American light tanks. Between the wars, between the lines ...

In 2014, I started writing a series of articles about American “interwar” tank development. Then it was not possible to complete the work and now I would like to return to the subject again.
So, let me remind you that the dawn of American tank building was marked by a wide field of creative search, multiple alterations of tractors into combat vehicles, and all sorts of wonderful wunderwaffe. However, as elsewhere. Great contribution to history tracked armored vehicles made such comrades as Harry Knox (tanks Cunningham) and John Walter Christie. About their work is written in sufficient detail, but a whole series of interesting machines was missed from the attention. I would like to tell you in more detail about what began what eventually turned into the M3 Stuart. Well, a little bit to understand the line of interwar machines.
Separately and once again cursed against the American alphanumeric indexing of military equipment. Just don’t try to understand why they have “five different M2, seven M1 and twenty-three T1”, and not all of them are tanks, take it as it is.
Formed in the First World American Tank Corps in 1919, it was disbanded, and all the available vehicles were transferred to the maintenance of infantry units. In 1920, the United States adopted an act according to which the organization of armored units as a separate branch of the military was simply prohibited, and work on the development and introduction of new weapons was imputed to the Chief of the Ground Forces Headquarters, in whose apparatus a special commission was created. Mahra, of course, tried to get a good domestic tank, but the budget was also badly cut. However, the attempts did not stop. In 1927, they even tried to create an experimental tank unit consisting of light vehicles, but the Great Depression that had begun had prevented this business. In 1931, General Douglas MacArthur became the commander of the land forces and the army mechanization policy changed dramatically. The country slowly "faded" after the crisis. Now tanks began to be developed for cavalry, as for a priori more mobile kind of troops.
Design engineer Harry Knox, together with Cunningham from 1920 to 1932, developed a series of light tanks T1, as well as self-propelled guns based on them. In 1928, they were tried to adopt under the symbol Light Tank M1, but the design was somewhat damp and acceptance was postponed, and in 1931, John Christie “shot” with his M1931, which was adopted with the indexes Medium Tank T3 (3 pieces produced). ) for infantry and Combat Car T1 (made 4 units) for cavalry. These machines (М1931) received further independent development, but the engineer Christie himself fell into insanity, gradually quarreled with everyone and continued to do strange crafts until his death in the 1944 year. In the meantime, quite a good project T1 Cunningham was hacked down solely because of the appearance of the M1931 on the market. As a result, 1932, the normal modified serial light tank has not yet appeared, competition in the tank building business between engineers Christie and Knox did not lead to anything, and the military still needed a good tank. And further development did not stop. The inclusion of cavalry in the game led to new research. Nobody canceled the “Act on National Defense” in 30's, therefore, in order to circumvent the law, it was necessary to call machines for cavalry “combat car”, instead of “tank”, for infantry. From here we have two "branches of development", about which I will talk separately.
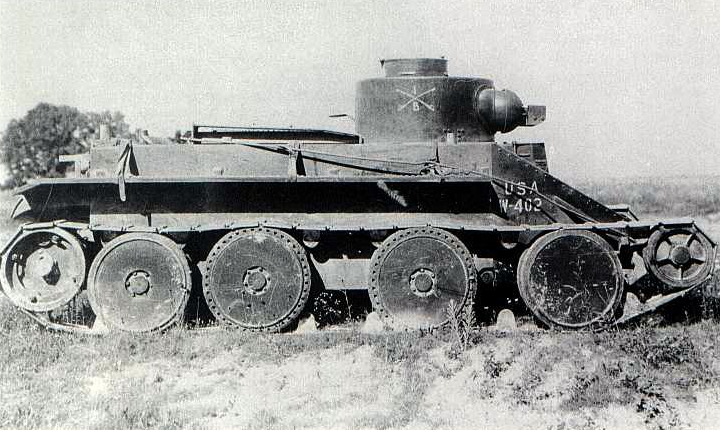
Combat Car T1
Essence is the tank Christie M1931, adopted by the cavalry.
Combat Car T2
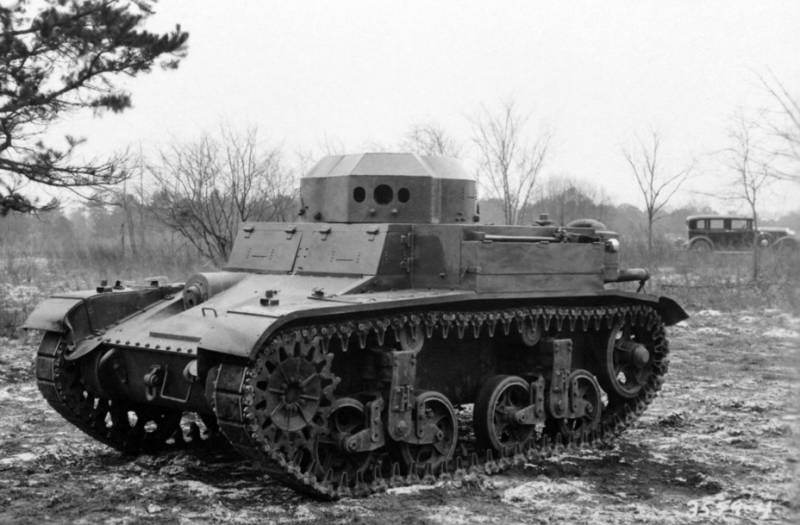
Harry Knox and Cunningham naturally also saw the potential of cavalry as armored customers, and made another attempt to compete with Christie. Available sources indicate that this car was originally developed as Armored Car T5, and subsequently subsequently renamed Combat Car T2.
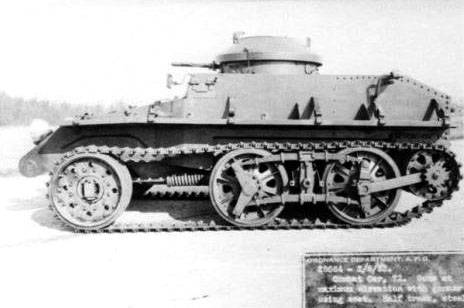
The product turned out curious, but not viable. If Christie brought the idea of a wheeled-tracked tank chassis almost to perfection, then the T2 was a de facto wheeled armored vehicle with wheels wrapped by caterpillars. Subsequently, Knox a year and a half tried to bring the car to mind, but even Combat Car T2E1 did not arouse any interest in the military.
