprene gloves used by combat swimmers.
Butt rifle G36 plastic frame, with a rubber butt pad height 142 and width 32 mm. It develops on the right side of the receiver, while maintaining the possibility of firing. The design of the butt and the reflective mechanism is thought out in such a way as to ensure the unobstructed ejection of the sleeves through the folded butt. The only inconvenience in this case is left-handed arrows, which in this case are forced to use an "alien" left translator-fuse - the right one closes the folded butt. Like the G3, in the butt of the G36 rifle there are two pairs of holes into which the extracted axles are inserted to avoid loss during disassembly.
The plastic handguard is attached to the receiver with an axle and not connected to the barrel. Handguard is made long (330 mm) and can be used as a support. In order to improve the removal of hot air from the barrel, 19 rectangular holes are provided at the forearm: six on each side (size 6х20 mm) and seven at the bottom of the forearm (10x20 mm). At the front end of the forearm, there is also an axle, which simultaneously performs the role of a hinge for attaching a belt and an assembly for mounting bipods.
The rifle sights are mounted on a carrying handle and consist of an upper collimator sight and a lower optical sight. Both are manufactured by Hensoldt AG. The German military decided to abandon the traditional mechanical sight, since combat experience showed that inexperienced shooters achieve significantly better results when shooting with optics, they learn marksmanship faster and, under stress, optics provide less aiming time. For the first time, such a combined sight (collimator + optical sight) was tested on one of the prototypes of the G11 rifle. He was taken as the basis for the sights of the future G36.
The collimator sight is the simplest optical system of lenses projecting an image on the 1: 1 scale. It is equipped with a photo receiver, closed by a safety shutter. It captures daylight and forms from it a light beam with a wavelength of 650 nm, directed into the eye of the shooter. This beam passes through the light filter and is perceived by the shooter as a red dot (aiming mark). The light filter is designed in such a way as to delay the light flux in the spectral range of the aiming mark and to allow the rays of other spectra to pass unhindered. The lenses of the collimator sight are made of a special sort of glass that absorbs the red color reflected by the light filter in the direction of the target, which the arrow can give to the enemy.
At dusk or at night, you can turn on a battery-operated photodiode and form an aiming mark. The battery is designed for 60 hours, which is quite enough, since in practice the backlight turns on only for relatively short periods of time. When using the backlight, a special sensor adjusts the brightness of the aiming mark depending on the illumination. In addition, you can press the button to put the diode in high power mode. After 30 seconds, normal mode will automatically recover.
The collimator sight is used at distances up to 200 m, at long distances the arrow needs to use a lower, telescopic sight.
The Hensoldt ZF 3x40 optical sight is made of glass fiber reinforced polyamide and weighs only 30 grams. It has a threefold magnification and serves for aiming at distances from 200 to 800 m. The optical system of the sight includes a lens, a lens with an aiming grid, a turning lens and an eyepiece. The aiming grid consists of a crosshair and a circle, the center of which is the intersection of the threads of the sight. The center of the crosshair corresponds to the distance 200 m, the rifle is aimed at this distance. The circle around the crosshairs has several settings. Its diameter corresponds to the height of a human figure with a height of 1,75 m at a distance of 400 m. The lower point of intersection of the circle with the vertical thread of the sight corresponds to the firing range of 400 m. Sight serve for shooting at moving targets. They correspond to the lead value when firing at a running soldier (target speed 600 km / h) at a distance of 800 m. In addition, there is a rangefinder scale on the sight grid, which allows you to estimate the distance to the target from the height of the human figure.
For shooting at night, a Hensoldt NSA 80 night sight can be mounted on a rifle. It is mounted on the handle for carrying a rifle and is used in conjunction with a day sight. Due to this, weight is saved (weight NSA 80 with 1,2 power supply kg), rifle operation is facilitated, as a soldier uses a familiar sight with a familiar scale when firing at night. The device is equipped with an automatic brightness control and receives current from two standard batteries, guaranteeing its continuous operation for 90 hours. The NSA 80 is also the standard night sight for the Panzerfaust 3 grenade launcher and the MG 4 machine gun.
