Combat amphibious assault vehicle "Wiesel" and "Wiesel-2" (Wiesel)
Germany was one of the first to start the formation of the airborne troops and the first to widely use them during the fighting in 1940-1941, but for a long time remained aloof from the "mechanization" of the landing forces. Here they were considered as light highly mobile infantry and limited to only partial "motorization" in the form of half-track motorcycles, although plans for landing tanks and existed. Having begun in 1957 the revival of the airborne troops, the FRG retained the same approach. In 1971, the Bundeswehr adopted the concept of a wider use of airborne assault forces: in an offensive, airborne brigades were to be thrown to a depth of 80-100 km in the interests of army corps, and on defense serve as an airborne reserve. This required greater independence, maneuverability, more difficult weaponsand that means own vehicles. The 1 airborne division (25,26 and 27 brigades) and the airborne detachments of the 1 mountain rifle division began to receive light vehicles "Kraka640" company "Faun" (KRAKA - from Kraftkarren, which can be translated as "two-wheeled motor") . This non-four-wheel-drive car with an opposed two-cylinder engine and a folding frame (originally created, by the way, as an agricultural motoblock), in addition to transport targets, was used to install heavy weapons - recoilless guns, anti-tank missile systems (ATGM) Tou or Milan, automatic guns Rh202.
But at the same time, it was already planned that the airborne forces would receive light airborne assault vehicles. There were samples such as the American air assault tank МХNUMX "Sheridan" or the Soviet military transport vehicle BMD. The Germans decided to create a small armored vehicle, primarily as a weapon carrier for the replacement of the Krak (new all-wheel drive vehicles were considered as vehicles and special vehicles). Accordingly, the armored vehicle required a combination of compactness with a load capacity not less than that of the Krak, a sufficiently high operational (transport by medium military transport aircraft and transport helicopters, landing and parachute landing) and tactical (speed, throughput, power reserve, throttle response, turning ) mobility, the minimum necessary armor protection and ease of management. Requirements for such a machine were transferred to Porsche in the middle of 551 for the development of a draft design.
The car was supposed to serve as a carrier of the 20-mm automatic cannon, the Khotrovo Hot Tank (in development) and 120-mm mortar with ammunition, while being transported by C-130 Hercules and C-160 Tranceall helicopters and CH helicopters -53G, parachute on the parachute platform, so the machine’s own weight was limited to 2,75 t, length - 3,3 m, height to the body - 1,3 m. After reviewing the draft design, military experts issued updated tactical and technical requirements. In particular, the mass was reduced to 2,5, in the version of self-propelled ATGM the French-West German system “Hot” was replaced with the American “Tou”, the crew was increased to 3 people. The CH-53G transport helicopter was supposed to transfer two cars in a cargo cabin or one on an external sling. 5 July 1973 of the Army Command approved the project Waffentrager LL (“airborne weapon carrier”, in the future we will use the definition of “airborne assault vehicle” or BMD) to arm airborne brigades. In accordance with the tradition of giving predatory names to combat vehicles, the BMD was called Wiesel (Wiesel).
The project was attended by five West German companies - Porsche, Faun (the creator of the car Kraka), GST, IBH, Reinsch-tal. "Faun" took up the project of wheeled armored vehicles, the rest - tracked. 18 April 1974 Porsche was announced as the general contractor for the project.
October 9 1975. Porsche, together with the company KUKA, presented a full-size wooden model of the future version of the Wiesel machine with a 20-mm automatic cannon. Back in April, 1975 determined the size of the future order - 270 machines (170 with Tou ATGM and 100 with 20-mm cannon), which later could be brought to 500 (170 and 330, respectively). The company should have delivered the first batch of BMD in February 1977 - May 1978. In parallel with this site, the companies KUKAH "Tehdok" began the preparation of a set of operating and maintenance manuals for the new machine. And in October — November 1977, the 1-I school of technical troops in Aakheiye and the school of the airborne troops in Altenstadt began to prepare relevant training programs.
However, starting with 1975, Porsche built only six prototypes of an armored vehicle weighing about 2,5 tons with a 2 — 3 human crew and a commercial carburetor engine. The problems of developing a machine that fits into such severe restrictions have forced us to shift the deadlines for completing the project.
There was a kind of revival of the idea of the wedge, because the “classical” wedge, the British Carden-Lloyd, was once carried out in variants of the reconnaissance vehicle, the carrier of anti-tank and anti-aircraft weapons. After World War II, they tried to return to the wedge heels. For example, in France in 1953 — 1958. 1,5-t tested armored tracked chassis VP-90 (by the way, with the engine "Porsche"), but did not take it into service.
Combat amphibious assault vehicle "Wiesel".
In 1978, the German Ministry of Defense for financial reasons terminated the contract with Porsche, and the company transferred the rights to revision and production of a new Krupp-Ma K machine.