Combat Car T3
Attempt to sell cavalry T1EX1 Cunningham. Unsuccessful.
Combat Car T4
Refusal from further use of T1 machines caused their outrageous cost. It wanted better and cheaper, but every engineer knows that the first thing to do is get the technical task from the customer. In 1932, an entire conference was convened to form the final requirements for a cavalry tank. The new machine was supposed to weigh 7,7 tons, speed 64 / 35 km / h on wheels and tracks, respectively, and the use of two machine guns (12,7 and 7,62 mm) was used as armament. Suddenly, Major Gladeon Barnes, Chief of the Aberdeen Proving Ground, appeared in the arena of tank designers. Taking the car Christie (Combat Car T1), he completely redid the chassis, set the shock-absorbing candles at an angle and redid the weights, thereby reducing the height of the case. The side plates could now be placed at a slight angle, which was done. The water-cooling engine was replaced with a more powerful air one, in addition by assembling it with the transmission, which led to a decrease in the amount of MTO.

The machine received the designation Combat Car T4, and quite successful tests passed in August 1933 of the year. In general, I liked the tank, but some modifications were needed.
Thus was born the T4EX1. In it, the diameter of the tower shoulder strap was increased from 1118 mm to 1420 mm and, accordingly, the tower was redone, machine guns instead of a paired installation were set separately, also added coursework and two machine guns in the corners of the front sheet, and zenith to the heap.
Tanchik as a hedgehog bristled, the mass has grown to 9 tons, although the driving characteristics due to the new transmission even improved. And everything seems to be fine, but around the same time, the Combat Car T5 was tested, which was significantly lighter and twice as cheap. So a competitor was recommended for adoption. The created prototype was not left alone, and in the winter 1935 was remade in Combat Car T4Е2. The tower was removed, and in its place the armored housing was welded in, two machine guns from the corners of the ILD were smashed around the sides and another was placed in the aft logging room.
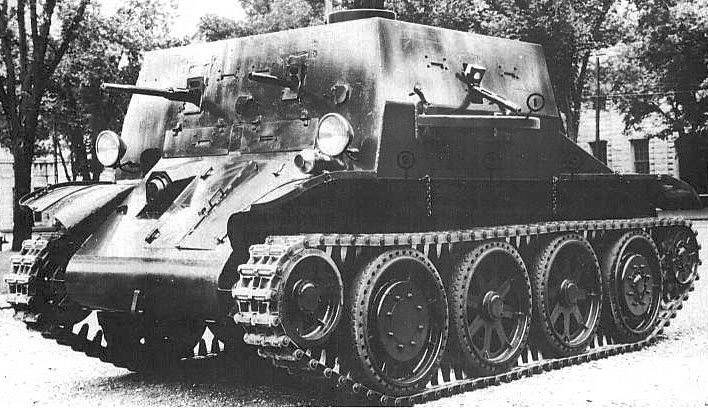

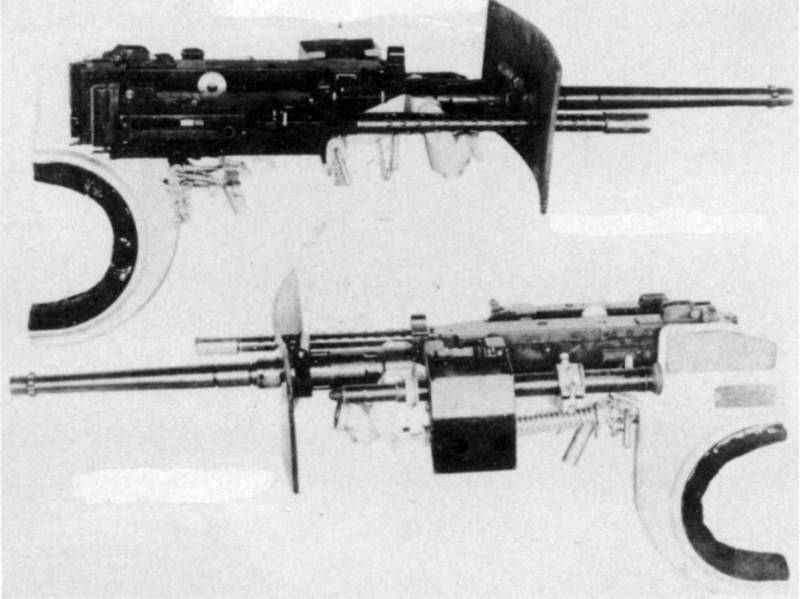
Thus, the armament of the machine consisted of five 7,62 machine guns and one 12,7 Browning, but, again, the experiments remained experiments. This is where the story of Barnsovskaya Machine, as a tank for cavalry, ends and begins for the infantry, however, about this later ...