 A complete rejection of the mechanical sight was quite a bold step on the part of the military, but it gave rise to a number of problems associated with the operation of optics. When it rains or at high humidity, optical sighting devices may mist over, they are very sensitive to the ingress of dirt and mechanical effects. Since the manufacturers did not provide protective devices for optics, in Afghanistan the soldiers of the Bundeswehr made their covers for sights from cloth. Now, however, German firms have established the production of such camouflage covers. Such a case is fastened on an eyelet to the carrying handle and has a velcro-lock that allows you to quickly remove it from the sight with lightning speed.
A complete rejection of the mechanical sight was quite a bold step on the part of the military, but it gave rise to a number of problems associated with the operation of optics. When it rains or at high humidity, optical sighting devices may mist over, they are very sensitive to the ingress of dirt and mechanical effects. Since the manufacturers did not provide protective devices for optics, in Afghanistan the soldiers of the Bundeswehr made their covers for sights from cloth. Now, however, German firms have established the production of such camouflage covers. Such a case is fastened on an eyelet to the carrying handle and has a velcro-lock that allows you to quickly remove it from the sight with lightning speed.
The mechanical sight (more precisely, some of its similarity) on the G36 is still present. It is a simple fly and a primitive slot on the carrying handle, but it is impossible to use it because of the installed collimator sight. It is necessary only for some models of export rifles supplied without a collimator. The presence of this rudimentary sight gave rise to one of the most popular in the Bundeswehr jokes about G36. Its essence lies in the fact that in a combat situation in the event of a breakdown of the optics, it is prescribed to bring down the collimator with a handy heavy object in order to take advantage of the backup mechanical sight. However, in practice it is impossible - trying to knock tightly, the optics planted and fastened with screws will not lead to anything except for the failure of the handle itself and all three sights.
The G36 rifle magazine holds 30 rounds - 10 more than the G3 magazine. In addition, its body is made of transparent plastic for visual control of the flow rate of cartridges. On the side surface of the stores there are two protrusions, allowing to connect them together. Similarly, without the use of adhesive tape or special fastening clips, you can combine up to three stores, increasing the ready-to-fire and ammunition worn with weapons to 90 cartridges. This bundle of stores is recommended to be used when installing the NSA 80 night sight, since additional stores compensate for the change in the position of the center of mass of the weapon caused by mounting the forward-shifted sight. The method of connecting plastic stores is somewhat reminiscent of the principle of the Lego children's designer, so G36, which has a large number of plastic parts, was nicknamed "Lego-Gewehr" ("Lego-rifle").
When performing special tasks, the G36 can be equipped with the Beta C - Mag drum shop from the MG36 light machine gun with an 100 cartridges capacity. This shop consists of two drums for 50 cartridges laid inside the "snail". Its weight with cartridges is 2 kg.
Also optional for the G36 is a pip. It is mounted in front of the forearm. In the stowed position or when shooting with the hands, the bipod racks can be folded, located under the forearm. The length of the racks is 27,5 cm, weight - 0,21 kg. At the ends of the racks there are thickenings with holes with a diameter of 10 mm. These holes are used for mounting ski poles when shooting from skis.
Thanks to them, a comfortable and high support for standing is constructed from ski poles and a bipod.
G36 rifle belt is a multifunctional design. It is made of high-strength nylon and made double, so that the rifle can be worn in addition to classical methods - behind the shoulder, across the back or across the chest - also biathlon (like a backpack behind), at the hip or hunting. The length of the belt is adjustable (maximum 2 m), width 2,5 cm, weight 110 g. The only part borrowed from the G3 belt is steel carbines. The front belt is attached to the swivel in the front of the forearm, behind - depending on the individual characteristics of the shooter. Right-handers can fasten a belt to the antab on the left side of the receiver, left-handers have the opportunity to attach the belt to one of the holes in the butt that serve to place the axes during disassembly. There is another option for attaching the belt, suitable for both left-handed and right-handed users - with one more hole located in the back of the butt.
Versions
MG36 - light machine gun based on the G36 rifle. The military wanted an assault rifle and a light machine gun of the same caliber armed with an infantry unit. Therefore, MG36 should have entered service as an addition to the MG3 single machine gun, but this did not happen. The light machine gun differed from the base rifle only by a slightly weighted barrel, a larger magazine and the presence of a bipod. The MG36 machine gun could not conduct a long automatic fire, so after long deliberation it was decided to equip the troops with a new MG4 machine gun of 5,56 mm caliber with a quick-change barrel and belt feed. They refused to equip the troops with MG36 machine guns, making a compromise decision: the fry and the drum shop were supplied to G36 as additional accessories. With them, G36 is used as a light vehicle for infantry fire support.