By that time, apparently, the choice between tracked and wheeled PM was not finally made (although it was still at the stage of preliminary design that the wheeled vehicle did not fit into the weight and size limitations). So, at the exhibition “Armored wheeled and tracked vehicles”, held on 3 in September of 1981 in Hammelburg, two prototypes of the Wiesel tracked vehicle were shown, but a little later, Daimler-Benz presented its prototype wheeled machine (4XXNNXX formulas). Nevertheless, in March, 4 was given a task to continue the work on tracked PM. Requirements for the car continued to clarify.
At 1984, Krupp-Ma K presented two prototypes of a machine with an 20-mm cannon and a Tou ATGM at an exhibition of weapons in Athens and announced plans to refine it - in particular, to replace the 2-liter 5-cylinder carburetor engine Volkswagen diesel engine with turbocharging.
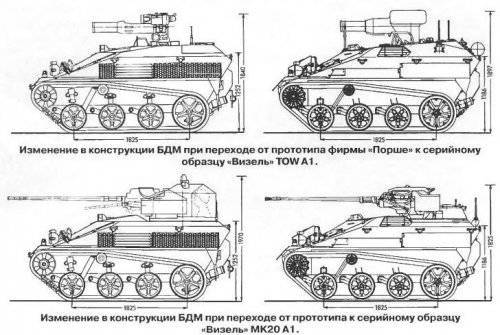
The development of 20 variants was proposed, including a command and control vehicle, a self-propelled air defense missile system, a mortar, a flamethrower, a commander, communications and ambulance vehicles, as well as a conveyor on an extended chassis. In 1986, the Bundeswehr tested four advanced prototypes with a diesel engine and an automatic transmission instead of a semi-automatic one. In the process of refinement, both the design details and the appearance of the paper machine were changed. In connection with the new power unit and the finalization of the weapons installation, the roof above the engine, the driver's seat and the roof of the fighting compartment were raised, the blinds on the port side moved higher. The brackets, the location of attachment points on the landing systems, the manhole covers, and the installation of antennas have changed. The undercarriage underwent changes in the drive wheel and the stops of the balancers of the road wheels. The decision on the adoption of the "Wiesel" was adopted by 5 June 1987.
In 1988, Krupp-Ma K was contracted to supply 312, and at the end of the same year - 31 machines (total 210 in Tou option and 133 in MK20 version with automatic gun). The total cost of the order was 208 million. West German brands.
Later, the number of machines ordered was brought to 350, of which 210 with the Tou ATGM, and the rest with a cannon. Deliveries of the Wiesel to the Bundeswehr were calculated from September 1989 to December 1992.
Wiesel has ripened to reorganize the airborne troops of the Bundeswehr under the program "Structure-2000", and great hopes were pinned on this small car. In the spring of 1990, the commander of the 1 Airborne Division (Airborne Division), Major General G. Bernhard, stated that with the Wiesel, airmobile forces would be able to defend positions on a larger front and greater depth. Playing the role of cover, airmobile units will be able to withstand the mechanized enemy. Wiesel will allow the blocking forces to be closer to the enemy, ground reconnaissance will not be limited to foot patrols. ” That is, the actions of airborne assault forces became more active and more maneuverable in the context of the supposed "struggle against the Soviet armored armadas." 1 August of the same year, the 1-I Airborne Division received the first two serial Wiesel PMs. Earlier, seven vehicles were purchased by the United States for testing in the 9 Infantry Division. Norway, Greece, the United Arab Emirates, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Thailand also showed interest in Wiesel. As a result, BMD was tested in the conditions of the desert, the tropics, in the "Arctic" conditions.
Krupp-Mak Mapshienbau in Kiel became the main contractor for the production of Wiesel, subcontractors — Jung-Ugental (building), Volkswagen-Werke (engine), Tandradfabrik Friedrichshafen [T ¥, transmission), “Clowes”, “Dil Remscheid” Caterpillars), “Rheinmetall” (20-mm cannon), C & V- “Vertechnik” (tower). The 1989 Xenumx for the German Bundeswehr was built 1992 machines "Wiesel" ("Wiesel" A345).
Description of the construction WDM.