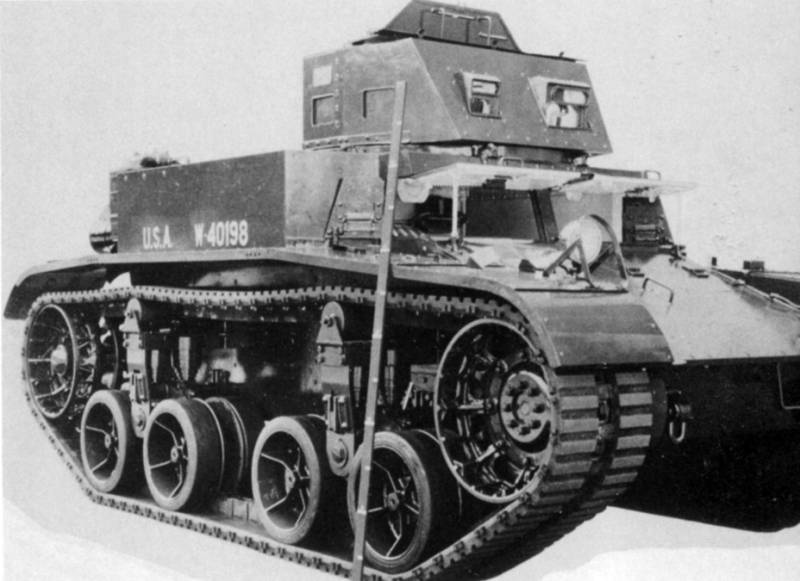
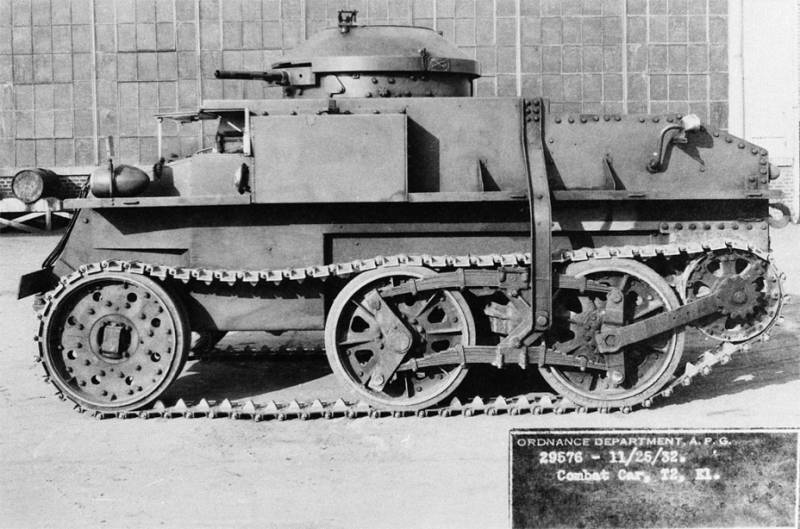
Combat Car T5
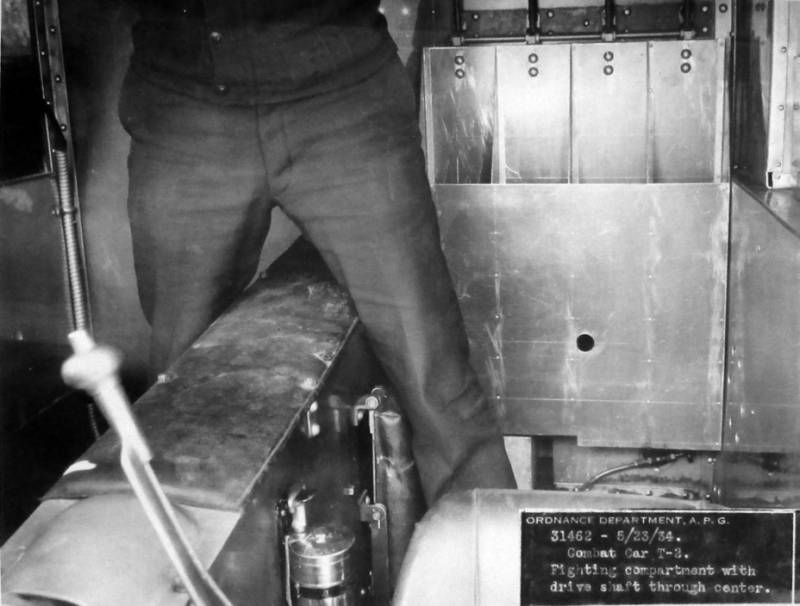
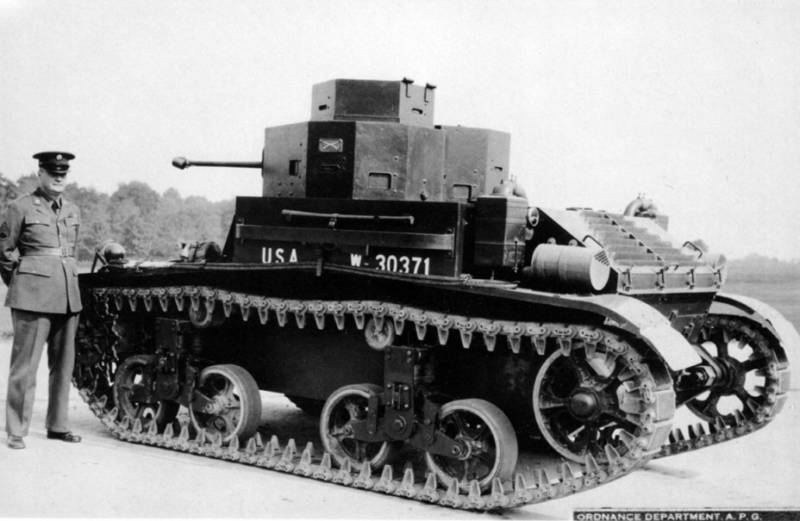
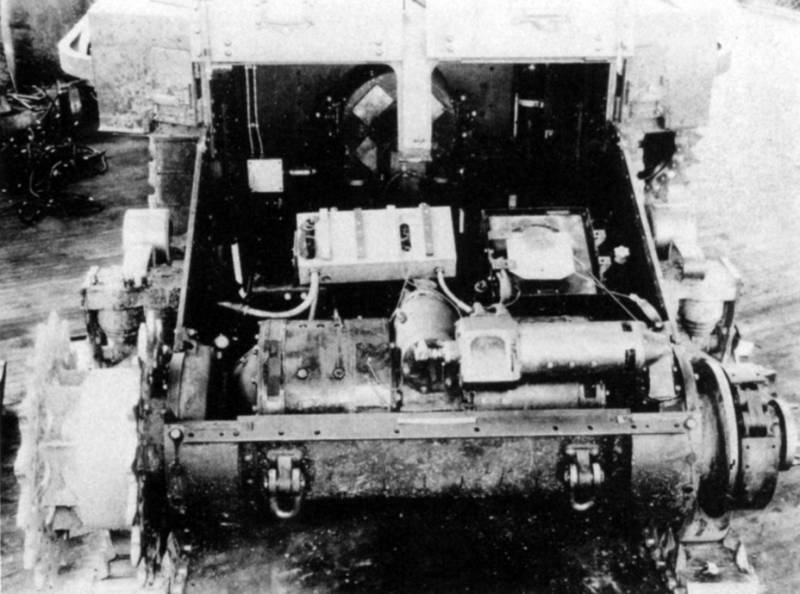
When it became clear that the Light Tank T1, even in the modification of the E6, was not going to take into service, the engineer Harry Knox, together with the Arms Department in 1933, began developing two machines simultaneously: for the cavalry - Combat Car T5 and for the infantry - Light Tank T2. The specification was adopted the same as for the T4 - weight 7,5 tons, speed 48 km / h, three machine guns and bulletproof armor. Having received approval from the Arms Committee for the manufacture of a prototype, Knox began to translate the idea into metal. Specially for the tank, a new suspension with vertical springs was developed. For lack of a sufficiently powerful car engine, I had to take it again aviation Star-shaped seven-cylinder Continental R-670. And then the specifics of the star-shaped scheme, in which the crankshaft is in the center, were fully manifested. The transmission is in front, the engine is behind, as a result, the shaft going through the entire fighting compartment, located inside the casing, is literally “knee-high”. Naturally, it was not so good to jump over the commander and the loader in a cramped tank. The problem was solved radically, by installing not one, but two towers