G36K (Short) - shortened version with a barrel length 318 mm. Designed for the KSK Special Forces. The length of the weapon with folded butt 615 mm, and the weight, compared with the base version, reduced by 0,33 kg. Due to the shortening of the barrel, a slightly different flame arrester design was used. On the right side of the forearm can be mounted IR-laser, on the left - a tactical flashlight.
G36C (Compact) - An even shorter version with the 228-mm barrel. Equipped with a pikatini strap. In Germany, used in the KSK, combat swimmers and military police.
G36V(previously designated G36) - export version in which the collimator sight, and the standard optical sight is replaced by a simplified 1,5-multiple.
Detailsincomplete disassembly G36
G36KV (G36KE) - shortened export version.
G36A1 - A modernized version. Delivered to troops from 2002 year.
G36A2 - second rifle upgrade (2004 year). It has a new collimator sight and a modified forearm with a tire for mounting tactical accessories (usually LTS LLM-01).
G36KA1 и G36KA2 - modernized shortened versions. Level "picatini", a tire for accessories under the forearm, it is possible to install a silencer. Unlike the KA2, the KA1 variant does not have an integrated optical sight.
SL8 - civilian version of G36, developed primarily for reservists. In accordance with Article 37 of the German Weapons Act, a number of design changes are made in it that do not allow the rifle to be classified as military weapons: the automatic fire mode and flame arrestor are removed, the magazine capacity is limited to 10 cartridges, the folding butt is replaced with a permanent cheek piece, - the extended tire for installation of various types of sights. Other differences include a thickened and somewhat elongated barrel, butt adjustment in length, reduced descent force, due to the sporty bias of the model.
SL9 - sniper rifle based on SL8 chambered for 7,62x37 (developed by H&K based on the .300 Whisper cartridge). A muffler is installed on the 33-cm barrel, which not only reduces the noise of the shot, but also modifies it so that it does not look like a normal shot. Used in the anti-terrorist GSG-9.
G36 rifle was very well thought out and respectable design. When accepting rifles by the military at a range of 100 m, the STN series deviation from 5 shots is no more than 6 cm and the radius of dispersion is not higher than 10, see. The accuracy and accuracy of G36 shooting is much better than these standards.
It should be noted extremely low returns, making shooting even automatic fire very comfortable.
The large pulse of the 7,62x51 cartridge of the G3 rifle led to a strong dispersion of hits in the queues, so the charter ordered firing from it in short bursts only "when a numerically superior enemy suddenly appeared in a short distance." In other cases, it was prescribed to conduct shooting single shots. On the contrary, G36 is perfectly controlled when firing automatic fire and allows you to conduct accurate shooting in short bursts, even from unstable positions. Shooting from G36 is more acceptable for women who make up today the 15% of the Bundeswehr contingent.
Another plus G36 - ergonomics. The controls are conveniently located, equally accessible to control the right and left hand. The cocking handle is foldable and does not interfere with the carrying of the weapon, and there is also no risk of it catching and accidentally taking the bolt back.
The protruding parts of the rifle is very small. The telescopic sight is located low, but it is quite convenient for aiming, since shooting with it is mainly conducted from a prone position. On the contrary, the upper arrangement of the collimator is favorable when shooting while standing and from the knee. Thanks to the use of plastics, G36 is one of the lightest assault rifles.
To date, a total of 36 countries have purchased the G35 rifle, and in the armed forces of Germany, Spain, Latvia, Lithuania, Indonesia and Malaysia, it has been adopted as a standard model of infantry weapons. The G36 and its compact versions are especially popular in various police services, border guards, among "commandos" and special forces. The G36 was well received in the German army, although a number of shortcomings made it the target of criticism. The most serious of them are low reliability with very heavy pollution and the absence of a mechanical sight. It is possible that these shortcomings will be eliminated in a new assault rifle, which is currently being developed at Heckler & Koch as a replacement for the G36.
- I. Shaidurov
- http://kalashnikov.ru"rel =" nofollow ">http://kalashnikov.ru





Information