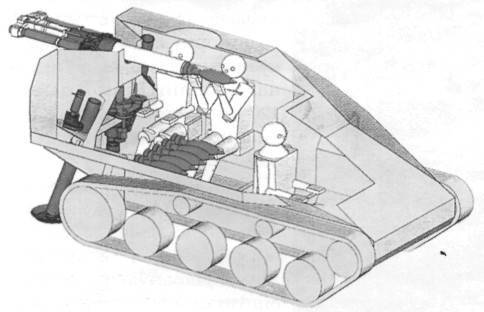
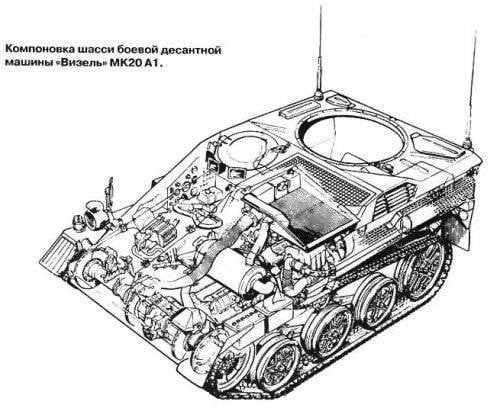
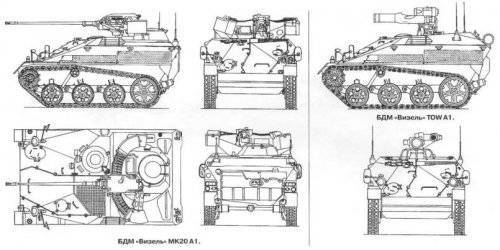
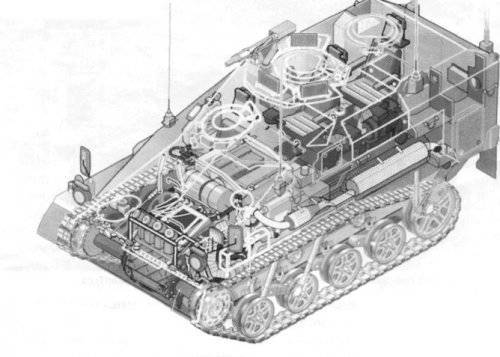
Wiesel has a layout with a front-mounted gearbox compartment. Right and slightly behind it is the driver's seat. In the stern of the shooter is located (he is - the commander of the machine) or the calculation of ATGM. The car body is welded from sheets of rolled steel armor and is designed to protect against bullets of small arms of caliber 7,62 mm and light fragments of artillery shells and mines. Security is somewhat increased by the slope of the armor plates, as well as by the front engine, but the main protection of the car is its mobility and low visibility. The upper frontal sheet is set at a large angle of inclination and is bent at the edges, forming a frontal cheekbones. In its left part there is a large manhole with a hinged lid, in which there is also a small oval hatch. On the right side of the sheet is made the second hatch for transmission service. The sides of the hull with direct and reverse tilt resemble German armored vehicles from the Second World War. The roof of the case is raised in the middle part in order to knead the engine cooling system and the place of the driver. For the last in the roof there is a hatch with a flip-up lid. In the back, depending on the version of the machine, a single tower with a round hatch is installed, or a wide hatch is made in the hull roof with a hinged up-back cover.
In front of the case on the left there is a power unit, which unites the engine, transmission units, cooling system and air cleaner. Engine - 4-stroke in-line 5-cylinder diesel
Volkswagen turbocharged. Engine displacement is 1,986 L, cylinder diameter is 76 mm, piston stroke is 86 mm. The maximum power (86l.s.) develops at the rotational speed of the crankshaft 4500 r / min, the maximum force - at 2750 r / min. Blinds of a radiator of water cooling are executed in a roof of the case. There is a preheater. The exhaust pipe is derived from the left side along the fender, equipped with a silencer and a mesh grid that reduces the temperature (and hence the thermal signature) of the exhaust gases. At the stern of the car, a protective tank with a capacity of 80 l, made of fiberglass with rubberized fabric, providing self-sinking of small holes, is installed. Polyurethane foam filler prevents an explosion when the tank is punctured by a bullet or splinter.
The T ¥ ZNR22 transmission includes an automatic three-speed planetary gearbox with a torque converter, a two-stage output gearbox, a Keltrek-type differential turning mechanism with disc brakes and final drives. The transmission gives three speeds when moving forward and two speeds back and together with a high (about 31 hp / t) power density of the engine provides high mobility and acceleration. From a place, the car is on a flat road in 5 from accelerates to 32 km / h, in 28 from - to 75 km / h.
The stop foot brake has a hydraulic drive, the hand parking is mechanical. Again, as in the old wedge heels, commercial machines were widely used in the Wiesel. Motion control with the help of a semi-steering wheel is not much different from a car, which speeds up the development of the car by the crews. Quick disconnect connections of pipelines and cables allow replacing the power unit in field conditions in 15 min.
The chassis is somewhat unusual for modern armored vehicles. First of all, it is distinguished by the rubber caterpillar "Dill-Kette". The rubber tape is reinforced with steel cord (wire), which perceives traction, and steel cross-pieces, defining the track pitch, are vulcanized inside it. The outer surface of the truck is divided into squares for better grip.
Previously, solid rubber tracks of a similar design were limitedly used on light transport vehicles, attempts were made to put them on wedges - the American Marmont Harring-Tone (1935) and the French UR-90 (1953) mentioned.
The chassis of the Wiesel includes on board three dual track rollers and a single support roller. The road wheels have an individual torsion bar suspension, vertical 170 stroke mm, spring arm buffers. The guide wheel is also suspended on the lever, to increase the bearing surface is lowered to the ground - a technique popular in 1930 — 1940-rm. With a diameter it exceeds the track rollers and has a vertical stroke of 150 mm. To facilitate the rollers are skitsovannymi and not rubberized. On the front suspension assemblies installed hydraulic shock absorbers.