of circular rotation, having received a number of design flaws in the load. The prototype was ready in April 1934, "empty", weighing 5,6 tons, towers without roofs (weight reduction, but also a number of problems), wind shields for the driver and suspension, very different from the Light Tank T1. It consisted of four road wheels, locked in two trolleys on board, a sloth attached to the rear trolley. The new suspension proved to be quite good and in tests the experienced tank was able to reach a speed of 68 km / h, which significantly exceeded the specification requirements. Subsequently, the car received a new rubber-metal caterpillar developed by Knox.
In March, 1935, as part of further modernization work, redesigned the prototype machine as ТХNUMXЕ4. They made a cutting box, turned the machine guns around and saw what happened. And it turned out Combat Car T2E5, inconvenient, because you can not concentrate and generally manage the fire and hot, because MTO partially tucked under the wheelhouse. This design has not received further development.
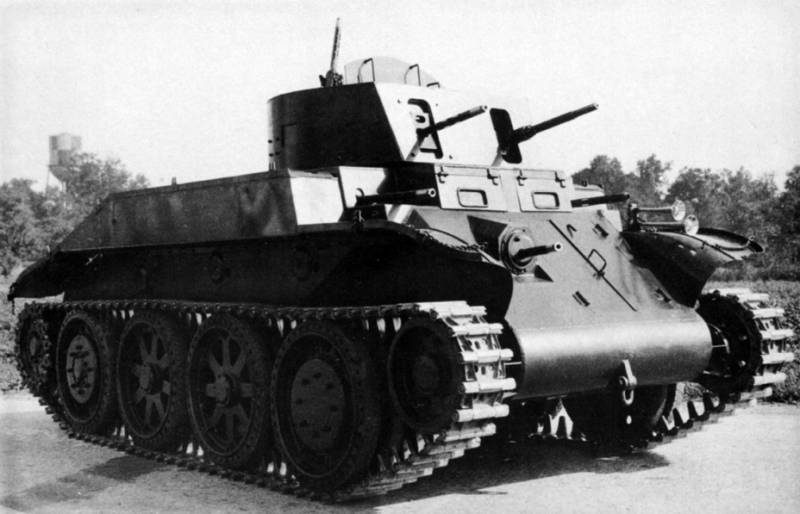
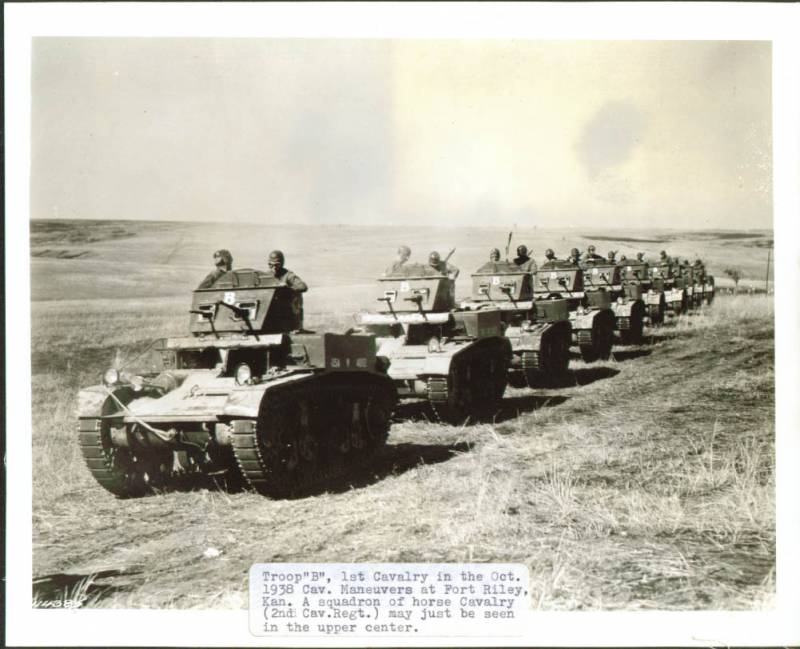
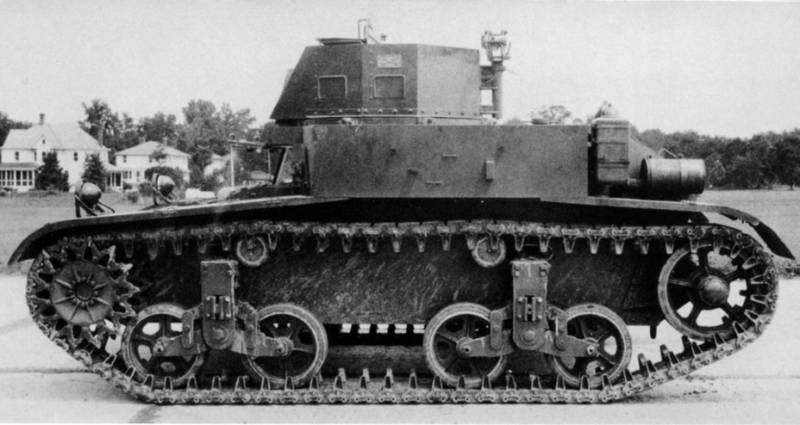
A little later, they built the Combat Car T5E2 tank, reworking the suspension, the hull and installing the enlarged turret, and also installed the Browning M1919 anti-aircraft machine gun. It was this car that was put into service as a Combat Car M1.
A total of 1935 to 1937 years, 90 machines were released (including a prototype). Made them in Arsenal Rock Island. In the process of mass production, they simplified the design of the tower and the shield of the engine compartment.
Investigations over the experimental machine T5, meanwhile, continued. First, in the year 1936 tried to put a diesel engine Guiberson T-1020. The tank became T5EX3. The motorboat is not bad in general, but the launch was rather complicated. But all the same, according to the results of tests, three serial М1 were equipped with such engines and we got the Combat Car M1E1.
Service in the army also revealed a number of shortcomings. For example, they tried to solve a strong longitudinal swing by slightly “stretching” the suspension. The car that received the Combat Car M1E2 index really turned out to be much more stable in this regard.
In 1938, Rock Island Arsenal released the Combat Car M24A1 1 tank, a slightly modified version, seven of which were M1A1Е1 - with diesel engines.
1940 year brought the American cavalry latest modification of the tank - Combat Car M2, structurally similar to the infantry Light Tank M2A4. М2 compared with T5 significantly heavier. Weight increased right up to 11,5 tons, which resulted in the processing of the suspension. The initial order was already on the 292 typewriter (the Second World War was already in full swing), well, to the heap the cunning cavalrymen wanted to take the Light Tank M2A1 and M2A2 off the infantry. Here are just these plans crossed out a few fat "but."
The machine-gun tanks showed their complete failure on the battlefields, and the anti-bullet armor was not long enough for the tank; nevertheless, the anti-tank case did not stand either. In the end, the cavalry managed to snatch only 34 Combat Car M2 machines (some of them are diesel ones). The 1940 year brought not only the M2, but also the repeal of the National Defense Act. The conspiracy lost all meaning, so Combat Car M1 was renamed to Light Tank M1A1, and Combat Car M2 to Light Tank M1A2. In the same year, the formation of tank divisions began.
Actually on this story Combat Car T5 ends. Just to mention a few more experiments with the very first chassis. In 1937-1938, they experimented with rubber torsion bars in the suspension and a new five-cylinder diesel engine - Combat Car Т5Е4.
In the same 1938, an experienced chassis with a rubber-metal track and bandaged rollers was installed on one of the M1А1, while at the same time trying to solve the problem of the duct with the shaft in the middle of the crew compartment. Tank received Combat Car M1E3 index. In both cases, further experiments did not work.
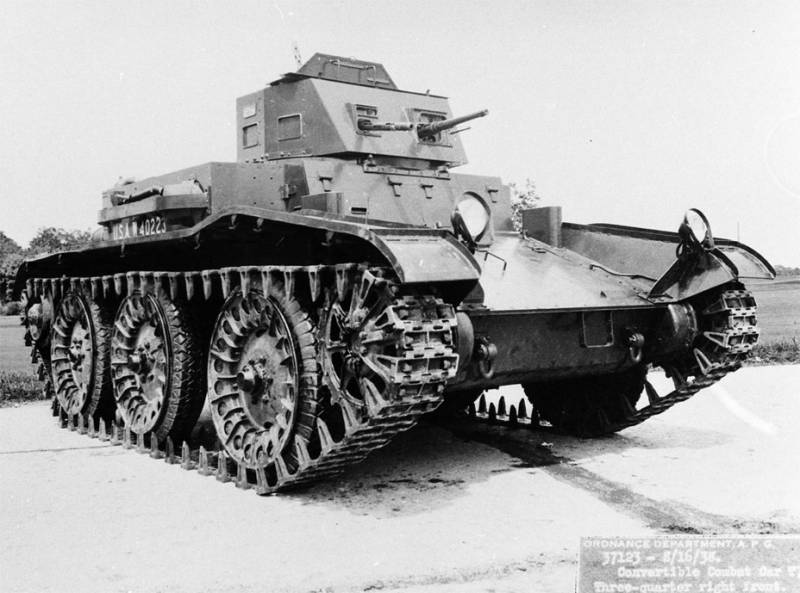
Combat Car T6
Another, the third in a row, cavalry attempt to get a wheeled-tracked tank. Crew of five, Wright Whirlwind engine R-975 400 horsepower and the combat mass of 10,5 tons, in general, that's all that is known for this machine. At the end of 1935, the design work was stopped because the new car came out too heavy and nothing more than the M1. There are no photos or thumbnails currently online.
Combat Car T7
A year later, at 1936, the army leadership decided to go a different way to the wheeled-tracked tank. They took the last released serial Combat Car М1А1 and converted it to Combat Car T1937 by 7. At the base of the undercarriage used three wheels on board with pneumatic tires instead of tires. When driving on wheels, the drive was carried out to the rear, and the front was driven. By the 1937-th tank entered testing, but by the 1939 year, all work in this direction was suspended, since the wheeled-tracked circuit has completely lost its relevance.
Light Tank T1
About this machine is described in some detail in the article “Tanks of the Cunningham factory”.