Stamped drive wheel - front, gearing caterpillars - for the central ridge. Tension adjustment is made automatically by a special mechanism. The length of the track bearing surface is 1,83 m, the track width is 1,62 m. Such a ratio (1,13: 1) provides high tilting, and low specific pressure provides permeability. The normal turning radius is 7,2 m, with the use of parking brakes 4,7 m, with one slowed track, the turn is made on the spot. In speed and power reserve, the Wiesel tracked armored car surpassed the unarmored Krakas, and even more so surpassed it in all terrain. The small length of the bearing surface reduces the forces on the belt when turning and the danger of its twisting and falling. The rubber track facilitates the chassis, provides cushioning of support rollers, reduces running noise, does not destroy the road surface. Low resistance to combat damage, apparently, was not taken into account, based on the characteristics of the use of the machine - in the rear of the enemy and almost "one-time". Fenders are complemented at both ends with stamped wings and rubber dirt breakers.
The BU! -BEM 80 radio station (linear machines have one such radio station installed, two commanding radio stations), working on whip antennas installed in the stern, they lean forward during transportation. It is possible to equip the Wizel machine station with radio stations of the general military information and control system NESSGZ. Three periscopic viewing units are installed in front of the driver's hatch, the middle unit can be replaced with a night vision device. In the front of the case, folding mirrors are reinforced. Headlights are installed ahead, next to them on the fencing shelves - - parking lights. Protection systems against weapons of mass destruction is not provided. The SPTA boxes, camouflage net, towing cable and entrenching tools are mounted on the right fusible shelf and upper front plate. When landing and on the march, the tower or launcher may be covered with a cover. There are towing earrings at the front and rear of the hull, and along the perimeter of the hull there are vehicle attachment points on the landing craft or in the cargo cabin.
Modifications.
The main options for PM are different armament complex.
Wiesel MK20 A1 is armed with an automatic cannon in the E6-H-A1 KiKA single-seat turret with a mounted installation. The gun and two ammunition boxes are mounted on the three brackets to the turret. Even during the development of Wiesel, it was planned to arm the 25-mm Mk-25 "Mauser" cannon, but it was rejected by the Bundeswehr, and the BMD armed the 20-mm Mk20 Yap202 "Rhinemetall", which had a good reputation on the Marder BM, the BM, the BM, and the Bremer Surveillance Unit. "And as anti-aircraft. The gun has an automatic with a gas engine (removal of powder gases), double-sided tape; Part I, designed to combat ground and air targets. Maximum shooting range - 1000 shots / min. The ammunition includes shots with armor-piercing and high-explosive fragmentation projectiles. Subcaliber armor-piercing projectile with an initial speed of 1300 m / s punches at a distance.
1000 m armor thickness up to 20 mm at the meeting angle 60 °. The ammunition is 400 shots, 160 of which are loaded into ribbons and ready to fire. Curved armored ammunition boxes provide protection for the artillery unit, cartridges are supplied through flexible hoses.
In the left box there is a ribbon for 60 ammunition with an armor-piercing projectile, in the right box - for 100 ammunition with a fragmentation projectile. Another 230 (according to other data - 240) cartridges are placed in piles in the aft hull. The angle of horizontal rotation of the tower is 110 ° in both directions, the elevation angle of the installation 1-45 °, the declination of 10. For guidance is a periscopic sight with variable magnification and independent stabilization of the field of view, there is a laser range finder. Provides for the installation of night goggles. For training can be used laser simulator shooting BT-46 SAAB Swedish production.
Already in 1997, Mauser Werke offered to re-equip the Wiesel with its 30-mm RMK30 automatic cannon for a telescopic cartridge, but this proposal remained unfulfilled.
Wiesel TOW A1 is armed with the Tou ATGM system of the American company Hoes Aircraft. The launch tube with a sight and control equipment is mounted on a swivel base with a horizontal angle of 45e in both directions, elevation and declination angles of 10 ". The minimum firing range is 65 m, the maximum - 3750 m, guidance of the ATGM is semi-automatic with command transmission by wire .To attach the 1 launcher, the hinged support serves as a stopover. The open remote installation of ATGM allowed to place a crew of two people in the stern, which should shoot out of the hatch in front of the hatch. There are also ammunition from seven ATGMs in transport and launch containers (two of them are ready for immediate loading after the shot is in PU): it is believed that after launching two ATGMs, the self-propelled ATGM should change position. ATGM BGM- can be used 71C with 600 mm brokability or BGM-71 with a tandem warhead and 700 mm equivalent brobe penetration mm. It is possible to use the BGM-71F ATGM hitting the target from above. An AN / TAS-4 thermal imaging sight can be mounted on the PU. Later, TOW installed a launcher with a new sight designed for the use of BGM-71D ATGM with 152 mm BGM-71E ATGM (TG-2 ATGM and Tou-2A ATGM) designed to combat Soviet T-tanks. -72 and T-80 with dynamic protection).