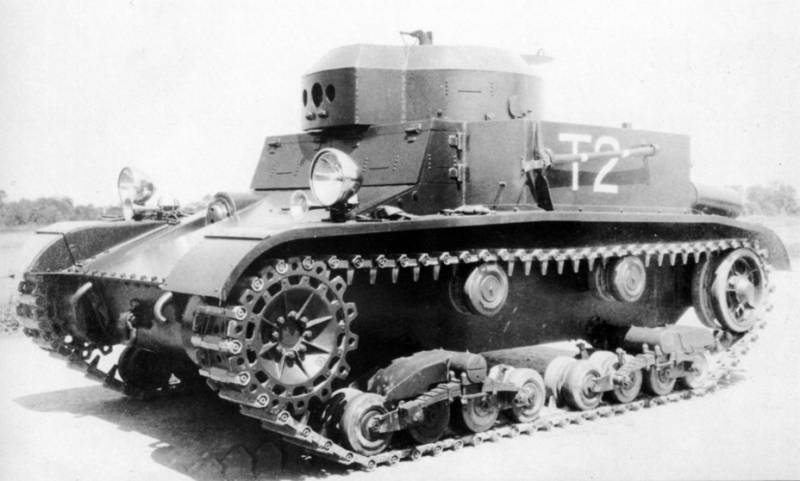
Light Tank T2 / M2
Having failed with T1 and not despairing, Harry Knox simultaneously with the development of Combat Car T5 and in fact, according to a single specification, began to invent the car that received the Light Tank T2 index.
If the T5 suspension was completely new, then in the T2 they used the developments with the T1Е4. The engine was taken as in T4, T5 - Continental R-670, only in T4 it was made as a single unit with transmission, and in T2 the transmission was installed in front, so, like in Combat Car T5, there was a box in the fighting compartment with a drive shaft and everything interfered.
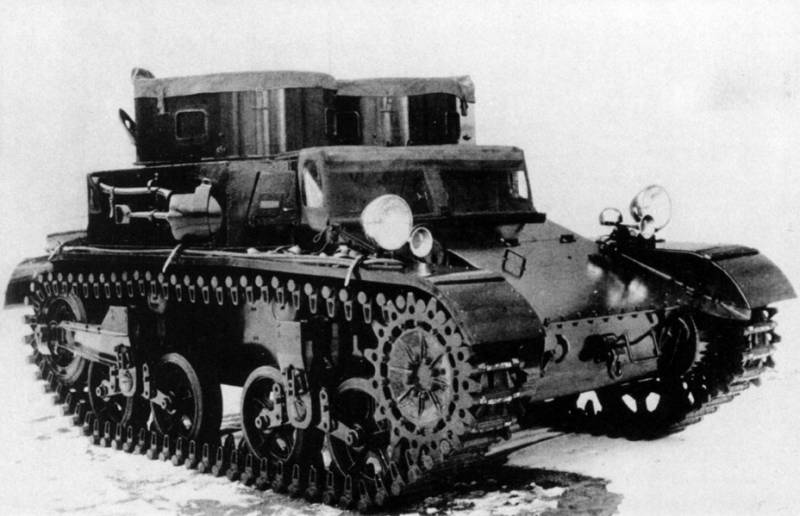
Both infantry and cavalry tanks arrived at the test site simultaneously in April 1934 of the year. In general, I liked the T2, but this casing ... And there was nothing to be done. The old chassis from the T1EX4 was considered unsatisfactory, and the fighting compartment was too noisy, which hampered the work of the crew. The list of comments was taken to work and already in October of the same year, the T2EX1 arrived at the test site - a substantially upgraded tank with a successful undercarriage, like the Combat Car T5.
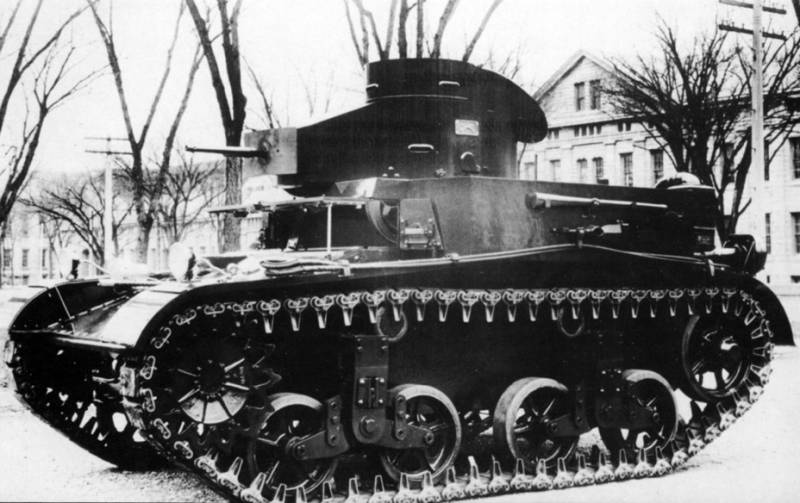
The tower was still alone, and the commander / gunner with the loader continued to jump over the cover when the tower was turning. To the heap, for the first time in American history, a rubber-metal caterpillar of Knox’s construction was used. A thing in itself and a business card of American armored vehicles. In January, 1935, the tank went to military trials at Fort Benning and successfully passed them. It was adopted as the Light Tank M2А1.
Thus ended the nine-year epic search for trial and error. From the original concept of a two-seater with a front engine and an 37-mm cannon, we ended up with a four-seater tank with a two-seater turret and purely machine-gun armament, a slider located at the rear and a front transmission.
On the way from the T2EX1 to the M2X1, the car became heavier by one and a half tons (to 8,5), however, the booking and dynamic characteristics remained the same, so the military closed their eyes to the excess weight. Unlike the cavalry tank, the armament was not placed in two towers or even separately, but in the twin installation Т7.
Total M2X1 produced 9 pieces.
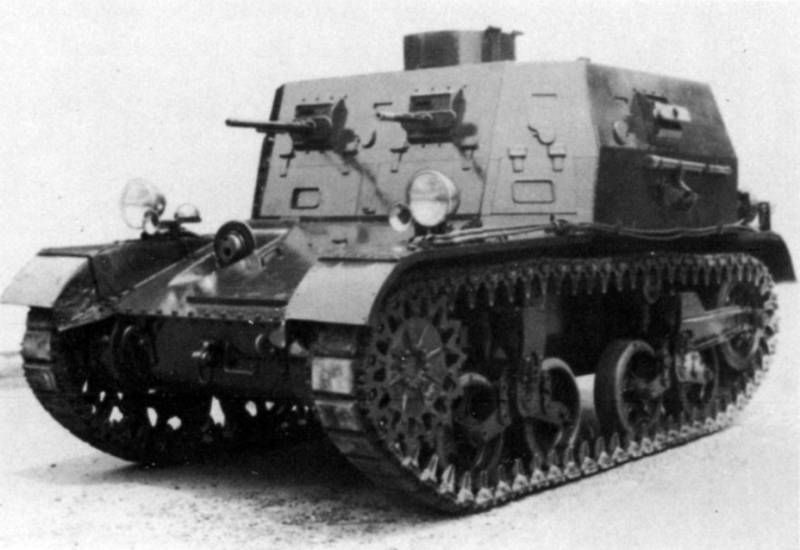
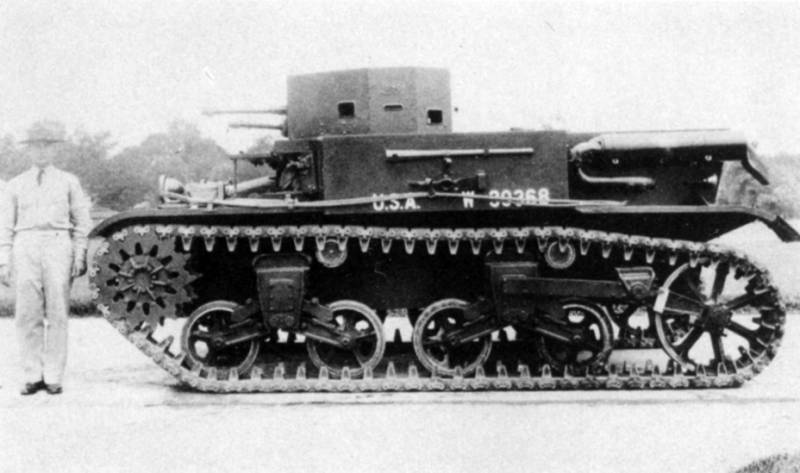
And yet, nevertheless, all the same ... The high casing really interfered, therefore, without further delay and having a positive experience with the Т5 / М1, the military simply installed two separate towers. In 1935, the double-totaled Light Tank T2E2 was released for testing, which was put into service as the Light Tank M2A2, practically simultaneously with the M2-1.
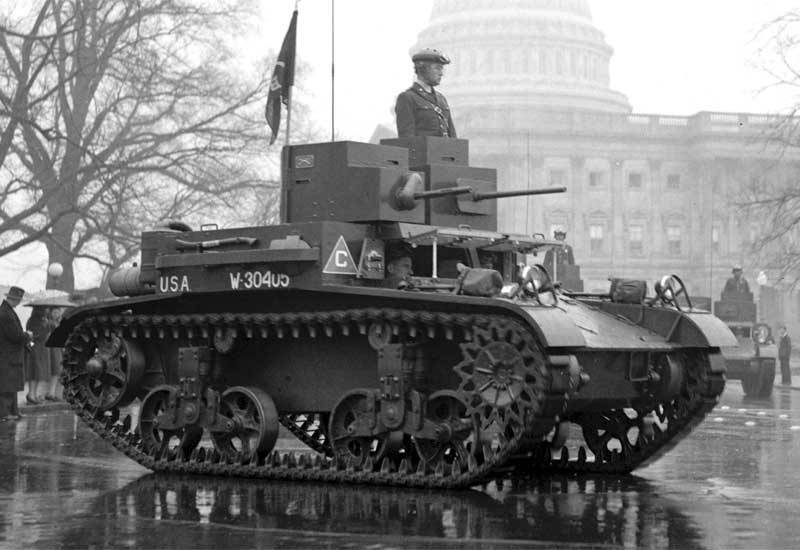

For 1935, we also managed to release 9 tanks. Well, then: orders fell down. In the 1936 year - 125 units, in 1937 - even on 104 machines. Thus, the new tank became the basis of the US tank fleet and replaced in parts the outdated M1917 Light Tank, which was essentially outdated by that time. They wrote about him in newspapers and filmed newsreels. He was a kind of new symbol of the army.
М2А2 also received a diesel engine as an experiment. Three cars were converted into MXNX-2-2.
М2А2Е2 - the last manufactured М2А2 tank with increased armor to 25 mm. This sample has become a kind of testing ground for various innovations. In the process of various alterations, they put an inline six-cylinder diesel engine General Motors 6 – 71, with a volume of 7 liters. This, of course, required an extension of the engine compartment and the processing of the chassis. What turned out was re-indexed in М2А2Е3 and at the beginning of July 1939 began to be tested.
Light Tank МХNUMXА2. The basis for this machine took the cavalry M3EX1 with an elongated chassis. The new tank turned out to be more stable, and with slightly modified turrets. According to the results of the study of fights in Spain, the thickness of the frontal sheet was increased to 2 mm in order to resist the fire of heavy machine guns. Since the summer of 22, Rock Island has produced 1938 machines of this type. 73 tanks of steel M8А2Е3 with diesel engines.
One of the serial М2А3 - turned into a test bench for installing Timken electric transmission. Although the shaft of the BO and disappeared, yet this type of design turned out to be cumbersome, over complicated. М2А3Е2 was not put into service and they didn’t go further experiments.
The last experiment with the platform received the designation МХNUMXА2Е2. It was an attempt to install a new V-shaped four-cylinder diesel V-3 – 4 from GM. The engine was heavy and longer than the native, which entailed reworking the undercarriage with increasing diameter of the sloth. The platform did not receive further development, but the undercarriage went to the light-weight tank M223 with almost no changes.