It is possible to land the BDM by parachute method (on the 4-ton modular parachute platform), however, preference was given to landing landing from airplanes during the landing of an operational landing force or by a helicopter during a tactical landing. Transport Boeing 747 accommodates 24 machines, C-5 Galaxy - 30, C-141 Starlifter - six, medium military transport C-160 "Transall" (standard in the German Air Force) - four, C-130 "Hercules" - three. To load the Wiesel on the platform, an airfield loader is used. The regular medium transport helicopter of the Bundeswehr CH-53G transports two Wiesel PMs in a cargo cabin or one car on an external sling, these are also the capabilities of the Chinook CH-47 helicopter. 14-60A Black Hawk or Super Puma helicopters can deliver one Wiesel BDM on an external sling. Krupp-Mak offered a removable “buoyancy kit” for the Wiesel, but it did not enter the order given to the company by the Bundeswehr.
The Bundeswehr also adopted the self-propelled radar ground reconnaissance RATAC-Sha landing gear "Wiesel" for reconnaissance battalions and artillery reconnaissance platoons. The radar was developed by Standard Electronics Lorenz together with the French Thomson and belongs to the pulse-Doppler frequency range 9,4 — 9,6 GHz. The antenna and transceiver are mounted on a lifting boom (lifting height up to 12 m), a digital signal processing system and a console with a display are inside the case. The station is used to detect and track targets in automatic or manual mode with the trajectory displayed on the display. The detection range of ground and low-flying targets is up to 35 — 40 km (at an elevation of the antenna), the accuracy of determining the coordinates is up to 10 m.
Also developed a number of other variants of the machine, remaining experienced. One of them was a light combat reconnaissance vehicle with a twin installation of 12,7-mm and 7,62-mm machine guns in the single-sided SAMM BTM 298 or BTM 108 turret. The option of installing a turret with a self-loading (automatic) 60-mm mortar and 7,62-mm machine gun was also offered.
A self-propelled ATGM with an ATM (Anti-Tank Modular) turret of the Euromissil consortium was presented, equipped with two Hot-Tactical missile launchers “Hot” (firing range up to 4 km), two-channel periscopic sight, television and infrared equipment on the extendable rack and 7,62-mm MG3 machine gun. The advantage of this option was the launch of the ATGM operator “because of the reservation,” but it was not put into service either in the Federal Republic of Germany or in France, where the British were tested. Later, for the Wizel, a turret with a Milan-2 ATGM was developed, as well as a new turret with an ATGM “Hot” and a set of heat and television equipment on a retractable bar. An ammunition transporter was also developed to replenish the Wiesel ammunition TOW A1.
The ASRAD / RB90 self-propelled air defense system was used in the Wiesel chassis of the Wiesel chassis using the RBS-70 Bofors man-portable air defense missile system. SAM can be used against both airborne and lightly armored ground targets. The roof of the hull is slightly raised, the installation with four missiles, the Atlas Electronic sighting system and a laser control system are mounted on the swiveling turret.
The US Department of Defense was considering the possibility of creating a crew-less “robotic battlefield machine” on the Wizel A1 base. Wiesel also served as a workhorse in more than one such program in Europe. An example is the PRIMUS complex assembled by the Dornier company (ЕАДС concern) on the landing gear chassis of the Wiesel aircraft. It includes a robotic machine with a video camera and a laser locator for viewing the terrain, a digital navigation system, an autonomous motion, decision-making and control module, as well as a self-propelled remote control point.
On the combat use of BMD "Wiesel".
By the time the delivery of the Wiesel W1 modification was completed, the reunification of the German Bundeswehr under the Structure-5 program began. Based on airborne brigades and army regiments aviation began to form airmobile connections, at the same time, rapid reaction forces were created. By 1995, the airborne brigade (UBR) was armed with 46 Vizel PM TOWA1 and 30 Vizel MK20A1, while each anti-tank company had nine TOWA1 Wizels and six MK20A1 Wizels. Eight CH-53G helicopters or four S-160 aircraft could be used to transport such a company. In addition, 16 TOW WIZEL PMs entered the anti-tank company of the 23rd Mountain Infantry Brigade (also included in airborne forces). The 25th Armed Forces battalion was included in the national airborne forces, it was also intended to be allocated to the UN peacekeeping force. In 27, the 31th Airborne Forces and the 1993st Mechanized Brigade were reorganized into the 31st Airborne Brigade and a year later included in the multinational airmobile division "Center" of the NATO Rapid Reaction Force. The 26th Armed Forces battalion was directly transferred to the NATO RBF.
Wedge wedge in Afghanistan.
The first "overseas business trip" of Wiesel cars was the participation of the German contingent in the UNOSOM-2 operation in Somalia, where the "blue helmets" of Germany arrived in the summer of 1993. Although airborne operations were not conducted here, of all the Bundeswehr armored vehicles, according to German specialists, " Wiesel A1 in its compactness and mobility was most suitable for solving patrol and reconnaissance tasks. After the NATO aggression against Yugoslavia in 1999, the German contingent entered Kosovo as part of KFOR, here the Wizel A1 BDM (as in Somalia - in both versions) was also used to patrol roads. However, the NATO forces, as is known, did not bring peace to Kosovo.
Wiesel-2.
During the development of Wiesel, it was proposed to create a more spacious version with an undercarriage elongated by one support roller. At the beginning of the 1990's NATO increasingly began to assert its influence by "peacekeeping" operations. The principle of non-use of the German armed forces abroad ceased to be mandatory, it took to expand the capabilities of combat vehicles of the rapid reaction forces.
The layout of the machine gun "Wiesel-2 in the version of the ammunition conveyor.
In the middle of 1994, the Mac Systems Gesellschaft (Kiel) presented a prototype of the Wiesel-2 PMM, developed on a proactive basis. Later, the Mac Systems was absorbed into the Rhinemetal Landsystem (included in Rheinmetall DeTECAG).
BDM "Wiesel-2" retained the layout scheme with the location of the MTO in the front of the hull on the left, the place of the driver to the right of the MTO and the fighting (amphibious) branch in the rear part. Somewhat changed the body of the machine. Upper front sheet continued back, so that the driver's door is already made in it. Three periscopic viewing units are installed in front of the driver's hatch, the middle one can be replaced by a backlit night vision device. Behind the driver in a protruding wheelhouse with the top hatch is placed commander. In the stern sheet of the hull there is a double door.
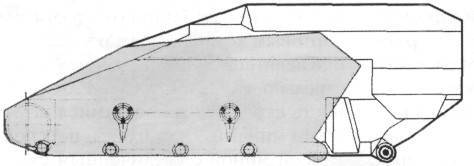
Comparison of the dimensions of the housing Wizel (in gray) and Wiesel-2.
In the undercarriage, a fourth track roller and a second support roller were added from each side, the length of the support surface increased to 2,43 m, shock absorbers were installed on the first and second suspension units.
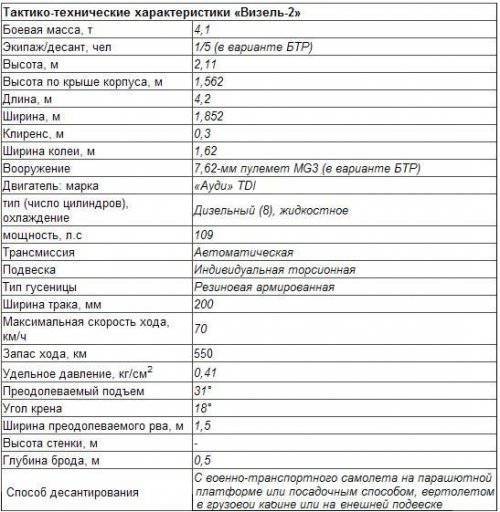
Wiesel-2 received a commercial-type Volkswagen-Audiia-TDI diesel engine equipped with a turbo-supercharger and developing HP 109 power, automatic transmission ZF LSG 300 / 4 (it was supposed to test electric transmission on experimental machines) and hydrostatic turning mechanism. Hydromechanical transmission includes: an automatic planetary gearbox with integrated hydrodynamic transmission, a steering mechanism assembled in one case with the gearbox, and two final drives. The gearbox has two modes of operation - for driving on highways and over rough terrain - and provides four forward and two reverse speeds. The rotation mechanism is a double controlled differential, at the ends of the shafts of which brakes are installed, the servo control system of the turn and brakes is hydrostatic. Turning radius - 4 — 6 m. The electronic control system allows you to “adapt” the operation of the engine and transmission to the combat weight of the vehicle (depending on the modification) and driving conditions. New tracks “Dil Type 622” with an increased resource are installed. Power reserve increased to 550 km by increasing the capacity of the fuel tank. The on-board network has a voltage of 24 volts, powered by two 12-volt batteries with a capacity of 45 Ah each.
The command and command vehicle on the Wiesel-2 chassis.
One can see the desire to create a family of BMD, somewhat resembling the Soviet BMD-BTR-D, although it is based on different approaches. It is worth noting that the Wiesel family is more adapted for tactical (helicopter) landings. A CH-53 helicopter can transport two Wiesel-2 cars in a cargo cabin, one Wiesel-2 can be deployed on an external suspension with a CH-53G or CH-47 helicopter. In 1994, the Bundeswehr entered into a contract with Rheinemetall Landsystem for the supply of 32 BMP Wiesel-2 during 2005 — 2007.
With the same aero-transportability and mobility, Wiesel-2 complements Wiesel A1 machines. Wizel-2 can be transferred by the same aircraft and helicopters, but the number of cars being transferred is on average one less: accordingly, in the C-160 “Transall” cargo compartment, you can transfer 3 machines, C-130 “Hercules” - 2, helicopters CH-53G - 1. At the same time, the almost doubled habitable volume allowed us to carry out a family of amphibious assault vehicles on the base of the Wizel-2. Among them are the combat reconnaissance vehicle, light armored personnel carrier, transport, sanitary-evacuation, command and command vehicles, self-propelled 120-mm mortar, radiation and chemical reconnaissance vehicle.
The Wizel-2 BRM is equipped with a complex of reconnaissance equipment, including a laser range finder, a thermal imaging and television camera, and a satellite navigation equipment mounted on a retractable mast, equipped with a machine gun.