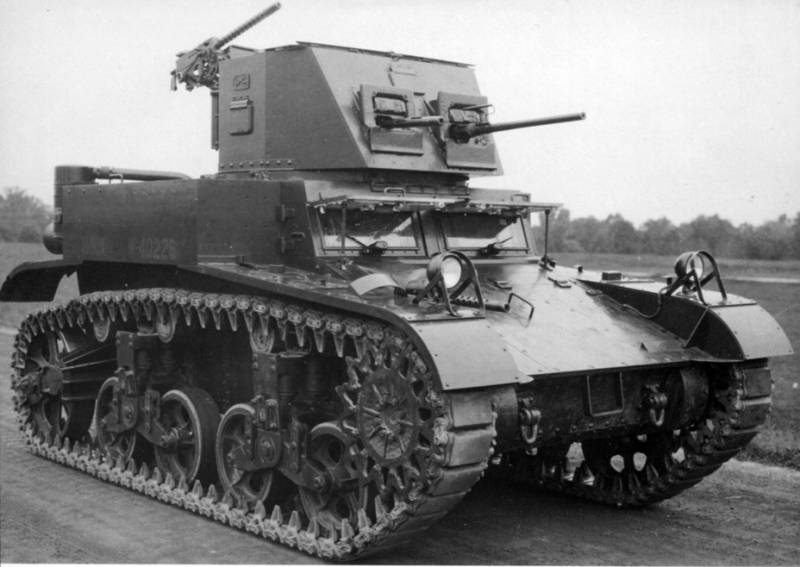
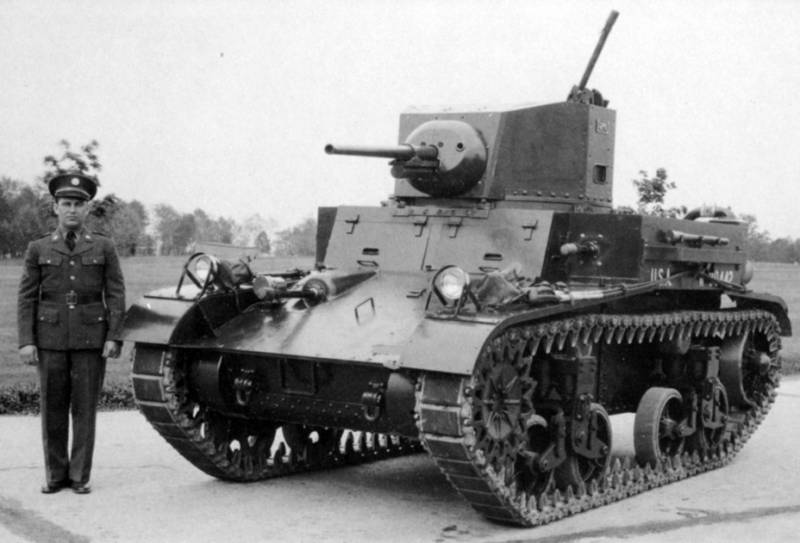
Light Tank МХNUMXА2. The development of this machine began in the year 4. After comparative tests of the “infantry” M1938 and the “cavalry” M2, the latter proved to be a clear winner, so the concept of an infantry support tank was decided to be revised. It became clear that the armament was rather weak, and the booking would not hurt to be improved while maintaining maneuverability. The military ministry specialists Knox, Crismes and Barnes suggested several options, even built an experienced chassis, but the military did not want to build a tank from scratch, so they had to sculpt from what it was. For the new tank, they took the M1А2 case with virtually no changes, but the turret was developed from scratch, made a double one and equipped with a 2-mm gun paired with a machine gun.
The thickness of the body armor was increased to 25 mm. The first sample immediately received the M2A4 index and in May 39 of the year drove to the tests, and according to the results with minor modifications, they approved the series. The tank began to do in May 1940, and only released 375 units. In general, already in the 1941 year, they started the production of the M3, so the machine was somewhat delayed with the appearance, but she even managed to make some war on Guadalcanale.

Light Tank T3
An experimental machine developed simultaneously with the T2-1. It was distinguished from the counterpart by a lower body and the only 12,7 mm machine gun in the superstructure.
Light Tank T6
Another fruit of the experiments, made in June 1939 of the year under the leadership of Major John Chrismes, as one of the options for replacing the M2А3. Of noteworthy is the use of paired automobile engines (unification and cheapening) and large-sized casting (a cast block with a transmission and final drives).
And do not even ask me where T4 and T5 have gone ... I don’t know, I don’t know yet.
This is where the history of light American tanks developed between World War I and World War II ends. Next was the military M3 Stuart. There is a line of medium machines, but about them in the next article.
Materials used:
http://www.aviarmor.net/tww2/tanks/usa/_usa.htm
http://www.aviarmor.net/tww2/armored_cars/usa/_usa.htm
http://warspot.ru/6799-na-maner-kristi
http://warspot.ru/7370-bronya-dlya-amerikanskoy-kavalerii
http://warspot.ru/5677-eksperimenty-na-idealnoy-platforme
http://warspot.ru/7439-dvuglavaya-lyogkost
http://warspot.ru/4529-dognavshiy-odnoklassnikov








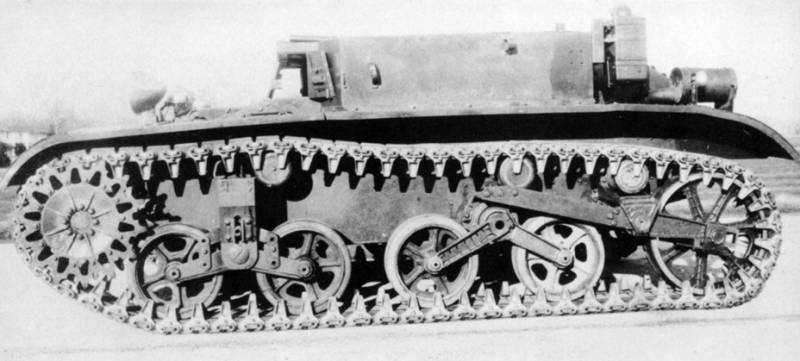











Information