The BTR has a 6 man's capacity, as well as the BRM, armed with an 7,62-mm MG3 machine gun above the rotating turret of a vehicle commander in the middle of the hull. Ammunition machine gun - 500 cartridges. Along the perimeter of the commander's turret installed 8 periscopic viewing units.
Presented in 1998, the KSHM Wiesel-2, with a crew of 3, is equipped with stations of the HERGIS information management system (developed by Siemens, Sema Group and InfoDas) with 7-inch displays, two VHF radio stations and one KB range and satellite navigation equipment. Such a machine was offered as an advanced point of reconnaissance and fire control of artillery, arming it for self-defense by a machine gun installation. Ammunition machine gun - 200 — 500 ammunition.
Sanitary evacuation vehicle on the Wiesel-2 chassis (SanTrp).
A transport vehicle on the Wiesel-2 chassis with a payload in 1,0 t is offered primarily as a conveyor of ammunition and can carry, for example, 20 shots to 120-mm mortar or 150 to 81-mm. It can also carry 22 — 27 20-liter fuel or water canisters.
The Wiesel-2 (SanTrp) sanitary-evacuation vehicle was demonstrated at 1997 and interested in the Bundeswehr. The machine has an enlarged hull with a large lump door, a crew of 2 people, in the aft hull of the hull you can place one lying (on a stretcher) and two sitting wounded, in another version - two lying injured (in two tiers) and one sitting or four sitting. In addition to medical equipment and first-aid equipment supplied by the German company Binz, the machine can be equipped with a water heater, HLF and air conditioning.
Self-propelled mortar on the chassis "Wiesel-2" and its layout.
Wiesel-2 was also proposed as a tractor-conveyor for 81-mm or 120-mm mortars equipped with a wheel drive. Calculation and mortar ammunition (20 shots for 120-mm or 75 for 81-mm) is transported inside the case.
Self-propelled mortar, presented by Rhinemetal Landsystem, has a crew (crew) 3 person. The 120-mm muzzle-loading mortar with wheel chops is mounted openly in the rear of the Wiesel-2 case. The stern also mounted two folding-opener jacks. In the stowed position and for loading the mortar barrel is lowered into a horizontal position, which allows the calculation to make loading of the mortar, while remaining under the cover of armor. To speed up the preparation of data for shooting and increase its accuracy, the machine is equipped with an on-board computer and an integrated navigation system. The rate of fire - 3 shot for 20 with, firing range of existing mines - up to 6,3 km, promising mine with increased replaceable charge - up to 8 km, ammunition load - 20 shots. On the same chassis can be performed transport-loading machine.
The Wiesel-2 chassis turned out to be more convenient for continuing work on the air defense system of the battlefield or light air defense system (LeFlaSys - Leichtes Flugabwehr System), designed for use by the rapid reaction forces. The complex was developed by order of the Bundeswehr firm STN "Atlas Electronics" with 1995 g .; in 1997, it was represented as part of three vehicles - a self-propelled air defense missile system, a self-propelled reconnaissance and fire control station and a surveillance vehicle. The first two are made on the Wiesel-2 chassis, the last on the Mercedes-Benz Wolf chassis (4x4, the car is designed for parachute landing from an airplane). Then the car of the UF / BF battery commander was introduced - also on the Wiesel-2 chassis.
The self-propelled short-range air defense missile system, known as the Ocelot (already tested in 2001), carried a remote-controlled rotary launcher in the stern (similar to the A1 tested on Wiesel), which can accommodate four missiles at the TPC from Stinger ". There are also options for the installation of missiles from Igla-1 MANPADS (the complexes remaining from the NNA GDR are used in the Bundeswehr for training) and RBS-70. Firing range - up to 6 km. The launch angle of the launcher horizontally is 360 °, vertically is from -10 to + 70 °, the launcher can be lowered for transportation of the Ocelot launcher by CH-53 helicopter. Installation reloading - manually.
The Ocelot SAM system is also equipped with the Gyro MK20 BGT orientation system, GPS PLGR AN-PSN satellite navigation equipment, SEM 93 VHF radio communication equipment, the British passive air warning system ADAD
Self-propelled PU complex "Ocelot".

Self-propelled reconnaissance and control station of the Ocelot air defense missile system.
"Tails Optronics" (the range of detection of the target type "aircraft" - up to 18 km, "helicopter" - up to 8 km). This allows the complex to act independently without targeting from the side. The calculation of the air defense system consists of a driver and commander. The combat mass of the SAM "Ocelot" - 4 t.
The self-propelled reconnaissance and fire control station is equipped with a three-coordinate HARD radar system of the centimeter range produced by the Swedish Erickson Microwave Systems with a target detection range of 20 km, which is an improved version of the RACS of the Swedish RBS90 air defense system, the “other-to-own” MSR 200 X-ray XRUM X-ray chimeter and the Chancers and the Ip chrometept masters. Information about the targets is automatically transmitted to the LR system via digital communication channels. Calculation station - 2 person (including the driver).
Each LeFlaSys system battery must include a battery commander’s car and three platoons, each with one command post and five Ocelot self-propelled air defense systems. For an earlier detection of air targets and the transfer of data about them through a digital communication channel, a battery can be attached to a battery observation machine.
Wiesel wedge armed with a 30 mm Mauser cannon.
In total, 67 machines of this complex were ordered on the Wiesel-2 chassis: 50 self-propelled SAMs, 10 reconnaissance and control stations and 7 machines of the battery commander with the end of deliveries to 2003. The Krauss-Maffei Wegman concern was attracted to the production. The machines for the first platoon were delivered at the start of 2001.
On the market, this short-range air defense system is presented under the designation ASRAD. Greece ordered it on the chassis of the Hummer car, Finland on the chassis of the Unimog 5000 car and on the SAM system of the RBS-70 complex (ASRAD-R).
Rheinmetall Landsystem presented an engineering reconnaissance vehicle on the Wiesel-2 chassis, equipped with equipment for reconstructing water obstacles and minefields, demining charges, HLF and armed with a machine gun. Taking into account the power to the chassis can be created and landing BREM.
Wedge "wedge" in the French army.
The Wizel-2 PM also served as the basis for the development of crewless robotic machines. The French built a Cyrano demo on this chassis, designed to demonstrate the very possibility of creating such a machine. The Rhinemetal Landsystem itself in 1996 introduced several experimental machines: the PRIMUS complex (Eads Dornier), including a robotic machine with a video camera and a laser scanner (operating at a distance of 50 m) for viewing the terrain, a digital navigation system, an autonomous module movement, control and decision-making and self-propelled remote control point (on the same chassis "Wiesel"); machine combining autonomous robotic control system of the new generation with remote control by wire and designed to work in the danger zone, demining, etc. Machines were presented in the form of platforms for the installation of various work equipment, reconnaissance equipment or weapons. The Wizel-2 ARGUS machine (was presented in the form of a mock-up) equipped with a sliding platform with the detection and surveillance equipment of the Atlas Electronic company STN, a set of control tools to perform the functions of reconnaissance, patrolling, supply, and also satellite navigation equipment, radio equipment with a digital communication channel, an auxiliary generator.
Wizel034.jpg Wizel035.jpg
The variant of the air defense system with a combination of missile defense systems "Igla-1" and RBS-70 on the chassis BDM "Wiesel" A1. Engineering reconnaissance vehicle on the Wiesel-2 chassis.
"Small" and "light"
Although the formation and development of the rapid reaction force and airmobile compounds has received much attention in many countries, it is difficult to find an analogue of the Wiesel machine in other countries. It differs from the Soviet (Russian) BMD and BTR-D both in terms of its “weight category” and its purpose. Among tracked vehicles close to Wiesel is the EE-T4 chassis of the Brazilian company Engesa with 3,6 t mass and front-mounted 125-strong engine and travels up to 75 km / h. The ЕЕ-Т4 was also offered in the BRM version with a machine gun or cannon, self-propelled anti-tank systems or mortars, however, it remained experimental.
Close to the destination 4,5-tracked chassis VRX-5000 was developed in France also for airborne units. From the mass-produced vehicles we can mention the French floating light armored car M11 “Panhard” - another return of the “old type” of armored vehicles (recall the Soviet D-12 and BA-20 in the landing party). All-wheel drive (4x4) MP 3,6 mass t entered service in 1990 g. As a reconnaissance and carrier weapons for rapid reaction forces, was supplied to a number of countries. The Italian OTO-Melara developed wheeled armored vehicles of the same purpose of the 2,5-3 class, the Turkish Otokar produces the Akrep armored vehicle with the 3,6 mass. In general, the modern wedge tanks Wiesel and its enlarged version Wiesel 2 ”- remain a unique family.
Literature and sources:
1. Vasily N.Ya., Gurinovich AL. Anti-aircraft missile systems. - Minsk: Potpourri, 2002.
2. Foreign Military Review, 1988, №10; 1991, No. 11; 1997, No. 3; 1999, No. 9; 2004, No. 5.
3. Messages ITAR-TASS, 25.08.04.
4. Foss CF Jane's. Tanks. Recognition Guide. - HarperCollins Publishers, 1996.
5. Armada Inernational, 2001, No. 4.
6. International Defense Review, 1984, #12.
7. Jane's Defense Weekly, 1998, 22.07.
8. Kampftruppen, 1986, No. 7.
9. McNab C. Military Vehicles. - London: Grange Books, 2003.
10. PC Week, 1999, 9 — 15fevr.
11. Sheibert M. Waffentra'ger Wiesel 1 // Waffen-Arsenal. Band 136. - Podzun-Pallas-VerlagGmbH, Friedberg, 1992.
12. Soldat und Technik, 2002, No.9.
13. The Directory of Modern Military Weapons. Edited by C. Bishop. - London: Greenwich Editions, 1999.
14. Tracked & Wheeled Light Armoured Vehicles // - IDR, 8/1986.
15. Wehrtechnik, 1993, No.2; 1994, No. 2,7; 1995, No. 1; 1996, No. 5,8.
16. Armored Weapon Carrier WIESEL. Prospect KRUPP-MAK.










Information